Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pert Chart
Uploaded by
James Novenson OmitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pert Chart
Uploaded by
James Novenson OmitCopyright:
Available Formats
Program Evaluation Review Technique
(PERT) Chart
What Is a Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT)
Chart?
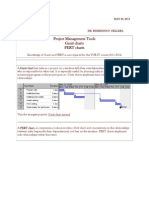
A PERT chart is a project management tool that provides a graphical
representation of a project's timeline. The Program Evaluation Review
Technique (PERT) breaks down the individual tasks of a project for
analysis. PERT charts are considered preferable to Gantt charts in some
cases because they identify task dependencies, but they're often more
difficult to interpret.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
PERT charts were first created by the U.S. Navy's Special Projects
Office in 1950s to guide the Polaris nuclear submarine project.
1
A PERT chart uses circles or rectangles called nodes to represent
project events or milestones. These nodes are linked by vectors, or
lines, that represent various tasks.
1
A PERT chart allows managers to evaluate the time and resources
necessary to manage a project.
How a PERT Chart Works
A PERT chart helps a project manager analyze a project's tasks and estimate
the amount of time required to complete each task in the project. Using this
information, the project manager can estimate the minimum amount of time
required to complete the entire project. This information also helps the
manager develop a project budget and determine the resources needed to
accomplish the project.
A PERT chart uses circles or rectangles called nodes to represent project
events or milestones. These nodes are linked by vectors or lines that
represent various tasks. Dependent tasks are items that must be performed
in a specific manner. For example, if an arrow is drawn from Task No. 1 to
Task No. 2 on a PERT chart, Task No. 1 must be completed before work on
Task No. 2 begins.1
Items at the same stage of production but on different task lines within a
project are referred to as parallel tasks. They're independent of each other,
but they're planned to occur at the same time. 1
Interpreting PERT Charts
A PERT chart is a visual representation of a series of events that must occur
within the scope of a project’s lifetime. The direction of arrows indicates the
flow and sequence of events required for project completion. Dotted activity
lines represent dummy activities—items that are located on another PERT
path. Numbers and time allotments are assigned and shown inside each
vector.
These charts have their distinct definitions and terms, the most important of
which anticipate how long it will take to finalize a project. "Optimistic time"
refers to the shortest duration. "Pessimistic time" is logically the longest it
might take. The "most likely time" indicates a reasonable estimate of the best-
case scenario, whereas "expected time" accounts for problems and
obstacles.1
Advantages and Disadvantages of PERT Charts
A PERT chart is similar to a critical path analysis (CPA), which is another
method that project managers use to chart tasks in a project. The main
difference between the two is that a PERT chart uses various time frames
and probability terms when estimating each project stage. As a project
management tool, PERT charts offer some distinct advantages and
disadvantages.
Advantages
A PERT chart allows managers to evaluate the time and resources necessary
to manage a project. This evaluation includes the ability to track required
assets during any stage of production in the course of the entire project.2
PERT analysis incorporates data and information from multiple departments.
This combining of information encourages department responsibility and it
identifies all responsible parties across the organization. It also improves
communication during the project and it allows an organization to commit to
projects that are relevant to its strategic positioning.
2
Finally, PERT charts are useful for what-if analyses. Understanding
the possibilities concerning the flow of project resources and milestones
allows management to achieve the most efficient and useful project path. 2
Disadvantages
The use of a PERT chart is highly subjective and its success depends on the
management’s experience. These charts can include unreliable data or
unreasonable estimations for cost or time for this reason. 2
PERT charts are deadline-focused and they might not fully communicate
the financial positioning of a project. Because a PERT chart is labor-
intensive, the establishment and maintenance of the information
require additional time and resources. Continual review of the information
provided, as well as the prospective positioning of the project, is required for
a PERT chart to be valuable. 2
Real World Example of PERT Charts
PERT charts were first created by the U.S. Navy's Special Projects Office in
1950s to guide the Polaris Fleet Ballistic Missile project. Using the PERT
model, Navy project managers were able to evaluate the progress of their
project, determine the validity of schedules, and estimate the effects of
proposed changes to established plans. The success of this initial use of
1
PERT charts has caused them to be used ever since all over the world and in
numerous industries.
