Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arthur Njeru SCT221-0543/2016 Information System Audit Cat 1
Uploaded by
ARTHUR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesThis document discusses several key topics relating to information systems auditing:
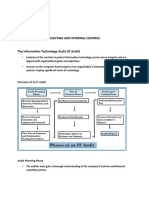
1. It defines an information systems audit as an examination of IT infrastructure management controls and a review of computer system security to ensure assets are protected and systems are operating effectively.
2. It distinguishes between financial and IS audits, noting financial audits generally occur after the financial year while IS audits can be conducted anytime.
3. It explains why skilled IS auditors are important for banking organizations to provide independent assurance of financial statements and maintain processing consistency and fraud detection.
4. It describes the significance of risk analysis for IT auditors to identify risks, threats, and necessary controls in the IT environment and systems.
Original Description:
Original Title
CAT 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several key topics relating to information systems auditing:
1. It defines an information systems audit as an examination of IT infrastructure management controls and a review of computer system security to ensure assets are protected and systems are operating effectively.
2. It distinguishes between financial and IS audits, noting financial audits generally occur after the financial year while IS audits can be conducted anytime.
3. It explains why skilled IS auditors are important for banking organizations to provide independent assurance of financial statements and maintain processing consistency and fraud detection.
4. It describes the significance of risk analysis for IT auditors to identify risks, threats, and necessary controls in the IT environment and systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesArthur Njeru SCT221-0543/2016 Information System Audit Cat 1
Uploaded by
ARTHURThis document discusses several key topics relating to information systems auditing:
1. It defines an information systems audit as an examination of IT infrastructure management controls and a review of computer system security to ensure assets are protected and systems are operating effectively.
2. It distinguishes between financial and IS audits, noting financial audits generally occur after the financial year while IS audits can be conducted anytime.
3. It explains why skilled IS auditors are important for banking organizations to provide independent assurance of financial statements and maintain processing consistency and fraud detection.
4. It describes the significance of risk analysis for IT auditors to identify risks, threats, and necessary controls in the IT environment and systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ARTHUR NJERU
SCT221-0543/2016
INFORMATION SYSTEM AUDIT
CAT 1
a) Explain your understanding of the term information systems Audit.
It’s an examination of the management controls for IT infrastructure and a complete
review of the security of computer systems. It determines whether information systems
are safeguarding assets, maintaining data integrity and operating effectively to achieve an
organization’s goals.
b) Explain the following terms as used in IT auditing.
I. Materiality
It’s a concept within auditing relating to the importance or significance of an
amount, transaction or discrepancy.
II. Self-Assessment audit
It’s a measure that an organizational performance against a selected business
excellence model.
III. Work papers
They refer to the documents prepared by or use by auditors as part of their works.
IV. Service level agreement
It’s a formal agreement between two or more parties that articulates the terms and
conditions of a particular service relationship.
c) Distinguish between financial audit and IS audit.
Financial audit generally starts after the close of the financial year and after making all
accounts ready and IS audit may be conducted at any time depends on the needs and
circumstances
d) Briefly discuss why a banking organization should employ a skilled IS auditor.
Skilled IS auditor are able to provide assurance to a banking organization’s financial
statements from an objective and independent opinion and they are also able to
maintaining consistency, finding errors in their processing, or detecting fraud
e) Describe the significance of Risk Analysis to an IT auditor.
It assists the IT auditor in identifying risks and the threats to an IT
environment and IS system- risks and threats that would need to be addressed by
management and in identifying system-specific internal controls.
f) Describe the following types of illegal activities which an IS auditor may be
interested in
unearthing.
i. Suppression
Is an act or instance of suppressing the books of accounts and ensuring that
they are kept against the rules stipulated in the Companies Act and hide the
books of accounts that shows the true and fair view of the state of affairs of
the company.
ii. Racketeering
Is the act of acquiring and divert funds from a legal business to use it for
illegal activities without the company’s knowledge.
g) Explain the following in relation to audit risks.
i. Detection risk
Is the chance that an auditor will fail to find material misstatements that exist
in an entity's financial statements. These misstatements may be due to either
fraud or error.
ii. Operational risk
Is the risk of loss resulting from ineffective or failed internal processes,
people, systems, or external events that can disrupt the flow of business
operations. The losses can be directly or indirectly financial.
h) Distinguish between circumstantial and direct types of evidence.
