Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1618398280-2. National Income Accounting
Uploaded by
Kuldeep Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe document discusses key concepts related to national income accounting including Gross Domestic Product (GDP), intermediate and final goods, stock and flow, GDP estimation methods, and related macroeconomic aggregates. It defines GDP as the monetary value of final goods and services produced domestically in a given time period. GDP is estimated using the product, expenditure, and income methods. Related concepts covered include GNP, NNP, NDP, and India's classification as a lower-middle income nation.
Original Description:
Original Title
1618398280-2. NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts related to national income accounting including Gross Domestic Product (GDP), intermediate and final goods, stock and flow, GDP estimation methods, and related macroeconomic aggregates. It defines GDP as the monetary value of final goods and services produced domestically in a given time period. GDP is estimated using the product, expenditure, and income methods. Related concepts covered include GNP, NNP, NDP, and India's classification as a lower-middle income nation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pages1618398280-2. National Income Accounting
Uploaded by
Kuldeep SharmaThe document discusses key concepts related to national income accounting including Gross Domestic Product (GDP), intermediate and final goods, stock and flow, GDP estimation methods, and related macroeconomic aggregates. It defines GDP as the monetary value of final goods and services produced domestically in a given time period. GDP is estimated using the product, expenditure, and income methods. Related concepts covered include GNP, NNP, NDP, and India's classification as a lower-middle income nation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
HARYANA – ECONOMY
LECTURE: 2 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
What will we cover
• Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Final,
• Intermediate, Consumer & Capital goods.
• Stock Vs Flow
• GDP Estimation Methodology
• GDP at FC, BP & MP + some other macroeconomic aggregates.
• Drivers of economic growth
• GDP & Welfare
GDP
• Adam Smith’s enquiry reveals what generates wealth of nations. According to him,
it is not the bounty of natural resources, but how they are used in generating the
flow of production that makes nations rich or poor.
• GDP - it is the monetary value of final goods and services produced in the domestic
territory of a country in a specific period of time.
• GDP measures the creation of wealth in a country in a year.
• It is the final output of an economy in a year.
• GDP in India is measured by NSO (National Statistical Organisation) which is under Ministry of statistics
and Programme Implementation
Goods
Intermediate Goods
• These are goods used as inputs in production of other goods including final goods. These are still in
active economic flow.
▪ Intermediate goods are not used In GDP estimation so as to prevent Double Counting
Final Goods
• These are goods which would undergo no more stages of production or transformation. These are
outside active economic flow.
▪ Consumer Goods
▪ Capital Goods
Consumer Goods
• A consumer good is a commodity that is used by a consumer to satisfy current wants or needs, rather
than to produce another good.
• Examples : Microwave, Clothes, food etc. - Certain consumer goods are durable in nature, thus they
are called “Consumer Durables”. Eg - TV, Fridge, A.C, Microwave etc.
Capital Goods
• It is a durable good that is used in the production process of other goodsand services, rather than being
bought by consumers.
• They form the crucial backbone of any production process - That part of our final output that comprises
1
of “capital goods” constitute“Gross Investment” of an economy.
Page
• Examples : Machines, tools, buildings, office spaces, Infrastructure etc.
Telegram: CBL- Haryana Civil Services Call / WhatsApp: 9779068345
Gross investment - Depreciation = Net Investment
• Depreciation - the deletion which is made from the value of gross investment in order to accommodate
regular wear and tear of capital.
For example
• Capital Stock before 2020 = Rs 500
• Gross Investment in 2020 = Rs 100
• Capital depreciated in 2020 = Rs 50
• Capital Stock after 2020 = Rs 550
▪ Therefore, net addition to capital stock = Rs 50 Hence, Net Investment = Rs 50
GDP = Final Output
• Consumption
• Investment
▪ Higher the investment in an economy, higher the capacity of that economy to produce more
goods and services
Stock Vs Flow
• Stock - it is an economic variable that can be measured at a point of time. Eg - Wealth, Debt, Capital
stock, Foreign exchange reserves etc.
• Flow - it is an economic variable that can be measured in a period of time. Eg - Income, Profit, GDP,
Gross Investment, Rent etc.
• Change in stock becomes a flow variable.
GDP Estimation Methodology
• Product or Value Added Method
• Expenditure Method
• Income Method
2
Page
Telegram: CBL- Haryana Civil Services Call / WhatsApp: 9779068345
Product or Value Added Method
• Value added by Firm(i) = (Value of goods produced - Value of intermediate goods used).
