Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economic Growth and Development-Microeconomics-Study Material
Economic Growth and Development-Microeconomics-Study Material
Uploaded by
Ellen RoaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economic Growth and Development-Microeconomics-Study Material
Economic Growth and Development-Microeconomics-Study Material
Uploaded by
Ellen RoaCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Kaldor Model – (Nicholas Kaldor) cites that technology should be included in the production of
capital goods as investment.
ECONOMIC GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Human Development Index and other Social Indicators
What is the difference between growth and development? ❖ Human Development Index (HDI) focuses on three measurable dimensions of human
❖ Growth – refers to the quantitative changes development: living a long and healthy life, having education, and having a decent standard of
❖ Development – refers to the qualitative and progressive changes that occur in the process. living. It could be summarized into measures of life expectancy, school enrolment, literacy, and
❖ Economic growth – refers to the steady process of increasing productive capacity of the income, allowing a broader view of a country’s development.
economy ❖ Human Poverty Index (HPI) – focuses on the proportion of people below threshold level in basic
❖ Economic development – refers not only to the steady increase in productive capacities of one dimensions of human development. HPI measures human poverty in developing countries.
economy but more specifically to a series of progressive or qualitative changes that occur such as ❖ The HDI further measures the average achievements of one’s country. The gender – related
capital accumulation and technology advancement that leads to a sustainable improvement of development index (GDI) - measures achievements in the same dimensions, using the same
both physical and human resources. indicators as the HDI.
❖ The gender empowerment measure (GEM) reveals whether women take an active role in both
THEORIES OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT economic and political life. GEM tracks the share of seats in parliament held by women; female
1. Laissez Faire – (French term) it denotes freedom from any intervention of all sorts, meaning legislators, senior officials, and managers; of female professional and technical workers and the
government should not interfere in economic affairs of the individual and society gender disparity in earned income.
2. Classical Theory – (Adam Smith) it explains how the wealth of a nation is created and
distributed. PREPARED BY:
3. Theory on Population – (Thomas R. Malthus) stated that population increases in geometric
ratio while food supply increases in arithmetic ratio. ELLEN NICY ROA
4. Theory on Comparative Advantage – (David Ricardo) it postulates that nations should export
the goods which they enjoy the greatest advantage and should not import the goods which they
have the greatest disadvantage.
5. Karl Marx Theory – (Karl H. Marx) emphasize the value of labor, stating that workers are the
real producers of goods, and the benefits of the production should go to the workers and not the
capitalists.
6. Theory on Progress and Poverty – (Henry George) during the economic growth in California
during the 1870’s, made him critical to analyze the distributive shares among the factors of the
production.
7. Keynesian Theory of Employment (Modern Theory of Employment) – emphasizes that the
cause of unemployment is high wages. There will be more employment if wages are low. This
theory, related to the demand and supply for labor, states that employment determines the
necessity of equating the aggregate supply of goods with the aggregate demand for goods.
MODELS OF GROWTH
1. Ricardian Growth Model – David Ricardo stresses the limits of economic growth brought
about by scarcity of land being fixed input. Land is the key factor to this theory.
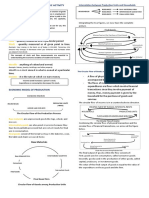
2. Harrod – Domar Model – this model is partnership effort between Sir Roy F. Harrod & Prof.
Evsey D. Domar. The important factor of this model is the production of capital goods such as
machinery, buildings and other equipment. This model shows the relationship between the
efficiency of the input and output. Efficiency of the output is measured in terms of effect.
