Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Convex (Diverging) Mirror: Help Sheet
Convex (Diverging) Mirror: Help Sheet
Uploaded by
Nyasha VincentOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Convex (Diverging) Mirror: Help Sheet
Convex (Diverging) Mirror: Help Sheet
Uploaded by
Nyasha VincentCopyright:
Available Formats
page
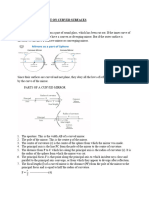
186 Convex (diverging) mirror Help
Sheet
These constructions are similar to those for a converging
mirror, but here the light is diverged away from the
principal focus, which is behind the mirror.
Construction 1
Parallel rays of light are reflected away from the
principal focus F (see Experiment 24.2 and page 172).
Construction 2
A ray of light travelling to the centre of the mirror is
reflected so that the angle of incidence = the angle of
reflection (i = r).
(Instead of using a protractor you can make sure that the
2 distances marked ‘d’ are equal.)
Drawing a ray diagram
The steps are the same as for a converging mirror.
Note that the image in a convex (diverging) mirror is always
erect,
diminished,
virtual.
Questions
1. An object 2 cm high is placed 10 cm from a diverging mirror
of focal length 10 cm.
Draw a ray diagram on graph paper (full size) to find the
position, size and nature of the image.
2. An object 5 cm high is placed 15 cm from a convex mirror of
focal length 10 cm.
Draw a ray diagram on graph paper (full size or 1/2-scale) to
find the position, size and nature of the image.
Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-837571-5 GCSE Physics for You, 5th edition © Keith Johnson & Sue Holt
You might also like
- Livestock Feed Formulation Using Locally SourcDocument111 pagesLivestock Feed Formulation Using Locally SourcNyasha Vincent100% (5)
- Broilers Production Training ModuleDocument16 pagesBroilers Production Training ModuleNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document8 pagesOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- Convex Mirrors: Mirror Sphere Parabolic Reflectors Reflecting Telescopes Spherical AberrationDocument8 pagesConvex Mirrors: Mirror Sphere Parabolic Reflectors Reflecting Telescopes Spherical AberrationBastab DeyNo ratings yet
- Science 11.9Document2 pagesScience 11.9준준챤No ratings yet
- 11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsDocument6 pages11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign2Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign2Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Sci Quiz 4 q2Document11 pagesSci Quiz 4 q2eslNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection NotesDocument8 pagesLight Reflection NotesSuperParthz GAMING100% (2)
- Assignment No 3Document10 pagesAssignment No 3Moaz RazaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesMirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Shedding Light On Curved MirrorsDocument14 pagesShedding Light On Curved MirrorsEyad Ahmed Hanafy Mahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 3Document10 pagesAssignment No 3Moaz RazaNo ratings yet
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Spherical Mirror ImagesDocument4 pagesSpherical Mirror ImagesD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Assign #1 (Optics)Document3 pagesAssign #1 (Optics)janmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chapter 10Document52 pagesClass 10 - Chapter 10Ramya L N100% (1)
- Curved Mirror & Thin Converging LensDocument38 pagesCurved Mirror & Thin Converging LensAndrewD2404100% (1)
- Reporting in Science About Curved MirrorsDocument26 pagesReporting in Science About Curved Mirrorsadrian pabyNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Binocular Optics and MechanicsDocument34 pagesBinocular Optics and MechanicsJayakumar D SwamyNo ratings yet
- Phy 102 (2) Curved Mirrors - 075230Document23 pagesPhy 102 (2) Curved Mirrors - 075230Pamela MagboNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorDocument23 pagesChapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Document12 pagesSci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn Malig100% (1)
- Physics PRDocument10 pagesPhysics PRanirudhas708No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12-Feb-2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 12-Feb-2022Aditya GamingNo ratings yet
- 10 Reflection of LightDocument8 pages10 Reflection of LightMugdhaNo ratings yet
- Lens & MirrorsDocument219 pagesLens & MirrorsChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument31 pagesLensesDejaunae LawsonNo ratings yet
- Ray DiagramDocument47 pagesRay Diagramjimmy cocoNo ratings yet
- WK 4reflection of Light On Curved SurfacesDocument4 pagesWK 4reflection of Light On Curved Surfacesonyedikachukwuoffonze815No ratings yet
- 2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1Document12 pages2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1shashwatraipro1No ratings yet
- What Is A Plane MirrorDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Plane Mirrorassis alihNo ratings yet
- XJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RDocument38 pagesXJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport11Document9 pagesPHYS101L LabReport11Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Plane, Curve Mirrors and LensesDocument75 pagesPlane, Curve Mirrors and LensesJiasmin Claire Bactad Tiqui100% (1)
