Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RTN 300 V100R009C00 Feature Configuration Guide 01
Uploaded by
Abo HodhaifaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RTN 300 V100R009C00 Feature Configuration Guide 01
Uploaded by
Abo HodhaifaCopyright:
Available Formats
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
V100R009C00
Feature Configuration Guide
Issue 01
Date 2018-07-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2018. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide About This Document
About This Document
Related Versions
The following table lists the product versions related to this document.
Product Name Version
OptiX RTN 380 V100R009C00
iManager U2000–T V200R018C50
Intended Audience
This document describes how to configure various services on the equipment. This document
describes the basic information and configuration process, and uses configuration examples to
show how to set specific parameters.
The intended audiences of this document are:
l Installation and commissioning engineer
l Data configuration engineer
l System maintenance engineer
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol Description
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide About This Document
Symbol Description
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, may result in minor
or moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in
equipment damage, data loss, performance
deterioration, or unanticipated results.
NOTICE is used to address practices not
related to personal injury.
Calls attention to important information,
best practices and tips.
NOTE is used to address information not
related to personal injury, equipment
damage, and environment deterioration.
GUI Conventions
The GUI conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Boldface Buttons, menus, parameters, tabs, window, and dialog titles
are in boldface. For example, click OK.
> Multi-level menus are in boldface and separated by the ">"
signs. For example, choose File > Create > Folder.
Updates in Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Based on Product Version
V100R009C00
This issue is the first release for the product version V100R009C00.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Network Management Features..................................................................................................1
1.1 Configuration Process (IP DCN).................................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Configuration Process (L2 DCN Solution).................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Configuration Process (NE Anti-Theft Solution)........................................................................................................... 8
1.4 Configuration Example (IP DCN).................................................................................................................................. 9
1.4.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.4.2 Configuration Procedure..............................................................................................................................................9
1.5 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with NMS and NE IP Addresses Using the Same Network Segment)... 15
1.5.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................. 15
1.5.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................15
1.6 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with Different Network Segments)......................................................... 19
1.6.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................. 19
1.6.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................20
1.7 Configuration Example (NE Anti-Theft Solution)....................................................................................................... 23
1.7.1 Network Diagram...................................................................................................................................................... 23
1.7.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................24
2 Ethernet features.......................................................................................................................... 26
2.1 Configuration Process (QinQ-based E-Line Services)................................................................................................. 27
2.2 Configuration Process (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service)........................................................................ 28
2.3 Configuration Procedure (MSTP)................................................................................................................................ 29
2.4 Configuration Process (QoS/HQoS).............................................................................................................................30
2.5 Configuration Process (Ethernet Service OAM).......................................................................................................... 33
2.6 Configuration Process (Ethernet Port OAM)............................................................................................................... 36
2.7 Configuration Process (Bandwidth Notification)......................................................................................................... 37
2.8 Configuration Process (ERPS on a Single-ring Network)............................................................................................39
2.9 Configuration Example (QinQ-based E-Line Services)............................................................................................... 41
2.9.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................. 41
2.9.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................43
2.10 Configuration Example (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service).................................................................... 45
2.10.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 45
2.10.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................46
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iv
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
2.11 Configuration Example (MSTP).................................................................................................................................48
2.11.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 48
2.11.2 Configuration Process..............................................................................................................................................49
2.12 Configuration Example (QoS)....................................................................................................................................50
2.12.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 50
2.12.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................51
2.13 Configuration Example (HQoS)................................................................................................................................. 53
2.13.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 53
2.13.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................54
2.14 Configuration Example (Ethernet Service OAM)...................................................................................................... 57
2.14.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 57
2.14.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................58
2.15 Configuration Example (Ethernet Port OAM)........................................................................................................... 61
2.15.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 61
2.15.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................62
2.16 Configuration Example (Bandwidth Notification)..................................................................................................... 63
2.16.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 63
2.16.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................64
2.17 Configuration Example (ERPS on a Single-ring Network)........................................................................................67
2.17.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................... 67
2.17.2 Configuration Procedure..........................................................................................................................................68
3 Configuring Clock Features...................................................................................................... 71
3.1 Configuration Process(IEEE 1588v2).......................................................................................................................... 71
3.2 Configuration Process (ITU-T G.8275.1).....................................................................................................................75
3.3 Configuration Example (Networkwide Time Synchronization)...................................................................................78
3.3.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................. 79
3.3.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................79
3.4 Configuration Example (Transparent Transmission of Time Signals)......................................................................... 82
3.4.1 Networking Diagram................................................................................................................................................. 82
3.4.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................83
3.5 Configuration Example (ITU-T G.8275.1)...................................................................................................................85
3.5.1 Network Diagram...................................................................................................................................................... 85
3.5.2 Configuration Procedure............................................................................................................................................86
4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features..........................................................................................91
4.1 Configuration Process (MPLS Tunnel)........................................................................................................................ 92
4.2 Configuration Process (Configuring ETH PWE3 Services).........................................................................................98
4.3 Configuration Procedure (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)....................................................................................................... 104
4.4 Configuration Procedure (LSP Ping/Traceroute)....................................................................................................... 105
4.5 Configuration Procedure (MPLS APS)...................................................................................................................... 108
4.6 Configuration Procedure (PW OAM_Y.1711)............................................................................................................113
4.7 Configuration Process (PW Ping/Traceroute)............................................................................................................ 114
4.8 Configuration Process (PW APS/PW FPS)................................................................................................................ 116
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. v
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
4.9 Configuration Process (MPLS-TP OAM).................................................................................................................. 125
4.10 Configuration Example (MPLS Tunnels with No Protection)................................................................................. 136
4.10.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 136
4.10.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................137
4.11 Configuration Example (E-Line Services Carried by PWs).....................................................................................139
4.11.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 139
4.11.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................140
4.12 Configuration Example (E-LAN Services Carried by PWs)....................................................................................141
4.12.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 141
4.12.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................142
4.13 Configuration Example (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)....................................................................................................... 143
4.13.1 Network Diagram.................................................................................................................................................. 143
4.13.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................144
4.14 Configuration Example (LSP Ping/Traceroute)....................................................................................................... 144
4.14.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 145
4.14.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................145
4.15 Configuration Example (MPLS APS)...................................................................................................................... 146
4.15.1 Network Diagram.................................................................................................................................................. 146
4.15.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................147
4.16 Configuration Example (PW OAM_Y.1711)........................................................................................................... 148
4.16.1 Network Diagram.................................................................................................................................................. 148
4.16.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................149
4.17 Configuration Example (PW Ping/Traceroute)........................................................................................................ 150
4.17.1 Network Diagram.................................................................................................................................................. 150
