Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of Metals
Uploaded by
Harshit RajputOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of Metals
Uploaded by
Harshit RajputCopyright:
Available Formats
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Elements are classified as metals and non-metals based on different properties. The
properties of metals and non-metals are given in the form of the table below-
Metals Non-metals
Metals are lustrous, that is, they have a They are not lustrous, that is, they do not
Page | 1 property to shine. have a shining surface except, graphite and
iodine.
All metals exist as solids except mercury They are generally soft, except for
which is liquid at room temperature. diamonds.
They can be drawn into wires, this is known They are non-ductile.
as Ductility.
Metals can be converted into sheets, this is They are non-malleable
known as Malleability, except mercury
They are good conductors of electricity and They are poor conductors of electricity and
heat. Except for Lead and mercury. heat. Exception-graphite is a good
conductor of electricity
They have high density and high melting They have low density compared to metals
point. Exception-sodium and potassium and low melting point except for Diamond
have low melting points. which has a high melting point.
Chemical Properties of Metals
Metals react with air or oxygen to form metal oxide.
For Example, Copper reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide.
Metal + O2 → Metal oxide
2Cu + O 2 → 2CuO
4Al + 3O 2 → 2Al 2 O 3
Oxides of metals can react with both acids and bases to produce salt and water. Such
oxides are known as Amphoteric Oxides.
Al 2 O 3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl 3 + H 2 O
Metals also react with water to form metal oxide. Metal oxide in turn can react with
water to form metal hydroxide. For Example
2Na + 2H 2 O → 2NaOH + 1H 2
2Al + 3H 2 O → Al 2 O 3 + 3H 2
Metals also react with dilute acids to form salt and hydrogen. For example, magnesium
reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and hydrogen.
Metal + Acid → Metal Salt + Hydrogen
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Chemical Properties of Nonmetals
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metal oxide.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metal oxide
C + O2 → CO2
Non-metals do not react with water and acids to evolve hydrogen gas.
Page | 2 Non-metals can react with salt solution; the more reactive element will displace t he
less reactive non-metal.
2 NaBr (aq) + Cl2(aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + Br2 (aq)
Non-metals can also react with hydrogen to form hydrides.
H2(g) + S(l) → H2S(g)
Reactivity Series
The series in which metals are arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity is kno wn as
the Reactivity Series.
Fig.1. Reactivity Series
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Ionic Compounds
Compounds formed due to the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non -metal are
known as Ionic Compounds.
Page | 3
Covalent Bond
A bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between the two atoms. They share their
valence electrons to gain stability.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
They are generally hard and solid.
They have a high melting and boiling point.
They are soluble in water but insoluble in inorganic solvents such as ether etc.
They are conductors of electricity in molten and solution states.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Occurrence of Metals
Elements or compounds which occur naturally in earth crust are known as Minerals.
Minerals from which pure metals can be extracted are known as Mineral Ores.
Page | 4
Extraction of pure metals from its ores/steps for extraction of metals from its ore
The first step is the enrichment of the ore
The second step includes extraction of metals
Third steps involve refining of metal
Gangue - Ores contain different impurities in it such as sand, soil etc. These impurities
are known as Gangue.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Extracting Metals which are low in activity series
Metals which are low in the activity series are unreactive. The oxides of such metals can
be reduced to metals by heating alone. For Example, Cinnabar (HgS)
Page | 5
Extracting Metals in the middle of the Activity Series
These metals are moderately reactive. They exist as sulphides or carbonates in nature.
Before reduction, metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted into metal oxides.
Sulphide ores are converted into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of excess air,
this is known as Roasting. Carbonate ores are converted into oxides by heating in
limited air. This is known as Calcination.
Roasting
Calcination
Reduction-metal oxides can be reduced to metals using a reducing agent such
as Carbon.
Extracting metals towards the top of the activity series
The metals are highly reactive. They cannot be obtained by heating. For Example,
Sodium, magnesium and calcium are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten
chlorides.
