Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toxicology 2
Uploaded by
BRYAN BALDOMEROOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Toxicology 2
Uploaded by
BRYAN BALDOMEROCopyright:
Available Formats
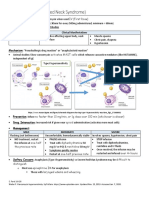
1. List down and explain the different diagnostic tests used in determining poisons in the human body.
According to the video “Poisoning and Toxidromes: Definitions, Types & Diagnosis – Emergency
Medicine” presented by Lecturio Medical, the application of differential diagnosis (drug-to-drug
approach) is impossible on poisoning circumstances in real life settings. Since the pharmacology,
pharmacokinetics, and clinical manifestations of drugs can be overlapping and obviously it is time
consuming. Hence, the term “toxidromes” (specific group of autonomic-related signs and symptoms
that were caused by certain groups of medications or chemicals) are created to successfully narrow
down toxicologic differential. Five traditional or most commonly encountered toxidromes (relying on
observable findings in the eyes, skin, secretions, and vital signs) were mentioned in the video:
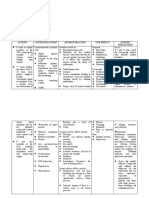
TYPES SYMPTOMS MANAGEMENT and ANTIDOTE
Sympathomimetic/Adrenergic - excess Tachycardia, Mydriasis, Hypertension, Gastric decontamination
stimulation on alpha-adrenergic, beta- Diaphoresis, Hyperthermia ANTIDOTE: BZD
adrenergic, dopamine, and serotonin
receptors
-CAUSE: Stimulants
Anti-cholinergic - under Unopposed sympathetic tone: IV fluids
stimulation/inhibition of cholinergic Tachycardia, Mydriasis , Hypertension, For HIGH TOXICITY
neurotransmission in the muscarinic Hyperthermia (very common) INGESTION: GI
receptor sites Loss of cholinergic innervation on the decontamination
mucosa and skin (ANHYDROSIS and ANTIDOTE: Physostigmine
-COMMON CAUSE/S: Overdosing of OTC DEHYDRATED)
anti-cholinergic medications (anti- Mnemonics: mad as a hatter, blind as a
histamines, TCAs, antiemetics, etc.) bat, red as a beet, hot as a hare, and dry
as a bone
Cholinergic - over-stimulation at a Diarrhea/Diaphoresis, Urination, Miosis, Decontaminate, intubate
neuromuscular junction due to an Bronchorrhea, Bradycardia, Emesis, early, and high oxygen flow
excess of acetylcholine (ACh) Lacrimation, Salivation ANTIDOTE: Atropine
-Can be CAUSED by
ORGANOPHOSPHATES (pesticides)
Sedative-Hypnotic Somnolence IV access, provide oxygen,
Apnea and perform aggressive
POTENTIAL respiratory depression supportive care
ANTIDOTE: Flumenazil
Opioid – drug overdosing for MIOSIS (pin-point) Support respiration, and
recreational/suicides FATAL respiratory depression oxygenation
CNS depression ANTIDOTE: Naloxone
Apnea
You might also like
- Powerpoint PresentationDocument34 pagesPowerpoint Presentation88AKK100% (2)
- Pharmacotherapy of CoughDocument51 pagesPharmacotherapy of CoughIqra Butt100% (3)
- Steel Grade AnaloguesDocument8 pagesSteel Grade AnaloguesandreahankNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Competency Notes CompleteDocument37 pagesToxicology Competency Notes CompleteNouf Cathrese BarrozoNo ratings yet
- General Management of PoisoningDocument22 pagesGeneral Management of Poisoningranjithajay100% (1)
- Kodex LDocument48 pagesKodex Lamitdwivedi11No ratings yet
- Organophosphorus Insecticides and Nerve Gas Agents PoisoningDocument42 pagesOrganophosphorus Insecticides and Nerve Gas Agents PoisoningBhavanadhar PentaNo ratings yet
- IA Hotline0115 3DEBF4D037254Document2 pagesIA Hotline0115 3DEBF4D037254ahmedsobhNo ratings yet
- Printed Material ModuleeeeDocument56 pagesPrinted Material ModuleeeeShang MacarayonNo ratings yet
- Neral Approach For Med. Stud.Document30 pagesNeral Approach For Med. Stud.sara.sms1No ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugDocument10 pagesPsychiatric DrugKollebeng Pangda PasiwatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Medicinal PPDocument19 pagesChemistry of Medicinal PPLê Thị Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument56 pagesRespiratory DrugsIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- 1 Anticholinergic DrugsDocument24 pages1 Anticholinergic DrugskiranNo ratings yet
- Capitol Intoxicatii 3Document17 pagesCapitol Intoxicatii 3AncaNo ratings yet
- Sign, Sypmtoms and Tretment of PosioningDocument18 pagesSign, Sypmtoms and Tretment of PosioningmaryamNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Opioids - The Lecturio Online Medical LibraryDocument10 pagesPharmacology - Opioids - The Lecturio Online Medical Libraryjean PiedraNo ratings yet
- Anti Allergic DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Allergic Drugsaamer niaziNo ratings yet
- Anti-Psychotic Drugs: Submitted ToDocument28 pagesAnti-Psychotic Drugs: Submitted Torho 998No ratings yet
- Antidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, OpioidsDocument3 pagesAntidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, Opioidskaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument73 pagesDrugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemMarin ChianuNo ratings yet
