Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 4
Uploaded by
Buliga MarianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 4
Uploaded by
Buliga MarianCopyright:
Available Formats
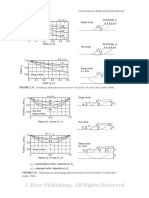
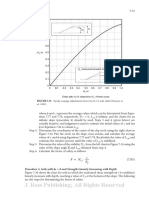
Slope Stability 7-53
No water in crack β=0
1.0
0.9 30°
Factor µt
0.8 Toe and 60°
0.7 slope circles
90°
0.6 No water in
crack Slope circle
0.5
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 b :1 Ht
Ratio Ht / H β
No water in crack d=∞
1.0
1.0
0.9 0.5
Factor µt
0.8 0
0.7 Deep circles Toe circle
0.6 No water in b :1 Ht
crack β
0.5
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
Ratio Ht / H
Crack filled with water β = 0 Deep circle
1.0 d = D/H
0.9 b :1 Ht
30° β H
Factor µt
0.8 Toe and 60°
0.7 slope circles D
90°
0.6 Crack filled
with water
0.5
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
Ratio Ht / H
Crack filled with water d = ∞
1.0
1.0
0.9 0.5
Factor µt
0.8 0
0.7 Deep circles
0.6 Crack filled
with water
0.5
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
Ratio Ht / H
FIGURE 7.33 Tension crack adjustment factors for φ = 0 and φ > 0 soils (after Janbu 1968).
Procedure 2. Soils with > 0, c > 0 and Uniform Strength
The slope stability charts for φ > 0 soils are presented in Figure 7.34. These charts can be used
for both total and effective stress analysis. The adjustment factors for surcharge pressure,
seepage and submergence, and tension cracks are obtained from the charts presented in
Figures 7.31–7.33 for φ = 0 soils.
The stability numbers in Figure 7.34 are calculated using a toe circle, which is mostly the
case for slopes in uniform soils with φ > 0. In nonhomogeneous soils, or if water is present
outside the slope, a circle other than the toe circle may be critical. In estimating the location
of the critical circle, the following criteria may be used:
J. Ross Publishing; All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 3Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 3Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Consider a reservoir with the following data 0.17 1 1 80,000 ft 40,000 ft 10,000 STB/D Viscosity data: μ = 1.05 cp μ = 2.5+ 36 12 Fractional flow dataDocument3 pagesConsider a reservoir with the following data 0.17 1 1 80,000 ft 40,000 ft 10,000 STB/D Viscosity data: μ = 1.05 cp μ = 2.5+ 36 12 Fractional flow dataVictor Pugliese ManotasNo ratings yet
- Design of StructuressanDocument95 pagesDesign of StructuressanSamir Rawat100% (1)
- Clevis and Lug Design V0001Document2 pagesClevis and Lug Design V0001Ben FriskneyNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Pressure Calculation For Sump: Bending Moment Diagram Hoop Tension DiagramDocument8 pagesHydrodynamic Pressure Calculation For Sump: Bending Moment Diagram Hoop Tension Diagramepe civilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Design Tables for Stress Concentration FactorsDocument10 pagesMechanical Engineering Design Tables for Stress Concentration FactorsĞôřqûî ĀğūîřřêNo ratings yet
- Madany 2018Document38 pagesMadany 2018mohamed magdyNo ratings yet
- Syphonic System CalculationDocument9 pagesSyphonic System CalculationLeslie LeeNo ratings yet
- Interaction Diagrams for Steel BeamsDocument48 pagesInteraction Diagrams for Steel BeamsGeorge Henry Perez Cruz100% (1)
- For Gate EstimateDocument6 pagesFor Gate EstimateMarkko Buaya TalonNo ratings yet
- Uji GeserDocument1 pageUji GeserMachpud SagapNo ratings yet
- Stability analysis of L-type retaining wallDocument42 pagesStability analysis of L-type retaining wallSiva SundarNo ratings yet
- Layout K1SG-RHDocument11 pagesLayout K1SG-RHNPD TEAM HosurNo ratings yet
- Kali AnyarDocument4 pagesKali AnyarTeguh PrihantoNo ratings yet
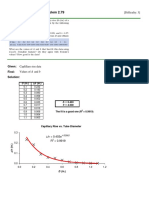
- Problem 2.79 PDFDocument1 pageProblem 2.79 PDFKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem #22Document8 pagesSample Problem #22Dozdi0% (1)
- Tank Wall ThicknessDocument1 pageTank Wall Thicknessjack macNo ratings yet
- Tarea DestilacionDocument12 pagesTarea DestilacionAnyy Ocon TtitoNo ratings yet
- Pressure DropDocument4 pagesPressure Dropmartin.rubenNo ratings yet
- GD FL: Units Engineering Consultancy P LTDDocument2 pagesGD FL: Units Engineering Consultancy P LTDMegh Raj KCNo ratings yet