You might also like
- Project Estimating and Cost ManagementFrom EverandProject Estimating and Cost ManagementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Construction Studies Portfolio LayoutDocument3 pagesConstruction Studies Portfolio Layoutnathan fennelly100% (1)
- Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) : Project Planning & Construction Management CE-3201Document12 pagesProgram Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) : Project Planning & Construction Management CE-3201G.M. Nahid RaihanNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review TechniquesDocument2 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review TechniquesMay Rachel L. NarragaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Programme Evaluation and Review Technique, Gantt Chart and Management by ObjectiveDocument14 pagesSeminar On Programme Evaluation and Review Technique, Gantt Chart and Management by Objectiveanamika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3 - Pert and CPM and Bar ChartDocument6 pagesAssignment - 3 - Pert and CPM and Bar ChartGauri WaikarNo ratings yet
- PertDocument6 pagesPertJeffrey SantanderNo ratings yet
- PERT, Gannt, MBODocument9 pagesPERT, Gannt, MBORiya JoyNo ratings yet
- Expose of Pert ChartDocument3 pagesExpose of Pert ChartArsene Junior Fotso WaboNo ratings yet
- Project SchedulingDocument7 pagesProject SchedulingkookyymwaNo ratings yet
- Optimizing The ProjectDocument10 pagesOptimizing The ProjectRiddhi PirogiwalNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation Review Technique (Pert)Document9 pagesProgram Evaluation Review Technique (Pert)April Joy FabialaNo ratings yet
- Assignment OR Vishal ShakyaDocument13 pagesAssignment OR Vishal Shakyashyamsingh4930No ratings yet
- The PERT ChartDocument2 pagesThe PERT ChartSaikiran SunnyNo ratings yet
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (Pert) of Project Scheduling Project Evaluation and Review Technique (Pert) of Project SchedulingDocument8 pagesProject Evaluation and Review Technique (Pert) of Project Scheduling Project Evaluation and Review Technique (Pert) of Project SchedulingChristine IreshaNo ratings yet
- Time Series AnalysisDocument6 pagesTime Series AnalysisminalNo ratings yet
- Ed-Unit-Iii-Pert & CPMDocument55 pagesEd-Unit-Iii-Pert & CPMTinandaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Construction Manamgment (17 - 19)Document2 pagesAssignment 3 Construction Manamgment (17 - 19)Simarleen BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Assesment 1Document5 pagesAssesment 1Kaneez BatoolNo ratings yet
- Advantages Dis Advantages Pert PDMDocument2 pagesAdvantages Dis Advantages Pert PDMWella Wella WellaNo ratings yet
- Pert Time/ Cost: An Aid To Agribusiness ManagementDocument62 pagesPert Time/ Cost: An Aid To Agribusiness ManagementPangga TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Mr. Yogesh A. DengaleDocument33 pagesPresented By-Mr. Yogesh A. Dengalesandeepv08No ratings yet
- Network Techniques For Project Management: StructureDocument15 pagesNetwork Techniques For Project Management: StructureManita DhandaNo ratings yet
- PERT ChartDocument2 pagesPERT ChartninupgNo ratings yet
- Operations Research AssignmentDocument17 pagesOperations Research AssignmentMARYAM ALHAMDINo ratings yet
- PERT Chart: Statistics-III Pert and CPMDocument7 pagesPERT Chart: Statistics-III Pert and CPMMd Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools Gantt Charts PERT ChartsDocument4 pagesProject Management Tools Gantt Charts PERT ChartsImage MakerNo ratings yet
- Application of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project ManagementDocument14 pagesApplication of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project Managementgcc_5083708No ratings yet
