Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan HYPERTENSION
Uploaded by
Jasmin T. Regaspi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views3 pagesNursing Care Plan HYPERTENSION
Uploaded by
Jasmin T. RegaspiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Nursing Care Plan: Hypertension
Nursing care planning goals for hypertension include lowering or controlling blood pressure, adherence to the therapeutic regimen, lifestyle
modifications, and prevention of complications.
Here are six nursing diagnoses for hypertension nursing care plans:
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output
Risk for Impaired Cardiovascular Function
Decreased Cardiac Output
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Tissue Perfusion
NANDA Definition: Inadequate blood pumped by the heart to meet metabolic demands of the body.
Blood pressure is the product of cardiac output multiplied by peripheral resistance. Hypertension can result from an
increase in cardiac output (heart rate multiplied by stroke volume), an increase in peripheral resistance, or both.
Decreased Activity Tolerance
NANDA Definition: Insufficient physiological or psychological energy to endure or complete required or desired daily
activities.
Another nursing diagnosis for hypertension is Decreased Activity Tolerance, which frequently occurs due to alterations in
cardiac output and side effects of antihypertensive medications.
Acute Pain
NANDA Definition: Pain is whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever the person says it does; an
unpleasant sensory and emotional experience arising from actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of
such damage sudden or slow onset of any intensity from mild to severe with an anticipated or predictable end and a
duration of.
Elevation in resting blood pressure means a progressive reduction in sensitivity to acute pain, which could result in a
tendency to restore arousal levels in the presence of painful stimuli.
Ineffective Coping
NANDA Definition: Inability to form a valid appraisal of the stressors, inadequate choices of practiced responses, and/or
inability to use available resources.
The general well-being (“I’m not feeling sick”), the complexity of the therapeutic regimen, required lifestyle changes, and
side effects of medications usually result in the inability of the patients to cope.
Overweight
NANDA Definition: Intake of nutrients that exceeds metabolic needs.
Excess weight or being overweight is an added risk in causing hypertension. Studies suggest that weight gain may
pathophysiologically contribute to blood pressure elevation.
Deficient Knowledge
NANDA Definition: Absence or deficiency of cognitive information related to a specific topic.
The patient’s understanding of the disease process, therapeutic regimen, and lifestyle changes are key in controlling
hypertension. In nursing diagnosis Deficient Knowledge the nurse must emphasize the concept of controlling
hypertension rather than curing it.
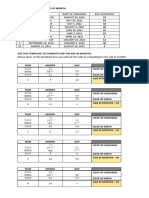
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Decreased Activity After 8 hrs. of nsg. Independent:
“Lagi po akong Tolerance related to interventions, the pt. Assess and record vs Baseline data for assessment After 8 hrs. of nsg.
nahihilon, imbalanced will: Note each of the factors Fatigue affects both the client’s actual and interventions, the pt.
between oxygen that contribute to fatigue perceived ability to participate in activities.
nanghihina at Participate in Able to met the goal.
supply and demand Evaluate the patient’s Provides comparative baseline and provides
mabilis pong desired activities Blood pressure
as evidenced by degree of activity information about needed education
mapagod. Mataas Use identified decreased from 140/110
verbal report of intolerance and when it and interventions regarding the quality of life.
din po ang BP ko” fatigue and techniques to to 120/80. The pt. was
enhance activity occurs.
as verbalized by the weaknesses, and Monitor how the patient Noting pulse rate more than 20 beats per min able to participate in
abnormal blood tolerance
patient. responds to activity faster than resting rate; marked increase in BP activities that reduce
pressure response Report a
measurable (pulse, heart rate, chest during and after activity (systolic pressure BP/cardiac workload
to activity. pain, dizziness, excessive increase of 40 mm Hg or diastolic pressure
Objective: increase in and; Risk for decreased
T- 35 °C activity tolerance. fatigue, etc.). increase of 20 mm Hg); dyspnea or chest pain; cardiac output is lessen.
excessive fatigue and weakness; diaphoresis;
BP- 140/110
dizziness or syncope. The stated parameters
mmHg help assess physiological responses to the
PR- 64 bpm stress of activity and, if present, are indicators
RR- 21bpm of overexertion.
