Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Compaction Test
Uploaded by
Zahim HarkiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil Compaction Test
Uploaded by
Zahim HarkiCopyright:
Available Formats
SORAN UNIVERSITY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
Soil Lab
Soil Compaction test
NAME OF STUDENTS: Daniz Ismail, Zahem Ihsan, Yahya Omar, Ahmad
Babir, Bilal Muhamad, Didar Awni
SUPERVISED BY: Rzgar A. Omar
EXPERIMENTAL NO: 4
EXPERIMENTAL NAME: standard compaction test
CLASS: 3rd
GROUP NO: one
DATE OF TEST: 10, May, 2022
DATE OF SUBMISSION: 17, May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ............................................................................................. i
Introduction ..................................................................................................... 1
Objective (Aims of the test) ............................................................................ 2
Apparatus ........................................................................................................ 3
Procedure ........................................................................................................ 3
Calculations: - ................................................................................................. 6
Graphs: -.......................................................................................................... 9
Table of result:- ............................................................................................. 11
Conclusion .................................................................................................... 13
References ..................................................................................................... 14
Appendix A : Data Sheet .............................................................................XV
Rizgar A. Omar -i- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Introduction
Soil compaction is the process of minimizing the void space between soil particles by
exerting mechanical compactive effort. When particles are forced together to close the
space between them, this is known as compaction. Because highly compacted soils have
fewer voids, they have a higher unit weight (mintekresources, 2020).
Compaction degree is influenced by soil properties, the type and amount of energy
delivered by the compaction process, and the water content of the soil. Every soil has a
maximum moisture capacity for which it can endure maximum compression. In other
words, a soil reaches its maximum dry unit weight (Yd max) at an optimum water content
level for a particular compactive effort (wopt).
The most common laboratory test for soil compaction is the Proctor compaction test. The
type of compaction and the provided energy for a given soil volume are standard and,
thus, the test focuses on the change of a sample’s moisture content to derive the optimum
water content (wopt).
Rizgar A. Omar -1- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Objective (Aims of the test)
The aim of this test was to find maximum dry unit weight at an optimum water content,
and to know how important the test is which is soil compaction.
Compaction increases the shear strength of soils by adding friction from the
interlocking of particles. Future settlement of soils is reduced by increasing the
stiffness and eliminating voids creating a densified soil. The removal of voids
reduces the chance of the soil settling or shrinking or expanding and it decreases
water seepage that would lead to deleterious shrinking and swelling soil properties
(geoengineer, n.d.).
Compaction of the soil and removing air voids generally increases the soil’s
strength, decreases its compressibility, and decreases its permeability. It will reduce
the voids ratio making it more difficult for water to flow through soil.
Those factors are crucial in structures and engineering applications such as earth
dams, embankments, support of pavements, or support of foundations.
Rizgar A. Omar -2- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Apparatus
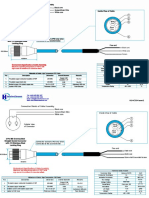
➢ Cylindrical Metal Mold (figure 1). ➢ Sieve No.4 (figure 4).
➢ Rammer, weighing 2.5 kg & ➢ Tray & scoop (figure 5).
having fall of 30.5 cm (figure 2). ➢ Oven (figure 6).
➢ Sensitive Balance & Moisture
containers (figure 3).
Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3
Figure 4 Figure 5 Figure 6
Rizgar A. Omar -3- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Procedure
I. For the test to be accurate, sample needs to be dry-oven and hence the sample was
put to oven for 24 hours, a day in advance of the test day.
II. Each group needs an amount of 2.5 Kg of the dry sample, which means an
amount of 10 Kg (totally for four groups) was sieved through sieve number 4
(4.75mm) as shown in figure (1) according to given speciation’s and guidelines.
III. The sample had clumps of soil and it needed to be fined a bit so that it can pass
through the sieve, for that a compaction force of a hammer was used which is
shown in figure (2).
IV. The proper amount of sample which was 2.5 Kg multiplied by the given water
ratio to each group, resulted in the required amount of water content (325ml) to be
mixed with the sample, once it was measured, the water got poured onto the
sample slowly and then it was mixed properly with hands as shown in figure (3).
Figure 1 sample getting sieved.
Figure 3 mix sample with hands and
add water slowly.
Figure 2 big clumps getting smaller with
hammer crash power.
Rizgar A. Omar -4- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
V. The molds volume needs to be calculated before pouring the wet sample into it,
its weight (empty mold) also needs to be scaled as shown in figure (4).
