Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci Reviewer by Roaa 2ND QT
Uploaded by
Ice Sulleza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
SCI-REVIEWER-BY-ROAA-2ND-QT (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesSci Reviewer by Roaa 2ND QT
Uploaded by
Ice SullezaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SCI REVIEWER
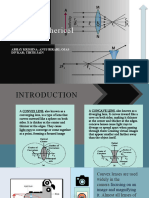
-Thicker in the edges than at centre
LENSES -causes parallel light rays to diverge
(spread out) after refraction.
Lenses-are transparent objects that are
used to refract light to help form an Uses of a concave lens
image.
The concave lenses are used in correcting
eyeglasses for nearsightedness (myopia). It
is used in flashlights to spread out the beam
of light to cover a wide area. It can also be
used
as a peephole on the door to your house or
apartment to see a wide view outside the
Door.
Uses of Concave MIRROR
Shaving mirrors
Converging lens (Convex Lens)-Thicker in
Ophthalmoscope
the centre than at the edges
Headlights of vehicles
-causes parallel light rays to converge
Dental mirrors
(come together) to a single focus point after
Solar furnace
refraction.
A solar furnace is an optical system to
Uses of Convex LENS
provide concentrated solar radiation. The
Magnifying glasses
concentrated energy of sunlight can be used
Eyeglasses
to:
Cameras
Microscopes
-Simple heating of a material.
Telescopes
-Plastic or paint ageing experiments
Projectors
-Endothermic chemical reactions
Uses of Convex MIRROR
The convex mirror is used as side-view
mirror on the passenger’s side of a car
because it forms an erect and smaller image
for the way behind the car.
The convex mirror is suitable for convenient
shops, and big supermarkets and any other
corner for anti-thief purposes. It is used in
turning off the road and parking.
Diverging lens (Concave Lens) Three Ray Rules to Locate Image
-To obtain this type of numerical information, it
-Ray parallel to axis bends through the focus. is necessary to use the Lens Equation and the
-Ray through the focus bends parallel to the Magnification Equation.
axis.
-Ray through the centre of the lens passes
straight
Through.
Characterizing the Image;Images are
characterized in the following way
TYPE: Virtual or Real The Thin-Lens Equation Sign Convention
ORIENTATION: Upright or Inverted -Distances: positive for real
MAGNIFICATION: Reduced, Enlarged, -negative for virtual
Same Size -Heights : positive above axis
DIVERGING LENSES (concave lenses) -negative below axis
Concave Lens Ray Tracing
-Ray parallel to axis refracts as if it comes from
the first focus.
-Ray which lines up with the second focus
refracts parallel to the axis.
-Ray through the centre of the lens doesn’t
bend.
Image Formed by Concave Lens
Image is always
Virtual,Upright, Reduced.
Concave Lens Image Distance
-As object distance decreases
-Image distance decreases
-Image size increases
LENS EQUATION
-Ray diagrams provide useful information
about object-image relationships, yet fail to
provide the
information in a quantitative form.
You might also like
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Q2 HandOuts M678Document2 pagesQ2 HandOuts M678technotrialzNo ratings yet
- Applications of Spherical Mirrors and Lenses: Submitted By: Aadrika Goyanka X-A 8941 Roll No. 2Document5 pagesApplications of Spherical Mirrors and Lenses: Submitted By: Aadrika Goyanka X-A 8941 Roll No. 2aadrika goyankaNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsArque John Bertumen AbieraNo ratings yet
- Notes in Uses of Mirrors and Lenses in Optical DevicesDocument2 pagesNotes in Uses of Mirrors and Lenses in Optical DevicesNins SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Science ArticlesDocument3 pagesScience Articleswenifredoalcantara142No ratings yet
- Comparitive Study States Karnataka and Uttarakhand - Physics Term 2Document8 pagesComparitive Study States Karnataka and Uttarakhand - Physics Term 2Dhruv MishraNo ratings yet
- Lens & Its ApplicationsDocument10 pagesLens & Its ApplicationsYang ZhenyanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysics16mis3050No ratings yet
- Mirrors & LensesDocument12 pagesMirrors & LensesTimo TheoNo ratings yet
- Types of Mirror and LensDocument1 pageTypes of Mirror and LensRonald DonorNo ratings yet
- Class 7 MirrorExtra Questions and NotesDocument5 pagesClass 7 MirrorExtra Questions and NotesBaha RoxanneNo ratings yet