O2Sat- 97% Instruct the patient in It helps reduce energy expenditure, thereby
energy-saving techniques assisting the equalization of oxygen supply and
demand.
Encourage progressive Gradual activity progression prevents a sudden
activity and self-care increase in cardiac workload. Providing
when tolerated. assistance only as needed encourages
independence in performing activities.
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Risk for Decreased After 8 hrs. of nsg. Independent:
“Lagi po akong Cardiac Output interventions, the pt. Assess and record vs Baseline data for assessment After 8 hrs. of nsg.
nahihilo at secondary to will: Elevate HOB Gravity decrease blood return to the heart thus interventions, the pt.
hypertension decreasing volume and pressure.
tumataas po ang Decrease blood Able to met the goal.
BP ko” as pressure from Auscultate heart tones S4 heart sound is common in severely Blood pressure
140/110 to and breath sounds. hypertensive patients because of atrial
verbalized by the decreased from 140/110
120/80 hypertrophy (increased atrial volume and
patient. pressure). Development of S3 indicates to 120/80. The pt. was
Participate in
ventricular hypertrophy and impaired able to participate in
activities that
Objective: reduce functioning. The presence of crackles, wheezes activities that reduce
T- 35 °C BP/cardiac may indicate pulmonary congestion secondary BP/cardiac workload
BP- 140/110 workload. to developing or chronic heart failure. and; Risk for decreased
mmHg Risk for Observe skin color, The presence of pallor; cool, moist skin; and cardiac output is lessen.
decreased moisture, temperature and delayed capillary refill time may be due to
PR- 64 bpm
cardiac output capillary refill time. peripheral vasoconstriction or reflect cardiac
RR- 21bpm decompensation and decreased output.
O2Sat- 97% will be lessen.
Provide calm and restful To provide comfort and rest.
environment and
encourage rest
Maintain activity To lessens physical stress and tension that
restrictions affect blood pressure and course of
Emphasize importance of hypertension
low salt, low fat diet Restriction can help manage fluid retention that
is associated with hypertensive response.
Dependent:
Administer Losartan Administer as ordered to help reduce blood
50mg 1tab as ordered. pressure.
Collaborative:
Referred to dietician for For co-management and formulation of proper
low salt, low fat diet. diet plan.
You might also like
- Complications Bariatric SurgeryDocument8 pagesComplications Bariatric SurgeryThita Orrego100% (1)
- Heart Failure Guide for NursesDocument54 pagesHeart Failure Guide for NursesKacelyn QuibanNo ratings yet
- Care of The Acutely Unwell FinalDocument100 pagesCare of The Acutely Unwell Finalgireeshsachin100% (1)
- HypertensionDocument5 pagesHypertensionCia Yee YeohNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs of PregnancyDocument3 pagesDanger Signs of PregnancyNesly Khyrozz LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Code Blue ManagemnetDocument36 pagesCode Blue ManagemnetPreethi BNo ratings yet
- Frequency Specific MicrocurrentDocument2 pagesFrequency Specific MicrocurrentAngela Pagliuso50% (2)
- GROUP 3 - CASE STUDY - TraumaDocument5 pagesGROUP 3 - CASE STUDY - TraumaDinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Case 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)Document2 pagesCase 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)je-ann catedralNo ratings yet
- JjjjokjhDocument4 pagesJjjjokjhWajiha Esmula TiuNo ratings yet
- Assess Patients HolisticallyDocument18 pagesAssess Patients HolisticallySavita Hanamsagar100% (1)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument19 pagesCongestive Heart FailureIlavenil PanduranganNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Case StudyDocument10 pagesHead Injury Case StudyJayd Lorenz Vicente ChuanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument34 pagesCase StudyBSNNursing101No ratings yet
- ChartingDocument41 pagesChartingArlene Saint AnthonieNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Board ExamDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Board Examrhenier_ilado86% (14)
- Wender Utah PDFDocument3 pagesWender Utah PDFFco CanaleNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument5 pagesResumeMal Di TaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesApproach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Transitional Care Case Study-Pulling It All TogetherDocument13 pagesTransitional Care Case Study-Pulling It All TogethermatthewNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade and ManagementDocument42 pagesCardiac Tamponade and Managementأم حمدNo ratings yet