VI. The mold is oiled 1st then the wetted sample is poured into the mold shown in
figure (5) in 3 layers, each layer must be compacted with the Rammer as shown in
figure (6) 25 times.
VII. At the end of the last layers compaction, the extension piece of the mold is
removed & only the bottom piece of the mold is taken into account and
considered hence it is weighed.
VIII. A sample of it will be put into a can (keep in mind that the can must be weighed
emptily beforehand) and then put into the for 24 hours, then it has to be weighed
too, with all those data in hand, the required data’s are achieved through various
calculations which are given on the datasheet and a graph of the data is graphed,
which help us determine the MDD and OWC of the sample, this needs 4 samples
data, not just one, so the other data’s were gathered from the other 3 groups.
Figure 4 with extension part Figure 5 the sample is poured
removed, the empty mold into the mold in 3 layers. Figure 6 each layer gets
gets weighed. compacted 25 times with
a rammer.
Rizgar A. Omar -5- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Calculations: -
Empty
Wt.of mold + Empty can Empty can
Weight mold Volume of Can can + dry
Trail wet sample weight + wet soil
(W1) mold no soil
(W2) (C1) (C2)
(C3)
1 4263.7 g 5893.8 g 938.93 1 32.30 g 80.31 g 73.75 g
Solid soil weight = 2500 gm ,
w.c used = % 13,
2500gm * 0.13 = 325 gm
325 ml of water weighted
Rizgar A. Omar -6- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Empty
Wt.of mold + Empty can Empty can
Weight mold Volume of Can can + dry
Trail wet sample weight + wet soil
(W1) mold no soil
(W2) (C1) (C2)
(C3)
2 4263.7 g 6069 g 938.93 2 32 g 96 g 87.7 g
Solid soil weight = 2000 gm ,
w.c used = % 16,
2000gm * 0.16 = 320gm
320 ml of water weighted
Rizgar A. Omar -7- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Empty
Wt.of mold + Empty can Empty can
Weight mold Volume of Can can + dry
Trail wet sample weight + wet soil
(W1) mold no soil
(W2) (C1) (C2)
(C3)
3 4258 g 6078 g 938.93 3 29.7 g 86.47 g 76.36 g
Solid soil weight = 2000 gm ,
w.c used = % 19
2000gm * 0.19 = 380 gm
380 ml of water weighted
Rizgar A. Omar -8- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Empty
Wt.of mold + Empty can Empty can
Weight mold Volume of Can can + dry
Trail wet sample weight + wet soil
(W1) mold no soil
(W2) (C1) (C2)
(C3)
4 4285 g 6110 g 938.93 4 45.5 g 174 g 150.01 g
Solid soil weight = 2000 gm ,
w.c used = % 21,
2000gm * 0.21 = 420 gm
420 ml of water weighted
Rizgar A. Omar -9- 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Graphs: -
MDD= 16.43
W.c = % 14.920
KN/m^3 OMC %
16.43 14.920 %
Rizgar A. Omar - 10 - 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Table of result:-
Stander Proctor Test
Wt.of
Empty Empty Empty
Weight mold +
Volume Can can can + can + Water
Trail mold wet
of mold no weight wet soil dry soil content
(W1) sample
(C1) (C2) (C3)
(W2)
Unit
gm gm Cm^3 Kn/m^3 gm gm gm % Kn/m^3
1 4263.7 5893.8 938.93 17.0244 1 32.3 80.31 73.75 15.826 14.698
2 4263.7 6069 938.93 18.854 2 32 96 87.7 14.901 16.409
3 4258 6078 938.93 19.008 3 29.7 86.47 76.36 21.667 15.623
4 4285 6110 938.93 19.06 4 45.5 174 150.01 22.955 15.502
Rizgar A. Omar - 11 - 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Discussion
Soil compaction is a process where the desired site of construction is compacted through
various machines and devices i.e., smooth roller, sheep roller, dynamic compaction, vibro
compaction etc.… which benefits the soil e.g., improves soil quality, adds density,
prevents/decreases occurrence of soil settlement, increases bearing capacity etc.…
Proctor compaction test is conducted in order to find out the soil’s maximum dry density
corresponding to its optimum water content by testing the sample in different phases of
various water contents which were (13, 16, 19 &21%) with the same soil sample, the
graph which is the combination of all 4 tests that determines the soil sample at its
maximum dry state is a density of 16.43 kN/m3 and an optimum water content of
14.920%.
