Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment Theory Statistic
Uploaded by
Sudhanshu ShekharOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment Theory Statistic
Uploaded by
Sudhanshu ShekharCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTOGRAM
A Histogram is a graphical representation of data points organized into user-
specified ranges. The histogram condenses a data series into an easily
interpreted visual by taking many data points and grouping them into logical
ranges or bins.
KEY POINTS
A Histogram is a bar graph-like representation of data that buckets a
range of classes into columns along the horizontal x-axis.
The vertical y-axis represents the number count or percentage of
occurrences in the data for each column.
USE OF HISTOGRAM
A Histogram can be used whenever there's a need to display a
comparison of the distribution of certain numerical data in various
ranges of intervals. Histogram examples can help an audience see and
understand quickly and easily essential meanings and patterns related
to a large amount of data.
PAI CHART
The Pai Chart is also known as a circle chart, dividing the circular statistical
graphic into sectors or sections to illustrate the numerical problems. Each
sector denotes a proportionate part of the whole. To find out the composition
of something, Pie-chart works the best at that time. In most cases, pie charts
replace other graphs like the bar graph, line plots, histograms, etc.
KEY POINTS
Categorize the data.
Calculate the total.
Divide the categories.
Convert into percentages.
USES OF PAI CHART
Within a business, it is used to compare areas of growth, such as
turnover, profit and exposure.
To represent categorical data.
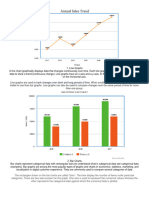
BAR CHART
The pictorial representation of grouped data, in the form of vertical or
horizontal rectangular bars, where the lengths of the bars are equivalent to the
measure of data, are known as bar graphs or bar charts.
KEY POINTS
All the bars should have a common base.
Each column in the bar graph should have equal width.
The height of the bar should correspond to the data value.
The distance between each bar should be the same.
USES OF BAR CHART
Bar graphs are used to match things between different groups or to trace
changes over time. Yet, when trying to estimate change over time, bar graphs
are most suitable when the changes are bigger.
SCATTER PLOT
Scatter plots are the graphs that present the relationship between two
variables in a data-set. It represents data points on a two-dimensional plane or
on a Cartesian system. The independent variable or attribute is plotted on the
X-axis, while the dependent variable is plotted on the Y-axis. These plots are
often called scatter graphs or scatter diagrams.
KEY POINTS
The scatter diagram graphs numerical data pairs, with one variable on
each axis, show their relationship.
USES OF SCATTER PLOT
For a large set of data points given
Each set comprises a pair of values
The given data is in numeric form
REFFERENCE = INVESTOPIDIA, BYJU’S.
You might also like
- Big data Visualization and common adopattation issuesDocument34 pagesBig data Visualization and common adopattation issuesCelina SawanNo ratings yet
- IT Assignment 1Document3 pagesIT Assignment 1Neha KhanNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Charts and GraphsDocument18 pagesInterpreting Charts and Graphsapi-296317938No ratings yet
- Graphs Are Picture Representatives For 1 or More Sets of Information and How These Visually Relate To One AnotherDocument3 pagesGraphs Are Picture Representatives For 1 or More Sets of Information and How These Visually Relate To One AnotherHani Delas AlasNo ratings yet
- Estudiar 1Document7 pagesEstudiar 1Marck MuñozNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 7 BING4102Document8 pagesDiskusi 7 BING4102istiqomahNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Bar PlotDocument24 pagesAssignment-1: Bar PlotANDELA LAHARI 2139465No ratings yet
- Bar Charts NOTESDocument8 pagesBar Charts NOTESlastnotes84No ratings yet
- Computer 7 Q2 Week 7-8Document11 pagesComputer 7 Q2 Week 7-8Jhonalene PerezNo ratings yet
- Visual Data RepresentationsDocument2 pagesVisual Data RepresentationsMuhammad Moazzam FaizNo ratings yet
- Basic Charts and Multidimensional VisualizationDocument33 pagesBasic Charts and Multidimensional VisualizationiyshwaryaNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphsDocument29 pagesTypes of GraphsParamita KaranNo ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument7 pagesPhysics PresentationZuliana NurvidiatiNo ratings yet
