Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Graphs Explained
Uploaded by
mclorenzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Graphs Explained
Uploaded by
mclorenzCopyright:
Available Formats
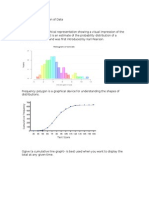
1.
Line Graphs
A line chart graphically displays data that
changes continuously over time. Each line graph
consists of points that connect data to show a
trend (continuous change). Line graphs have an
x-axis and a y-axis. In the most cases, time is
distributed on the horizontal axis.
2. Bar Charts
Bar charts represent categorical data with rectangular
bars (to understand what is categorical data
see categorical data examples). Bar graphs are among
the most popular types of graphs and charts in
economics, statistics, and marketing. They are
commonly used to compare several categories of data.
3. Pie Charts
When it comes to statistical types of graphs and charts,
the pie chart (or the circle chart) has a crucial place and
meaning. It displays data and statistics in an easy-to-
understand ‘pie-slice’ format and illustrates numerical
proportion.
4. Histogram
A histogram shows continuous data in ordered rectangular
columns (to understand what is continuous data see our
post discrete vs continuous data). Usually, there are no
gaps between the columns.
5. Scatter plot
The scatter plot is an X-Y diagram that shows a relationship
between two variables. It is used to plot data points on a
vertical and a horizontal axis. The purpose is to show how
much one variable affects another.
Usually, when there is a relationship between 2 variables, the
first one is called independent. The second variable is called
dependent because its values depend on the first variable.
You might also like
- Types of GraphDocument3 pagesTypes of Graphpcjohn computershopNo ratings yet
- Image Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionFrom EverandImage Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 7 BING4102Document8 pagesDiskusi 7 BING4102istiqomahNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphsDocument16 pagesTypes of GraphsBELENNo ratings yet
- Graphs Explained: Types, Uses & Analysis in ChemistryDocument29 pagesGraphs Explained: Types, Uses & Analysis in ChemistryMae DinDinNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs and Charts and Their UsesDocument17 pagesTypes of Graphs and Charts and Their UsesChreze If TorioNo ratings yet
- ChartsDocument11 pagesChartsRocel U. GinooNo ratings yet
- Graphs Are Picture Representatives For 1 or More Sets of Information and How These Visually Relate To One AnotherDocument3 pagesGraphs Are Picture Representatives For 1 or More Sets of Information and How These Visually Relate To One AnotherHani Delas AlasNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphsDocument29 pagesTypes of GraphsParamita KaranNo ratings yet
- PenaDocument4 pagesPenaKaizz Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- IT Assignment 1Document3 pagesIT Assignment 1Neha KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Theory StatisticDocument3 pagesAssignment Theory StatisticSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Graphs ExplainedDocument4 pagesGraphs ExplainedMari Escandor NatomokedNo ratings yet
- Research Unit 5 BbaDocument17 pagesResearch Unit 5 Bbayash soniNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationAtiqah RazifNo ratings yet
- Charts in ExcelDocument12 pagesCharts in Excelpoorna100% (1)
- Graphical Presentation of DataDocument4 pagesGraphical Presentation of DataMelissa BaileyNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Charts and GraphsDocument18 pagesInterpreting Charts and Graphsapi-296317938No ratings yet
- 05 Handout 1Document13 pages05 Handout 1raulNo ratings yet
- Charts and GraphsDocument28 pagesCharts and GraphsMJ LontokNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument20 pagesGraphsAli HaDi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Kinds of GraphsDocument5 pagesKinds of Graphsmickyist the greatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataDocument39 pagesLECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataJemdosquadNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentRo-Chelle Gian Glomar GarayNo ratings yet
- Creating Graphs in SPSSDocument13 pagesCreating Graphs in SPSSŚađia ÃbbašîNo ratings yet
- Tableau PGDMPharmaDocument6 pagesTableau PGDMPharmaAVANTI MHATRENo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Bar PlotDocument24 pagesAssignment-1: Bar PlotANDELA LAHARI 2139465No ratings yet
- Big data Visualization and common adopattation issuesDocument34 pagesBig data Visualization and common adopattation issuesCelina SawanNo ratings yet
- Block Chart: Mekko Charts Chart Mekko ChartsDocument2 pagesBlock Chart: Mekko Charts Chart Mekko Chartsmallireddy1234No ratings yet
- Instru CompensateDocument41 pagesInstru CompensateSharmaine Manahan-SipinNo ratings yet
- Visual Data RepresentationsDocument2 pagesVisual Data RepresentationsMuhammad Moazzam FaizNo ratings yet
- StrsasDocument3 pagesStrsasShane GerolagaNo ratings yet
- Visualize Statistical Data with GraphsDocument4 pagesVisualize Statistical Data with GraphsprojectboyNo ratings yet
- KKP mATHDocument6 pagesKKP mATHcegu efaNo ratings yet
- CHARTS" Excel Charts: Types & How to Create VisualizationsDocument14 pagesCHARTS" Excel Charts: Types & How to Create VisualizationsanamicaNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation o F DataDocument13 pagesGraphical Representation o F DataKaran ErNo ratings yet