4.17.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................151
4.18 Configuration Example (PW APS)...........................................................................................................................152
4.18.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 152
4.18.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................153
4.19 Configuration Example (PW FPS)........................................................................................................................... 155
4.19.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 155
4.19.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................155
4.20 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for Tunnels)...........................................................................................156
4.20.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 156
4.20.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................157
4.21 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for PWs)................................................................................................ 159
4.21.1 Networking Diagram............................................................................................................................................. 159
4.21.2 Configuration Procedure........................................................................................................................................160
5 Task Collection.......................................................................................................................... 163
5.1 Network Management Features..................................................................................................................................163
5.1.1 Creating an NE by Using the Search Method..........................................................................................................163
5.1.2 Creating an NE Manually........................................................................................................................................ 165
5.1.3 Changing an NE ID................................................................................................................................................. 166
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. vi
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
5.1.4 Changing an NE Name............................................................................................................................................ 167
5.1.5 Synchronizing NE Time.......................................................................................................................................... 168
5.1.6 Synchronizing NE Time with Local Time...............................................................................................................170
5.1.7 Configuring a Standard NTP Key........................................................................................................................... 171
5.1.8 Setting NE Communication Parameters.................................................................................................................. 172
5.1.9 Configuring DCCs................................................................................................................................................... 173
5.1.10 Setting the VLAN ID and Bandwidth for an Inband DCN................................................................................... 174
5.1.11 Configuring the Priorities of Inband DCN Packets............................................................................................... 175
5.1.12 Setting a Port for an Inband DCN......................................................................................................................... 176
5.1.13 Configuring Access Control.................................................................................................................................. 178
5.1.14 Creating a Static IP Route..................................................................................................................................... 179
5.1.15 Setting OSPF Protocol Parameters........................................................................................................................ 180
5.1.16 Creating an OSPF Area......................................................................................................................................... 181
5.1.17 Configuring the Network Information of an ABR................................................................................................ 182
5.1.18 Creating a Manual Route Aggregation Group.......................................................................................................184
5.1.19 Configuring Port IP Addresses for an ABR.......................................................................................................... 185
5.1.20 Configuring the OSPF Authentication Type..........................................................................................................186
5.1.21 Enabling the Proxy ARP........................................................................................................................................188
5.1.22 Enabling/Disabling the RSTP Protocol When the L2 DCN Solution Is Used...................................................... 189
5.1.23 Querying IP Routes............................................................................................................................................... 190
5.1.24 Verifying the Connectivity of an IP DCN Network.............................................................................................. 191
5.1.25 Setting SNMP Communication Parameters.......................................................................................................... 192
5.1.26 Configuring the Active and Standby Gateway NEs.............................................................................................. 194
5.1.27 Configuring an Electrical Interface for Ethernet Services as an Ethernet Network Management Interface.........194
5.1.28 Configuring the Ethernet NMS Port on an NE......................................................................................................195
5.1.29 Configuring Security Management Parameters for the WLAN Module...............................................................196
5.1.30 Configuring the Port IP Address of the WLAN Module.......................................................................................197
5.1.31 Configuring DHCP for the WLAN Module.......................................................................................................... 198
5.1.32 Configuring Channels for the WLAN Module......................................................................................................199
5.1.33 Enabling WLAN Whitelist.................................................................................................................................... 200
5.1.34 Configuring WLAN Whitelist............................................................................................................................... 201
5.1.35 Configuring LLDP ................................................................................................................................................202
5.1.36 Querying Information About an RTN NE's Neighboring Base Stations Based on LLDP.................................... 203
5.1.37 Generating a Pair of Public and Private Keys....................................................................................................... 204
5.1.38 Configuring NE Anti-Theft................................................................................................................................... 205
5.2 Managing Microwave Links.......................................................................................................................................206
5.2.1 Configuring Microwave Link Data......................................................................................................................... 206
5.2.2 Setting the Maximum Transmit Power and Power Thresholds............................................................................... 207
5.2.3 Enabling/Disabling AM Booster............................................................................................................................. 208
5.2.4 Configuring Ethernet Frame Header Compression and Error Frame Discarding at an Air Interface..................... 209
5.3 Ethernet Services and Features..................................................................................................................................210
5.3.1 Setting the Basic Attributes for an Ethernet Port.................................................................................................... 210
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. vii
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
5.3.2 Setting the Layer 2 Attributes of Ethernet Ports......................................................................................................211
5.3.3 Setting Layer 3 Attributes of Ethernet Ports........................................................................................................... 212
5.3.4 Setting the Advanced Attributes of Ethernet Ports..................................................................................................213
5.3.5 Setting the Basic Attributes of microwave Ports.....................................................................................................214
5.3.6 Setting the L2 Attributes for Microwave Ports....................................................................................................... 215
5.3.7 Setting the L3 Attributes for Microwave Ports....................................................................................................... 216
5.3.8 Setting the Advanced Attributes of Microwave Ports............................................................................................. 217
5.3.9 Configuring Flow Control for an Ethernet Port.......................................................................................................218
5.3.10 Creating VLAN Sub-Interfaces............................................................................................................................. 219
5.3.11 Creating a LAG......................................................................................................................................................221
5.3.12 Setting LAG Parameters........................................................................................................................................ 223
5.3.13 Creating an ERPS Instance....................................................................................................................................224
5.3.14 Setting Global ERPS Protocol Parameters............................................................................................................ 225
5.3.15 Setting ERPS Protocol Parameters........................................................................................................................ 226
5.3.16 Creating a Virtual Channel VLAN Forwarding Table...........................................................................................227
5.3.17 Setting Parameters for Switching Upon Multiple Failures....................................................................................228
5.3.18 Performing an External ERPS Switchover............................................................................................................ 229
5.3.19 Creating an Ethernet Service for Transmitting L2 Protocol Packets.....................................................................230
5.3.20 Configuring a VLAN Forwarding Table............................................................................................................... 232
5.3.21 Configuring a QinQ Link...................................................................................................................................... 233
5.3.22 Configuring an E-Line Service Carried by QinQ.................................................................................................. 234
5.3.23 Configuring an IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service............................................................................... 236
5.3.24 Configuring a Split Horizon Group....................................................................................................................... 237
5.3.25 Creating a Static MAC Address Entry.................................................................................................................. 238
5.3.26 Creating a Blacklist MAC Address Entry............................................................................................................. 239
5.3.27 Managing a Dynamic MAC Address Table...........................................................................................................240
5.3.28 Creating an MSTP Port Group.............................................................................................................................. 241
5.3.29 Setting MSTP Bridge Parameters..........................................................................................................................242
5.3.30 Setting CIST Parameters....................................................................................................................................... 243
5.3.31 Deleting an E-LAN Service...................................................................................................................................244
5.3.32 Modifying the Mapping for a DS Domain............................................................................................................ 245
5.3.33 Changing the Ports Applied to a DS Domain and Their Trusted Packet Types.................................................... 246
5.3.34 Enabling/Disabling DSCP Demapping at an Egress Port..................................................................................... 248
5.3.35 Setting Egress Queue Scheduling Policies............................................................................................................ 249