And cathode Na + + e - → Na
At anode 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Refining of Metals
Refining of impure metal is done using electrolytic refining. Impure copper is used as
anode and a strip of pure copper is used as Cathode. Acidified copper sulphate is used
as an electrolyte. When an electric current is passed through this, impure metal f rom the
Page | 6 anode gets deposited in the electrolyte solution, whereas pure metal from the electrolyte
is deposited at the cathode.
Deposition of insoluble residue formed from the dissolution of the anode during
commercial electrolysis.
Fig.2. Electrolytic refining
Corrosion
When exposed to moist air for a long period of time, metals become corroded. This is
known as Corrosion. For Example, Silver reacts with moist air and becomes black in
colour due to silver sulphide coating.
Iron + oxygen → Iron (III) oxide
Fe + O 2 → Fe 2 O 3
Prevention of Corrosion
Rusting of iron can be prevented by oiling, galvanising, painting, greasing etc.
To protect steel and iron from rusting, a thin layer of zinc is coated on them, this is
known as Galvanization.
Alloy
Mixture of two or more metals or metal and non-metal is known as Alloy. For Example,
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc.
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
Solder is an alloy of lead and tin.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
NCERT SOLUTIONS:-
Question 1.
Give example of a metal which
(a) is a liquid at room temperature
(b) can be easily cut with a knife
Page | 7 (c) is the best conductor of heat
(d) is the poorest conductor of heat.
Answer:
(a) Mercury
(b) Sodium
(c) Silver
(d) Lead.
Question 2.
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Malleable: The property due to which a substance can be beaten into sheets is
known as malleability. Metals are malleable in nature.
Ductile. The property due to which a substance can be drawn into wires is known as
ductility. Metals are ductile in nature.
Question 3.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil ? ( 2011)
Answer:
Sodium reacts with air and water both. It is a highly reactive metal. When kept in
open, it readily combines with oxygen present in air to form its oxide. Similarly, it
reacts with water vapours or moisture to form sodium hydroxide.
In order to preserve sodium metal, we generally keep it under kerosene so that
neither air nor moisture may come in its contact.
Question 4.
Write the equations for the reactions of
(a) iron with steam
(b) calcium with water
(c) potassium with water.
Answer:
(a) 3Fe(s) + 4H2O (steam) ———–> Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(b) Ca(s) + 2H2O(aq) ———–> Ca(OH)2(s) +H2(g)
(c) 2K(s) + 2H2O(aq) ———–> 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 5.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and were added to the following
solutions one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows :
Metal Solution to which metal is added
Page | 8
Iron(II) sulphate Silver nitrate
Copper(II) sulphate Zinc sulphate
A
No reaction Displacement — —
B
Displacement — No reaction „ —
Displacement
C No reaction No reaction No reaction
No reaction
D No reaction No reaction No reaction
Use the table given above to answer the following questions :
(a) Which is the most reactive metal ?
(b) What would you observe when B is added to solution of copper(II) sulphate ?
(c) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in order of increasing reactivity. ( 2011)
Answer:
Based on the activity series, the relative position of the metals in which involved in
solutions is : Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag. On the basis of the results given in the table .
Metal A is more reactive than copper and less reactive than iron.
Metal B is more reactive than iron and less reactive than zinc. –
Metal C is only more reactive than silver and less reactive than other metals.
Metal D is the least reactive in nature.
In the light of above information, we can conclude that
(a) Metal B is the most reactive.
(b) Since B is more reactive than iron, it is also more reactive than copper. This
means that it would displace copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. The blue
colour of solution will slowly fade.
(c) The decreasing order of reactivity of metals is: B>A>C>D.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 6.
Which gas is produced when a reactive metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid ?
Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4. ( 2010)
Answer:
Hydrogen gas (H2) is produced when a reactive metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric
Page | 9 acid. Iron and dilute H2SO4 react as follows :
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) ————> FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Hydrogen gas is evolved in this reaction also.
Question 7.
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate ? Write
the chemical reaction that takes place. ( 2010)
Answer:
The green colour of the solution would slowly disappear. Zinc would gradually
dissolve and iron would get precipitated at the bottom of the beaker.
Question 8.
(i) Write electron-dot structures for sodium, magnesium and oxygen.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are the ions present in these compounds ?
Answer:
(i)
(ii) Formation of sodium oxide (Na2O)
Formation of magnesium oxide (MgO)
(iii) For answer, consult structures given above.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 9.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points ? ( 2014)
Answer:
In the formation of ionic compounds, positive ions (cations) and negative ions
(anions) participate. These are closely packed and the ionic compounds exist as
Page | 10 crystalline solids. They have strong inter ionic forces of attraction and have high
melting and boiling points.
Question 10.
Define the following terms :
1. Minerals
2. Ores
3. Gang.
Answer:
1. Minerals : These are the combined states of metals and non-metals present in
earth’s curst.
2. Ores : The minerals from which metals can be conveniently and profitably
extracted, are called ores.
3. Gangue : It represents the earthy impurities such as mud, sand and clay
associated with the ore.
Question 11.
Name two metals which are formed in nature in free state.
Answer:
The metals are gold (Au) and platinum (Pt).
Question 12.
Which chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide ?
Answer:
The chemical process is known as reduction.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 13.
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following
metals. In which cases, will you find displacement reactions taking place ?
Page | 11
Metal Copper
Zinc Magnesium
Zinc oxide
Magnesium oxide
Copper oxide
Relative positions of these metals in the activity series are : Mg, Zn, Cu : In the light
of this :
Answer:
Magnesium (Mg) will displace both zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) from their oxides
Mg + ZnO ———-> MgO + Zn
Mg + CuO ———-> MgO + Cu
Zinc will displace copper from copper oxide.
Zn + CuO ———–> ZnO + Cu
Copper is least reactive and will not initiate displacement reaction.
Question 14.
Which metals do not corrode easily ?
Answer:
Metals such as gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) present at the bottom of the activity
series do not corrode easily.
Question 15.
What are alloys ? ( 2011)
Answer:
Alloys are the homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or even metals and non-
metals.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 1.
Which of the following will give displacement reactions ?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
Page | 12 (d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Answer:
(d). Only AgNO3 solution will give displacement reaction with copper (Cu) because
copper is placed above silver in the activity series.
Question 2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from
rusting ?
(a) applying grease
(b) applying paint
(c) applying a coating of zinc
(d) all the above.
Answer:
Theoretically all the three methods are helpful for preventing an iron frying pan from
rusting. However, the constituents of both grease and paint are mostly organic
compounds. They cannot withstand the heat and do not last. Therefore, applying a
coating of zinc (galvanisation) is the best method. Option (c) is correct.
Question 3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with high melting point. This
compound is also water soluble. The element is likely to be :
(a) Calcium
(b) Carbon
(c) Silicon
(d) Iron
Answer:
(a). Calcium (Ca) combines with oxygen to form calcium oxide (CaO) with very high
melting point. CaO dissolves in water to form calcium hydroxide
Question 4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) Zinc is costlier than tin
(b) Zinc has higher melting point than tin
(c) Zinc is more reactive than tin
(d) Zinc is less reactive than tin.
Answer:
(c). Zinc is more reactive than tin and reacts with organic acids present in food to
form poisonous compounds. Since tin is placed below zinc in the activity series, it is
less reactive and does not react with the organic acids. Therefore, (c) is the correct
option.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch :
(a) Flow could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non
metals ?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests to distinguish between metals and non
Page | 13 metals.
Answer:
(a) With the help of hammer, convert both the metal and non-metal (solid) in the form
of plates or rods. Metal will readily form these since they are malleable. Non-metals
being brittle will break when struck with hammer. They will form plates with difficulty
Now construct a cell in both the cases using these plates as electrodes and switch
on the current. If the bulb glows, this means that the electrodes are of metals. In
case, this does not glow, this means that the electrodes are of non-metals.
(b) From these tests, we may conclude that
1. Metals are malleable while non-metals are not.
2. Metals are good conductors of electricity while non-meals are not (graphite is
an exception).
Question 6.
What are amphoteric oxides ? Give examples of two amphoteric oxides.