- Picturing Distributions With GraphsDocument21 pagesPicturing Distributions With GraphsFernan CaboteNo ratings yet
- Chart HandoutDocument9 pagesChart Handoutapi-267395283No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 19Document5 pagesLab Assignment 19yash choudharyNo ratings yet
- VisualizationDocument27 pagesVisualizationsbapoorvaa1No ratings yet
- Eda01 (Assgmt2)Document4 pagesEda01 (Assgmt2)aljonNo ratings yet
- Charting BasicsDocument35 pagesCharting BasicsMahaAqeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Graphical Representations of Group DataDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Graphical Representations of Group DataSaqib ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- Chart: Chart Is A Graphical Representation of Data, in Which "The Data Is Represented by SymbolsDocument18 pagesChart: Chart Is A Graphical Representation of Data, in Which "The Data Is Represented by Symbolsjs cyberzoneNo ratings yet
- Graphs 2023Document14 pagesGraphs 2023michaelmangubatNo ratings yet
- Displaying Data Using Charts and GraphsDocument33 pagesDisplaying Data Using Charts and Graphsapi-272806063100% (1)
- Bar Charts NOTESDocument8 pagesBar Charts NOTESlastnotes84No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 2 Notes - StatisticsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 2 Notes - StatisticsVhuhwavhoNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument4 pagesIntroJoyce TutopNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Data Interpretation (DIDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Data Interpretation (DINavdeep AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Raheel AssignmentDocument5 pagesRaheel AssignmentediealiNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation Skills: Learn to Analyze Tables, Graphs & ChartsDocument23 pagesData Interpretation Skills: Learn to Analyze Tables, Graphs & ChartsArif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument7 pagesBio StatisticsBaloch Mubin tvNo ratings yet
- How To Construct A Bar Chart: The TitleDocument3 pagesHow To Construct A Bar Chart: The TitleFildzan Abdul PataNo ratings yet
- Types of ChartsDocument20 pagesTypes of ChartsSamNo ratings yet
- CCS 1A Excel Chart TypesDocument6 pagesCCS 1A Excel Chart TypesJohn Carlo AndayaNo ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument7 pagesPhysics PresentationZuliana NurvidiatiNo ratings yet
- Foundation Notes 2013Document25 pagesFoundation Notes 2013Anonymous wXV066fANo ratings yet
- Ang Sista Ni SisaDocument22 pagesAng Sista Ni SisaNelly Cabusas JorquiaNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICATIONDocument1 pageCERTIFICATIONmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Bla BlaDocument24 pagesBla BlamclorenzNo ratings yet
- Daniel A. Lanos: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesDaniel A. Lanos: ObjectivemclorenzNo ratings yet
- Résumé of Juniel Arabane Ybanez Seeking InternshipDocument2 pagesRésumé of Juniel Arabane Ybanez Seeking InternshipmclorenzNo ratings yet
- VanGogh Starry NightDocument18 pagesVanGogh Starry NightmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Ampalaya con Carne, Chop Suey and Beefstick IngredientsDocument3 pagesAmpalaya con Carne, Chop Suey and Beefstick IngredientsmclorenzNo ratings yet
- PR May 2018 Japan TitpDocument5 pagesPR May 2018 Japan TitpmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Sample Smart and Balanced Resume PDFDocument3 pagesSample Smart and Balanced Resume PDFidaNo ratings yet
- Create Manga and Comics From Start To Finish!Document1 pageCreate Manga and Comics From Start To Finish!mclorenzNo ratings yet
- Anti Virus & Malwarebytes Instructions PDFDocument1 pageAnti Virus & Malwarebytes Instructions PDFmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Cert SiribDocument3 pagesCert SiribmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Sample Smart and Balanced Resume PDFDocument3 pagesSample Smart and Balanced Resume PDFidaNo ratings yet
- Drawingtips PDFDocument1 pageDrawingtips PDFmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Sales Rep Resignation LetterDocument1 pageSales Rep Resignation LettermclorenzNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument4 pagesResumemclorenzNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument5 pagesMental HealthmclorenzNo ratings yet
- OLL Algorithms (Orientation of Last Layer) : Algorithm Presentation FormatDocument4 pagesOLL Algorithms (Orientation of Last Layer) : Algorithm Presentation FormatZORRO SWAT100% (1)
- Pangyan Elementary 2018 APP and PPMPDocument1 pagePangyan Elementary 2018 APP and PPMPmclorenzNo ratings yet
- CommunicativeDocument17 pagesCommunicativemclorenzNo ratings yet
- Saln Sto - Niño E.S. Marilog DistDocument12 pagesSaln Sto - Niño E.S. Marilog DistmclorenzNo ratings yet
- Clean Bandit - Symphony Violin and CelloDocument4 pagesClean Bandit - Symphony Violin and Cellomclorenz100% (1)
- Chemi-Source Repainting The Building and Replace The Cee Purlins, Repair The Louvers of The Air Breather and Repair Portion of Door #3Document2 pagesChemi-Source Repainting The Building and Replace The Cee Purlins, Repair The Louvers of The Air Breather and Repair Portion of Door #3mclorenzNo ratings yet
- PLL Algorithms GuideDocument2 pagesPLL Algorithms Guideamin124010No ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet