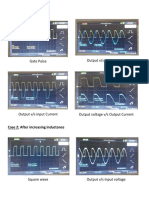
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 6
Uploaded by
Sakshi GargCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 6
Uploaded by
Sakshi GargCopyright:
Available Formats
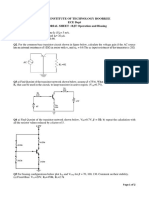
TUTORIAL 6.
1. A 450 volt, 50 Hz, ∆ connected, 4 poles, and 3-phase synchronous generator has a direct axis
reactance of 0.15Ω and quadrature axis reactance of 0.07Ω. Its armature resistance may be
neglected. At full load, the generator supplies 150A at a power factor of 0.8 lagging.
a) Find the internal generated voltage EA of this generator at full load, assuming that it has
cylindrical rotor reactance is Xd.
b) Find the generated internal voltage EA of this generator at full load assuming that it has a
salient pole rotor.
2. A single-phase enrol. no. last 4 digits volts (for example 20914098, then it is 4098 volts)
alternator has armature reactance of 2.84 Ω and resistance of 0.6 Ω. The voltage regulation of
alternator at 200A load at
a) 0.9 leading power factor
b) 0.9 lagging power factor
3. A three-phase synchronous generator produces an open circuit voltage of enrol. no. last 4
digits volts (for example 20914098, then it is 4098 volts) when the do exciting current is 40A.
The AC terminals are then short-circuited and the three-line currents are found to be 70A.
a) Calculate synchronous reactance per phase.
b) Calculate terminal voltage if three 8 Ω resistances are connected in wye across the
terminal.
4. From tests on a synchronous machine of 45-kVA, three-phase, Y-connected, 220-V (line-to-
line), six-pole, 60-Hz, we have the following data.
From the open-circuit characteristic:
Line-to-line voltage = 220 V Field current = 2.84 A
From the short-circuit characteristic:
Armature current (A) 118 152
Field current (A) 2.20 2.84
From the air-gap line:
Field current = 2.20 A line-to-line voltage = 202 V.
Compute the unsaturated value of the synchronous reactance, its saturated value at rated
voltage, and the short-circuit ratio. Express the synchronous reactance in ohms per phase and
in per unit on the machine rating as a base.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Final - QP-EEN-112-Nov-2021Document1 pageFinal - QP-EEN-112-Nov-2021Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Expt - 5 Lab ReportDocument7 pagesExpt - 5 Lab ReportSakshi GargNo ratings yet
- 303 Prac1Document2 pages303 Prac1Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4 BJT OPN and BiasingDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet 4 BJT OPN and BiasingSakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document9 pagesExperiment No 2Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document10 pagesExperiment No 2Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Phase Angles of Sinusoidal Transfer FunctionsDocument2 pagesPhase Angles of Sinusoidal Transfer FunctionsSakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3Document10 pagesExperiment No 3Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- IEQ-301 Assignment-3Document11 pagesIEQ-301 Assignment-3Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document1 pageTut 1Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Acidic Nature of Organic CompoundsDocument5 pagesAcidic Nature of Organic CompoundsSakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-06-30 13.25.38Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-06-30 13.25.38Sakshi GargNo ratings yet
- V Is The Instantaneous Speed. The Time Taken by The: AnswersDocument1 pageV Is The Instantaneous Speed. The Time Taken by The: AnswersSakshi GargNo ratings yet