Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary Worksheets
Uploaded by
Vena Grace MendezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary Worksheets
Uploaded by
Vena Grace MendezCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Grade and Section: Date:
Learning Competency:
Explain how protein is made using information from DNA (S10LTIIIc-37)
Activity # 1 - Getting to Know the DNA and RNA Structure
Objective:
Compare the structures of the DNA and RNA molecule
Materials:
DNA and RNA pictures
Procedure:
1. Read the given information carefully about DNA and RNA.
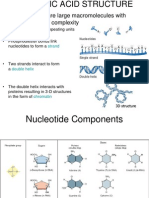
Nucleic acids are macromolecules or biopolymers. Moreover, they are the building
blocks of genetic material of an organism. They are comprised of nucleotide chains linked
via phosphodiester bonds between 5′ phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3′-OH
group of the adjacent nucleotide. Accordingly, there are two types of nucleic acids namely
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) which are vital compounds in living
organisms. A nucleotide is the basic unit of the nucleic acids. Accordingly, the
deoxyribonucleotide is the building block of DNA while the ribonucleotide is the building
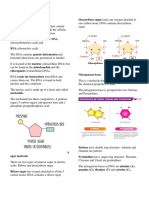
block of RNA. Structurally, there are three components in a nucleotide. They are a pentose
sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. These components differ between two
major types of nucleic acids. DNA contains deoxyribose sugar whereas RNA contains ribose
sugar.
What is DNA Structure?
Deoxyribonucleic acid is the genetic material of all eukaryotes and some prokaryotes.
Hence, it contains the genetic information that requires for the overall functioning of an
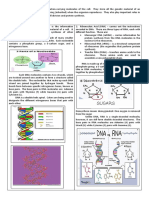
organism. DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell. . Structurally, DNA consists of two strands,
arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each
deoxynucleotide has three components; deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogenous base (adenine,
guanine, cytosine and thymine) and a phosphate group.
Figure 01: DNA Structure
Hydrogen bonds link the two strands of the DNA. Here, the hydrogen bonds occur
between nitrogenous bases. Adenine links with thymine by two hydrogen bonds while
cytosine binds with guanine by three hydrogen bonds. In the DNA helix, phosphate and
sugar moieties are situated on the outside of the helix whereas the bases remain in the
interior of the helix. Also, the two strands of DNA run in opposite directions. DNA is found in
the nucleus, with a small amount of DNA also present in mitochondria.
What is RNA Structure?
Ribonucleic acid or RNA is the second type of nucleic acid present in many living
organisms. RNA converts the genetic information contained within DNA to build proteins.
The genetic information hidden in the DNA molecule is converted into a mRNA molecule
through transcription. Once the transcription completes, mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus
and travels into the cytoplasm for translation. At the end of this process, it yields a protein.
Furthermore, RNA, for the most part, exists as a single strand, but it can form several
structural features due to the complementary base pairing within the single strand. Besides,
the RNA composes ribonucleotides. Ribonucleotides consist of the ribose sugar, a
phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Four nitrogenous bases present in RNA are
adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine.
Figure 02: RNA Structure
Guide Questions:
1. Complete the following table to describe the structure and functions of DNA and RNA
Table 1- DNA chart
DNA
Function DNA replicates and stores genetic information. It is a
blueprint for all genetic information contained within
an organism.
Number of strands DNA is structured as a double helix, with two
strands of DNA winding around.
Location in the cell DNA is found in the nucleus, with a small amount of
DNA also present in mitochondria.
Type of Sugar The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, which contains
one less hydroxyl group than RNA’s ribose.
Nitrogenous Bases The bases in DNA are Adenine (‘A’), Thymine (‘T’),
Guanine (‘G’) and Cytosine (‘C’).
Table 2- RNA chart
RNA
Function RNA converts the genetic information contained
within DNA to a format used to build proteins, and
then moves it to ribosomal protein factories.