Regarding errors, the mold had bit of its layers chipped off (the part where the base piece
and extension piece are linked together by set of screws) which effects the performance
of the apparatus, while we were trying to remove the extension piece at the end of the test
it was almost locked and was difficult to screw it off, and when the screws were undone a
bit of the sample got left over in the extension piece, so with a trowel we tried to put it
back on the top of the compacted sample and then compact it again with trowel, we can
clearly sense it that was a major error and we should not ignore it, another thing that can
be highlighted as an error was the rammer can’t be compacted properly as different
students did it with different power and some did it wrongly, so it was an error.
The test follows according to ASTM D698 that advises 25 blows and 3 layers in a 1000
cm3 volumetric mold & rammer mass of 2.5 kg.
Rizgar A. Omar - 12 - 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Conclusion
The test concentrated on finding a samples maximum dry density with its corresponding
optimum water content, that it explains the samples properties i.e., swelling, shrinking,
bearing capacity etc.… in the test a new apparatus was introduced, which is proctor
apparatus with its components: rammer, mold
in conclusion, proctor compacting test proved itself to be useful, especially in situ for
determining our site’s properties and profiles.
Rizgar A. Omar - 13 - 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
References
https://www.geoengineer.org/education/laboratory-testing/compaction-test
https://uta.pressbooks.pub/soilmechanics/chapter/compaction-test/
Rizgar A. Omar - 14 - 10 May, 2022
Soil Compaction
Appendix A : Data Sheet
Rizgar A. Omar - XV - 10 May, 2022
You might also like
- Soil Report#3Document8 pagesSoil Report#3zeinabNo ratings yet
- معمل سويل compaction (Document7 pagesمعمل سويل compaction (Hamida MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Practical Test 1: (A) Moisture Density Relationship of SoilsDocument8 pagesPractical Test 1: (A) Moisture Density Relationship of SoilsBernard KitosiNo ratings yet
- معمل سويل CompactionDocument8 pagesمعمل سويل CompactionHamida MahmoudNo ratings yet
- G3 (S1) Standard Proctor TestDocument26 pagesG3 (S1) Standard Proctor Testwee yekNo ratings yet
- ECG263 Lab 6 (STANDARD PROCTOR TEST)Document3 pagesECG263 Lab 6 (STANDARD PROCTOR TEST)naqibkamarozamanNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines 983 Aurora Boulevard Cubao, Quezon CityDocument9 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines 983 Aurora Boulevard Cubao, Quezon CityJansen Parallag0% (1)
- LAB 7 - STANDARD PROCTOR (Level 1)Document5 pagesLAB 7 - STANDARD PROCTOR (Level 1)Doris AsmaniNo ratings yet
- CompactionDocument3 pagesCompactionスルタンリスクNo ratings yet
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestDocument7 pagesStandard Proctor Compaction TestshuhadaNo ratings yet
- Light CompactionDocument4 pagesLight Compactionmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 10: Modified ProctorDocument20 pagesLab 10: Modified Proctorkim suarezNo ratings yet
- Linear ShrinkageDocument13 pagesLinear ShrinkageZahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lab ReportDocument7 pages3rd Lab ReportSunilNo ratings yet
- Proctor Test-: Kabul University Engineering Faculty Civil DepartmentDocument4 pagesProctor Test-: Kabul University Engineering Faculty Civil DepartmentAssad YaqubiNo ratings yet
- Full Report (2G) L2Document36 pagesFull Report (2G) L2Mohd Afiq AminNo ratings yet
- Report Fix PDFDocument21 pagesReport Fix PDFTriet TruongNo ratings yet
- Hand Auger MethodDocument4 pagesHand Auger Methodnrsyhira salihinNo ratings yet
- Soil CompleteDocument84 pagesSoil CompleteAbdqawim NordinNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization Practical Report Grp2Document18 pagesSoil Stabilization Practical Report Grp2Olowoniwa MarvellousNo ratings yet
- Compaction Test Lab Report Group EDocument13 pagesCompaction Test Lab Report Group EseifNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 6Document10 pagesLab No. 6Johnrev Philip AcopioNo ratings yet
- Laboratory No 5-6Document7 pagesLaboratory No 5-6mapoygenesislanaNo ratings yet
- AGTE-1 Degrevised2Document51 pagesAGTE-1 Degrevised2Vaishali PawarNo ratings yet
- Lec On CompactionDocument52 pagesLec On Compactionsimpi kumariNo ratings yet
- Compaction TestDocument12 pagesCompaction Testaidil adhaNo ratings yet