5.3.36 Configuring a Flow Based on the Port Policy....................................................................................................... 250
5.3.37 Configuring Port Shaping...................................................................................................................................... 252
5.3.38 Setting Traffic Shaping for Egress Queues............................................................................................................253
5.3.39 Setting the Congestion Management Mode for Egress Queues............................................................................ 254
5.3.40 Creating a Service WRED Policy..........................................................................................................................255
5.3.41 Configuring a V-UNI Egress Policy...................................................................................................................... 256
5.3.42 Configuring a V-UNI Group..................................................................................................................................258
5.3.43 Creating a PW Policy............................................................................................................................................ 259
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. viii
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
5.3.44 Configuring a QinQ Policy....................................................................................................................................261
5.3.45 Applying Policies.................................................................................................................................................. 262
5.3.46 Configuring Bandwidth Limitation for MPLS Tunnels........................................................................................ 263
5.3.47 Configuring Bandwidth Limitation for PWs......................................................................................................... 264
5.3.48 Configuring QinQ Link Bandwidth Limitations................................................................................................... 265
5.3.49 Creating an MD..................................................................................................................................................... 266
5.3.50 Creating an MA..................................................................................................................................................... 267
5.3.51 Creating an MEP................................................................................................................................................... 269
5.3.52 Creating a Remote MEP in an MA........................................................................................................................270
5.3.53 Creating an MIP.....................................................................................................................................................271
5.3.54 Performing a CC Test............................................................................................................................................ 272
5.3.55 Performing an LB Test...........................................................................................................................................273
5.3.56 Performing an LT Test........................................................................................................................................... 274
5.3.57 Activating AIS....................................................................................................................................................... 276
5.3.58 Checking the Packet Loss Ratio, Delay, or Delay Variation of Ethernet Services................................................276
5.3.59 Enabling OAM Auto-discovery.............................................................................................................................278
5.3.60 Enabling Link Event Notification..........................................................................................................................279
5.3.61 Changing the OAM Error Frame Monitoring Threshold...................................................................................... 280
5.3.62 Performing a Remote Loopback............................................................................................................................281
5.3.63 Enabling Local Loopback Detection..................................................................................................................... 282
5.3.64 Configuring LPT....................................................................................................................................................283
5.3.65 Configuring Bandwidth Notification.....................................................................................................................284
5.4 Managing MPLS Tunnels...........................................................................................................................................285
5.4.1 Creating ARP Static Entries.................................................................................................................................... 286
5.4.2 Setting Basic MPLS Attributes................................................................................................................................286
5.4.3 Configuring Global OAM Parameters.....................................................................................................................287
5.4.4 Changing the MPLS Tunnel/PW OAM Standard....................................................................................................288
5.4.5 Creating a Unidirectional MPLS Tunnel................................................................................................................. 289
5.4.6 Creating a Bidirectional MPLS Tunnel................................................................................................................... 290
5.4.7 Deleting MPLS Tunnels.......................................................................................................................................... 292
5.4.8 Setting MPLS OAM (Y.1711) Parameters.............................................................................................................. 293
5.4.9 Enabling/Disabling FDI...........................................................................................................................................294
5.4.10 Starting/Stopping CV/FFD Detection for MPLS Tunnels.....................................................................................295
5.4.11 Clearing OAM Configuration Data for MPLS Tunnel OAM (Y.1711).................................................................296
5.4.12 Performing an LSP Ping Test................................................................................................................................ 297
5.4.13 Performing an LSP Traceroute Test.......................................................................................................................297
5.4.14 Configuring MEP Parameters for MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM.................................................................................. 298
5.4.15 Creating MIPs of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM............................................................................................................299
5.4.16 Starting a CC Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM......................................................................................................300
5.4.17 Starting an LB Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM....................................................................................................301
5.4.18 Starting an LT Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM.................................................................................... 302
5.4.19 Testing the Delay and Delay Variation of an MPLS Tunnel................................................................................. 303
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ix
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide Contents
5.4.20 Setting the LCK Status of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM.............................................................................................. 304
5.4.21 Starting a TST Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM....................................................................................305
5.5 Managing MPLS APS Protection Groups.................................................................................................................. 306
5.5.1 Creating an MPLS APS Protection Group.............................................................................................................. 306
5.5.2 Querying MPLS APS Status....................................................................................................................................307
5.5.3 Triggering MPLS APS Switching........................................................................................................................... 308
5.5.4 Enabling/Disabling MPLS APS Protection............................................................................................................. 309
5.6 Managing PWs........................................................................................................................................................... 310
5.6.1 Querying Information and Running Status of PWs.................................................................................................310
5.6.2 Creating an MS-PW.................................................................................................................................................311
5.6.3 Setting PW OAM (Y.1711) Parameters................................................................................................................... 313
5.6.4 Performing a PW Ping Test..................................................................................................................................... 314
5.6.5 Performing a PW Traceroute Test........................................................................................................................... 315
5.6.6 Configuring MEP Parameters for MPLS-TP PW OAM......................................................................................... 316
5.6.7 Creating MIPs of MPLS-TP PW OAM...................................................................................................................317
5.6.8 Starting a CC Test of MPLS-TP PW OAM.............................................................................................................318
5.6.9 Starting an LB Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM......................................................................................................319
5.6.10 Starting an LT Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM.................................................................................... 320
5.6.11 Testing the Packet Loss Ratio, Delay, and Delay Variation of a PW.....................................................................321
5.6.12 Setting the LCK Status of MPLS-TP PW OAM................................................................................................... 322
5.6.13 Starting a TST Test of MPLS-TP PW OAM......................................................................................................... 323
5.7 Managing a PW APS/PW FPS Protection Group...................................................................................................... 324
5.7.1 Creating a PW APS Protection Group.....................................................................................................................324
5.7.2 Creating a PW FPS Protection Group..................................................................................................................... 326
5.7.3 Configuring Slave Protection Pairs of PW APS......................................................................................................328
5.7.4 Querying PW APS/PW FPS Status......................................................................................................................... 329
5.7.5 Triggering PW APS/PW FPS Switching................................................................................................................. 330
5.7.6 Enabling/Disabling PW APS Protection................................................................................................................. 331
5.8 Managing the IEEE 1588v2 Clock............................................................................................................................. 332
5.8.1 Querying or Modifying the PTP System Time........................................................................................................332
5.8.2 Configuring the PTP Profile.................................................................................................................................... 333
5.8.3 Setting the PTP NE Attributes.................................................................................................................................334
5.8.4 Creating a PTP Clock Port.......................................................................................................................................335
5.8.5 Setting PTP Clock Port Attributes...........................................................................................................................336
5.8.6 Setting Parameters Clock Packets........................................................................................................................... 338
5.8.7 Configuring the Delay Offset for Asymmetric Transmission Between NEs...........................................................340
5.8.8 Modifying the BMC Algorithm Parameters for an NE Clock.................................................................................341
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. x
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
1 Network Management Features
About This Chapter
This part describes data communication networks (DCNs) and various DCN solutions.