You might also like
- Start Up Business QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesStart Up Business Questionnaireatia khanNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Full PowerpointDocument84 pagesEconomic Development Full PowerpointDamir Jovic100% (1)
- Topic 3 - Todaro, Economic Development - Ch.3 (Wiscana AP)Document4 pagesTopic 3 - Todaro, Economic Development - Ch.3 (Wiscana AP)Wiscana Chacha100% (1)
- Barangay San Miguel BGPMSDocument47 pagesBarangay San Miguel BGPMSRachel Lalaine Marie Sialana100% (4)
- Meaning of DevelopmentDocument7 pagesMeaning of DevelopmentRamite BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Theories of DevelopmentDocument5 pagesTheories of DevelopmentJahedHossain100% (1)
- Livelihoods Through CSR Skill Development PDFDocument65 pagesLivelihoods Through CSR Skill Development PDFGaurav DhakarNo ratings yet
- Overviewof The PNP P.A.T.R.O.L. Plan 2030 Short VersionDocument103 pagesOverviewof The PNP P.A.T.R.O.L. Plan 2030 Short VersionRicson Guiab100% (6)
- Philippine Economic DevelopmentDocument14 pagesPhilippine Economic DevelopmentJuan Jose SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Benefit/Cost Analysis and Public Sector EconomicsDocument29 pagesBenefit/Cost Analysis and Public Sector EconomicsMahmud RafiNo ratings yet
- NBFC CompaniesDocument10 pagesNBFC CompaniesSanju DurgapalNo ratings yet
- The Malaysian Public Sector ICT Strategic Plan - Powering Public Sector Digital Transformation 2011-2015Document48 pagesThe Malaysian Public Sector ICT Strategic Plan - Powering Public Sector Digital Transformation 2011-2015AdeNMNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concept of DevelopmentDocument16 pagesUnderstanding The Concept of DevelopmentEman NolascoNo ratings yet
- Classic Theories of Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument46 pagesClassic Theories of Economic Growth and DevelopmentCLUVER AEDRIAN AMODIANo ratings yet
- Submitted by Submitted To Ashish Kumar Dey M.Kunhaman Sir Roll No.:-T2018rd003Document5 pagesSubmitted by Submitted To Ashish Kumar Dey M.Kunhaman Sir Roll No.:-T2018rd003Ashish DeyNo ratings yet
- Ds 102 Lecture 2021-2022-Latest Version-FinalDocument232 pagesDs 102 Lecture 2021-2022-Latest Version-Finalkhalfani jumaNo ratings yet
- Development ExamDocument15 pagesDevelopment Examibrahim b s kamaraNo ratings yet
- Nidhi UpadhyayDocument14 pagesNidhi UpadhyayNidhi upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Intro To EconomicGrowth+HumanDevelopmentDocument38 pagesIntro To EconomicGrowth+HumanDevelopmentanushikha banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Putri Mahawati B K7620070Document7 pagesPutri Mahawati B K7620070putri mahawatiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Structural ChangeDocument9 pagesAnalysis of The Structural ChangeMia BumagatNo ratings yet
- Agri 116 6-8Document17 pagesAgri 116 6-8Marifer FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Edited Definition of DevelopmentDocument5 pagesEdited Definition of Developmentjaiyefemi2No ratings yet
- REMEDIO Sustainable Econ SystemsDocument17 pagesREMEDIO Sustainable Econ SystemsNiccolo G. ChiongbianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Development Studies Dev 1150: Simon Manda. PHD 2020 CohortDocument122 pagesIntroduction To Development Studies Dev 1150: Simon Manda. PHD 2020 CohortHendrix NailNo ratings yet
- Dev 1150 Slides - September - 2020Document48 pagesDev 1150 Slides - September - 2020Hendrix NailNo ratings yet
- International DevelopmentDocument15 pagesInternational DevelopmentMarvin CabantacNo ratings yet
- Indicators of DevelopmentDocument2 pagesIndicators of DevelopmentSarah Dane LisingNo ratings yet
- Chari Boru's Term Paper On The Role of Hca in Economic Growth PresentationDocument28 pagesChari Boru's Term Paper On The Role of Hca in Economic Growth PresentationCHARI BORUNo ratings yet
- CH 28Document16 pagesCH 28sayooj tvNo ratings yet