Answer:
These are the oxides which can act both as acids and bases. For example,
aluminium oxide (Al2O3) and zinc oxide (ZnO). The amphoteric character of the two
oxides are shown by the following reactions.
Question 7.
Name two metals which can displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals
which can not do so.
Answer:
Sodium and calcium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids Copper and silver can
not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 8.
In the electrolytic refining of metal M, name anode, cathode and electrolyte.
Answer:
Anode : Rod of the impure metal
Cathode : Rod of pure metal
Electrolyte : Aqueous solution of soluble salt of metal M.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas
evolved by inverting a test tube over it as shown in the figure.
Page | 14
What will be the action of gas on
1. dry litmus paper ?
2. moist litmus paper ?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
( 2011)
Answer:
The gas evolved upon heating sulphur powder on a spatula is sulphur dioxide
1. SO2(g) has no action of dry litmus paper.
2. SO2(g) dissolves in moisture (water) present in moist litmus paper to form
sulphurous acid. In acidic solution, moist litmus paper will change to red.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 10.
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
1. By applying a coating of grease or paint on the surface of iron.
Page | 15 2. By depositing a layer of zinc on the surface of iron. The process is called
galvanisation.
Question 11.
What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen ?
Answer:
The oxides are generally acidic in nature which means that when dissolved in water,
their solutions change blue litmus to red. For example,
Question 12.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal but still used for making cooking utensils.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the
process of extraction. ( 2013, 2014)
Answer:
(a) These metals placed at the bottom of the activity series are very little reactive in
nature. Gold and
platinum are known as noble metals. They are not affected by air, water and by
chemicals. Since they have bright lustre, jewellery can be made from these metals.
(b) There are reactive metals placed high in the activity series. In air, their surface
gets tarnished due to presence oxygen, water vapours and carbon dioxide in air.
With water, these react violently to evolve so much heat that is not possible to
handle them. These metals are generally kept under kerosene which does not
contain air and water.
(c) When exposed to air, the metal changes its oxide called aluminium oxide
(Al2CO3). It gets deposited over the surface of the metal and forms a protective
coating on the surface. Due to the presence of this layer, the metal becomes
unreactive and can be used in making cooking utensils.
(d) Both carbonate and sulphide ores of metals cannot be directly reduced to metallic
state. Flowever, metal oxides can be easily reduced with coke or other reducing
agents. Both are therefore, converted into their respective oxides by calcination
process (for carbonate ores) and by roasting process (for sulphide ores).
Metal oxides can be easily reduced to metallic form with coke (C) or any other
suitable reducing agent. Therefore, carbonates and sulphides are converted to the
oxide form by processes of calcination and roasting and are not directly reduced.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind
juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels. (
2014)
Answer:
Page | 16 Copper metal slowly reacts with water, carbon dioxide and oxygen present in air to
form basic copper carbonate which is green in colour. Its layer slowly gets deposited
on the surface of the metal. Now lemon
juice contains citric acid while tartaric acid is present is tamrind. Both these acids
react with basic copper carbonate to form soluble salts such as copper acetate (with
citric acid) and copper tartarate (with tartaric acid). The equations for the reactions
are complicated and are not given. These salts are removed from the surface of the
copper metal and the surface of the metal shines.
Question 14.
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter
on dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him
which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparked like new but their
weight was reduced drastically. The lady got upset and after a futile argument, the
man beat a hasty retreat. Can you predict the nature of the solution used by the
impositer ?
Answer:
The man had actually used the solution of aqua regia (mixture of cone. HCl and
cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 by volume) which has dissolved gold forming soluble
auric chloride (AuCl3). Since gold actually reacted, there was a loss in weight of the
gold bangles. With the removal of the dull layer of gold from the surface, there was
original shine on the bangles. The chemical reactions have been
Question 15.
Give reason as to why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an
alloy of iron).
Answer:
Copper is a better conductor of heat than steel which is an alloy of iron. Though
copper is costlier than steel, it is used to make hot water tanks for storing hot water
in preference to steel.