- PERT ChartDocument3 pagesPERT ChartGarima WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Path Method (CPM) Was Developed For Project Management in The Private Sector at About The SameDocument3 pagesPath Method (CPM) Was Developed For Project Management in The Private Sector at About The SameShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Project Management Group AssignmentDocument12 pagesProject Management Group AssignmentSteparies Martin100% (16)
- Terms ExplanationDocument8 pagesTerms ExplanationMy BusinessNo ratings yet
- Pert ExplanationDocument7 pagesPert ExplanationMuhammad Ayan MalikNo ratings yet
- Mahika Bansal A03Document2 pagesMahika Bansal A03Simarleen BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Gantt Charts: Origins of The ToolDocument9 pagesGantt Charts: Origins of The Toolzakaria dermishNo ratings yet
- Pert PPT PresentationDocument13 pagesPert PPT PresentationDhanjay Das100% (2)
- Project ManagementTechniquesDocument16 pagesProject ManagementTechniquesAbel EphraimNo ratings yet
- What Is Scheduling?Document11 pagesWhat Is Scheduling?Tahamid Hossain100% (1)
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)Document73 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)Nagulan NagulNo ratings yet
- PERTDocument34 pagesPERTAnusha Verghese71% (7)
- Interpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingDocument13 pagesInterpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingAyush SalveNo ratings yet
- Pert and CPMDocument18 pagesPert and CPMgowrimalleshNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique: Fall 2012Document14 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Technique: Fall 2012Naeem Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- MM MMM M M MM MMM MMMMMMMMM MMM!"M #M MM M M MMMMMMM M#M MM M M MMM #MM #MMMMM #M MM M M M M$M % M$ M$M M M$ M M MM MMMM MM MM&M MMDocument1 pageMM MMM M M MM MMM MMMMMMMMM MMM!"M #M MM M M MMMMMMM M#M MM M M MMM #MM #MMMMM #M MM M M M M$M % M$ M$M M M$ M M MM MMMM MM MM&M MMSatish KedarNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Gantt Charts: Mavenlink Wrike Smartsheet AceprojectDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Gantt Charts: Mavenlink Wrike Smartsheet AceprojectNovha CarbungcoNo ratings yet
- Advabtages and Disadvantages of PertDocument4 pagesAdvabtages and Disadvantages of PertAmber YounasNo ratings yet
- Name: Nana Mohammed Msellem REG NO: HDB212-C005-0444/2015Document7 pagesName: Nana Mohammed Msellem REG NO: HDB212-C005-0444/2015saeed BarzaghlyNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument32 pagesProject Management Tools and TechniquesReena Sanehi100% (2)
- Reaction Paper On Module 4Document2 pagesReaction Paper On Module 4tine.torio05No ratings yet
- Course: Project Management Course Code: Bmt1023Document5 pagesCourse: Project Management Course Code: Bmt1023PràßhánTh Aɭoŋɘ ɭovɘʀNo ratings yet
- Scheduling The WorkDocument18 pagesScheduling The WorkMaclins ColloNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique OM Session 10Document20 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Technique OM Session 10Revalina Dwi OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Bba - 6sem - Project Appraisal - Lecture 41,42&43Document7 pagesBba - 6sem - Project Appraisal - Lecture 41,42&43Jordan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Pert & Gantt ChartDocument10 pagesPert & Gantt ChartshivaNo ratings yet
- PERT Charts Vs Gantt ChartsDocument4 pagesPERT Charts Vs Gantt ChartsMUHAMMAD NOFIL BHATTYNo ratings yet
- Presentation On PertDocument61 pagesPresentation On PertVikrant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Gantt Charts and PERT Charts: Different But Not So DifferentDocument7 pagesGantt Charts and PERT Charts: Different But Not So DifferentAnkit GrewalNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Scheduling and Res AllocDocument15 pagesUNIT III Scheduling and Res AllocSindhiya RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument32 pagesProject Management Tools and Techniquesyadavmihir63100% (1)