- Reflection Spherical Mirrors BDocument49 pagesReflection Spherical Mirrors BEros James JameroNo ratings yet
- Lens PowerpointDocument28 pagesLens Powerpointdarellbarnes450No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesRhian PanaganeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document33 pagesUnit 6mirdulsahuNo ratings yet
- Lenses 1Document13 pagesLenses 1Yuni MuliaNo ratings yet
- P102LN2324Document35 pagesP102LN2324Ayush Birla100% (1)
- Reviewer For The Types of Mirrors and Lenses and Their PropertiesDocument10 pagesReviewer For The Types of Mirrors and Lenses and Their Propertiestrinidadsean2008No ratings yet
- SLK Q2 W5 Dimaano EditedDocument17 pagesSLK Q2 W5 Dimaano Editedmaricris.almuete24No ratings yet
- LensesDocument10 pagesLensesAudrina NorbertNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument26 pagesLensestagijip981No ratings yet
- Plane, Curve Mirrors and LensesDocument75 pagesPlane, Curve Mirrors and LensesJiasmin Claire Bactad TiquiNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images Formed by MirrorsDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images Formed by MirrorsGenina TejadaNo ratings yet
- Concave and Convex MirrorDocument6 pagesConcave and Convex MirrorVijayalakshmi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Cermin Lengkung-2Document23 pagesCermin Lengkung-2Ofik Mahesa ChannelNo ratings yet
- Physics Summary Class10Document38 pagesPhysics Summary Class10Anubhav Singh0% (1)
- SCIEPRACAPPDocument13 pagesSCIEPRACAPPErich Nicole LacambraNo ratings yet
- Differences: Concave Mirror Convex MirrorDocument3 pagesDifferences: Concave Mirror Convex MirrorGelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesDocument29 pagesChapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesrichardNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsDocument72 pagesQuarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer by Roaa 2ND QTDocument2 pagesSci Reviewer by Roaa 2ND QTIce SullezaNo ratings yet
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 pagesRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashNo ratings yet
- Light Physics Class 10 Part 1Document12 pagesLight Physics Class 10 Part 1Kishwar SachanNo ratings yet
- Physics SSS2 Note On Lenses...... ReDocument8 pagesPhysics SSS2 Note On Lenses...... RekumoyejoyNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions Physics Section BDocument17 pagesViva Questions Physics Section Bgauravgrover613No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Light Through Coloured Filters: Type in Your Name HereDocument21 pagesLight Through Coloured Filters: Type in Your Name HereNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Are Mobile Phones Safe?: Microwaves (See Pages 215, 220-221)Document1 pageAre Mobile Phones Safe?: Microwaves (See Pages 215, 220-221)Nyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes: Dispersion by A Prism To Produce A SpectrumDocument14 pagesTeacher's Notes: Dispersion by A Prism To Produce A SpectrumNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- 28 Colour: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)Document1 page28 Colour: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)Nyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Put Your Names HereDocument11 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum: Put Your Names HereNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- P4U Chap 24-d CurvedMirrors Checklist RevisionQuizDocument1 pageP4U Chap 24-d CurvedMirrors Checklist RevisionQuizNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- P4U Chap 28-I WaveEquation HelpSheetDocument1 pageP4U Chap 28-I WaveEquation HelpSheetNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY BIOLOGY Cells Exploration Activities PDFDocument16 pagesACTIVITY BIOLOGY Cells Exploration Activities PDFJoy Fernandez0% (1)
- P4U Chap 28-A ColourSpectrum TeacherMapDocument1 pageP4U Chap 28-A ColourSpectrum TeacherMapNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Biopreservation 181210105410Document113 pagesBiopreservation 181210105410Nyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Lenses and The Eye: Revision TestDocument14 pagesLenses and The Eye: Revision TestNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Growing Onions ProfitablyDocument8 pagesGrowing Onions ProfitablyNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Easy Gardening: Potatoes Sweet Potatoes Sweet PotatoesDocument3 pagesEasy Gardening: Potatoes Sweet Potatoes Sweet PotatoesNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Two Methods of Breeding Are Commonly Used in GoatsDocument4 pagesTwo Methods of Breeding Are Commonly Used in GoatsNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Broilers &layers Yaras MaccharlesDocument38 pagesBroilers &layers Yaras MaccharlesNyasha VincentNo ratings yet
- Beef Production For Smallholder Farmers in Zimbabwe (Shona)Document101 pagesBeef Production For Smallholder Farmers in Zimbabwe (Shona)Nyasha VincentNo ratings yet