- The Lens and Its CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesThe Lens and Its CharacteristicsEarl EyatidNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document8 pagesOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- Uses-Of-Mirrors-And-Lenses-230218085130-17383ef5 2Document27 pagesUses-Of-Mirrors-And-Lenses-230218085130-17383ef5 2Marie Antoinette TordaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Forensic PhotographyDocument2 pagesActivity 2. Forensic PhotographyElla Mei OralloNo ratings yet
- SCIEPRACAPPDocument13 pagesSCIEPRACAPPErich Nicole LacambraNo ratings yet
- Add Infos Chapter 3Document20 pagesAdd Infos Chapter 3Melchor SambranoNo ratings yet
- Sci Quiz 4 q2Document11 pagesSci Quiz 4 q2eslNo ratings yet
- Thin LensesDocument37 pagesThin LensesVianca Rein MilanNo ratings yet
- Application of Optical Instrument LeCtureDocument14 pagesApplication of Optical Instrument LeCtureNURSHAHADAH ISMAELNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument4 pagesScience ReportcherlonnclairealigamNo ratings yet
- Microscope REVIEWERDocument6 pagesMicroscope REVIEWERkjdobdin23No ratings yet
- Physics - Convex LensDocument15 pagesPhysics - Convex LensdivyapriyaNo ratings yet
- LENSESDocument9 pagesLENSESmafiamain160No ratings yet
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 pagesRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashNo ratings yet
- Adv Lalita Patil International SchoolDocument18 pagesAdv Lalita Patil International SchoolYash MahajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 Formation of ImagesDocument2 pagesLesson 2.3 Formation of ImagesJM OrtizNo ratings yet
- Assign #1 (Optics)Document3 pagesAssign #1 (Optics)janmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument3 pagesGeometric OpticsYeizmin KimNo ratings yet
- Evennett Oct2008 01 Principles-Of-MicrosDocument96 pagesEvennett Oct2008 01 Principles-Of-MicrosAjish joNo ratings yet
- Cri 227L - Assignment LensesDocument4 pagesCri 227L - Assignment LensesNovecio, Criesha GayleNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesMicroPara Lab Activity 2BernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument2 pagesMicroscopy ReviewKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- Science Mini TaskDocument1 pageScience Mini Taskdive iveNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses ReviewerDocument9 pagesMirrors and Lenses ReviewerVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Lenses and EYE WorksheetDocument17 pagesLenses and EYE WorksheetarjaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument36 pagesREVIEWEREmmanuel OdencioNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument40 pagesOPTICSJanelle Ann BacoNo ratings yet
- Science Concave and Convex MirrorsDocument2 pagesScience Concave and Convex MirrorsEnya OzNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeDocument7 pagesData Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeSohail SaripadaNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument34 pages1 MicroscopeBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Cassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CDocument10 pagesCassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CMehar FathimaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsMhais Angelika DyNo ratings yet
- EF Lens Work Book 10 enDocument25 pagesEF Lens Work Book 10 enSilvana HadžićNo ratings yet
- Uses of Concave Mirror PDFDocument5 pagesUses of Concave Mirror PDFAnanda ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- All About Microscope PresentationDocument11 pagesAll About Microscope Presentationearlyn angelie gopioNo ratings yet
- Uses of Mirrors and LensesDocument27 pagesUses of Mirrors and LensesRivera Sofia QueishaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument17 pagesParts of A MicroscopedamyangdcsNo ratings yet
- Microscope PartsDocument3 pagesMicroscope Partsako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- The Functions and Parts of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageThe Functions and Parts of A Microscopejayr ludoviceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesRhian PanaganeNo ratings yet
- Parts of The MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The MicroscopeFRANCO, Fame D.No ratings yet
- MICROSCOPE Types and PartsDocument2 pagesMICROSCOPE Types and PartsMazon, Dinah Melisse P.100% (1)
- Vip'S in PhotographyDocument93 pagesVip'S in PhotographyKaren PañoNo ratings yet