- Soil Lab I Chapter 9Document8 pagesSoil Lab I Chapter 9asia groupNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 CompactionTestDocument9 pagesExp 7 CompactionTestKelvin NgugiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 6 and 7Document8 pagesLab Manual 6 and 7Prabesh PokharelNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument65 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Laboratory Manualnitin anantNo ratings yet
- Exp-2 UnitWeight PDFDocument11 pagesExp-2 UnitWeight PDFMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Compaction TestDocument7 pagesCompaction TestJunrey LumangyaoNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Compaction-ReportDocument6 pagesIdoc - Pub Compaction-ReportShavin ChandNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesFaculty of Engineering: Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory ReportCarl MigaelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: Objective:-To Determine The Liquid Limit and Plastic Limit of Fine-Grained (Bentonite) Soil AsDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 3: Objective:-To Determine The Liquid Limit and Plastic Limit of Fine-Grained (Bentonite) Soil AsSUMRAT MEENANo ratings yet
- Standard Proctor TestDocument6 pagesStandard Proctor TestnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- LAB L4 (Determination of Dry Density)Document14 pagesLAB L4 (Determination of Dry Density)Sahrizanea Nurizmisa100% (1)
- Standard Compaction TestDocument6 pagesStandard Compaction Testجمانه العطويNo ratings yet
- Soil Mech Compaction FinalDocument18 pagesSoil Mech Compaction FinalScott MuthuriNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Compaction TestDocument9 pagesLab 4 - Compaction TestamNo ratings yet
- CE 232 CompactionDocument6 pagesCE 232 CompactionRebel Ba KaNo ratings yet
- CompactionDocument5 pagesCompactionSwapan PaulNo ratings yet
- Ce353-Ch6 Compaction PDFDocument31 pagesCe353-Ch6 Compaction PDFShamoyal KhanNo ratings yet
- Soil-Compaction Lab 1Document9 pagesSoil-Compaction Lab 1Abdulrahman Alnagar100% (1)
- Irjmets ArticleDocument7 pagesIrjmets ArticleSuraj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Standard Compaction-TestDocument6 pagesStandard Compaction-TestSalih MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Soil - Lab Report 7Document5 pagesSoil - Lab Report 7Maricar De LeonNo ratings yet
- Proctor Compaction TestDocument12 pagesProctor Compaction Testmathirenga88No ratings yet
- Tutorial TwoDocument19 pagesTutorial Twoshivan.adharNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Lab ProjectDocument20 pagesGeotechnical Lab ProjectMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Density Determination RegaladoDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Density Determination Regaladoshania RegaladoNo ratings yet
- The Liquid Limit of The SoilDocument2 pagesThe Liquid Limit of The SoilAnjoe Mhar NocheNo ratings yet
- University of Dar Es SalaamDocument10 pagesUniversity of Dar Es SalaamBernard KitosiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Standard Proctor Compaction Test ObjectiveDocument11 pagesExperiment 5 Standard Proctor Compaction Test Objectiveakmal hazimNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Technology Civil Engineering Department Soil LaboratoryDocument11 pagesFaculty of Engineering Technology Civil Engineering Department Soil LaboratoryAnas Abu-shawishNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Plastic Limit of SoilDocument43 pagesLecture 05 Plastic Limit of Soilmuhammad asimNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Lab: List of ExperimentsDocument57 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Lab: List of ExperimentsYash WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 DCC3103 - Geotechnic Sem 3Document3 pagesTutorial 1 DCC3103 - Geotechnic Sem 3farahaidasabriNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document32 pagesCH 6Zahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document17 pagesCH 4Zahim Harki100% (1)
- Linear ShrinkageDocument13 pagesLinear ShrinkageZahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture One - Introduction To RevitDocument23 pagesLecture One - Introduction To RevitZahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document31 pagesCH 3Zahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document18 pagesReport 2Zahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- Slump Test of Fresh Concrete (ASTM C143/C143M-05a) & (BS 1881: PART 102:83)Document17 pagesSlump Test of Fresh Concrete (ASTM C143/C143M-05a) & (BS 1881: PART 102:83)Zahim Harki100% (1)