• Value added by Firm(i) = Value of Sales + (Change in inventories) - Value of intermediate goods used.
• Value added by all the firms in the economy = Gross Value Added.
• Positive change in inventory is treated as “Capital” or “Investment”.
• Inventory is a stock variable, but change in inventory becomes a flow variable.
• Gross investment = Gross Capital Formation(GFC).
• Gross Capital Formation
▪ GFCF
▪ Change in Inventories
• GFCF = Gross Fixed Capital formation.
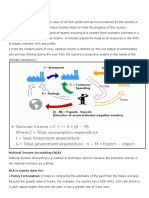
Expenditure Method
• Let Expenditure on Firm(i) be
• F(i) = C(i) + I(i) + G(i) + X(i)
▪ C(i) = Consumption Expenditure
▪ I(i) = Investment Expenditure
▪ G(i) = Government Expenditure
▪ X(i) = Export Expenditure
• GDP = Total Expenditure on Domestic Firms.
• GDP = ∑ F(i)
• GDP = C-Cm + I-Im + G-Gm + X
• Cm + Im + Gm = total import expenditure = M
• GDP = C+I+G+(X-M)
▪ C = Total Consumption Expenditure
▪ I = Total Investment Expenditure
▪ G = Total Government Expenditure
▪ X-M = Net Exports
Income Method
Final Output
• Rent
• Wages
• Interest
• Profit
• GDP = Total (Rent + Wages + Interest + Profit) in the economy.
Factor Cost, Basic Price & Market Price
• Factor Cost + Net Indirect Taxes = Market Price.
• (Taxes - Subsides) = Net Indirect Taxes.
• Indirect taxes/subsidies can be divided into two parts:
▪ Production Taxes - those taxes which are paid or received in relation to production and are
independent of the volume of production. Eg - Land Revenue, Stamp Duty etc.
3
▪ Product Taxes - those taxes which are paid per unit of product. Eg - GST, Excise duty, Custom duty
Page
etc.
Telegram: CBL- Haryana Civil Services Call / WhatsApp: 9779068345
• Factor Cost + Net Production Taxes = Basic Price
• Basic Price + Net Product Taxes = Market Price GVA
• GDP(FC) + Net Production Tax = GDP(BP)
• GDP(BP) + Net Product tax = GDP(MP)
Other Macroeconomic Aggregates
• Gross National Product (GNP) = GDP + Net Factor income from abroad
• Net Factor Income from Abroad = (Factor income earned by domestic factors of production employed
in the rest of the world) - Factor income earned by foreign factors of production employed in domestic
economy).
• Net National Product (NNP) = GNP - Depreciation
• Net Domestic Product (NDP) = GDP - Depreciation
• National Income = NNP (at factor cost)
Other Macroeconomic Aggregates
• Gross National Product(GNP) = GDP + Net Factor income from abroad
• Net Factor Income from Abroad = (Factor income earned by domestic factors of production employed
in the rest of the world) - Factor income earned by foreign factors of production employed in domestic
economy).
• Net National Product(NNP) = GNP - Depreciation
• Net Domestic Product(NDP) = GDP - Depreciation
• National Income = NNP(at factor cost)
India: Lower Middle Income Nation
Group July 1, 2020 (new) July 1, 2019 (old)
Low Income < 1,036 < 1,026
Lower-Middle Income 1,036 - 4,045 1,026 - 3,995
Upper-Middle Income 4,046 - 12,535 3,996 - 12,375
High Income > 12,535 > 12,375
4
Page
Telegram: CBL- Haryana Civil Services Call / WhatsApp: 9779068345
You might also like
- 2012 H - R Block ProgramDocument11 pages2012 H - R Block ProgramNASJRBNOLAOmbudsmanNo ratings yet
- Car Skoda Rapid 2013Document19 pagesCar Skoda Rapid 2013WILLIAM HASSETTNo ratings yet
- (Contributions in Military History, 26) Hans Delbrück - History of The Art of War - Within The Framework of Political History. Vol. 3. The Middle Ages. 3-Greenwood Press (1982)Document718 pages(Contributions in Military History, 26) Hans Delbrück - History of The Art of War - Within The Framework of Political History. Vol. 3. The Middle Ages. 3-Greenwood Press (1982)AdrianOchoyanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- Bicolandia Drug Corp Vs CIRDocument1 pageBicolandia Drug Corp Vs CIRDPMPascuaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- HE9091 Lecture 7Document60 pagesHE9091 Lecture 7XL TNo ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- GDPDocument19 pagesGDPxx69dd69xxNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document40 pagesSession 2Digvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Discussion B-3Document64 pagesDiscussion B-3Tahfim KhanNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document19 pagesSession 3Ramji TripathyNo ratings yet
- ch-7 NewDocument16 pagesch-7 NewSAKIB MD SHAFIUDDINNo ratings yet
- Economic Environment of Business-GdpDocument42 pagesEconomic Environment of Business-GdpBalajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Seamnia demoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 National Income AccountingDocument83 pagesUnit 2 National Income Accountingbrianmfula2021100% (1)
- Unit 7.national Income Accounting 1Document23 pagesUnit 7.national Income Accounting 1RaceSome MagarNo ratings yet
- PGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana TokasDocument30 pagesPGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana Tokasv_amyNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeDocument66 pagesConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Economics: Combined Version Edwin G. Dolan Best Value Textbooks 4 EditionDocument28 pagesEconomics: Combined Version Edwin G. Dolan Best Value Textbooks 4 EditionNaveed ShaukatNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- GDPDocument43 pagesGDPAbdullahNo ratings yet
- National Income: Concepts and MeasurementDocument34 pagesNational Income: Concepts and MeasurementQammer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument32 pagesNational IncomeSona VermaNo ratings yet
- Gyaan Kosh: Global EconomicsDocument19 pagesGyaan Kosh: Global EconomicsU KUNALNo ratings yet
- GDP Measurement - Identities - Session3Document37 pagesGDP Measurement - Identities - Session3Haardik GandhiNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- 1666496610-NSUT MBA UNIT 5A (National Income)Document22 pages1666496610-NSUT MBA UNIT 5A (National Income)Hitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document70 pagesModule 2PriyankaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting NotesDocument4 pagesNational Income Accounting NotesAkirha SoNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2 The Measurement and Structure of The National EconomyDocument39 pagesLecture # 2 The Measurement and Structure of The National EconomyMudassar ZuberiNo ratings yet
- 05 - GDPDocument16 pages05 - GDPCourtney WoodNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic Product: Module-2Document25 pagesGross Domestic Product: Module-2Manjesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument81 pagesEconomicsmadhusudan2005No ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 MacroeconomicsDocument63 pagesCH 2 MacroeconomicsYidid GetachewNo ratings yet
- Nations WealthDocument49 pagesNations WealthwomabaNo ratings yet
- National Income Final PPT Full Including PYQDocument69 pagesNational Income Final PPT Full Including PYQSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceDocument34 pagesLecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceAli zizoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- 1 National IncomeDocument17 pages1 National Incomealekya.nyalapelli03No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument49 pagesNational IncomeStive JohnNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- Me Unit-5Document7 pagesMe Unit-5Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesGross Domestic ProductABBAS ANo ratings yet
- 4 - Macroeconomics Board Exam Syllabus Part 1 Final PDFDocument53 pages4 - Macroeconomics Board Exam Syllabus Part 1 Final PDFastra_per_asperaNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument53 pagesNational Income AccountingAisa Castro Arguelles75% (4)
- Econ 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17Document48 pagesEcon 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17FatmahNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNPDocument27 pagesGDP and GNPKeerthikanthGubbalaNo ratings yet
- GNP, Consumption, Investment, Net Exports, Disposable Income EtcDocument18 pagesGNP, Consumption, Investment, Net Exports, Disposable Income EtcAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- The Measurement of National Income Chapter Twenty Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 1202.2BDocument21 pagesThe Measurement of National Income Chapter Twenty Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 1202.2BNayem ImtiazNo ratings yet
- National Income: Submitted byDocument85 pagesNational Income: Submitted byShrutiNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument20 pagesNational Income AccountingDhireshKulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Coach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesCoach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic Productapi-255899090No ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument36 pagesNational Income AccountingTashalee WynterNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Macroeconomics (Ch.23)Document36 pagesAn Introduction To Macroeconomics (Ch.23)jawadzaheerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 and 4 - MacroeconomicsDocument37 pagesLecture 3 and 4 - Macroeconomicsshubham solankiNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument46 pagesNational Income AccountingMohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Eco Quick RevisionDocument42 pagesEco Quick RevisionRitesh RajNo ratings yet
- CG Unit 3Document18 pagesCG Unit 3Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- CG Unit 1Document37 pagesCG Unit 1Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2-D Viewing Transformation Window To Viewport TransformationDocument16 pages2-D Viewing Transformation Window To Viewport TransformationKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- CG Unit 4Document28 pagesCG Unit 4Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neural NetworkDocument59 pagesNeural NetworkKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1618311762-1. Basic of MicroeconomicDocument3 pages1618311762-1. Basic of MicroeconomicKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1618486180-3. NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Part - 2Document4 pages1618486180-3. NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Part - 2Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Report Text Editor in JavaDocument10 pagesProject Report Text Editor in JavaKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Development and Classification: International Accounting, 6/eDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Development and Classification: International Accounting, 6/eSylvia Al-a'maNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For International Accounting 5th Edition by DoupnikDocument24 pagesTest Bank For International Accounting 5th Edition by Doupnikjaperstogyxp94cNo ratings yet
- (April-18) (MBC-106) Ii Semester Income Tax Law and Practice Time: 3 Hours Max - Marks: 60Document4 pages(April-18) (MBC-106) Ii Semester Income Tax Law and Practice Time: 3 Hours Max - Marks: 60Bhuvaneswari karuturiNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help System Laguna - JONELTA: Basic Education Department - Senior High SchoolDocument15 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System Laguna - JONELTA: Basic Education Department - Senior High SchoolGONZALES CamilleNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Tax II - Karim Final SY 2223 PG1-2v2Document4 pagesCourse Outline Tax II - Karim Final SY 2223 PG1-2v2Lucifer MorningstarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Scope of The StudyDocument56 pages1.2 Scope of The StudyArif Mohammad67% (3)
- IR Garg SonsDocument2 pagesIR Garg SonsAnshu MoryaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Constitutional Provisions Regarding Trade and Commerce in IndiaDocument13 pagesProject Report On Constitutional Provisions Regarding Trade and Commerce in IndiaAnantHimanshuEkka50% (2)
- Income Taxation ReviewerDocument51 pagesIncome Taxation ReviewerKevin Ken Sison GancheroNo ratings yet
- The Case Against Modern Monetary TheoryDocument2 pagesThe Case Against Modern Monetary TheoryAndres LakeNo ratings yet
- 2 (36) (C) (Application For Approval As Non-Profit Organization)Document2 pages2 (36) (C) (Application For Approval As Non-Profit Organization)Max ClerkNo ratings yet
- 02 Allowable DeductionsDocument56 pages02 Allowable DeductionsHazel ChatsNo ratings yet
- Bagatsing Vs Ramirez - DigestDocument1 pageBagatsing Vs Ramirez - DigestAnonymous 3cfBSXFNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Case StudyDocument7 pagesAssignment On: Case Studyimran mahmudNo ratings yet
- Options:: Short Questions & Answers On Accounting Standard 29Document2 pagesOptions:: Short Questions & Answers On Accounting Standard 29Dhirendra Kumar Dhal100% (1)
- Tutorial 3 MFRS8 Q PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 MFRS8 Q PDFKelvin LeongNo ratings yet
- Farm Laws: Confl Ating Deregulation With ModernisationDocument6 pagesFarm Laws: Confl Ating Deregulation With ModernisationRASHMI RASHMINo ratings yet
- L 1 Mockv 12016 DecemberpmquestionsDocument39 pagesL 1 Mockv 12016 DecemberpmquestionsNilotpal ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Penerapan Metode Cup Pada Transaksi Cpo Antara Pihak-Pihak Yang Memiliki Hubungan IstimewaDocument16 pagesPenerapan Metode Cup Pada Transaksi Cpo Antara Pihak-Pihak Yang Memiliki Hubungan Istimewakhunaina il khafa ainul NazilatulNo ratings yet
- Waller County Appraisal DistrictDocument4 pagesWaller County Appraisal DistrictO'Connor AssociateNo ratings yet
- Saurabh Pratap Singh - Activitas - NMIMS-B - Automobile Industry AnalysisDocument73 pagesSaurabh Pratap Singh - Activitas - NMIMS-B - Automobile Industry AnalysisSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- AASB 112 Fact SheetDocument4 pagesAASB 112 Fact SheetCeleste LimNo ratings yet
- Types of White Collar CrimesDocument2 pagesTypes of White Collar Crimesshah md musleminNo ratings yet
- Ebiz Answers Oracle R12 and Fusion One or Multiple Operating Units PDFDocument7 pagesEbiz Answers Oracle R12 and Fusion One or Multiple Operating Units PDFtiwarihereNo ratings yet
- Tolentino CaseDocument183 pagesTolentino CaseMary Joy NavajaNo ratings yet
- Myeg InvoiceDocument1 pageMyeg InvoiceRiaz KhanNo ratings yet