- StrsasDocument3 pagesStrsasShane GerolagaNo ratings yet
- Excel AssDocument2 pagesExcel AssFroi LanNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphsDocument16 pagesTypes of GraphsBELENNo ratings yet
- Block Chart: Mekko Charts Chart Mekko ChartsDocument2 pagesBlock Chart: Mekko Charts Chart Mekko Chartsmallireddy1234No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentRo-Chelle Gian Glomar GarayNo ratings yet
- Comparing Bar, Line and Pie GraphsDocument2 pagesComparing Bar, Line and Pie GraphsflordelynaNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics 2nd Quarter 7th Week Lesson Presentation and Analysis of Business DataDocument23 pagesBusiness Mathematics 2nd Quarter 7th Week Lesson Presentation and Analysis of Business DataDearla Bitoon67% (3)
- Graphical Presentation of DataDocument15 pagesGraphical Presentation of DataMalot Nunez MedilloNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs and Charts and Their UsesDocument17 pagesTypes of Graphs and Charts and Their UsesChreze If TorioNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of GraphsDocument44 pagesDifferent Kinds of Graphsabegail.ponteresNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics ToolsDocument21 pagesDescriptive Statistics Toolsvisual3d0% (1)
- ChartsDocument11 pagesChartsRocel U. GinooNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphDocument3 pagesTypes of Graphpcjohn computershopNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument18 pagesGraphBahauddin BalochNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataDocument39 pagesLECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataJemdosquadNo ratings yet
- Graphical Presentation of DataDocument4 pagesGraphical Presentation of DataArjay ValdemorNo ratings yet
- CCS 1A Excel Chart TypesDocument6 pagesCCS 1A Excel Chart TypesJohn Carlo AndayaNo ratings yet
- Subhashree.SDocument2 pagesSubhashree.SSubhashree.S IT 2018No ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationAtiqah RazifNo ratings yet
- Raheel AssignmentDocument5 pagesRaheel AssignmentediealiNo ratings yet
- Graphs ExplainedDocument4 pagesGraphs ExplainedMari Escandor NatomokedNo ratings yet
- G7 Math Q4 - Week 4 - 5 - Representation of DataDocument27 pagesG7 Math Q4 - Week 4 - 5 - Representation of DataJohn Paul Espiña CandoNo ratings yet
- Bar ChartDocument16 pagesBar ChartPreethi JeevaNo ratings yet
- Tableau PGDMPharmaDocument6 pagesTableau PGDMPharmaAVANTI MHATRENo ratings yet
- Statistical DiagramsDocument48 pagesStatistical DiagramsMathias TaylorNo ratings yet
- Chart Types in OfficeDocument13 pagesChart Types in OfficeJemielyn CornelioNo ratings yet
- Graphs Explained: Types, Uses & Analysis in ChemistryDocument29 pagesGraphs Explained: Types, Uses & Analysis in ChemistryMae DinDinNo ratings yet
- GraphicalDocument26 pagesGraphicalMary Joy DesaletNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 19Document5 pagesLab Assignment 19yash choudharyNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs ExplainedDocument2 pagesTypes of Graphs ExplainedmclorenzNo ratings yet
- San Carlos University Engineering Faculty Technical Language School Technical English 4 Eng. Carlos MuñozDocument17 pagesSan Carlos University Engineering Faculty Technical Language School Technical English 4 Eng. Carlos MuñozPablo José RosalesNo ratings yet
- Displaying Data Using Charts and GraphsDocument33 pagesDisplaying Data Using Charts and Graphsapi-272806063100% (1)
- Charts in ExcelDocument12 pagesCharts in Excelpoorna100% (1)
- Graphical Representation o F DataDocument13 pagesGraphical Representation o F DataKaran ErNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Charts and GraphsDocument28 pagesCharts and GraphsMJ LontokNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation OF Statistical DataDocument21 pagesGraphical Representation OF Statistical Datarmconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Statistical Data PresentationDocument39 pagesStatistical Data PresentationZC47No ratings yet
- Project IN Math: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument8 pagesProject IN Math: Submitted To: Submitted byChrissaNo ratings yet
- Creating Graphs in SPSSDocument13 pagesCreating Graphs in SPSSŚađia ÃbbašîNo ratings yet
- CHARTS" Excel Charts: Types & How to Create VisualizationsDocument14 pagesCHARTS" Excel Charts: Types & How to Create VisualizationsanamicaNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument20 pagesGraphsAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Data Visualization - Chapter1Document66 pagesData Visualization - Chapter1bovas.biju2021No ratings yet
