Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHE 112 - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Martias WambiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHE 112 - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Martias WambiCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1
1. Carbon is an element in group 14 (or group 4) of the periodic table and this element is
considered as very unique. Explain/describe the uniqueness of carbon atom.
2. What are the conditions for bond formation?
3. (i) Write the electronic configuration of the element carbon and silicon.
(ii) Describe the valence electrons of carbon atom.
(iii) The 2p orbital of carbon has two singly occupied electrons and this implies that two
covalent bonds will be formed. However, we know of an organic compound, methane CH4
which has four hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atom. How is this possible?
4. (i) What is meant by the word “hybridisation” in chemistry?
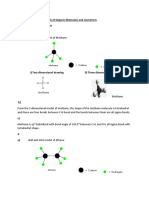
(ii) By aid of diagrams describe the following hybridisation in carbon atom: sp3, sp2 and sp1.
(iii) Explain what sigma (σ) and pi(π) bonds are and in what kind of molecules do you find σ or π
bond.
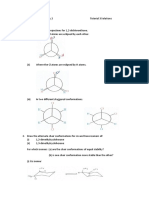
5. (i) Describe the type of hybridisation and bond types (σ and π) present in the molecular
structures given below. Give the bond angles and the expected geometry for the indicated
hybridisation as well.
(ii) In which of the given molecules above, would you find π bonds? How are π bonds formed?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ELT 491 - Lecture 4Document17 pagesELT 491 - Lecture 4Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- ELT 491 - Lecture 2Document14 pagesELT 491 - Lecture 2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- ELT 491-Lecture 6Document11 pagesELT 491-Lecture 6Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Lesson Plan: 5 MinsDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Physics Lesson Plan: 5 MinsMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- CHE 112 - Lecture 2Document103 pagesCHE 112 - Lecture 2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Edy 424-Assignment #1Document4 pagesEdy 424-Assignment #1Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument18 pagesBloom's TaxonomyMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- Isotherms of Liquid-Gas Phase Transition: V X V X V X XDocument20 pagesIsotherms of Liquid-Gas Phase Transition: V X V X V X XMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- SCI 392 - Assessment Task #1Document4 pagesSCI 392 - Assessment Task #1Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Certification of Records: Don Bosco Technological InstituteDocument4 pagesCertification of Records: Don Bosco Technological InstituteMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- NPNPNG - NSL 2023Document6 pagesNPNPNG - NSL 2023Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- EDY 3310 - Assignment Task #1Document5 pagesEDY 3310 - Assignment Task #1Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Upper Secondary PhysicsDocument42 pagesSyllabus Upper Secondary PhysicsMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- CH112 Tutorial 3 SolutionDocument3 pagesCH112 Tutorial 3 SolutionMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- PHY 331 - Physics of Earth, Literature Review - 2022Document8 pagesPHY 331 - Physics of Earth, Literature Review - 2022Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 2Document61 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- ST Paul's Lutheran Secondary School-Pausa Po - Box 301, WABAG, Enga Province, Papua New Guinea Department of Science Grade 9 Lower Secondary ScienceDocument5 pagesST Paul's Lutheran Secondary School-Pausa Po - Box 301, WABAG, Enga Province, Papua New Guinea Department of Science Grade 9 Lower Secondary ScienceMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- CH 112 P2Document5 pagesCH 112 P2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Uog RMCN Approval LetterDocument1 pageUog RMCN Approval LetterMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae For Miss Leah Nathan (: Contact InformationDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae For Miss Leah Nathan (: Contact InformationMartias WambiNo ratings yet
- DBTI TRANSCRIPT at 2020Document8 pagesDBTI TRANSCRIPT at 2020Martias WambiNo ratings yet