1.1 Configuration Process (IP DCN)
Configuring IP data communication network (DCN) includes configuring communication
data at the near end and creating NEs on a network management system (NMS).
1.2 Configuration Process (L2 DCN Solution)
The L2 DCN solution configuration process includes configuring communication data on NEs
and creating NEs on the NMS. The core configuration task is to set the DCN protocol used by
the DCCs or inband DCN channels to L2 DCN.
1.3 Configuration Process (NE Anti-Theft Solution)
This section describes the process of configuring NE anti-theft. The process includes
generating a key pair and enabling NE anti-theft.
1.4 Configuration Example (IP DCN)
In this example, all NEs belong to the same OSPF area.
1.5 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with NMS and NE IP Addresses Using the
Same Network Segment)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure the L2 DCN solution based on
network conditions. In this example, all NEs belong to the same L2 DCN subnet and
communicate with the NMS through the L2 network.
1.6 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with Different Network Segments)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure the L2 DCN solution based on
network conditions. In this example, all NEs belong to the same L2 DCN subnet and
communicate with the NMS through the L2 network.
1.7 Configuration Example (NE Anti-Theft Solution)
This section provides an example of how to configure NE anti-theft.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
1.1 Configuration Process (IP DCN)
Configuring IP data communication network (DCN) includes configuring communication
data at the near end and creating NEs on a network management system (NMS).
Flowchart
Figure 1-1 shows the flowchart for configuring IP DCN.
Figure 1-1 Flowchart for configuring IP DCN
Required Start
Optional
Set basic NE attributes.
Configure DCCs.
Configure inband DCN.
Configure IP routes.
Create NEs on a
centralized NMS.
End
Process
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support multi-area OSPF. Therefore, the ABR settings in the process are not
applicable to the RTN 360.
Table 1-1 Process of configuring IP DCN
Ste Operation Remarks
p
1 Setting 5.1.3 Changing an NE Required.
basic NE ID
attributes
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Ste Operation Remarks
p
5.1.8 Setting NE Required.
Communication NOTE
Parameters l If the IP address of an NE has not been
changed manually, the IP address defaults
according to the NE ID and is always
0x81000000 + NE ID.
l For a gateway NE that communicates with the
NMS using the access control function
(through a service port), plan its IP address in
the same way as for a non-gateway NE
2 5.1.27 Configuring an Electrical Optional.
Interface for Ethernet Services as
an Ethernet Network Management
Interface
3 5.1.9 Configuring DCCs Required.
4 Configuri 5.1.10 Setting the If the VLAN ID and bandwidth of the inband
ng inband VLAN ID and DCN planned for the OptiX equipment do
DCN Bandwidth for an not take their default values, set the VLAN
Inband DCN ID and bandwidth for an inband DCN. (The
default VLAN ID is 4094 and the default
bandwidth is 512 kbit/s.)
NOTE
Use the same VLAN ID for inband DCN
communication over the entire network.
5.1.12 Setting a Port Required when RTN 300 ports are
for an Inband DCN interconnected with ATN/CX equipment
through a DCN or a VLAN needs to be
independently configured for the DCN over
RTN 300 ports.
5.1.13 Configuring Required when a gateway NE must
Access Control communicate with the NMS through a third-
party network.
5.1.11 Configuring the Required when DCN packets must be
Priorities of Inband prioritized.
DCN Packets
5 Configuri 5.1.15 Setting OSPF Required.
ng IP Protocol Parameters
routes
Changing the network Required for an ABR.
segment of the
backbone area to
which an ABR belongs
5.1.16 Creating an If a network is divided into multiple OSPF
OSPF Area areas, create the non-backbone area to which
an ABR belongs.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Ste Operation Remarks
p
Adding an ABR into a Required when an ABR is in an area with
network segment multiple network segments.
5.1.20 Configuring the Required when OSPF authentication must be
OSPF Authentication performed.
Type NOTE
l none indicates no authentication.
l If Authentication Type is set to none, all
preset authentication passwords are cleared.
l MD5 Key is available only when
Authentication Type is MD5.
5.1.18 Creating a If automatic route aggregation is unavailable,
Manual Route configure manual route aggregation on an
Aggregation Group ABR to reduce the number of routes.
NOTE
An area can have a maximum of eight manually
aggregated routes.
5.1.19 Configuring For an ABR NE, set IP Address and Subnet
Port IP Addresses for Mask to those of its non-backbone area port.
an ABR NOTE
l The IP address of the backbone area port on
an ABR NE always uses the NE IP address.
l If not specified, the NE IP address is used.
5.1.21 Enabling the l If the IP addresses of a third-party NMS
Proxy ARP and third-party NEs are on the same
network segment and an OptiX
transmission network provides an IP
route between the third-party NMS and a
third-party NE, enable proxy Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) on the OptiX
NE connected to the third-party NMS and
on the OptiX NE connected to a third-
party NE.
l If the IP addresses of the NMS, gateway
NE, and non-gateway NEs are on the
same network segment and the NMS
must have access to the non-gateway NEs
directly, enable proxy ARP for the
gateway NE.
5.1.14 Creating a Configure static routes for NEs according to
Static IP Route the network plan. If the IP addresses of the
gateway NE and NMS are on different
network segments, configure a static route
from the gateway NE to the NMS.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Ste Operation Remarks
p
5.1.23 Querying IP In normal cases:
Routes l The gateway NE has a route to the NMS.
l The gateway NE has routes to non-
gateway NEs, and non-gateway NEs have
routes to the gateway NE.
l If a third-party NE connects to the third-
party NMS through an RTN 300 NE, the
RTN 300 NE automatically has routes to
the third-party NMS and to the third-
party gateway NE.
NOTE
You can check route status by testing route
connectivity in addition to querying IP routes.