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
SHIKSHA GROUP EDUCATION
Question 16.
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of chemical properties.
For the distinction in the chemical characteristics,
Property Non-metals
Page | 17 Metals
Oxides of the metals are Oxides of non-metals are
1. Nature of oxides generally basic in nature mostly acidic in nature
(Exception : ZnO and Al2O3 are (Exception : CO and N2O are
amphoteric oxides). neutral oxides).
Non-metals normally form
Metals normally form cations by
2. Electrochemical anions by the gain of
the loss of electrons. This
behaviour electrons. This means that
means that these are
these are electronegative in
electropositive in nature.
nature.
Active metals evolve hydrogen
Non-metals do not react with
3. Action with dilute acids on reacting with dilute HCl and
dilute acids
dilute H2SO4.
Compounds of non-metals
The compounds of metals are
4. Nature of compounds are mostly covalent although
mostly ionic in nature.
there are many exceptions.
Metals act as reducing agents Non-metals act as oxidising
5. Oxidising and reducing as their atoms lose electrons. agents as their atoms accept
nature For example, electrons. For example,
Na —— > Na+ + e– Cl + e–——–>Cl–
CH-3 METALS AND NON-METALS NOTES WITH SOLUTION
Prepared by-Jitendra Sir
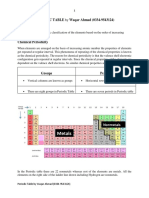
Elements contain only one kind of atoms like Na, Mg, Cl2, O2 etc.
They are categorised further as metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Metals Non-metals Metalloids
They are electronegative elements, i.e. have a They possess the properties of metals as
tendency to form anion by gaining electron(s) well as non-metals. They are very few in
losing electron(s), e.g. Cu, Fe, Au, Na etc e.g. iodine (I2), sulphur (S),hydrogen (H2) etc. numbers, e.g. Ge, Ga etc.
Metal Extraction
Physical Properties
Metallurgy Physical Properties
●
Malleability It is the property of
metals to get converted into thin It is the process of extraction
of metals from their ores.
● Metallic Lustre Non-metals except
sheets on beating and is maximum iodine and graphite, do not possess
in gold and silver. metallic lustre.
●
Ductility It is the property of metals ● Conductivity Non-metals are
due to which these can be drawn Minerals generally poor conductors of heat
into wires. It is maximum in gold. The compounds in the form of which and electricity because of the
●
Conductivity Metals are generally metal occur naturally are called minerals. absence of free electrons.
good conductors of heat and
electricity because of the presence
of free electrons. Ores and Gangue
The minerals from which metal is
extracted profitably are called the ores Chemical Properties
Chemical Properties and the impurities associated with them ● Reaction with Oxygen Non-metals
● Reaction with Water In this are called gangue. also form oxides but their nature is
reaction, metal oxide and generally acidic, (e.g. P2O5, SO2 and
hydrogen are obtained. Metal CO2 as they produce acid with water)
oxide further reacts with water to Steps of Extraction
or neutral, (e.g. CO, H2O, NO2 etc.)
form metal hydroxide.
Concentration of Ore ● Formation of Covalent Compounds
● Reaction with Dilute Acids It is the process of removal of Non-metals react with other non-
Reactive metals generally form impurities of sand, clay etc., from metals to form covalent compounds
salt and hydrogen with HCl or the metal. like H2S,H2O etc.
H2SO4, but not with HNO3.
● Reaction with Solution of
Other Metals Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
Reactive metals displace the Metals of Metals of Metals of The bond formed by the complete
less reactive metals from their High Reactivity Medium Reactivity Low Reactivity
transfer of an electron from a metal
salt solution.
atom to a non-metal atom is called
e.g. A+BC → AC+B. ionic bond.
Electrolysis of
or Cu+AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2+2 + Ag molton ore
Sulphide ores
The order of reactivity is
K>Na>>Ca>Mg>Al>Zn>Fe Properties of Ionic Compounds
>Sn>H>Cu>Hg>Ag>Au. Pure metal Roasting ● They are brittle and have high melting
This series is called reactivity and boiling point.
series. ● They are soluble in water.