Number of strands DNA is structured as a double helix, with two
strands of DNA winding around
Location in the cell RNA forms in the nucleolus, and then moves to
specialised regions of the cytoplasm depending on
the type of RNA formed.
Type of Sugar RNA contains ribose sugar molecules, without the
hydroxyl modifications of deoxyribose.
Nitrogenous Bases RNA shares Adenine (‘A’), Guanine (‘G’) and
Cytosine (‘C’) with DNA, but contains Uracil (‘U’)
rather than Thymine.
2. Using a Venn diagram, list down the similarities and differences of DNA and
RNA.
DNA RNA
Single stranded
Ribose
Double stranded
Uses A, C Modified 5’ cap and 3’ poly A tail
Structured into chromosomes
And G. Uses uracil
Deoxyribose
Stores info about protein
Uses thymine
structure
Is read by polymerases Has sugar
Read by ribosomes
Stores genetic information + phosphate
Can have multiple structures
Can self-replicate backbone
Does not usually last
Can last for a long time
for a long time
Is read 3’->5’
Is formed in 5’->3’
You might also like
- DNA StructureDocument38 pagesDNA Structuremuhdmoosa100% (3)
- DNA Structure and FunctionDocument35 pagesDNA Structure and FunctionSeemaNo ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna Structureapi-315792432No ratings yet
- The Importance of DNA and RNADocument13 pagesThe Importance of DNA and RNAJamieNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesDNA Structure and FunctionJomar Ison100% (2)
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Document95 pagesTypes of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument16 pagesDNA StructureMohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA: Teacher Notes and AnswersDocument4 pagesStructure of DNA: Teacher Notes and Answersyawahab100% (1)
- Structure and Function of DNADocument29 pagesStructure and Function of DNAMatthew Justin Villanueva GozoNo ratings yet
- A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocument83 pagesA1.2 Nucleic AcidsGhenwa DimachkiNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Evolution Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesEvidences of Evolution Activity SheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- DNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonDocument6 pagesDNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Dna and Cental Dogma 1Document3 pagesLecture Notes Dna and Cental Dogma 1antonettenakpilNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity: Mendel's Methods and DiscoveriesDocument18 pagesGenetics and Heredity: Mendel's Methods and DiscoveriesLovely Syre LaysonNo ratings yet
- DNA - RNA Introduction AssignmentDocument18 pagesDNA - RNA Introduction AssignmentIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- DNA vs RNA: Key DifferencesDocument2 pagesDNA vs RNA: Key DifferencesMegat AmirulNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- DNA vs RNA: A Comparison of Genetic StructuresDocument28 pagesDNA vs RNA: A Comparison of Genetic StructuresLeilani Joy Rivera GabitoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Functions & StructuresDocument2 pagesNucleic Acids Functions & StructuresFares SamirNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNA Building BlocksDocument1 pageNucleic Acids - DNA and RNA Building Blocksasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- COT3Document27 pagesCOT3Vincent Franciz FernandezNo ratings yet
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Paper - IV Molecular BiologyDocument236 pagesPaper - IV Molecular BiologyNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA: The Molecules of LifeDocument10 pagesDNA and RNA: The Molecules of LifeAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument14 pagesHEREDITYTrisha Faye SagadalNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument6 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- Character Kingdom Habitat Algae FungiDocument10 pagesCharacter Kingdom Habitat Algae FungiShane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and the Central DogmaDocument94 pagesDNA Replication and the Central Dogmameklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Materi GenetikDocument3 pagesMateri GenetikAKMELIA NAJWANo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument36 pagesNucleic AcidsAman UllahNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LDocument7 pagesStudy Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LPepitinNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna PDFDocument16 pagesDna and Rna PDFEliza Adrianne Cordero100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidDocument14 pagesNucleic AcidNathasha Mitch FontanaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument62 pagesUnit 7 Nucleic AcidsGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids Structure and FunctionMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument1 pageDNA and RNADaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument14 