- Use of Diagrams in ReportsDocument23 pagesUse of Diagrams in ReportsRamanbhardwaj100% (3)
- Charting BasicsDocument35 pagesCharting BasicsMahaAqeelNo ratings yet
- Picturing Distributions With GraphsDocument21 pagesPicturing Distributions With GraphsFernan CaboteNo ratings yet
- Session 1-2 - Starbucks - Schultz Back in The BrewDocument18 pagesSession 1-2 - Starbucks - Schultz Back in The BrewsanjaanNo ratings yet
- Country Market Entry Strategy AnalysisDocument39 pagesCountry Market Entry Strategy AnalysisSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1Document3 pagesAttachment 1Sudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Violet and Red Geometrical Technology Roadmap PresentationDocument25 pagesViolet and Red Geometrical Technology Roadmap PresentationSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Line Differential Protection and Control RED615Document116 pagesOperation Manual: Line Differential Protection and Control RED615Mirza AtayevNo ratings yet
- Cloud MigrationDocument50 pagesCloud MigrationGeorgios GiannakopoulosNo ratings yet
- Data-Cloud-Consultant SalesforceDocument13 pagesData-Cloud-Consultant Salesforcelopez.cin90No ratings yet
- Nisheeth Joshi - Hands-On Artificial Intelligence With Java For BeginnersDocument140 pagesNisheeth Joshi - Hands-On Artificial Intelligence With Java For BeginnersRichard BerengerNo ratings yet
- PSEN Op2b/1 SeriesDocument67 pagesPSEN Op2b/1 SeriesMindaugas RimkusNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document11 pagesCH 5nishilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Variables and Dashboard Prompts: ORA291 Introduction To Oracle BIEE AnswersDocument35 pagesLesson 7: Variables and Dashboard Prompts: ORA291 Introduction To Oracle BIEE AnswersnareshreddyguntakaNo ratings yet
- Scan Disk SchedulingDocument2 pagesScan Disk SchedulingYzza Veah Esquivel50% (4)
- Specialized Reporting ChapDocument40 pagesSpecialized Reporting ChapAseem KumarNo ratings yet
- Configuring Frame-Mode MPLS On IOSDocument71 pagesConfiguring Frame-Mode MPLS On IOSRafael A Couto CabralNo ratings yet
- Light Is Networked: Hubsense: A New Experience of Com-Missioning Radio-Based Lighting ControlDocument6 pagesLight Is Networked: Hubsense: A New Experience of Com-Missioning Radio-Based Lighting ControlAbdelKarim BaariniNo ratings yet
- Dual OptDocument11 pagesDual OptShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- VC Sessions Through Webrtc & Their ControlsDocument15 pagesVC Sessions Through Webrtc & Their ControlsNitesh ChandawatNo ratings yet
- OpenLDAP Admin GuideDocument267 pagesOpenLDAP Admin Guidejonas leonel da silvaNo ratings yet
- Dual Inverter Gate: Features DescriptionDocument19 pagesDual Inverter Gate: Features DescriptionYaju JotosNo ratings yet
- OPC UA Client DriverDocument46 pagesOPC UA Client DriverSidney Chaves de LimaNo ratings yet
- Parallel Test - Q1 - GEN MATHDocument3 pagesParallel Test - Q1 - GEN MATHEmma SarzaNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain in 200 Lines of Code - by Lauri Hartikka - MediumDocument6 pagesA Blockchain in 200 Lines of Code - by Lauri Hartikka - MediumAbu Hayat M HasnatNo ratings yet
- Phonic Summit 1383126546Document2 pagesPhonic Summit 1383126546K SNo ratings yet
- HP Laserjet MFP M438 Series: Data SheetDocument5 pagesHP Laserjet MFP M438 Series: Data Sheetbharat_boradNo ratings yet
- CPS 356 Lecture Notes: CPU Scheduling AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesCPS 356 Lecture Notes: CPU Scheduling Algorithmssad cclNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Test ManagementDocument44 pagesChapter 8 - Test ManagementHoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Ananya Lakshmi CSC Project DocumentDocument16 pagesAnanya Lakshmi CSC Project Documentyaazhini.No ratings yet
- Errors While Importing Matplotlib:: General FAQ's of Week-3 (PDS)Document5 pagesErrors While Importing Matplotlib:: General FAQ's of Week-3 (PDS)Ragunathan SmgNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/21Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/21Shop AliceNo ratings yet
- CSE Higher Education NetworkDocument9 pagesCSE Higher Education NetworkManeth PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IBISDocument9 pagesIntroduction To IBISabhishekmath123No ratings yet
- Podman Part4Document5 pagesPodman Part4anbuchennai82No ratings yet
- Detailed Solution Description PIG DetectorDocument2 pagesDetailed Solution Description PIG DetectorsinteNo ratings yet
- 32HL95 Toshiba Manual de ServicioDocument39 pages32HL95 Toshiba Manual de ServiciojonnycoolNo ratings yet