6 Creating 5.1.2 Creating an NE Recommended when one or more NEs must
NEs on a Manually be added to a large-scale network.
centralize
d NMS 5.1.1 Creating an NE Recommended in all other cases.
by Using the Search
Method
1.2 Configuration Process (L2 DCN Solution)
The L2 DCN solution configuration process includes configuring communication data on NEs
and creating NEs on the NMS. The core configuration task is to set the DCN protocol used by
the DCCs or inband DCN channels to L2 DCN.
Flowchart
Figure 1-2 shows the flowchart for configuring the L2 DCN solution.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Figure 1-2 Flowchart for configuring the L2 DCN solution
Required Start
Optional
Change NE IDs.
Set NE communication
parameters.
Configure DCCs.
Configure the inband DCN.
Enable RSTP.
Create NEs on the NMS.
End
Process
Table 1-2 Process of configuring the L2 DCN solution
Ste Operation Remarks
p
1 Changing NE IDs Required. Set parameters as follows:
l Set ID according to the DCN plan.
l If a specific extended NE ID is required,
change the value of Extended ID.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Ste Operation Remarks
p
2 Setting NE Communication Required.
Parameters l Set IP Address and Subnet Mask
according to the plan.
l The IP addresses of NEs in the same L2
DCN subnet must belong to the same
network segment.
3 5.1.27 Configuring an Electrical Optional.
Interface for Ethernet Services as
an Ethernet Network Management
Interface
4 Configuring DCCs Required.
L2 DCN can be enabled for either the inband
DCN channel or outband DCN channel of a
microwave link. Therefore, the DCC must be
disabled over the microwave port.
5 Configuri Setting the VLAN ID Required if the VLAN ID and bandwidth
ng the and Bandwidth for the planned for the inband DCN do not take their
inband Inband DCN default values (the default VLAN ID is 4094
DCN and the default bandwidth is 512 kbit/s.)
NOTE
The same VLAN ID must be used for inband
DCN communication over the entire network.
Configuring Access Required. Disable access control on inband
Control DCN-enabled ports in the L2 DCN.
Enabling Inband DCN Required.
on Ports l To prevent impact on base stations, it is
recommended that you set Enabled
Status to Disabled for ports connected to
base stations and set Enabled Status to
Enabled (default value) for other ports.
l Set Protocol Type to L2DCN for inband
DCN channels in the L2 DCN subnet.
Configuring Priorities Required when priorities need to be specified
for Inband DCN for DCN packets.
Packets
6 Enabling RSTP for the L2 DCN Optional.
7 Creating Creating NEs It is recommended that you perform this
NEs on Manually operation to add one or more NEs to a large
the NMS existing network on the centralized NMS.
Creating NEs Using It is recommended that you perform this
the Search Method operation to create NEs on the centralized
NMS in other cases.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
NOTE
To prevent loops in an L2 DCN and further prevent broadcast storms, the STP/RSTP protocol needs to
be enabled for all switches that are connected to the L2 DCN.
1.3 Configuration Process (NE Anti-Theft Solution)
This section describes the process of configuring NE anti-theft. The process includes
generating a key pair and enabling NE anti-theft.
Figure 1-3 Flowchart for configuring NE anti-theft
Table 1-3 Flowchart for configuring NE anti-theft
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.1.37 Generating a Pair of Public and Private Keys Required when NE
anti-theft needs to
be configured.
2 5.1.38 Configuring NE Anti-Theft Required when NE
anti-theft needs to
be configured.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
1.4 Configuration Example (IP DCN)
In this example, all NEs belong to the same OSPF area.
1.4.1 Networking Diagram
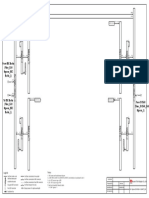
This section describes the networking of NEs.
In Figure 1-4, the network has only RTN 300s and must be managed through the network
management system (NMS) in a unified manner. On the microwave transmission network:
l All NEs are in the network segment of 129.9.0.0. Figure 1-4 illustrates the IP address of
each NE.
l Access control is enabled for the P&E port of NE1, the gateway NE. The port IP address
is in the 10.0.0.0 network segment, which is different from that of the NE IP address.
l NE2 and NE3 are connected by a GE fiber.
l The RTN 300s use D1 to D3 bytes in microwave links or a portion of Ethernet service
bandwidth in GE links for internal data communication network (DCN) communication.
The RTN 300s also use IP protocols for communication.
l Configure a static route from NE1 to the NMS and enable the OSPF route spreading
function, so that NE 2, NE 3, and NE 4 can obtain routes to the NMS and the NMS has
direct access to NE 2, NE 3, and NE 4.
l NE2 and NE3 receive services from base stations through P&E ports.
Figure 1-4 Networking diagram for IP DCN
1.4.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring IP data communication network (DCN).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example Planning Principle
DCN l Change the VLAN IDs of all l The default IP DCN solution is
inband DCN channels to 4094 recommended.
(default) and the bandwidth to l The VLAN ID of inband DCN
512 kbit/s (default). channels must be different from
l To prevent impact on base service VLAN IDs.
stations, disable the inband DCN
function on the P&E ports of NE2
and NE3.
NE ID and See the following figure. l Each NE must have a unique NE
NE IP ID and IP address.
address l For a gateway NE that
communicates with the NMS
through an NMS port, set NE IP
and Subnet Mask according to the
external DCN plan. If the gateway
NE communicates with the NMS
using the access control function,
set the NE IP as a non-gateway
NE IP.
l For a gateway NE, set the default
gateway according to the external
DCN plan.
l For a non-gateway NE, it is
recommended that you set NE IP
to 0x81000000+NE ID if a single
OSPF area is configured for the
DCN subnet. For example, if an
NE ID is 0x090001, set NE IP to
129.9.0.1. Set subnet mask to
255.255.0.0.
l For a non-gateway NE, it is
recommended that you plan the
NE IP addresses of different areas
in different network segments and
plan the NE IP addresses of the
same area in the same network
segment, if multiple OSPF areas
are configured for the DCN
subnet.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Item Value in This Example Planning Principle
Connectio Common+Security SSL l Generally, it is recommended that
n Mode Connection Mode take the
default value Common+Security
SSL. If you need to configure the
NMS to connect to a gateway NE
in SSL connection mode, set
Connection Mode to Security
SSL.
l If Connection Mode is set to
Common+Security SSL for a
gateway NE, it is recommended
that Connection Mode be set to
Security SSL for the NMS.