- Determination of Initial Setting Time of Cement With Vicat's Apparatus (ASTM C191 - 04b) .Document15 pagesDetermination of Initial Setting Time of Cement With Vicat's Apparatus (ASTM C191 - 04b) .Zahim Harki100% (1)
- Density, (Relative Density) Specific Gravity & Absorption of Coarse Aggregate (ASTM C127 - 04)Document13 pagesDensity, (Relative Density) Specific Gravity & Absorption of Coarse Aggregate (ASTM C127 - 04)Zahim HarkiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Athropometric DataDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Athropometric DataJan Wesley MoridoNo ratings yet
- L-Shaped FootingDocument10 pagesL-Shaped FootingDAWITNo ratings yet
- Tos 1Document5 pagesTos 1Allyanna Elise Diam100% (1)
- Physics - Test 1 - WatermarkDocument45 pagesPhysics - Test 1 - WatermarkJeevikaNo ratings yet
- Waves SL and HL MCQ StructuredDocument58 pagesWaves SL and HL MCQ StructuredRAVI NISHADNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Integrated Science Topic: Electricity and Lighting: Electric CurrentDocument8 pagesGrade 11 Integrated Science Topic: Electricity and Lighting: Electric CurrentShannell ShawNo ratings yet
- Tputty 506 Series: Gap Filler MaterialDocument1 pageTputty 506 Series: Gap Filler MaterialSergio FernandesNo ratings yet
- X60822 (Me2026 10122mee17 Me606 Ptme2026)Document2 pagesX60822 (Me2026 10122mee17 Me606 Ptme2026)saranNo ratings yet
- 1 Descriptive Analysis CompleteDocument11 pages1 Descriptive Analysis CompleteM WaleedNo ratings yet
- Exp 4ADocument6 pagesExp 4AHemanth HemuNo ratings yet
- 2 Pin Overmoulded Fly EndDocument8 pages2 Pin Overmoulded Fly EndBURIN SITTIMONGKONNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Laurent PolynomialsDocument20 pagesOrthogonal Laurent PolynomialsLeonardo BossiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Earthquake-Induced Cracking of Embankment DamsDocument21 pagesEvaluation of Earthquake-Induced Cracking of Embankment DamsszarnaniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Behavior of Hydrogen NaturDocument6 pagesThermodynamic Behavior of Hydrogen NaturisvpNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Related Parameters of Vortex Bladeless Wind Tur-Bine by Using Deep Learning MethodDocument18 pagesPredicting The Related Parameters of Vortex Bladeless Wind Tur-Bine by Using Deep Learning MethodJosafatNo ratings yet
- CEE 3710 - Strength Versus StiffnessDocument3 pagesCEE 3710 - Strength Versus StiffnessSandeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Effect of The Ho Chi Minh City Tunnel Settlement On The Adjacent BuildingsDocument9 pagesAnalysis of The Effect of The Ho Chi Minh City Tunnel Settlement On The Adjacent Buildingsnguyen tuanNo ratings yet
- TPS65131-Q1 Positive-And Negative-Output DC-DC Converter: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument35 pagesTPS65131-Q1 Positive-And Negative-Output DC-DC Converter: 1 Features 3 DescriptionsachinNo ratings yet
- Math 9-4-5Document5 pagesMath 9-4-5Kim ReiNo ratings yet
- Std. 12 SCIENCE MATHS (050) (GSHSEB) : Year 2020 - 21 Deleted Portion & Non Deleted PortionDocument3 pagesStd. 12 SCIENCE MATHS (050) (GSHSEB) : Year 2020 - 21 Deleted Portion & Non Deleted PortionTwisha ParmarNo ratings yet
- 3-Tectonica de PlacasDocument41 pages3-Tectonica de PlacasJoao AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Simple Bending TheoryDocument8 pagesSimple Bending Theorybryan9422100% (2)
- CubicandquarticequationsDocument6 pagesCubicandquarticequationssyed junaid ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- 11G6 Topic - Thermal Properties and TemperatureDocument6 pages11G6 Topic - Thermal Properties and TemperatureAminaNo ratings yet
- B. Eng (Hons) Chemical Engineering: Course OutlineDocument9 pagesB. Eng (Hons) Chemical Engineering: Course OutlinemarkNo ratings yet
- 8rxCAT-en Catalog PDFDocument388 pages8rxCAT-en Catalog PDFanne smithNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoDocument15 pagesRay Optics - JEE Main 2023 January Chapter Wise Questions by MathonGoS DASNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Enhanced Heat Transfer: Sujoy Kumar Saha Hrishiraj Ranjan Madhu Sruthi Emani Anand Kumar BhartiDocument111 pagesIntroduction To Enhanced Heat Transfer: Sujoy Kumar Saha Hrishiraj Ranjan Madhu Sruthi Emani Anand Kumar Bhartiebrar totoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MOTION IN A PLANEDocument25 pagesChapter 6 MOTION IN A PLANEJust CharacterNo ratings yet
- hw3 6120Document1 pagehw3 6120YeasminNo ratings yet