Carbonate Sulphide Metal ● They are conductor of electricity in
● Alloy formation Alloys are ore ore
homogeneous mixtures of two or aqueous solution or in molten state
more metals or a metal and a because of the presence of free ions.
non-metal. Alloy of metal with Calcination Roasting Refining
Hg (mercury) is called amalgam.
Oxide to metal Reduction to metal Purification of Metal
You might also like
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Properties and ReactionsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Properties and ReactionsKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- DCM Group Of Schools - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument40 pagesDCM Group Of Schools - Metals and Non-Metalsgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Bhavya JangidNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedDocument15 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedCyber Atharv100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesMustafa Khan100% (1)
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesAzeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non Metalsbhumika motiyaniNo ratings yet
- uydzUwWvUSKaN61mmJc4Document6 pagesuydzUwWvUSKaN61mmJc4varshatagade126No ratings yet
- MetalsDocument7 pagesMetalsritesh kavuruNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals N 1Document8 pagesMetals and Non Metals N 1rincyNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non Metalsvishwath donepudiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Metals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyDocument13 pagesMetals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-metalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non-metalsmonkey.luffy.kenNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals G LudhianaDocument7 pagesProperties of Metals G Ludhianaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument41 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsPawan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy 2024Document13 pagesMetallurgy 2024pokeninjazxNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 Revision NotesAn SaNo ratings yet
- Metals OlevleDocument9 pagesMetals OlevleaayannisarNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- Science: (Chemistry)Document22 pagesScience: (Chemistry)Isaiah JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Document9 pages10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1varunNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument9 pagesPeriodic TableXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDocument5 pagesMaterials Metals and Non-Metalssidhantm823No ratings yet
- DownloadedDocument12 pagesDownloadedAniket shuklaNo ratings yet
- Element Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesElement Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsInsha Hasan 10DNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsKISHORE ADITYA DHINESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Metals and Non MetalsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Metals and Non Metalskush96122No ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Document10 pages10 Science Notes 03 Metals and Non Metals 1Rishu KaulNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument3 pagesMetals and Non Metals NotesVUDATHU SHASHIK MEHERNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument72 pagesMetals and Non MetalssimoneNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Chapter - 8 MetalDocument12 pagesChapter - 8 Metalamit_idea1No ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesMetals and Non MetalsKaran MahajanNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument5 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemistryvisheshsingla411No ratings yet
- C13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesDocument39 pagesC13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- Metals vs Non-Metals: A Comparison of Key PropertiesDocument9 pagesMetals vs Non-Metals: A Comparison of Key PropertiesHoang HaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Properties and UsesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Properties and UsesAtharv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals and Non Metals2erwr100% (2)
- Chemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsBhavesh BhaveshNo ratings yet
- Notes On Materials Metals and Non MetalsDocument6 pagesNotes On Materials Metals and Non Metalsmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsKunal HazarikaNo ratings yet
- 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pages3 Metals and Non Metalsmazharpunjabi67% (3)