Direct evidence is direct proof of a fact such as testimony by a witness about what that
witness personally saw or heard or did and Circumstantial evidence is indirect evidence,
that is, it is proof of one or more facts from which one can find another fact.
i) Distinguish between the following types of IT audit.
a) Compliance audit
It’s an assessment as to whether the provisions of the applicable laws,
rules and regulations made there under and various orders and instructions
issued by the competent authority are being complied with
b) Integrated audit
It considers the relationship between information technology, financial
and operational controls in establishing an effective and efficient internal
control environment.
j) The auditing environment is usually very wide and each environment has a specific
way in which audit can be carried out. Identify the specific ICT Audit environment.
Giving examples explain how audit can be carried out in the environments you have
identified.
• Technological position audit - This audit reviews the technologies that the
business currently has and that it needs to add in its inventory. The technologies are
characterized as being either base, key, pacing or emerging.
• Technological innovation process audit - This audit constructs a risk profile for
existing and new projects. The audit will assess the length and depth of the company's
experience in its chosen technologies, as well as its presence in the organization of each
project, relevant markets and the structure of the portion of the industry that deals with
this project or product, organization and industry structure.
• Innovative comparison audit - This audit is an analysis of the innovative abilities
of the company being audited, in comparison to its competitors in the market. This
requires examination of company's research and development facilities, as well as its
track record in actually producing new products.
You might also like
- Auditing Information Systems: Enhancing Performance of the EnterpriseFrom EverandAuditing Information Systems: Enhancing Performance of the EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- Audit Theory Paper 7 August 2015 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAudit Theory Paper 7 August 2015 Solutionsahmad.khalif9999No ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Study and Evaluation of Controls ProcessRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Risk AsssesmentDocument13 pagesRisk Asssesmentutkarsh agarwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Audit BasicsDocument6 pagesLecture 1 Audit BasicsDaniel KingNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 1Document15 pages02 Handout 1Zednem JhenggNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Effective Internal Management System Audits: Implementing internal audits as a risk management toolFrom EverandA Guide to Effective Internal Management System Audits: Implementing internal audits as a risk management toolRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- ICT Assignment 1Document4 pagesICT Assignment 1AndiNo ratings yet
- Nama: Anissa Dinar Paraswansa NIM: 12030122410010 Chapter 11 Internal Control and COSO FrameworkDocument6 pagesNama: Anissa Dinar Paraswansa NIM: 12030122410010 Chapter 11 Internal Control and COSO FrameworkAnissa DinarNo ratings yet
- Auditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlFrom EverandAuditing Information Systems and Controls: The Only Thing Worse Than No Control Is the Illusion of ControlNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument6 pagesInternal ControlVarun jajalNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeFrom EverandComprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- OrganisationDocument1 pageOrganisationWen Xin GanNo ratings yet
- Sulaiha Wati - Chapter 8 NewDocument6 pagesSulaiha Wati - Chapter 8 Newsulaiha watiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Internal Control: CA Inter - Auditing and Assurance Additional Questions For Practice (Chapter 4)Document4 pagesRisk Assessment and Internal Control: CA Inter - Auditing and Assurance Additional Questions For Practice (Chapter 4)Annu DuaNo ratings yet
- At.3508 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control RiskDocument9 pagesAt.3508 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control RiskJohn MaynardNo ratings yet
- Auditing, Assurance, and Internal Control: Review QuestionsDocument18 pagesAuditing, Assurance, and Internal Control: Review QuestionsJoris YapNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Solution Manual Information Technology Auditing 2nd Ed James Hall - EDP Auditing Class - Jakarta State UniversityDocument21 pagesCH 01 Solution Manual Information Technology Auditing 2nd Ed James Hall - EDP Auditing Class - Jakarta State UniversitySjifa Aulia80% (10)
- Lesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal ControlsDocument24 pagesLesson 7 - Accounting System and Related Internal Controlskipngetich392No ratings yet
- 20181211005-Rizkania Arum - Tugas SIA II Pert 10Document7 pages20181211005-Rizkania Arum - Tugas SIA II Pert 1020181211005 RIZKANIA ARUM PUTRINo ratings yet