- VIOME+E-book Microbiom PDFDocument43 pagesVIOME+E-book Microbiom PDFNaša DjecaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumDocument6 pagesBy Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs MeasurementDocument17 pagesVital Signs MeasurementEly TalledoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANANo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Acute BronchitisDocument38 pagesAcute BronchitisNikko MelencionNo ratings yet
- White Turqoise Creative Simple Medical Personnel Nurse ResumeDocument1 pageWhite Turqoise Creative Simple Medical Personnel Nurse ResumeRaymond EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Case PresentationDocument32 pagesHypertension Case PresentationAnnaMaeGacutanMarantanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment:: Intervention Rationale Independent InterventionsDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment:: Intervention Rationale Independent Interventionsnananana123No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument4 pagesHeart FailureDane WrightNo ratings yet
- Cardiac NSG DiagnosisDocument5 pagesCardiac NSG DiagnosisShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Standardized Toolbox for Pediac Surgery: Abdominal Masses of ChildhoodDocument30 pagesStandardized Toolbox for Pediac Surgery: Abdominal Masses of ChildhoodririlibertiNo ratings yet
- Administration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyDocument8 pagesAdministration of Inotropes Evidence Based Nursing PolicyRonald ThakorNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationDocument64 pagesLeft-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Pericarditis NCLEX Review: Serous Fluid Is Between The Parietal and Visceral LayerDocument2 pagesPericarditis NCLEX Review: Serous Fluid Is Between The Parietal and Visceral LayerlhenNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bronchitis Case PresentationDocument28 pagesPediatric Bronchitis Case PresentationJoshua DulayNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Hypertension CaseDocument2 pagesHeart Failure and Hypertension CasePaulo Arwin BaduriaNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY FORMAT (Kidney Transplantation)Document12 pagesCASE STUDY FORMAT (Kidney Transplantation)ashnaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument14 pagesCongestive Heart FailureBella Trix PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Managing Respiratory Failure in Myasthenia Gravis and Guillain-Barré SyndromeDocument7 pagesManaging Respiratory Failure in Myasthenia Gravis and Guillain-Barré SyndromePutri Cindy Claudia PandoyoNo ratings yet
- Health Teachings On CHFDocument6 pagesHealth Teachings On CHFfLOR_ZIANE_MAENo ratings yet
- Generic Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationDocument3 pagesGeneric Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationAnselle CasilNo ratings yet
- MR Elamin ShockDocument70 pagesMR Elamin ShockMohammed Abd AlgadirNo ratings yet
- Assignmen 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesAssignmen 1 AnswersAlasl BobyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument64 pagesCase Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaHazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process 3Document10 pagesNursing Process 3Shubhra Sheoran100% (1)
- NursingCare PlanDocument8 pagesNursingCare PlanSunSearra Kennedy RuffinNo ratings yet
- (Osborn) Chapter 56: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)Document19 pages(Osborn) Chapter 56: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)KittiesNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation OF Acute Tonsillitis: Nueva Ecija University of Science andDocument38 pagesCase Presentation OF Acute Tonsillitis: Nueva Ecija University of Science andBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) ExplainedDocument23 pagesTransurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) ExplainedColeen Comelle HuertoNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation IM DDHDocument12 pagesCase Presentation IM DDHAishwarya BharathNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Pericardial EffusionDocument2 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Pericardial EffusionAgung Alber0% (3)
- Nstemi: How To Risk Stratify?Document32 pagesNstemi: How To Risk Stratify?dhannibernadetNo ratings yet
- Anemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsDocument7 pagesAnemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsSahara GalayNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- MARCOS - Legal Issues of ElderlyDocument2 pagesMARCOS - Legal Issues of ElderlyArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromDocument38 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndrompatriaindraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of ArrhythmiasDocument15 pagesPathophysiology of ArrhythmiasJonathan MontecilloNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid ChartDocument2 pagesIV Fluid Charthady920No ratings yet
- February 2024 OSHEMAC I Acceptance Letter and Registration FormDocument2 pagesFebruary 2024 OSHEMAC I Acceptance Letter and Registration FormadorabletwhindingwiNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Insulin PDFRetno WulanNo ratings yet
- Patient DT STEMI CaseDocument18 pagesPatient DT STEMI CaseZNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis overview and nursing careDocument18 pagesHepatitis overview and nursing careAnne B. BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy: Types and UsesDocument11 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy: Types and UsesHayashi Breads MaaNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveFrom EverandHealthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveNo ratings yet
- Vascular Responses to PathogensFrom EverandVascular Responses to PathogensFelicity N.E. GavinsNo ratings yet
- Calculate Age Months TemplateDocument2 pagesCalculate Age Months TemplateJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HeparinDocument2 pagesDrug Study HeparinJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FormatDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FormatJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care Plans: 6 Diagnoses & InterventionsDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care Plans: 6 Diagnoses & InterventionsJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Breastfeeding WatermarkDocument83 pages2020 Breastfeeding WatermarkJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- Data PersonilDocument74 pagesData Personilpanji_208No ratings yet
- Dengue Shock SyndromeDocument17 pagesDengue Shock SyndromehwelpNo ratings yet
- Kellett - Paranoid Personality Disorder Treatm.Document14 pagesKellett - Paranoid Personality Disorder Treatm.Caramel GazelleNo ratings yet
- DiethylcarbamazineDocument8 pagesDiethylcarbamazinePrakob GikokNo ratings yet
- What Are The Signs of Autism in GirlsDocument8 pagesWhat Are The Signs of Autism in GirlsAna Sofia Nunes JorgeNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance Guidelines 2020-21Document25 pagesHealth Insurance Guidelines 2020-21NIRAJ BAHEKARNo ratings yet
- Caliciviridae: A Family of Important Human and Animal VirusesDocument26 pagesCaliciviridae: A Family of Important Human and Animal VirusesabybrrNo ratings yet
- Quarter ApplicationDocument1 pageQuarter ApplicationSouvik DasNo ratings yet
- KRT Lucas Meliala, Guru Besar Luar Biasa Bagian Ilmu Penyakit SarafDocument43 pagesKRT Lucas Meliala, Guru Besar Luar Biasa Bagian Ilmu Penyakit SarafWawanHarimawanHardjowinotoNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument472 pagesHiv AidsDevendrapratapdpNo ratings yet
- The Montgomery Borgatta Caregiver Burden ScaleDocument22 pagesThe Montgomery Borgatta Caregiver Burden ScalehjhjkNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Nervosa PDFDocument6 pagesAnorexia Nervosa PDFmist73No ratings yet
- Metaplastic (Chronic) Atrophic Gastritis - UpToDate PDFDocument16 pagesMetaplastic (Chronic) Atrophic Gastritis - UpToDate PDFDinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- Dust Work QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesDust Work QuestionnaireHykidNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeAlfred BucabucaNo ratings yet
- Benha University Hospital, Egypt E-Mail: Elnashar53@Document58 pagesBenha University Hospital, Egypt E-Mail: Elnashar53@khadzx100% (3)
- Angiogenesis in CancerDocument4 pagesAngiogenesis in CanceranonymousNo ratings yet
- Acute pancreatitis symptoms, causes and diagnosisDocument12 pagesAcute pancreatitis symptoms, causes and diagnosisAmol DhopteNo ratings yet
- Fresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualDocument20 pagesFresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualCesar AlfaroNo ratings yet
- NAMA BARANG LIST AND PRICESDocument51 pagesNAMA BARANG LIST AND PRICESlevely rizkiNo ratings yet
- Cough NCPDocument2 pagesCough NCPMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet