Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orthdromic Vs Antidromic SVT, and Why It Matters
Uploaded by
Henry Leroy Lewis BatresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orthdromic Vs Antidromic SVT, and Why It Matters
Uploaded by
Henry Leroy Lewis BatresCopyright:
Available Formats
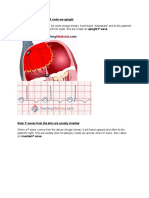
SVT: Orthodromic or Antidromic? And why does that matter?
This is a way of classifying AV reentrant tachycardia, the one with an accessory pathway.
Orthodromic conduction = through the AV node
Antidromic conduction = through the accessory pathway
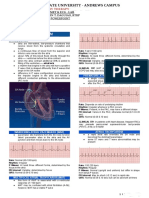
Widened bizarre QRS
RULES OF THUMB: complexes, caused by
Antidromic is usually narrow-complex. simultaneous
depolarization of the
Orthodromic is always broad-complex. ventricles from both
the AV node and the
but why?... accessory pathway An atrial ectopic near
the AV node starts the Negative P waves
SVT cycle follow the QRS
Orthodromic conduction: the “Right Way” complexes
The action potential travels through the AV node; the QRS
complex would not show any pre-excitation. After the
ventricles conduct the action potential, it comes back
around and enters the atria via the accessory pathway.
THEREFORE:
- the p-wave is always “retrograde” in this situation;
the atria depolarize RIGHT AFTER the ventricles. Delta wave QRS complexes are now narrow
Thus the P waves will be embedded in the ST and normal-looking, because the
segment accessory pathway plays no role in
- The QRS complex is usually normal-looking, or their initiation.
with BBB- this is because the conduction from the
AV node to the ventricles is completely normal.
- Even in WPW, the QRS will be NORMAL because
the accessory pathway is not pre-exciting the
ventricle- instead it is excited BY the ventricle.
Antidromic conduction: the “Opposite Way” Widened bizarre QRS
The action potential travels through the accessory pathway; complexes, because
in order for this to happen, this pathway must be well away the ventricle is wholly
from the AV node (at least 4cm away, so the action potential pre-excited
gets to the pathway first). The action potential first
depolarizes the ventricles and then conduct it back up the
AV node.
- The P waves are negative, if visible at all.
- The QRS is WIDENED because most of the
ventricular conduction occurs via the sluggish
ventricular fibers, not the His-Purkinje system.
- in WPW, the QRS will HAVE DELTA WAVES Delta wave
because practically ALL of the ventricle will be
excited by the accessory pathway.
WHATS THE POINT OF ALL THIS?
ORTHODROMIC: ANTIDROMIC:
The site of antegrade conduction is the AV node; hence it The site of antegrade conduction is the accessory pathway; its
is the crucial weak point. One can attack the tachycardia conduction speed relies on fast sodium channels. Therefore
there by lengthening the AV refractory period. Class 1 drugs are preferred, such as Flecainide. You can
- vagal manoeuvres also attack the AV node with adenosine, to slow retrograde
Adenosine and verapimil ONLY is its certain that its not AF conduction. In fact, that works surprisingly often.
Why not Adenosine? Adenosine on its own can cause AF, as well as blocking the AV node. If the poor fool
has AF and you block the gate-keeping AV node, the fast accessory pathway will be in charge of conducting the AF
impulses. Of which there are 300 or so per minute. And it will be 1:1 conduction. Beta blockers don’t shorten the pathways’
refractory period as much as the AV nodes’ refractory period. Likewise verapimil. So you may induce VF in a patient with an
accessory pathway, by using adenosine, verapimil or beta-blockers. Of course if that happens, you can always shock them.
You might also like
- ECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsDocument23 pagesECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsHitesh Deora100% (2)
- Quick Ekg ReferenceDocument23 pagesQuick Ekg Referencekowaikowar100% (1)
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocument50 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationmariaNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Workshop For ParamedicsDocument75 pagesBasic ECG Workshop For ParamedicsRobyn FormosoNo ratings yet
- Rhythm Description Schematic Diagram Egc Characteristics Sample TraceDocument6 pagesRhythm Description Schematic Diagram Egc Characteristics Sample TraceJhenne Kyle Ko Dee100% (1)
- ACLS Provider Manual 2015 NotesDocument5 pagesACLS Provider Manual 2015 Notescrystalshe93% (14)
- Arrythmia Review TableDocument6 pagesArrythmia Review TablealobrienNo ratings yet
- Learning Medicine - 1.0Document206 pagesLearning Medicine - 1.0Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Avnrt AvrtDocument21 pagesAvnrt AvrtRima Rovanne Wenas100% (1)
- Critical Care: ElectrophysiologyDocument180 pagesCritical Care: ElectrophysiologyArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsDocument11 pagesElectrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsJoezelle0% (1)
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Risks, Heart Failure, AMIDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Pathology: Risks, Heart Failure, AMIbmhsh100% (2)
- Ecg Made EasyDocument130 pagesEcg Made EasyJOHN ARBIE TATTAO, RN96% (49)
- Echotech Reporting Guidelines Version 15Document30 pagesEchotech Reporting Guidelines Version 15AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Bantuan Hidup Dasar: Update of 2020 GuidelinesDocument27 pagesBantuan Hidup Dasar: Update of 2020 GuidelinesRJP Nurse Gaming100% (1)
- NSG 6001 Week 1 DiscussionDocument4 pagesNSG 6001 Week 1 DiscussionrachaelNo ratings yet
- Heart Block PPT by SibaDocument36 pagesHeart Block PPT by Sibaritumitu_ritumitu100% (1)
- RV (Dys)function assessment by echocardiographyDocument52 pagesRV (Dys)function assessment by echocardiographyNag Mallesh RaoNo ratings yet
- 11 AvrtDocument32 pages11 AvrtthetlwinagNo ratings yet
- Pre-Excitation SyndromesDocument85 pagesPre-Excitation SyndromesAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- The Bradyarrhythmias: Disorders of The Atrioventricular NodeDocument34 pagesThe Bradyarrhythmias: Disorders of The Atrioventricular NodeRho Vince Caño MalagueñoNo ratings yet
- ECG Criteria to Distinguish SVT From VTDocument48 pagesECG Criteria to Distinguish SVT From VTlichumo murryNo ratings yet
- Rule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightDocument13 pagesRule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Understanding ECG's 2Document41 pagesUnderstanding ECG's 2Ben HarperNo ratings yet
- Beta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewDocument1 pageBeta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- EKG Arrhythmia Identification GuideDocument47 pagesEKG Arrhythmia Identification Guidemithaa octoviagnesNo ratings yet
- Ekg #8Document3 pagesEkg #8SAM dabombdigNo ratings yet
- Muzakkir-Takikardi PDFDocument32 pagesMuzakkir-Takikardi PDFThono HartonoNo ratings yet
- ECG Arrhythmia2006Document28 pagesECG Arrhythmia2006rickyfauzanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrythmia For PathophysiologyDocument47 pagesCardiac Arrythmia For PathophysiologywilzmaxNo ratings yet
- ECG Arrhythmia2006Document28 pagesECG Arrhythmia2006aris rifkhiNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousDocument79 pagesTachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousEstiningtiyas RahayuNo ratings yet
- ArrhytmiaDocument70 pagesArrhytmiaAfied FitrahNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDDocument8 pagesAtrial Fibrillation in The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: ECG Recognition and Treatment in The EDyohanadebritarerekoliNo ratings yet
- Types and Symptoms of Supraventricular TachycardiasDocument24 pagesTypes and Symptoms of Supraventricular TachycardiasEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- Wolff Parkinson White SyndromeDocument1 pageWolff Parkinson White SyndromeKuliner JailoloNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Guide: Tachycardias and Supraventricular RhythmsDocument83 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Guide: Tachycardias and Supraventricular Rhythmsmargareth hoyan SilabanNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities in ECG MeasurementsDocument1 pageAbnormalities in ECG MeasurementsLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Document2 pagesAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeNo ratings yet
- PG - Quick Look On Arrhythmia in ED - JCU 2021Document71 pagesPG - Quick Look On Arrhythmia in ED - JCU 2021Afied FitrahNo ratings yet
- SVT CaseDocument11 pagesSVT CaseZakiy AzzuhdiNo ratings yet
- ECG Junctional & Ventricular Arrhythmias GuideDocument21 pagesECG Junctional & Ventricular Arrhythmias GuideMorad KananNo ratings yet
- Understanding ECG's KingsholmDocument53 pagesUnderstanding ECG's KingsholmBen HarperNo ratings yet
- Arrythmias and EKGs 2Document20 pagesArrythmias and EKGs 2Nur Ima ErvianaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY OF CARDIAC SYSTOLE AND DIASTOLEDocument14 pagesPHYSIOLOGY OF CARDIAC SYSTOLE AND DIASTOLEDexter TurlaNo ratings yet
- Schilling Differential DiagnosisDocument80 pagesSchilling Differential Diagnosishaiderjbbr72No ratings yet
- Cheat ECGDocument3 pagesCheat ECGNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: WPW vs LGL SyndromesDocument1 pageArrhythmias: WPW vs LGL SyndromesKhaled OmerNo ratings yet
- WPW With Af Case ReportDocument4 pagesWPW With Af Case Report王怡君No ratings yet
- Curs 7 - Bradiaritmii TahiaritmiiDocument88 pagesCurs 7 - Bradiaritmii Tahiaritmiijhonny12321No ratings yet
- Electrocardiography of Atrioventricular BlockDocument7 pagesElectrocardiography of Atrioventricular Blockdarkangelmx1No ratings yet
- AV BlocksDocument53 pagesAV Blocksrebebravoiniguez642No ratings yet
- E Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabDocument8 pagesE Lectrocardiography ECG: Practical Physiology 2020-2021 LabBushra AlkaqaniNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers - Fact SheetDocument7 pagesPacemakers - Fact Sheettalha.k.rajpootNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachyarrythmiasDocument172 pagesSupraventricular TachyarrythmiasAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- Relationship of P Waves To QrssDocument1 pageRelationship of P Waves To QrssJessica PuentesNo ratings yet
- Width of The QRS Complex: - Wide VT, SVT With Aberrant Conduction - Narrrow SVTDocument11 pagesWidth of The QRS Complex: - Wide VT, SVT With Aberrant Conduction - Narrrow SVTWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath NairDocument17 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath Nairwindar baquero100% (1)
- SVT Notes: Paris Lovett, MD July 2004Document9 pagesSVT Notes: Paris Lovett, MD July 2004Joseph MensaNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument41 pagesECG InterpretationgjdbfiuvaNo ratings yet
- The Wolf-Parkinson-White ECG Pattern - Assessing The Mortality RiskDocument10 pagesThe Wolf-Parkinson-White ECG Pattern - Assessing The Mortality RiskPutri WijayaNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 - Station 6Document17 pagesLAB 1 - Station 6william atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT)Document24 pagesAtrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT)Radya Agna100% (1)
- Decoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonFrom EverandDecoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonAfzal SohaibNo ratings yet
- Xiao Et Al 2019 Diet and Breasca 8.408Document22 pagesXiao Et Al 2019 Diet and Breasca 8.408Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- An Overview of the Eight Stages of Consciousness DevelopmentDocument6 pagesAn Overview of the Eight Stages of Consciousness DevelopmentHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- HtannsaidsDocument11 pagesHtannsaidsHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Turk Adawi Et Al 2017 Cardiovascular in Easternmed 49.421Document14 pagesTurk Adawi Et Al 2017 Cardiovascular in Easternmed 49.421Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Patient Education HIV AIDS The Basics 1-30-18Document3 pagesPatient Education HIV AIDS The Basics 1-30-18Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Tahrani 2016Document27 pagesTahrani 2016Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Covis 2021Document25 pagesCovis 2021Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer PatohDocument27 pagesAlzheimer PatohHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Cannabinoids' Acute and Chronic Effects on CognitionDocument27 pagesCannabinoids' Acute and Chronic Effects on CognitionHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Summary Bachelor Thesis HLDocument4 pagesSummary Bachelor Thesis HLHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Asp MetaforasDocument11 pagesAsp MetaforasHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Silberman 1968Document12 pagesSilberman 1968Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Immune Mediated My Opa ThiesDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Immune Mediated My Opa ThiesHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Martin 2012Document8 pagesMartin 2012Henry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Functioning of Long-Term Heavy Cannabis Users Seeking TreatmentDocument10 pagesCognitive Functioning of Long-Term Heavy Cannabis Users Seeking TreatmentHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) RehabilitationDocument3 pagesLateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) RehabilitationHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Physostigmine - ClinicalKeyDocument11 pagesPhysostigmine - ClinicalKeyHenry Leroy Lewis BatresNo ratings yet
- Revascularization in Stable Coronary Artery Disease Review BMJDocument17 pagesRevascularization in Stable Coronary Artery Disease Review BMJucicardiocovid ocgnNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cardiomyopathy: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Cardiomyopathy: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentZukmianty SuaibNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorders Nursing Practice QuizDocument5 pagesRenal Disorders Nursing Practice QuizblaireNo ratings yet
- Uptodte TSVDocument215 pagesUptodte TSVcrilala23No ratings yet
- Presentation 1 - DR Martin RoyleDocument66 pagesPresentation 1 - DR Martin Royleশরীফ উল কবীরNo ratings yet
- Cardio HPNDocument12 pagesCardio HPNHajime NakaegawaNo ratings yet
- AVRT Treatment and AblationDocument32 pagesAVRT Treatment and AblationFitria ArifinNo ratings yet
- Cystatin C StandardizationDocument9 pagesCystatin C StandardizationJoonseok ParkNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case 1Document31 pagesClinical Case 1reginaNo ratings yet
- Important Causes of Sudden Cardiac DeathDocument2 pagesImportant Causes of Sudden Cardiac DeathTausif AbbasNo ratings yet
- JNC guidelines for hypertension classificationDocument1 pageJNC guidelines for hypertension classificationWindyanissa RecitaNo ratings yet
- LDL Particle Number As Assessed by NMR SpectrosDocument17 pagesLDL Particle Number As Assessed by NMR SpectrosCTAFDocuments100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: AmiodaroneDocument32 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Amiodaroneabd hamzaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Disease and Risk of Cardiovascular Morbidity-MortalityDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Disease and Risk of Cardiovascular Morbidity-MortalityPaola QuindeNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument14 pagesAtrial FibrillationNur Atiqah ZainalNo ratings yet
- Title 42 Letter To Dr. Walensky From MGB & HMS ColleaguesDocument14 pagesTitle 42 Letter To Dr. Walensky From MGB & HMS Colleaguesdialynn dwyerNo ratings yet
- Minoca AhjDocument3 pagesMinoca AhjSundaresan SankarNo ratings yet
- CKD STAGE V CASE REPORTDocument6 pagesCKD STAGE V CASE REPORTesti wandiraNo ratings yet
- Acs Guideline PDFDocument56 pagesAcs Guideline PDFPrimasari HijriyahNo ratings yet
- Holid Fauzi, Suningsih, Setyo Adi NugrohoDocument6 pagesHolid Fauzi, Suningsih, Setyo Adi NugrohoKholifatun NaziroNo ratings yet
- Iabp 3Document10 pagesIabp 3Diana Marcela Franco SanchezNo ratings yet