pagesGroup 4 PresentationJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- Biology Report - Nucleic AcidDocument12 pagesBiology Report - Nucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument29 pagesNucleic Acidshatdog adadaNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Lecture DNA and RNADocument2 pagesScience-10 Q3 Lecture DNA and RNAbruh669No ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Difference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameHisham MustafaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3-DNA SCIENCE 10Document29 pagesQuarter 3-DNA SCIENCE 10Rubeliza LawengNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesDNA and RNA Structure and FunctionSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Rna and Its Structure, Function and TypesDocument12 pagesRna and Its Structure, Function and TypesBaikuntha SabarNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA: DefinitionDocument1 pageDNA RNA: Definitionkatrina668No ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument19 pagesDna and Rnasamanthanicolecalingasan3No ratings yet
- Class 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDocument4 pagesClass 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Basis of ComparisonDocument2 pagesBasis of ComparisonJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- Developmental Activity - A Virtual Tour On The EM WavesDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Activity - A Virtual Tour On The EM WavesVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Genetic EngineeringDocument2 pagesActivity Sheets Genetic EngineeringVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Connection StatusDocument2 pagesConnection StatusVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Planet Chart A4Document1 pagePlanet Chart A4Vena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Movie NamesDocument1 pageMovie NamesVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No 9258 - Guidance and Counseling Act of 2004Document8 pagesRepublic Act No 9258 - Guidance and Counseling Act of 2004Vena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Wedding ThemesDocument1 pageWedding ThemesVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Stage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureDocument41 pagesStage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureKassyKasNo ratings yet
- Levels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesLevels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDianne Joy LeybaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 & 7.1 DNA Structure HL Caitlin WORDDocument4 pages3.3 & 7.1 DNA Structure HL Caitlin WORDCaitlin BarrettNo ratings yet
- The Proto Nucleic Acid Builder A Software Tool Forconstructing Nucleic Acid AnalogsDocument11 pagesThe Proto Nucleic Acid Builder A Software Tool Forconstructing Nucleic Acid AnalogsAngela HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYoussef samehNo ratings yet
- BASC02 Full PDFDocument70 pagesBASC02 Full PDFndarubagusNo ratings yet
- Chengde Mao - The Emergence of Complexity: Lessons From DNADocument3 pagesChengde Mao - The Emergence of Complexity: Lessons From DNALpeo23No ratings yet
- Dna 2Document27 pagesDna 2Louis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- DNA Primary and Secondary StructureDocument20 pagesDNA Primary and Secondary StructureRuth AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNADocument53 pagesNucleic Acids - DNA and RNATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Forensics EvidenceDocument80 pagesForensics EvidenceSony BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Mcqs 2020Document3 pagesBiological Molecules Mcqs 2020PakistanWaqarMughalNo ratings yet
- IV. Nucleic AcidsDocument44 pagesIV. Nucleic AcidsAngel Hope MacedaNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation Lecture 1Document15 pagesGene Regulation Lecture 1fredajw90No ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument4 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy Inc.: Heredity: Inheritance and VariationMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- DNA Conformation and Transcription Pag. 145 SupercoilingDocument215 pagesDNA Conformation and Transcription Pag. 145 SupercoilingDiegoNo ratings yet
- Ds83-Replication Review Formative AssessmentDocument4 pagesDs83-Replication Review Formative Assessmentapi-110789702No ratings yet
- 12-1 Science NotebookDocument4 pages12-1 Science Notebooksantosh_dhandeNo ratings yet
- Nukleotida, DNA, RNA OKDocument42 pagesNukleotida, DNA, RNA OKSylvia AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- David W. Ussery - DNA Structure: A-, B - and Z-DNA Helix FamiliesDocument7 pagesDavid W. Ussery - DNA Structure: A-, B - and Z-DNA Helix FamiliesUylrikkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document216 pagesUnit 1ShekharNo ratings yet