- Development Economics 2Document7 pagesDevelopment Economics 2AbbieNo ratings yet
- Development ParadigmsDocument11 pagesDevelopment ParadigmsAswin Sreenivasan100% (1)
- Midterm October 15 Fall 2017 Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesMidterm October 15 Fall 2017 Questions and Answerssukayna4ameenNo ratings yet
- Growth NddevelopmentDocument10 pagesGrowth Nddevelopmentkoushik royalNo ratings yet
- Hdi and PqliDocument22 pagesHdi and PqliSwati DhadwadNo ratings yet
- Eco 101 PDFDocument7 pagesEco 101 PDFRaeanna De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3+4Document3 pagesChapter 3+4Linh HaNo ratings yet
- Ae12 Course File Econ DevDocument49 pagesAe12 Course File Econ DevEki OmallaoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTheories of Economic Growth and DevelopmentLisa HeronNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Notes M1Document4 pagesEcon Dev Notes M1Cyra Paulin VistaNo ratings yet
- REVISIONDocument31 pagesREVISIONK59 NGUYEN KHANH LINHNo ratings yet
- ECON F313 IED 2018 TB Chapter Concept SummariesDocument4 pagesECON F313 IED 2018 TB Chapter Concept SummariesbingoNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentDocument11 pagesDevelopmentSoumay Rai GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: Malabanan Avegail Bsa 1-CDocument8 pagesReflection Paper: Malabanan Avegail Bsa 1-Craymark felloneNo ratings yet
- Economics For 2nd PUC - ToPIC 1Document16 pagesEconomics For 2nd PUC - ToPIC 1Vipin Mandyam KadubiNo ratings yet
- ECODEV Lesson2Document6 pagesECODEV Lesson2henzonchariseNo ratings yet
- 3 WEG - Patterns of Development and ChangeDocument60 pages3 WEG - Patterns of Development and ChangeTuyến BắpNo ratings yet
- 05th - O8aug 2020 1st LectureDocument41 pages05th - O8aug 2020 1st LectureSWETCHCHA MISKANo ratings yet
- Allan WitienyiDocument6 pagesAllan WitienyiMercy KileoNo ratings yet
- Standard of Living Solvency Cash Flow Person Economic Entity Job SecurityDocument17 pagesStandard of Living Solvency Cash Flow Person Economic Entity Job SecuritydaniyaldannyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Global DevelopmentDocument12 pagesChapter 6 - Global DevelopmentVictoria Margarett N. FangNo ratings yet
- 203 AssimntDocument5 pages203 AssimntEmmaruiz jbNo ratings yet
- ECODEV Report Group 2Document39 pagesECODEV Report Group 2Fav TangonanNo ratings yet
- The Philippine EconomyDocument17 pagesThe Philippine EconomyKrysh AlorroNo ratings yet
- The Notion of DevelopmentDocument18 pagesThe Notion of DevelopmentTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Economic DevelopmentDocument33 pagesGroup 3 Economic DevelopmentNuarin JJNo ratings yet
- Economic Development (Prelims)Document7 pagesEconomic Development (Prelims)JeanieNo ratings yet
- BBA-508 - Economic Planning and PoliciesDocument11 pagesBBA-508 - Economic Planning and PoliciesSimanta KalitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment DSTDocument6 pagesAssignment DSTkenneth kayetaNo ratings yet
- PED - Class - 7 NewDocument33 pagesPED - Class - 7 NewAlejandro álvarez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Conceptions and Dimensions of Development 1Document47 pagesConceptions and Dimensions of Development 1jmdaradal26No ratings yet
- Sekhampu TJ Chapter2Document25 pagesSekhampu TJ Chapter2Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesReviewer in Contemporary WorldBenjo BataoNo ratings yet
- 9 August 2021Document38 pages9 August 2021copabNo ratings yet
- Econ ReviewerDocument6 pagesEcon Reviewerbeamari22.dimaandalNo ratings yet
- Econ DevelopmentDocument6 pagesEcon DevelopmentlmaxinekateNo ratings yet
- Economicdevelopment 151008113013 Lva1 App6892Document34 pagesEconomicdevelopment 151008113013 Lva1 App6892RAVENDAVE ATIENZANo ratings yet