- Law On Partnership and Corporation Study GuideDocument18 pagesLaw On Partnership and Corporation Study GuideKelvinIvanLorenzoVelascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IT AuditDocument20 pagesChapter 1 IT AuditMr Siwada S ThabeloNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument6 pagesInternal ControlSumbul SammoNo ratings yet
- (SM) Chapter 1Document20 pages(SM) Chapter 1randomlungs121223No ratings yet
- IS Audit 2022Document7 pagesIS Audit 2022Jay KibeNo ratings yet
- 14 and 15 - Overview of Internal Control Fraud and ErrorDocument7 pages14 and 15 - Overview of Internal Control Fraud and ErrorNiña YastoNo ratings yet
- 01 CIS Audit - Auditing and Internal Control PDFDocument16 pages01 CIS Audit - Auditing and Internal Control PDFKyle Jezrel GimaoNo ratings yet
- Stakeholders Material Legal PersonDocument3 pagesStakeholders Material Legal Personansari naseem ahmadNo ratings yet
- Aud CisDocument5 pagesAud Cisgerald paduaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1auditing and Internal ControlReview Questions1Document2 pagesChapter 1auditing and Internal ControlReview Questions1spellblade del mariaNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument11 pagesAuditingJabonJohnKennethNo ratings yet
- Cis Recitpart2Document19 pagesCis Recitpart2Queenielyn TagraNo ratings yet
- Audit Module 5 - Internal Control & Internal Check PDFDocument20 pagesAudit Module 5 - Internal Control & Internal Check PDFTanishq RastogiNo ratings yet
- Testing Ingine KaliDocument30 pagesTesting Ingine KaliIngiaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Information Technology Auditing 4th Edition by HallDocument20 pagesSolution Manual For Information Technology Auditing 4th Edition by HallZenn Maia Guerrero0% (1)
- AT Lecture 7 - Internal Control (June 2020)Document6 pagesAT Lecture 7 - Internal Control (June 2020)Sophia TenorioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Overview of AuditDocument24 pagesLecture 1 Overview of AuditMs. VelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Internal ControlDocument55 pagesChapter 4 Internal ControlHussien AdemNo ratings yet
- CA Inter Audit Question BankDocument315 pagesCA Inter Audit Question BankKhushi SoniNo ratings yet
- Modern AuditingDocument76 pagesModern Auditingjklein2588100% (1)
- Chapter One 1.1. Background of The StudyDocument70 pagesChapter One 1.1. Background of The StudyPrincewill Henry Jedidiah Nenziu100% (7)
- Accounting Information Systems The Processes Controls 2nd Edition Turner Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesAccounting Information Systems The Processes Controls 2nd Edition Turner Solutions Manualmrsamandareynoldsiktzboqwad100% (26)
- Control Testing and Control RiskDocument48 pagesControl Testing and Control Riskaleahrey monganganNo ratings yet
- The Information Systems Audit ProcessDocument56 pagesThe Information Systems Audit ProcessMehar QasimNo ratings yet
- CA Intermediate Auditing & Assurance Dec 2021 Suggested AnswersDocument11 pagesCA Intermediate Auditing & Assurance Dec 2021 Suggested AnswersAshish KansalNo ratings yet
- Ais Chapter SixDocument6 pagesAis Chapter Sixtarekegn gezahegnNo ratings yet
- Audting II AnsDocument12 pagesAudting II Ansfikremaryam hiwiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - CISDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - CISChristian De LeonNo ratings yet
- Accounting System1Document13 pagesAccounting System1Nwogboji EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 3 319 90521 11Document14 pages10.1007@978 3 319 90521 11Ibtissam EljedaouyNo ratings yet
- Answer-Internal ControlDocument5 pagesAnswer-Internal ControlKathlene BalicoNo ratings yet
- What Is An 'Audit': Financial StatementsDocument13 pagesWhat Is An 'Audit': Financial StatementsRashmeet Kaur BangaNo ratings yet
- Ch01 - Auditing Assurance & Intrnal CTRLDocument46 pagesCh01 - Auditing Assurance & Intrnal CTRLLean SegundoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Midterm ReviewDocument1 pageAccounting Information System Midterm ReviewSintos Carlos MiguelNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Internal Control: Prepared By: Ambrocio, Sheila Mae BDocument31 pagesAuditing and Internal Control: Prepared By: Ambrocio, Sheila Mae BLeslie DiamondNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Internal Control: Structure of An IT AuditDocument6 pagesAuditing and Internal Control: Structure of An IT AuditMervidelleNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management ProtocolDocument37 pagesSimple Network Management Protocolgames mediaNo ratings yet
- Functional ProgrammingDocument20 pagesFunctional Programminggautham_atluriNo ratings yet
- Assessment TU6214Document3 pagesAssessment TU6214AWANGKU MUHAMMAD AFFIF OMAR BIN AWANG RADUANNo ratings yet
- Alex Khang - Professional WPF and C# Programming - Practical Software Development Using WPF and C#-Independently Published (2019)Document406 pagesAlex Khang - Professional WPF and C# Programming - Practical Software Development Using WPF and C#-Independently Published (2019)Bez VezeNo ratings yet