- Refraction Through Lenses & Optical Instruments5Document144 pagesRefraction Through Lenses & Optical Instruments5geniusamahNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Vision LightingDocument32 pagesVision LightingLidia LOPEZ / CALVEKNo ratings yet
- Cultural Center RRL ForeignDocument4 pagesCultural Center RRL ForeignJoedel CapillanNo ratings yet
- Current Trends On Deep Learning Models For Brain Tumor Segmentation and Detection - A ReviewDocument5 pagesCurrent Trends On Deep Learning Models For Brain Tumor Segmentation and Detection - A ReviewPadmavathy VelayudhamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 7 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Grade 7 3rd QuarterDanny EspañolaNo ratings yet
- DB and DBM: Sound Pressure, Sound Level and Db. Sound Is Usually Measured With Microphones andDocument5 pagesDB and DBM: Sound Pressure, Sound Level and Db. Sound Is Usually Measured With Microphones andpathmakerpkNo ratings yet
- Say It With Charts - McKinsey-32Document4 pagesSay It With Charts - McKinsey-32YONGXING CHENNo ratings yet
- American Accounting AssociationDocument13 pagesAmerican Accounting AssociationRahmat Pasaribu OfficialNo ratings yet
- A3 DomainModelingDocument5 pagesA3 DomainModelingJaspreet Singh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Influence of Soil Structure Interaction On Seismic Demands - 2019 - EngineeringDocument15 pagesInfluence of Soil Structure Interaction On Seismic Demands - 2019 - Engineeringabubaker ahmedNo ratings yet
- Organizational Comm OutlineDocument4 pagesOrganizational Comm OutlineDon AldNo ratings yet
- Department: Uils: Environmental Law & Wildlife Protection Amanat Kahlon Assistant Professor Chandigarh UniversityDocument7 pagesDepartment: Uils: Environmental Law & Wildlife Protection Amanat Kahlon Assistant Professor Chandigarh UniversityHarneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Assignment Brief Course No.:: 010303100: Functional MathematicsDocument10 pagesAssignment Brief Course No.:: 010303100: Functional MathematicsEng-Mohammed TwiqatNo ratings yet
- GE1 (Mathematic in The Modern World) SyllabusDocument8 pagesGE1 (Mathematic in The Modern World) SyllabusTrish LaguitanNo ratings yet
- Acr-Rpms TrainingDocument4 pagesAcr-Rpms TrainingHardy MisagalNo ratings yet
- Optimus Prime - : Age of ExtinctionDocument4 pagesOptimus Prime - : Age of ExtinctionDaniel Leon AlcaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Analogy AssignmentDocument10 pages1 Cell Analogy AssignmentDaniel Cueva TorresNo ratings yet
- Iec TR 62343-6-8-2011Document14 pagesIec TR 62343-6-8-2011Amer AmeryNo ratings yet
- WWW Samsung Com - TranslateDocument5 pagesWWW Samsung Com - TranslateÇAĞATAY ÇALIŞKANNo ratings yet
- IAS - Chemistry - SB1 - Practs - CP4 - Student SheetDocument3 pagesIAS - Chemistry - SB1 - Practs - CP4 - Student SheetHadeel Al QteishatNo ratings yet
- Electroplating Know How II Know HowDocument5 pagesElectroplating Know How II Know HowrankeenNo ratings yet
- Preferences and Positivist Methodology in EconomicsDocument21 pagesPreferences and Positivist Methodology in EconomicsAndrés GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Workforce Diversity and Internal Organizational Communication of The Five International Organizations in The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesWorkforce Diversity and Internal Organizational Communication of The Five International Organizations in The PhilippinesCarlo FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lec29 PDFDocument32 pagesLec29 PDFVignesh Raja PNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automation: BITS PilaniDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Automation: BITS PilaniymsyaseenNo ratings yet
- CPM Precalculus Homework AnswersDocument7 pagesCPM Precalculus Homework Answerscqxxvzhlf100% (1)
- Bevington Buku Teks Pengolahan Data Experimen - Bab 3Document17 pagesBevington Buku Teks Pengolahan Data Experimen - Bab 3Erlanda SimamoraNo ratings yet
- 10C21Document26 pages10C21Trần ThịnhNo ratings yet
- The Complete Strategy LandscapeDocument1 pageThe Complete Strategy LandscapeHmoud AMNo ratings yet
- Determinant and OtherDocument9 pagesDeterminant and Otherpema karmoNo ratings yet
- Agnihotra Seminar Brochure FinalDocument14 pagesAgnihotra Seminar Brochure Finalarvind351No ratings yet
- Resonant Column Testing ChallengesDocument9 pagesResonant Column Testing ChallengesMarina Bellaver CorteNo ratings yet