- THE CIRCULAR FLOW OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY - Study MaterialDocument2 pagesTHE CIRCULAR FLOW OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY - Study MaterialEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Agrarian Reform - Study MaterialDocument3 pagesPhilippine Agrarian Reform - Study MaterialEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- DEMAND and SUPPLY-BASIC ANALYSIS-STUDY MATERIALDocument3 pagesDEMAND and SUPPLY-BASIC ANALYSIS-STUDY MATERIALEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Economics - Study MaterialDocument3 pagesBasic Concept of Economics - Study MaterialEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- Conflict Mapping - Culture of PeaceDocument5 pagesConflict Mapping - Culture of PeaceEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- Culture of Peace Conflict MappingDocument6 pagesCulture of Peace Conflict MappingEllen RoaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking TopicDocument31 pagesIELTS Speaking TopicDhara Milan PatelNo ratings yet
- LAWS & EXECUTIVE ISSUANCES (1900-2014) : ENERGY Part 1Document1,136 pagesLAWS & EXECUTIVE ISSUANCES (1900-2014) : ENERGY Part 1LIRMD-Information Service DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Part A Introduction To The Project Real Estate SectorDocument15 pagesPart A Introduction To The Project Real Estate SectorsharadNo ratings yet
- Stadiums ReportDocument26 pagesStadiums ReportRicardo S AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility:Initiatives and Examples: Anand Corporate Services LimitedDocument7 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility:Initiatives and Examples: Anand Corporate Services LimitedFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Trade and Industry: Nueva Vizcaya Provincial OfficeDocument20 pagesDepartment of Trade and Industry: Nueva Vizcaya Provincial OfficeRoel Jr Pinaroc DolaypanNo ratings yet
- List of Important International Organizations and Their Headquarter 2017Document6 pagesList of Important International Organizations and Their Headquarter 2017Kalaivani BaskarNo ratings yet
- Ghana NSDFF - Executive SummaryDocument59 pagesGhana NSDFF - Executive SummaryChatiJerryNo ratings yet
- Ocl Book Reading Order Single Pages Webversion PDFDocument152 pagesOcl Book Reading Order Single Pages Webversion PDFLawal EstherNo ratings yet
- Ges 402 NotesDocument95 pagesGes 402 NotesAzarael ZhouNo ratings yet
- Arab Regional Conference On Population - ReportDocument26 pagesArab Regional Conference On Population - ReportAly ShaimaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis - 2 Sports SchoolDocument4 pagesSynopsis - 2 Sports SchoolMedha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Yezid Sayigh, Owners of The Republic: An Anatomy of Egypt's Military EconomyDocument360 pagesYezid Sayigh, Owners of The Republic: An Anatomy of Egypt's Military EconomySakala BakalaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Architecture Arch 511/512: Urban Agri-Tecture: A Sustainable Low-Cost Vertical HousingDocument43 pagesBachelor of Science in Architecture Arch 511/512: Urban Agri-Tecture: A Sustainable Low-Cost Vertical HousingRon AgamataNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Paper JetirDocument4 pagesDissertation Paper JetirVIVEK DESAINo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Part 2) - Sustainable DevelopmentDocument3 pagesUnit 2 (Part 2) - Sustainable DevelopmentEsai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- A Term Paper On Development Management, Section B, Chapter OneDocument25 pagesA Term Paper On Development Management, Section B, Chapter OneJohnny DeppNo ratings yet
- The Physical Economy of National Development (Definitivo) - Jonathan TennenbaumDocument191 pagesThe Physical Economy of National Development (Definitivo) - Jonathan TennenbaumFelipe QuintasNo ratings yet
- 120113-DCCBs in Maharashtra by SunilDocument7 pages120113-DCCBs in Maharashtra by SunilGauresh NaikNo ratings yet
- Nation Builidng STSDocument24 pagesNation Builidng STSIan CastroNo ratings yet
- Cep NoteDocument6 pagesCep Notesorianojayem2No ratings yet
- NIS BookDocument186 pagesNIS BookRadhika PerrotNo ratings yet