- MIS Final Review: List and Describe The Components of IT Infrastructure That Firms Need To ManageDocument8 pagesMIS Final Review: List and Describe The Components of IT Infrastructure That Firms Need To ManageLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Version Description DocumentDocument4 pagesVersion Description DocumentSabahat HussainNo ratings yet
- Case - Study - IDQDocument11 pagesCase - Study - IDQDeepa NairNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Commerce Platform For Your BusinessDocument5 pagesChoosing The Right Commerce Platform For Your BusinessShafeer VpNo ratings yet
- AZ-104 - AnsDocument112 pagesAZ-104 - AnsDigambar S TatkareNo ratings yet
- OracleDocument96 pagesOracleshanysunnyNo ratings yet
- NIIT PimpriDocument8 pagesNIIT PimpriAnujith AnuNo ratings yet
- VHDL Cookbook 3Document6 pagesVHDL Cookbook 3Charbel TadrosNo ratings yet
- XPEDITER/TSO - Stepping Through Program Execution: General QuestionsDocument20 pagesXPEDITER/TSO - Stepping Through Program Execution: General QuestionspagbarrosNo ratings yet
- EPDS 025 EN-2001-nGeniusONE Nse21Document3 pagesEPDS 025 EN-2001-nGeniusONE Nse21James WangNo ratings yet
- AdvancedPricingManual-1 0 0Document20 pagesAdvancedPricingManual-1 0 0Innovative ExtensionsNo ratings yet
- Gta V RGHDocument3 pagesGta V RGHBog DannNo ratings yet
- Veeam Backup 9 0 EventsDocument14 pagesVeeam Backup 9 0 EventsRavindra “Ravi” SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Aomei ManualDocument84 pagesAomei ManualDouglas PierreNo ratings yet
- Rheinwerk Verlag Sap PressDocument3 pagesRheinwerk Verlag Sap PressantonydonNo ratings yet
- Multi-Tenant Data ArchitectureDocument17 pagesMulti-Tenant Data ArchitectureFirdaus100% (1)
- E0 Training Material JMeterDocument34 pagesE0 Training Material JMeteraustinfruNo ratings yet
- My XMLDocument57 pagesMy XMLdoruttd77No ratings yet
- CheatSheet FortiAnalyzer 6.0Document1 pageCheatSheet FortiAnalyzer 6.0eppoxroNo ratings yet
- Erp Life Cycle Phases Final PresentationDocument24 pagesErp Life Cycle Phases Final PresentationSyed Bilal MahmoodNo ratings yet
- DRAFT CIS Apache HTTP Server 2.4 Benchmark v2.0.0Document231 pagesDRAFT CIS Apache HTTP Server 2.4 Benchmark v2.0.0Angel López CarrilloNo ratings yet
- NSCO&A TRAINING PRESENTATION Student v22.50Document431 pagesNSCO&A TRAINING PRESENTATION Student v22.50Mecachis PiachisNo ratings yet
- 003-Storage Array Technology V1.13Document61 pages003-Storage Array Technology V1.13Phan AnNo ratings yet
- Cross Validation Rules in Oracle Apps - Oracle Apps Knowledge SharingDocument4 pagesCross Validation Rules in Oracle Apps - Oracle Apps Knowledge SharingVijay KishanNo ratings yet
- 7139 - Colorkrew - Full Stack Engineer (Junior)Document3 pages7139 - Colorkrew - Full Stack Engineer (Junior)Tanmayi AdhavNo ratings yet
- 9.1.1.7 Lab - Encrypting and Decrypting Data Using A Hacker Tool - OK PDFDocument6 pages9.1.1.7 Lab - Encrypting and Decrypting Data Using A Hacker Tool - OK PDFInteresting facts ChannelNo ratings yet
- The Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessFrom EverandThe Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Internal Controls: Guidance for Private, Government, and Nonprofit EntitiesFrom EverandInternal Controls: Guidance for Private, Government, and Nonprofit EntitiesNo ratings yet
- (ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideFrom Everand(ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Amazon Interview Secrets: A Complete Guide to Help You to Learn the Secrets to Ace the Amazon Interview Questions and Land Your Dream JobFrom EverandAmazon Interview Secrets: A Complete Guide to Help You to Learn the Secrets to Ace the Amazon Interview Questions and Land Your Dream JobRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachFrom EverandMastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Internal Audit Quality: Developing a Quality Assurance and Improvement ProgramFrom EverandInternal Audit Quality: Developing a Quality Assurance and Improvement ProgramNo ratings yet
- A Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersFrom EverandA Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Guide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyFrom EverandGuide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyNo ratings yet
- Executive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceFrom EverandExecutive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Building a World-Class Compliance Program: Best Practices and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandBuilding a World-Class Compliance Program: Best Practices and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Financial Shenanigans, Fourth Edition: How to Detect Accounting Gimmicks & Fraud in Financial ReportsFrom EverandFinancial Shenanigans, Fourth Edition: How to Detect Accounting Gimmicks & Fraud in Financial ReportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- A Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowFrom EverandA Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowNo ratings yet