- PertDocument8 pagesPertDahlia E. MakataNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting and Organisational Change: An Exploratory Study in Malaysian Manufacturing FirmsDocument22 pagesManagement Accounting and Organisational Change: An Exploratory Study in Malaysian Manufacturing FirmsPutu Meira Jayanti PutriNo ratings yet
- Cluster Evaluation: In: Evaluation For The 21st Century: A HandbookDocument9 pagesCluster Evaluation: In: Evaluation For The 21st Century: A HandbookanisNo ratings yet
- UAVs Over AustraliaDocument16 pagesUAVs Over AustraliaUAVs Australia100% (1)
- JER Azlia Maharani 324-334Document11 pagesJER Azlia Maharani 324-334Bùi Thị Phương UyênNo ratings yet
- Process Safety CholaDocument12 pagesProcess Safety CholaKrishnan RajappanNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency QDocument9 pagesCumulative Frequency QDinesCidNo ratings yet
- Micro Tunneling On SiteDocument3 pagesMicro Tunneling On SitemhetrajkarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Role of Literature Review in ResearchDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Role of Literature Review in Researchafdtalblw100% (1)
- Opt OutDocument30 pagesOpt Outapi-463548515No ratings yet
- REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE-evaluationDocument16 pagesREVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE-evaluationMaylyn Fecog SARA-ANNo ratings yet
- A Risk Assessment of Two Automobile Repair CentresDocument12 pagesA Risk Assessment of Two Automobile Repair CentressajinNo ratings yet
- Final Report For Travel Time Data CollectionDocument5 pagesFinal Report For Travel Time Data CollectionN TNo ratings yet
- Students' Attitudes Towards Research of College of Teacher Education: Input To Action PlanDocument8 pagesStudents' Attitudes Towards Research of College of Teacher Education: Input To Action PlanJ3h FerreraNo ratings yet
- Readings in Philippine History by John Lee Candelaria 2018 1docx CompressDocument152 pagesReadings in Philippine History by John Lee Candelaria 2018 1docx CompressBlock escape100% (2)
- IGNOU MBA MS-58 Solved AssignmentDocument22 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-58 Solved AssignmenttobinsNo ratings yet
- Data Driven Product Manager HandbookDocument30 pagesData Driven Product Manager Handbookyuvalei100% (1)
- Descriptive Method Is Used To Observe-Pr1Document9 pagesDescriptive Method Is Used To Observe-Pr1Donna VallesteroNo ratings yet
- Analyzing ArgumentsDocument9 pagesAnalyzing ArgumentsJason ToddNo ratings yet
- Rula SheetDocument2 pagesRula Sheetjmmos207064No ratings yet
- Radio Propagation Channel Model Tuning - MentumDocument22 pagesRadio Propagation Channel Model Tuning - MentumTinh Dong50% (2)
- @2018 Extreme Gradient BoostingDocument12 pages@2018 Extreme Gradient BoostinghnavastNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influenced Fashion Trends Among Students in Uitm PerakDocument18 pagesFactors That Influenced Fashion Trends Among Students in Uitm PerakFaiz Fitri NoorizanNo ratings yet
- Investigating Water Meter Performance in Developing Countries: A Case Study of Kampala, UgandaDocument8 pagesInvestigating Water Meter Performance in Developing Countries: A Case Study of Kampala, Ugandashucayb cabdiNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Revision Pack (198 Marks)Document27 pagesPaper 2 Revision Pack (198 Marks)Cora OliveraNo ratings yet
- NSTP CWTS - Lesson 2Document21 pagesNSTP CWTS - Lesson 2Ramon Carlit CartagenaNo ratings yet
- BRM-Research DesignDocument20 pagesBRM-Research DesignVipul SinghNo ratings yet
- Truss and Cable ElementsDocument9 pagesTruss and Cable ElementsArnel KirkNo ratings yet
- Reading List: Introduction To Academic WorkDocument8 pagesReading List: Introduction To Academic Workuju01No ratings yet
- Sports Betting and Nigerian Youths: A Study of Sports Betting in Edo StateDocument13 pagesSports Betting and Nigerian Youths: A Study of Sports Betting in Edo StateIjahss JournalNo ratings yet