- General Principles Involved in The Management of PoisoningDocument19 pagesGeneral Principles Involved in The Management of Poisoningvinneth vineethNo ratings yet
- Total Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEDocument1,601 pagesTotal Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEClaire Cura100% (1)
- General Anesthetic 2016Document33 pagesGeneral Anesthetic 2016Harsha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Urti Lrti Drugs 2023Document8 pagesUrti Lrti Drugs 2023dlabdon0310No ratings yet
- Compilation of Ms NotesDocument49 pagesCompilation of Ms Noteschoyaks100% (1)
- General Principles of PosioningDocument19 pagesGeneral Principles of PosioningAndyana SabtisanNo ratings yet
- Pearls Merged 4Document18 pagesPearls Merged 4api-493355126No ratings yet
- Drugs On RespiratoryDocument17 pagesDrugs On RespiratoryIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Agents: By: Paula Rose Mae Cuario Evita Lalaine Del Mundo Dennis Ragudo Sheena ZarsueloDocument80 pagesPsychiatric Agents: By: Paula Rose Mae Cuario Evita Lalaine Del Mundo Dennis Ragudo Sheena ZarsueloDennis RagudoNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument7 pagesAnesthesiajgcriste100% (9)
- Dangerous Drugs (Juris)Document12 pagesDangerous Drugs (Juris)Naomi YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Clin Tox Lab 1Document4 pagesClin Tox Lab 1Czariana Cassidy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- 3 ParasympatholyticsDocument35 pages3 ParasympatholyticsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Poisoning ANISH FINALDocument92 pagesManagement of Acute Poisoning ANISH FINALAnish JoshiNo ratings yet
- 5 Opioids 01 08 2023Document33 pages5 Opioids 01 08 2023ashwin kNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Delos SantosDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - Delos SantosJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Aim High With GOD!! PDFDocument110 pagesAim High With GOD!! PDFJulian Parada100% (4)
- Toxidromes: Patricia Evans, M.D. Georgetown University-Providence Hospital Family Practice ResidencyDocument50 pagesToxidromes: Patricia Evans, M.D. Georgetown University-Providence Hospital Family Practice ResidencyHernan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic Drugs or Parasympatholytic DrugsDocument4 pagesAnticholinergic Drugs or Parasympatholytic DrugsNishant KatiyarNo ratings yet
- General AnestheticsDocument18 pagesGeneral AnestheticsDivyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs of Abuse: OpioidDocument35 pagesDrugs of Abuse: Opioidmalak amerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer: Chapter 27: General and Local Anesthetic AgentsDocument10 pagesPharmacology Reviewer: Chapter 27: General and Local Anesthetic AgentsKyla CastroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Poisoning Drug OverdosageDocument53 pagesPoisoning Drug OverdosageMeg AmoonNo ratings yet
- Drugs of Abuse-Opioids, Sedatives, HypnoticsDocument16 pagesDrugs of Abuse-Opioids, Sedatives, HypnoticsMARIA TELLEZNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeDocument29 pagesPengantar Toksikologi Dan ToxindromeCalvin Tanuwijaya Stick BolaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Unknown Drug OverdoseDocument3 pagesApproach To Unknown Drug OverdoseRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacology Bpharm Pmy 3210 2020-2021Document70 pagesRespiratory Pharmacology Bpharm Pmy 3210 2020-2021Harriet ChilufyaNo ratings yet
- OpioidAnalgesics EricaRamirezDocument28 pagesOpioidAnalgesics EricaRamirezKM MINo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Suspected or Known PoisoningDocument56 pagesApproach To A Patient With Suspected or Known PoisoningMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- W9 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesW9 PharmacologyEh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Antiasthmatics and Drugs Used in Cough 2019Document34 pagesAntiasthmatics and Drugs Used in Cough 2019salva sambaaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Farmasi: AntihistaminDocument25 pagesKimia Farmasi: AntihistaminchristinaNo ratings yet
- Autacoids and Related DrugsDocument21 pagesAutacoids and Related DrugsNishant KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 1 AnalgesicsDocument10 pages1 Analgesicsalhesham141No ratings yet
- NAPZA IntoksikasiDocument46 pagesNAPZA IntoksikasiaprinalNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry QuestionnaireDocument17 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry QuestionnaireBRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key (PINK PACOP)Document20 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key (PINK PACOP)BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- PHARCHEM BlueDocument33 pagesPHARCHEM BlueJoslin Roz GalileaNo ratings yet
- G Organic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument15 pagesG Organic Pharmaceutical ChemistryZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Answer Key-PINK PACOPDocument29 pagesBiochemistry Answer Key-PINK PACOPMicah Lou Calamba100% (2)
- Biochemistry (GREEN)Document18 pagesBiochemistry (GREEN)BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Biochemistry (PACOP RED) ANSWER SHEETDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical Biochemistry (PACOP RED) ANSWER SHEETBRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Toxicology 4Document2 pagesToxicology 4BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Answer Key-BLUE PACOPDocument26 pagesBiochemistry Answer Key-BLUE PACOPChengD100% (1)
- Biochemistry (VIOLET)Document53 pagesBiochemistry (VIOLET)BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Toxicology 3Document2 pagesToxicology 3BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Toxicology 1Document2 pagesToxicology 1BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- PSMA - General Chemistry Part 1Document10 pagesPSMA - General Chemistry Part 1BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- Bench - Mark Ouiz: ASME B 31.3 Process PipingDocument4 pagesBench - Mark Ouiz: ASME B 31.3 Process PipingMichael AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- The Role of Titanite (CaTiSiO ) in PCD ExplorationDocument9 pagesThe Role of Titanite (CaTiSiO ) in PCD ExplorationMarco Augusto Robles AncajimaNo ratings yet
- TITLE: Osmosis AIM: To Observe Osmosis in A Storage Organ Equipment: Knife Materials: Salt Distilled Water PotatoDocument3 pagesTITLE: Osmosis AIM: To Observe Osmosis in A Storage Organ Equipment: Knife Materials: Salt Distilled Water PotatoericaNo ratings yet
- The Light BulbDocument4 pagesThe Light BulbJonas SarmientoNo ratings yet
- IGC2 Element 1 HazardsDocument70 pagesIGC2 Element 1 HazardsAlaaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Acceptability of Oral Paediatric Medicines: A ReviewDocument16 pagesEvidence of Acceptability of Oral Paediatric Medicines: A ReviewDenise Yanci DemiarNo ratings yet
- Dic Epoxy enDocument18 pagesDic Epoxy enSoonwook JangNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy Absorption TableDocument7 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy Absorption TableAmalinda Kharisma AdhaniNo ratings yet
- Square Planar Substitution and Trans Effect-2Document10 pagesSquare Planar Substitution and Trans Effect-2aliyyaNo ratings yet
- MitomapDocument1,079 pagesMitomaproymalindoNo ratings yet
- Draft SystemDocument5 pagesDraft Systemmkchy12No ratings yet
- Tech Tool Adapters and Cables V1 3 2Document72 pagesTech Tool Adapters and Cables V1 3 2Julito CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Strain-Rate Effects On The Mechanical Behavior of The AISI 300 Series of Austenitic Stainless Steel Under Cryogenic EnvironmentsDocument11 pagesStrain-Rate Effects On The Mechanical Behavior of The AISI 300 Series of Austenitic Stainless Steel Under Cryogenic EnvironmentsHugo IgrejaNo ratings yet
- Paper+Cutting+Knives+englDocument23 pagesPaper+Cutting+Knives+englbelan_80No ratings yet
- 5 PlasterDocument3 pages5 PlasterMuhammad AgungNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Condensers Selection GuideDocument16 pagesAir Cooled Condensers Selection GuideelmerbayhonNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable Polymers For Bone Tissue Engineering: M. Susana Cortizo and M. Soledad BelluzoDocument29 pagesBiodegradable Polymers For Bone Tissue Engineering: M. Susana Cortizo and M. Soledad BelluzoRajeshwari MalliNo ratings yet
- Tensar Basetex Technical Info (April 2003)Document4 pagesTensar Basetex Technical Info (April 2003)sandycastleNo ratings yet
- Anti Icing T4Document13 pagesAnti Icing T4Mansooooor12345No ratings yet
- SdarticleDocument25 pagesSdarticleCees van ApeldoornNo ratings yet
- Extracting Bromine From Sea WaterDocument4 pagesExtracting Bromine From Sea WaterRaja Ji100% (2)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Chemistry (4CH1) Paper 2CRDocument15 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2022: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Chemistry (4CH1) Paper 2CRMohamed MuhajireenNo ratings yet
- Modular Air Cooled Chillers PDFDocument22 pagesModular Air Cooled Chillers PDFBehnamNo ratings yet
- Causes of KicksDocument14 pagesCauses of KicksGhavban DavidNo ratings yet
- Lakshya JEE AIR Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageLakshya JEE AIR Organic ChemistryShardul DucheNo ratings yet
- Radon-222 Exhalation From Danish Building Material PDFDocument63 pagesRadon-222 Exhalation From Danish Building Material PDFdanpalaciosNo ratings yet
- Brief Company Profile: Manuli Rubber Industries (MRI)Document36 pagesBrief Company Profile: Manuli Rubber Industries (MRI)Le Anh DangNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - Group 3Document49 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - Group 3N Un-knowNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE OF MIX DESIGN .R.s.Document11 pagesEXAMPLE OF MIX DESIGN .R.s.Ramkiran TalariNo ratings yet