Access Access control is enabled on the P&E If access control is enabled on the
Control port (IP address: 10.0.0.1) of NE1. Ethernet port of the gateway NE,
Access control is enabled for other ensure that the IP address of this
interfaces by default and the setting is Ethernet port is in the same network
not modified. segment as the IP address of the
NMS but in a different network
segment from the IP address of the
gateway NE.
Routing l On NE1, configure a static route -
informatio to the NMS whose IP address is
n 10.2.0.100, with the gateway IP
address being the port IP address
10.0.0.2 of the router 2.
l On NE1, enable the OSPF route
flooding function for the static
route so that NE2, NE3, and NE4
can obtain routes to the NMS.
l Retain the default values for other
OSPF protocol parameters.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Figure 1-5 Allocated IDs and IP addresses
Procedure
Step 1 Change an NE ID.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 2 Configure data communications channels (DCCs).
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 3 Enable the inband DCN function on ports of NE2 and NE3.
NOTE
To prevent impact on base stations, the inband DCN function must be disabled on the P&E ports of NE2 and
NE3.
NE2 is used as an example.
Step 4 Set Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) parameters
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 5 On NE1, create a static IP route.
Step 6 Querying IP routes.
The expected query results are as follows:
For NE 1:
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
l The IP address of the gateway NE is 10.0.0.1 for routes to the IP addresses of 129.9.0.2,
129.9.0.3, and 129.9.0.4.
l The IP address of the gateway NE is 10.0.0.2 for the route to the IP address of
10.2.0.100.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
To ensure communication between the network management system (NMS), the gateway NE,
and non-gateway NEs, perform the following settings:
l On the NMS, configure static routes to the network segment 129.9.0.0 to which the NE
IP address belongs.
l On routers 1 and 2, configure routes to the network segment 129.9.0.0 to which the non-
gateway NEs belong.
1.5 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with NMS
and NE IP Addresses Using the Same Network Segment)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure the L2 DCN solution based on
network conditions. In this example, all NEs belong to the same L2 DCN subnet and
communicate with the NMS through the L2 network.
1.5.1 Networking Diagram
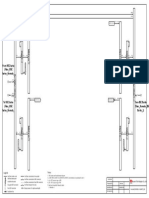
This section describes the networking of NEs.
As shown in Figure 1-6, RTN 300 NEs independently form a network and need to be
managed by the U2000 in a unified manner. On this network:
The NEs are connected using the L2 DCN. Their IP addresses are in the same network
segment as the U2000 IP address.
Figure 1-6 Networking diagram for the L2 DCN solution
NE 1 NE 2 NE 3 NE 4
NMS
L2 Switch P&E GE(o) GE(o)
Network
192.168.7.4/24
192.168.7.100/24 192.168.7.3/24
192.168.7.2/24
192.168.7.1/24
NodeB 1 NodeB 2
Ethernet link Radio link
1.5.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring the L2 DCN solution.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Data Preparation
Data Value in This Planning
Example Guidelines
NE ID and IP address See the following l Set a unique NE
figure. ID and IP
address for each
NE.
l For a gateway
NE that
communicates
with the NMS
through an NMS
port, set IP
address and
Subnet Mask
according to the
external DCN
plan.
l For a gateway
NE, set Gateway
IP Address if the
external DCN
requires a default
gateway.
l The IP addresses
of NEs in the
same L2 DCN
subnet must
belong to the
same network
segment.
Inband DCN VLAN ID and The default VLAN The same VLAN ID
bandwidth ID is 4094 and the must be used for
default bandwidth is inband DCN
1024 kbit/s. communication over
the entire network.
DCC protocol type L2DCN -
RSTP status Enabled (default -
value)
Access control Access control is -
disabled at the
inband DCN-
enabled ports in the
L2 DCN.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Figure 1-7 NE IDs and IP addresses
NMS
L2 Switch 9-1 9-2 9-3 9-4
192.168.7.1 192.168.7.2 192.168.7.3 192.168.7.4
Network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
192.168.7.100/24
NE 1 NE 2 NE 3 NE 4
Extended ID-Basic ID
Ethernet link Radio link IP address
Gateway
Procedure
Step 1 Change NE IDs.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 2 Set NE communication parameters.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 3 Configure DCCs.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 4 Disable access control at NE ports.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 5 Enable inband DCN on ports.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 6 Create NEs using the search method on the NMS.
The searched area is the network segment 192.168.7.0.
In normal cases, all NEs can be created on the NMS.
----End
1.6 Configuration Example (L2 DCN Solution with
Different Network Segments)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure the L2 DCN solution based on
network conditions. In this example, all NEs belong to the same L2 DCN subnet and
communicate with the NMS through the L2 network.
1.6.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
As shown in Figure 1-8, RTN 300 NEs independently form a network and need to be
managed by the U2000 in a unified manner. On this network:
The NEs are connected using the L2 DCN solution. Their IP addresses are not in the same
network segment as the U2000 IP address.
Figure 1-8 Networking diagram for the L2 DCN solution
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
1.6.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring the L2 DCN solution.
Data Preparation
Data Value in This Planning
Example Guidelines
NE ID and IP address See the following l Set a unique NE
figure. ID and IP
address for each
NE.
l For a gateway
NE that
communicates
with the NMS
through an NMS
port, set IP and
Subnet Mask
according to the
external DCN
plan.
l For a gateway
NE, set Gateway
IP Address to
the IP address of
the router.
l The IP addresses
of NEs in the
same L2 DCN
subnet do not
belong to the
same network
segment.
Inband DCN VLAN ID and The default VLAN The same VLAN ID
bandwidth ID is 4094 and the must be used for
default bandwidth is inband DCN
1024 kbit/s. communication over
the entire network.
DCC protocol type L2DCN -
RSTP status Enabled (default -
value)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Data Value in This Planning
Example Guidelines
Access control Access control is -
disabled at the
inband DCN-
enabled ports in the
L2 DCN.
Figure 1-9 NE IDs and IP addresses
Procedure
Step 1 Change NE IDs.
NE2 is used as an example.
Step 2 Set NE communication parameters.
NE1 is used as an example.
NOTE
Set Gateway IP Address when the L2 DCN solution involves different network segments.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 3 Configure DCCs.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 4 Disable access control at NE ports.
NE2 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
Step 5 Enable inband DCN on ports.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 6 Create NEs using the search method on the NMS.
The searched area is the network segment 10.68.40.80.
In normal cases, all NEs can be created on the NMS.
----End
1.7 Configuration Example (NE Anti-Theft Solution)
This section provides an example of how to configure NE anti-theft.
1.7.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
As shown in Figure 1-10, one hop of microwave links are managed by the U2000 and the NE
anti-theft function must be enabled.