- Notes_Metals ad Non-Metals_C-XDocument8 pagesNotes_Metals ad Non-Metals_C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 3 EmbibeDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 3 EmbibeIbrahim CheyoNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Metals: Properties and ReactivityDocument20 pagesMetals: Properties and ReactivityKivaNo ratings yet
- Metal and NonmetalDocument26 pagesMetal and NonmetalSudhanshu Sekhar PandaNo ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapte3Document9 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapte3PallaviGupta100% (1)
- Reading Material by NVS TeacherDocument12 pagesReading Material by NVS Teacher10E Yuvan Sarabeshan Thirumeninathan [3383]No ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Deterjent Powder PDFDocument9 pagesDeterjent Powder PDFMrutunjay PatraNo ratings yet
- SOP For House Keeping of Stores - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesSOP For House Keeping of Stores - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesranaNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterseal Traffic 1500 TdsDocument6 pagesBasf Masterseal Traffic 1500 Tdsjuli_radNo ratings yet
- BS Market SurveyDocument9 pagesBS Market SurveyPratik BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Polyurethane VarnishDocument2 pagesAsian Paints Polyurethane Varnishkalpani pelpolaNo ratings yet
- Installation Details IguzziniDocument133 pagesInstallation Details IguzziniimtiazNo ratings yet
- Indian Minerals Yearbook 2020: (Part-III: Mineral Reviews)Document7 pagesIndian Minerals Yearbook 2020: (Part-III: Mineral Reviews)k_pareshNo ratings yet
- ASTM A355 Steel Bars - Alloys For NitridingDocument2 pagesASTM A355 Steel Bars - Alloys For Nitridingnse mcxNo ratings yet
- ETAG006 2finDocument66 pagesETAG006 2finSerban RaduNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan For Anode MD5Document7 pagesInspection and Test Plan For Anode MD5congvt93No ratings yet
- 2 Storey 8cl PDFDocument18 pages2 Storey 8cl PDFGels GenovaNo ratings yet
- Mineral saturation and activity diagramsDocument7 pagesMineral saturation and activity diagramsAththur MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects, Causes & Correction: Leigh BaughurstDocument3 pagesWelding Defects, Causes & Correction: Leigh BaughurstankNo ratings yet
- Fix-Z-A4 Stainless Steel Design GuideDocument4 pagesFix-Z-A4 Stainless Steel Design GuidedineshNo ratings yet
- 420kV Shunt Reactor Technical SpecificationDocument38 pages420kV Shunt Reactor Technical SpecificationSE TPC-4No ratings yet
- Is 2394 1984Document25 pagesIs 2394 1984GAURAV mISHRANo ratings yet
- TLE6 Q3 Mod2 IA ConductingASimpleSurveyUsingTechnology OtherDataGatheringMethod v5Document20 pagesTLE6 Q3 Mod2 IA ConductingASimpleSurveyUsingTechnology OtherDataGatheringMethod v5Lolorns McgallsNo ratings yet
- Excito-B: Based On "QM" Cartridge Type 5 Stage Ultrafiltration SystemDocument2 pagesExcito-B: Based On "QM" Cartridge Type 5 Stage Ultrafiltration SystemNegoita CiprianNo ratings yet
- NCR Log Sheet (CBPL)Document6 pagesNCR Log Sheet (CBPL)lavekushNo ratings yet
- A.Y. Dadabhai Technical Institute, Kosamba: A Project Report OnDocument26 pagesA.Y. Dadabhai Technical Institute, Kosamba: A Project Report OnrutvikNo ratings yet
- KITZ 3K & 6K Ball Valves Dropsheets-2015-F2Document2 pagesKITZ 3K & 6K Ball Valves Dropsheets-2015-F2Sarmiento HerminioNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry II Module Chem451 Finasubmitted 1 1Document206 pagesIndustrial Chemistry II Module Chem451 Finasubmitted 1 1tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Masonry Design Example Comparisons Using ASD and SD: OutlineDocument25 pagesMasonry Design Example Comparisons Using ASD and SD: OutlineRicardo Muñiz DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Data and Health Hazards of Welding ElectrodeDocument1 pageReactivity Data and Health Hazards of Welding ElectrodeSona MahardhikaNo ratings yet
- Battery TerminalDocument9 pagesBattery TerminalW MoralesNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Ventilation HazardsDocument180 pagesConfined Space Ventilation HazardsShuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- KC-Chemical Inventory SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesKC-Chemical Inventory SpreadsheetRocky BisNo ratings yet
- EARLY WORKS - Civil & Preliminary BOQDocument1 pageEARLY WORKS - Civil & Preliminary BOQDeepa Junnarkar DegwekarNo ratings yet
- ColaMulse FEDocument1 pageColaMulse FEmndmattNo ratings yet
- Course No.: FS-244 Course Title: Building Construction and Cost Estimation Semester: Iv Credits: 2 (1+1)Document3 pagesCourse No.: FS-244 Course Title: Building Construction and Cost Estimation Semester: Iv Credits: 2 (1+1)dineshwayendeshkatNo ratings yet