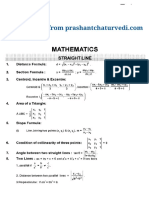
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normalization Document
Uploaded by
manpreetCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normalization Document
Uploaded by
manpreetCopyright:
Available Formats
Score Normalization
About Normalization
Normalization means adjusting values measured on different scales to a notionally common scale
Need for Normalization in Exam
Exam pertaining for a particular post/course could be spread across multiple shifts which will have
different question paper for each shift. The normalization is to be done by considering the
difficulty level of each set, since the questions may be different in different sets and difficulty level
of a particular set may be different from other sets.
Hence the normalization of scores need to be carried out for all the candidates who had written
the exam, across shifts for the same post/course.
Normalization Method
The following has to be calculated for every shift for all the candidates who have written the exam
for the same post:
a. Average score for each Shift
Xav = total marks scored by candidates in a shift divided by no. of candidates in the shift.
b. Standard Deviation of score for each Shift. Standard Deviation is a measure that is used to
quantify the amount of variation of a set of data values:
N = Number of candidates
X = Raw score of candidates
L = Total Raw score for all candidates in a shift
Xav = Average which is total marks divided by no. of candidates.
x = Raw Score of Candidate - Simple Average (X-Xav)
Standard Deviation (S) = (∑ x²)/N
Normalization Formula
Normalized Score for each candidate (Xn) = Xn = (S2 / S1) * (X - Xav) + Yav
Is the SD of the shift with the Highest Average Score taken as Base for normalization
(Criteria for choosing the base for normalization is generally taken as the shift with
S2 ‘Highest Average’ of raw scores)
S1 Standard Deviation for the corresponding shift (to be scaled to S2)
X Raw score of a candidate
Xav Simple average of the Shift
Average corresponding to shift with highest Average (taken as Base for
Yav normalization)
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- % To Fraction TableDocument6 pages% To Fraction TablemanpreetNo ratings yet
- AAI ATC Mathematics FormulasDocument30 pagesAAI ATC Mathematics FormulasmanpreetNo ratings yet
- InformationDocument2 pagesInformationmanpreetNo ratings yet
- DMRC Recruitment 2022Document6 pagesDMRC Recruitment 2022manpreetNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper BrochureDocument3 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper BrochuremanpreetNo ratings yet
- 3rd ShiftDocument45 pages3rd ShiftmanpreetNo ratings yet
- Result JE (ATC) 7 20150511Document2 pagesResult JE (ATC) 7 20150511manpreetNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)