- Av02 2228en Ds HLMP Cx1a 2013 05 22-1827913Document13 pagesAv02 2228en Ds HLMP Cx1a 2013 05 22-1827913Daniel PradoNo ratings yet
- Table A. Equivalent Length, (L/D) of Valves and Pipe FittingsDocument7 pagesTable A. Equivalent Length, (L/D) of Valves and Pipe Fittingst_i_f_anoNo ratings yet
- The Graph of Refracted Angle Versus Incident AngleDocument3 pagesThe Graph of Refracted Angle Versus Incident AngleKuna KunavathiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of CC BlockDocument1 pageAnalysis of CC Blockrasel lokmanNo ratings yet
- Expantion N Contraction Joint (Section 12)Document12 pagesExpantion N Contraction Joint (Section 12)nurul falakh akhmadNo ratings yet
- Optimization of distillation column parametersDocument5 pagesOptimization of distillation column parametersShada ZhafiraNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 Center of Pressure: Student NamesDocument10 pagesExperiment #1 Center of Pressure: Student NamesAnas Abu-shawishNo ratings yet
- Geser Langsung (ASTM D 3080 - 82) : Proyek: Lokasi: Titik/KedalamanDocument1 pageGeser Langsung (ASTM D 3080 - 82) : Proyek: Lokasi: Titik/KedalamanSofyan AriNo ratings yet
- Stress Concentration Factors Chart 2.7, Page 87, (Ktu Vs Ktalfa)Document4 pagesStress Concentration Factors Chart 2.7, Page 87, (Ktu Vs Ktalfa)Mehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- Pile AbutmentDocument41 pagesPile AbutmentArdiaTiaraRNo ratings yet
- Cci Heat Pipe Design Guide: Rev: D01Document22 pagesCci Heat Pipe Design Guide: Rev: D01yuhan3No ratings yet
- SP 16 ChartsDocument12 pagesSP 16 Chartsabhijeetchaudhary7779No ratings yet
- Objective Flow in PipeDocument3 pagesObjective Flow in PipeFatin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- RMF and RMCDocument1 pageRMF and RMCdewi sintia RekaNo ratings yet
- 19bme1186 FM Ex 9Document6 pages19bme1186 FM Ex 9Koushik Ch 19BME1186No ratings yet
- Turap BaruDocument35 pagesTurap BaruAbadi YusufNo ratings yet
- Determining Major Loss Through Annular Pipe FlowDocument6 pagesDetermining Major Loss Through Annular Pipe FlowKoushik Ch 19BME1186No ratings yet
- Volume Magnetic Susceptibility of MnSO4Document5 pagesVolume Magnetic Susceptibility of MnSO4Ankit PatelNo ratings yet
- PL4-EMAG (Recuperado Automaticamente)Document6 pagesPL4-EMAG (Recuperado Automaticamente)Gonçalo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Công ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeDocument3 pagesCông ngh ệ khai thác Petroleum Production Engineering: Chapter 5. Single phase in pipeTu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- Nilai K (Minor Losses)Document3 pagesNilai K (Minor Losses)Andri PaiNo ratings yet
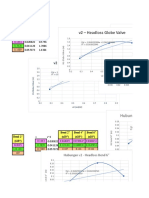
- Headloss Globe Valve and Gate Valve ChartDocument8 pagesHeadloss Globe Valve and Gate Valve ChartClarita BangunNo ratings yet
- Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowDocument24 pagesConcentric Tube Heat Exchanger: Parallel FlowFalcon KingdomNo ratings yet
- Program CanalDocument5 pagesProgram CanalShem ArguillaNo ratings yet
- Flume AnalysisDocument11 pagesFlume AnalysisLarizza TesicoNo ratings yet
- Lampiran B Contoh Perhitungan: B.1 Membuat Larutan 200 ML Naoh 1 NDocument5 pagesLampiran B Contoh Perhitungan: B.1 Membuat Larutan 200 ML Naoh 1 NImmanuel HutagaolNo ratings yet
- Temperature Profile Along ReactorDocument3 pagesTemperature Profile Along Reactorjoebug34No ratings yet
- 08 Viscous FlowDocument40 pages08 Viscous FlowJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Perambatan PanasDocument16 pagesContoh Soal Perambatan PanasMuchammad Yusup FNo ratings yet
- PLUMBING Booster Pump (AS PER IPC) - 13Document55 pagesPLUMBING Booster Pump (AS PER IPC) - 13Mohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Tank Calculation TemplateDocument4 pagesTank Calculation TemplateKazehaya AliNo ratings yet
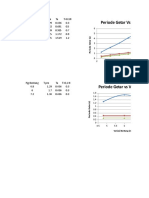
- Periode Getar Vs Variasi LantaiDocument2 pagesPeriode Getar Vs Variasi LantaiSaefullah EfulNo ratings yet
- Dual Row Right Angle SMT Pin Header 2037 SeriesDocument1 pageDual Row Right Angle SMT Pin Header 2037 SeriesEstefaniaNo ratings yet
- Rep025 011Document11 pagesRep025 011Ilhame HarNo ratings yet
- Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler Design and OperationDocument9 pagesCirculating Fluidized Bed Boiler Design and OperationSanket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Longets Run Section Pressure Plenum 0 0.5 0Document11 pagesLongets Run Section Pressure Plenum 0 0.5 0IanNo ratings yet
- PCC Toe WallDocument4 pagesPCC Toe WallSambhav PoddarNo ratings yet
- Modulo IIDocument9 pagesModulo IIjose antonio manchaNo ratings yet
- Template Uji Umur Simpan Kadar Air KritisDocument11 pagesTemplate Uji Umur Simpan Kadar Air Kritisanisa zNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002)Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002)Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 3Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 3Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 1Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 1Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 6Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 6Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002)Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002)Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 Rockfill Layer or Blockade With Natural Stones: AdvantagesDocument1 page3.1.3 Rockfill Layer or Blockade With Natural Stones: AdvantagesBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 5Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 5Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 2Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 2Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Building Permit Application Thickness (M) Line Name Starting (CH.) Ending (CH.) Length (M)Document1 pageBuilding Permit Application Thickness (M) Line Name Starting (CH.) Ending (CH.) Length (M)Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Advantages:: 3.1.9 Geocells Filled With Granular Material For Slope Protection in CutsDocument1 pageAdvantages:: 3.1.9 Geocells Filled With Granular Material For Slope Protection in CutsBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 6Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 6Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- S4-13-Bridge Design W ECs Tschumi 20121002-Ispra 5Document1 pageS4-13-Bridge Design W ECs Tschumi 20121002-Ispra 5Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 1Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 1Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Granular Layer (For Cut and Embankment) : Table 4: Aplicability For Soil Replacement SolutionDocument1 pageReinforced Granular Layer (For Cut and Embankment) : Table 4: Aplicability For Soil Replacement SolutionBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Designers' Guides To Eurocodes, by Telford: Seminar Bridge Design With Eurocodes' - JRC Ispra, 1-2 October 2012Document1 pageDesigners' Guides To Eurocodes, by Telford: Seminar Bridge Design With Eurocodes' - JRC Ispra, 1-2 October 2012Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- S4-13-Bridge Design W ECs Tschumi 20121002-Ispra 4Document1 pageS4-13-Bridge Design W ECs Tschumi 20121002-Ispra 4Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Curs 10Document1 pageCurs 10Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Curs 9Document1 pageCurs 9Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- EN 1991 EN 1991 - 2 2 - CONTENTS (Continued) CONTENTS (Continued)Document1 pageEN 1991 EN 1991 - 2 2 - CONTENTS (Continued) CONTENTS (Continued)Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Curs 5Document1 pageCurs 5Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 5Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 5Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Preface: J. Ross Publishing All Rights ReservedDocument1 pagePreface: J. Ross Publishing All Rights ReservedBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Combinations of Actions: EN 1990 EN 1990 - Annex A2 (Amendment A1) Annex A2 (Amendment A1) - ContentDocument1 pageCombinations of Actions: EN 1990 EN 1990 - Annex A2 (Amendment A1) Annex A2 (Amendment A1) - ContentBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- J. Ross Publishing All Rights Reserved: Slope StabilityDocument1 pageJ. Ross Publishing All Rights Reserved: Slope StabilityBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Editor-in-Chief: J. Ross Publishing All Rights ReservedDocument1 pageEditor-in-Chief: J. Ross Publishing All Rights ReservedBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Handbook Chapters on Shallow Foundations, Pile Foundations, Retaining WallsDocument1 pageGeotechnical Engineering Handbook Chapters on Shallow Foundations, Pile Foundations, Retaining WallsBuliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Curs 10Document1 pageCurs 10Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Braja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 10Document1 pageBraja M Das - Geotechnical Engineering Handbook, Volumes 1 - 3-John Wiley & Sons (2002) - 10Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Autonomy From ParentsDocument7 pagesAutonomy From ParentsUzair RiazNo ratings yet
- Iptc 15508 MSDocument10 pagesIptc 15508 MSreservoir_ffNo ratings yet
- A InstantonDocument61 pagesA InstantonbayareakingNo ratings yet
- Probability ProblemsDocument3 pagesProbability Problemsembers poggerNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 2 PDFDocument2 pagesPractice Set 2 PDFDipendra GiriNo ratings yet
- Influence and Correlation in Social Networks: Aris Anagnostopoulos Ravi Kumar Mohammad MahdianDocument9 pagesInfluence and Correlation in Social Networks: Aris Anagnostopoulos Ravi Kumar Mohammad MahdianSean TongNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument8 pagesBrochureCristian Jhair PerezNo ratings yet
- Ilya Prigogine - Creativity in Art and Nature PDFDocument4 pagesIlya Prigogine - Creativity in Art and Nature PDFameliaNo ratings yet
- ME6511 Dynamics Lab ExperimentsDocument3 pagesME6511 Dynamics Lab Experimentsraj_klnceNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Dragged To US Court Over AI Copyright - WorldDocument13 pagesChatGPT Dragged To US Court Over AI Copyright - WorldAlexia JacksonNo ratings yet
- F5 Networks Training BIG IP LTM V10 EssentialsDocument108 pagesF5 Networks Training BIG IP LTM V10 Essentialsvelramsen100% (1)
- Control of Corrosion and ScalingDocument63 pagesControl of Corrosion and ScalingTalang AkarNo ratings yet
- Anju Talwar: Senior Vice President and Global Hiring and Training LeaderDocument4 pagesAnju Talwar: Senior Vice President and Global Hiring and Training LeaderVince RochaNo ratings yet
- CPM/ PERT in Industrial EngineeringDocument80 pagesCPM/ PERT in Industrial EngineeringSuneel Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 - Case Study Part 1 InstructionsDocument5 pagesAssignment #2 - Case Study Part 1 InstructionsJordanne ChristieNo ratings yet
- Intuitionistic Hesitant Fuzzy Filters in BE-AlgebrasDocument7 pagesIntuitionistic Hesitant Fuzzy Filters in BE-AlgebrasEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Profibus ProfinetDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Profibus ProfinetSyariefNo ratings yet
- Ch13 - NLP, DP, GP2005Document76 pagesCh13 - NLP, DP, GP2005Sonya DewiNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction Samsung ProjDocument57 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Samsung ProjVikas Gupta MirzapurNo ratings yet
- District Training on Test Construction and TOSDocument65 pagesDistrict Training on Test Construction and TOSShikinah Glory Padilla100% (15)
- Real Research PaperDocument4 pagesReal Research Paperapi-252255976No ratings yet
- Install and boot macOS High SierraDocument3 pagesInstall and boot macOS High SierraDavid GatoNo ratings yet
- Create Learning Stations: Flexible Seating PlanDocument15 pagesCreate Learning Stations: Flexible Seating PlanlevyNo ratings yet
- Formal EmailDocument15 pagesFormal EmailThu Lan TrầnNo ratings yet
- Nick Winkelman Coaching ScienceDocument15 pagesNick Winkelman Coaching ScienceDiego LacerdaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 Normalization 2Document54 pagesLec 8 Normalization 2Banda Shravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Nowhere Girls ExcerptDocument97 pagesNowhere Girls ExcerptSimon and SchusterNo ratings yet
- Curative International MarketingDocument6 pagesCurative International MarketingSAYOUBA GANEMTORENo ratings yet
- Sped Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesSped Lesson Plansapi-264477124No ratings yet
- 303 - Data WarehousingDocument14 pages303 - Data WarehousingManohar AkulaNo ratings yet