Figure 1-10 Network Diagram
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
1.7.2 Configuration Procedure
This section provides an example of how to configure NE anti-theft.
Data Preparation
Table 1-4 Data prepared for NE anti-theft
Item Value in This Example
Anti-theft State Enabled
Control Policy Configuration
Procedure
Step 1 Generate a pair of public and private keys.
Step 2 Configure NE anti-theft.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 1 Network Management Features
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
2 Ethernet features
About This Chapter
This section describes the Ethernet features.
2.1 Configuration Process (QinQ-based E-Line Services)
Before configure QinQ-based E-Line services, delete the default 802.1d-bridge based E-LAN
services.
2.2 Configuration Process (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service)
Before you configure an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service, delete the IEEE 802.1D
bridge-based E-LAN service that is configured by default.
2.3 Configuration Procedure (MSTP)
To use the MSTP protocol, you need to configure the port group, set the bridge parameters
and CIST parameters, and then enable the MSTP protocol.
2.4 Configuration Process (QoS/HQoS)
Configure QoS/HQoS policies, and then apply them to quality of service (QoS/HQoS)
objects.
2.5 Configuration Process (Ethernet Service OAM)
When you use the Ethernet service OAM function, you need to define appropriate OAM
maintenance points according to the actual situation and then perform OAM operations as
required.
2.6 Configuration Process (Ethernet Port OAM)
When using the Ethernet port OAM function, select OAM operations as required.
2.7 Configuration Process (Bandwidth Notification)
When bandwidth notification is used, an egress maintenance end point (MEP) that matches
the MEP on the interconnected router must be created on the microwave equipment.
2.8 Configuration Process (ERPS on a Single-ring Network)
The key to configuring Ethernet ring protection switching (ERPS) for an Ethernet ring
network is creating Ethernet ring protection (ERP) instances. ERPS V1 or ERPS V2 can be
deployed on a single-ring network to protect Ethernet services. ERPS V1 is used as an
example here.
2.9 Configuration Example (QinQ-based E-Line Services)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure QinQ-based E-Line
services according to network conditions.
2.10 Configuration Example (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based
E-LAN service based on network conditions.
2.11 Configuration Example (MSTP)
This topic uses an example to describe how to plan and configure the MSTP according to the
conditions of the network.
2.12 Configuration Example (QoS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure QoS based on network
conditions.
2.13 Configuration Example (HQoS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure HQoS according to
network conditions.
2.14 Configuration Example (Ethernet Service OAM)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure Ethernet service OAM based
on network conditions.
2.15 Configuration Example (Ethernet Port OAM)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure Ethernet port OAM.
2.16 Configuration Example (Bandwidth Notification)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure bandwidth notification based
on network conditions.
2.17 Configuration Example (ERPS on a Single-ring Network)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure Ethernet ring protection
switching (ERPS) for a single-ring network based on network conditions.
2.1 Configuration Process (QinQ-based E-Line Services)
Before configure QinQ-based E-Line services, delete the default 802.1d-bridge based E-LAN
services.
Flowchart
Figure 2-1 shows the flowchart for configuring QinQ-based E-Line services.
Figure 2-1 Flowchart for configuring QinQ-based E-Line services
Required Start
Optional
Delete an E-LAN service
Configuring QinQ-based
E-Line services
End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
NOTE
For the RTN 320, RTN 380A or RTN 380H, no E-LAN service is configured by default. Therefore, the step
of deleting E-LAN services is not required for the RTN 320 or RTN 380H.
The steps in the flowchart are described as follows.
Configuring QinQ-based E-Line Services
Table 2-1 Configuring QinQ-based E-Line services
Operation Remarks
5.3.31 Deleting an E-LAN Service Required when an NE is being
initially configured.
NOTE
By default, RTN 310, RTN 380, or RTN
360 is configured with an IEEE 802.1D
bridge-based E-LAN service, which is
mounted to the Ethernet ports and
microwave port on the RTN 300 NE.
Before configuring NNI port or UNI port
attributes, delete the service. If you do not
delete the service, Encapsulation Type
cannot be configured for the port.
5.3.22 Configuring an E-Line Service Carried Required.
by QinQ
2.2 Configuration Process (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-
LAN Service)
Before you configure an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service, delete the IEEE 802.1D
bridge-based E-LAN service that is configured by default.
Flowchart
Figure 2-2 shows the flowchart for configuring an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN
service.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-2 Flowchart for configuring an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service
Required Start
Optional
Delete the existing E-LAN
service.
Create an IEEE 802.1ad
bridge-based E-LAN service.
End
NOTE
For the RTN 320, RTN 380A or RTN 380H, no E-LAN service is configured by default. Therefore, the step
of deleting E-LAN services is not required for the RTN 320 or RTN 380H.
The operations in the configuration flowchart are described as follows.
Process
Table 2-2 Process of configuring an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service
Operation Remarks
5.3.31 Deleting an E-LAN Service Required when an NE is being initially
configured.
NOTE
By default, RTN 310, RTN 380, and RTN 360 are
configured with an IEEE 802.1D bridge-based E-LAN
service, which is mounted to all Ethernet ports and
microwave ports on the NEs. Before configuring
NNI/UNI attributes, delete the service. Otherwise,
Encapsulation Type of the NNI/UNI cannot be
changed.
5.3.23 Configuring an IEEE 802.1ad Required.
Bridge-based E-LAN Service
2.3 Configuration Procedure (MSTP)
To use the MSTP protocol, you need to configure the port group, set the bridge parameters
and CIST parameters, and then enable the MSTP protocol.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support MSTP.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-3 Flowchart for configuring MSTP
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support MSTP.
Table 2-3 Procedure for configuring the MSTP
Step Operation Description
1 5.3.28 Creating an Required when you need to configure the MSTP.
MSTP Port Group
2 5.3.29 Setting MSTP Optional.
Bridge Parameters Use the default value unless otherwise specified.
3 5.3.30 Setting CIST Optional.
Parameters Use the default value unless otherwise specified.
2.4 Configuration Process (QoS/HQoS)
Configure QoS/HQoS policies, and then apply them to quality of service (QoS/HQoS)
objects.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-4 Flowchart for configuring QoS/HQoS
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Table 2-4 Process of configuring QoS
Ste Operation Remarks
p
1 5.3.32 Modifying the Required if the default mapping for the DiffServ
Mapping for a DS Domain (DS) domain is inapplicable.
2 5.3.33 Changing the Ports Required if the priority type of an Ethernet service is
Applied to a DS Domain not CVLAN, which is the default packet type trusted
and Their Trusted Packet by ports in the DS domain.
