Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 3 Medical Surgical Nursing
Uploaded by
Elaine Marie SemillanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 3 Medical Surgical Nursing
Uploaded by
Elaine Marie SemillanoCopyright:
Available Formats
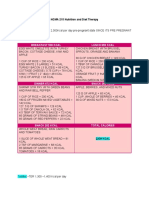
INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE
1. Encourage the client to take several deep It promotes oxygenation before controlled
breaths coughing
2. Encourage the client to take a deep breath, This moves air down to the bottom areas of the
hold for 2 seconds, and cough two or lungs. Band opens up the air passages and moves
three times in succession the mucous out; coughing is also easier
3. Encourage use of incentive spirometry, as This incentive spirometer is a hand-held breathing
appropriate exercise device to help the patient breathe deeply.
4. Promote systemic fluid hydration, as Adequate fluid intake enhances dissolving
appropriate of pulmonary secretions and facilitates
expectoration of mucus
5. Monitor rate, rhythm, depth, and effort of Provides a basis for evaluating adequacy of
respirations ventilation.
6. Note chest movement, watching for Presence of nasal erupting and utilization
symmetry, use of accessory muscles, and of embellishment muscles of breaths may happen
supraclavicular and intercostal muscle in light of incapable ventilation.
retractions
7. Auscultate lung sounds after treatments to It is important to distinguish normal respiratory
note results sounds from abnormal ones for example crackles,
wheezes, and pleural rub in order to make correct
diagnosis
8. Monitor client’s respiratory secretions Assists in evaluating prescribed treatments and
client outcomes
9. Monitor client’s ability to cough Respiratory tract infections alter the amount
effectively and character of secretions. An ineffective
cough compromises airway clearance and
prevents mucus from being expelled
10. Monitor for increased restlessness, These clinical manifestations would be early
anxiety, and air hunger indicators of hypoxia
You might also like
- COURSE TASK #4 RizalDocument7 pagesCOURSE TASK #4 RizalElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 23Document2 pagesCourse Task 23Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Semillano, Elaine Marie Rizal ReviewerDocument26 pagesSemillano, Elaine Marie Rizal ReviewerElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Population DynamicsDocument2 pagesPopulation DynamicsElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 2Document5 pagesCourse Task 2Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 2Document4 pagesCourse Task 2Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 4Document3 pagesCourse Task 4Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 25Document6 pagesCourse Task 25Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- RUBRIC Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningDocument4 pagesRUBRIC Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Course Task 10Document2 pagesCourse Task 10Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Hormones Which Produce A Particular Response in The Target Tissues. Overall, The System Regulates Major Physiological Processes in The Human BodyDocument3 pagesHormones Which Produce A Particular Response in The Target Tissues. Overall, The System Regulates Major Physiological Processes in The Human BodyElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Thymus Right Lymphatic Duct Axillary Lymph Node Thoraric Duct Tonsils Inguinal Lymph NodeDocument3 pagesThymus Right Lymphatic Duct Axillary Lymph Node Thoraric Duct Tonsils Inguinal Lymph NodeElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Indicate Whether The Sentence or Statement Is True or FalseDocument2 pagesIndicate Whether The Sentence or Statement Is True or FalseElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 15 Respiratory System I. Assessment Answer Each Item Guided by The Specific Instructions For Each Question Set. A. True/FalseDocument2 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 15 Respiratory System I. Assessment Answer Each Item Guided by The Specific Instructions For Each Question Set. A. True/FalseElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)