Types
3 5.3.34 Enabling/Disabling If DSCP-based DiffServ is enabled and if you do not
DSCP Demapping at an want the DSCP values to be changed by demapping
Egress Port at egress ports, you can disable DSCP demapping.
4 5.3.36 Configuring a Flow Required if CAR or ACL needs to be configured for
Based on the Port Policy a flow received through the port with access control
enabled, or the flow needs to be mapped to a
specified PHB class.
5 5.3.35 Setting Egress Required if a port is required to schedule traffic
Queue Scheduling Policies according to a specified queue scheduling policy
when traffic congestion occurs. The default queue
scheduling policy is SP+WRR (SP is short for strict
priority and WRR for weighted round robin). AF1 to
AF4 queues are WRR queues (allocated the same
weight) and the other queues are SP queues.
6 5.3.38 Setting Traffic Required if the bandwidth for egress port queues
Shaping for Egress Queues needs to be restricted.
7 5.3.39 Setting the Required if WRED needs to be applied on an egress
Congestion Management port queue.
Mode for Egress Queues
8 5.3.37 Configuring Port Required if the bandwidth in the egress direction of a
Shaping port needs to be restricted.
9 5.3.40 Creating a Service Required if the service WRED policy needs to be
WRED Policy created.
5.3.41 Configuring a V- Required if queue scheduling and shaping policies
UNI Egress Policy need to be created for V-UNI egress queues, and
WRR and discarding policies need to be specified.
10 5.3.42 Configuring a V- Required if a V-UNI group needs to be created and
UNI Group bandwidth limitations need to be specified for the V-
UNI group.
11 5.3.44 Configuring a QinQ Required if queue scheduling and shaping policies
Policy need to be created for QinQ queues, and WRR and
discarding policies need to be specified.
12 5.3.45 Applying Policies Required if QinQ or V-UNI egress policies need to
be applied to services.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Ste Operation Remarks
p
13 5.3.48 Configuring QinQ Required if QinQ link bandwidth limitations need to
Link Bandwidth be specified for QinQ services.
Limitations
2.5 Configuration Process (Ethernet Service OAM)
When you use the Ethernet service OAM function, you need to define appropriate OAM
maintenance points according to the actual situation and then perform OAM operations as
required.
Figure 2-5 Flowchart for configuring Ethernet Service OAM
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Table 2-5 Procedure for configuring Ethernet service OAM
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.3.49 Creating an MD Required for NEs on which two Ethernet
ports involved in a service test are located.
Set parameters as follows:
l Set Maintenance Domain Name and
Maintenance Domain Level to the
same at both ends.
l To test Ethernet services between two
edge NEs, set Maintenance Domain
Level to the default value 4. To test
Ethernet services between two
intermediate NEs, set Maintenance
Domain Level to a value less than 4.
2 5.3.50 Creating an MA Required for NEs on which two Ethernet
ports involved in a service test are located.
Set parameters as follows:
l Set Maintenance Domain Name to the
same value as Maintenance Domain
Name from the previous step.
l Set Maintenance Association Name to
the same at both ends.
l Set Relevant Service to the same at
both ends.
l Set CC Test Transmit Period to 1s.
3 5.3.51 Creating an MEP Required for NEs on which two Ethernet
ports involved in a service test are located.
Set parameters as follows:
l Set Maintenance Association Name to
the same value as Maintenance
Association Name from the previous
step.
l Set Port to the Ethernet port that is
involved in the service test.
l Set MEP ID to different values for
MEPs in the same MD.
l If the OAM flow initiated by an MEP
passes the packet switching unit on the
local NE, set Direction to Ingress. If
the OAM flow initiated by an MEP
does not pass the packet switching unit
on the local NE, set Direction to
Egress.
l Set CC Status to Active because an
MEP ID in an LB test identifies the
sink MEP.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step Operation Remarks
4 5.3.52 Creating a Remote MEP in Required for NE on which Ethernet ports
an MA involved in OAM operations are located.
Set parameters as follows:
l Set Maintenance Domain Name to the
same value as Maintenance Domain
Name from the previous step.
l Set Maintenance Association Name to
the same value as Maintenance
Association Name from the previous
step.
l To ensure that an MEP can respond to
OAM operations initiated by the other
MEP in the same MA, configure the
other MEPs as remote MEPs.
NOTE
If two MEPs are on the same NE, you do not
need to configure the remote MEPs.
5 5.3.53 Creating an MIP Required when you need to perform LT
tests and divide the faulty part into sections
l Set Maintenance Domain Name to the
value of Maintenance Domain Name
that is set in the first step.
l Set Board and Port to the board and
port through which the Ethernet service
passes.
l In the same MA, the value of MIP ID
must be unique.
6 5.3.54 Performing a CC Test Required when you need to perform a CC
test.
5.3.55 Performing an LB Test Required when you need to perform an LB
test.
5.3.56 Performing an LT Test Required when you need to perform an LT
test.
5.3.57 Activating AIS Required when the AIS function needs to
be activated at an MP.
If several MDs exist on a link, you can
locate a fault accurately by setting AIS
Status and setting Client Layer Level for
suppressing AIS information. After an MP
with AIS activated detects a fault, the MP
sends an AIS packet to notify the upper
level MP of this fault.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step Operation Remarks
5.3.58 Checking the Packet Loss Required when you need to perform an
Ratio, Delay, or Delay Variation of LM, DM, or VM test.
Ethernet Services
2.6 Configuration Process (Ethernet Port OAM)
When using the Ethernet port OAM function, select OAM operations as required.
Figure 2-6 Flowchart for configuring Ethernet Port OAM
Table 2-6 Process for configuring Ethernet port OAM
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.3.59 Enabling OAM Auto- Required. Set parameters as follows:
discovery l Set Enable OAM Protocol to
Enabled.
l Set OAM Working Mode to Active
for the NE that initiates a discovery.
The default value is Active.
2 Monitoring 5.3.60 Enabling Link Optional.
link Event Notification Set Link Event Notification to
performance Enabled if the opposite NE must be
informed of faults or performance-
threshold-crossing events that have
been detected.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step Operation Remarks
5.3.61 Changing the Optional.
OAM Error Frame Perform this operation to adjust
Monitoring performance thresholds.
Threshold
Performing a 5.3.62 Performing a Optional.
remote Remote Loopback Set Remote Side Loopback Response
loopback to Enabled to perform a remote
loopback.
3 Performing 5.3.63 Enabling Local Optional.
local Loopback Detection Set Loopback Check to Enabled to
loopback perform local loopback detection for a
detection port.
NOTE
Skip steps 1 and 2 for local loopback
detection.
The negotiation types of the port can't be
Half Duplex .
2.7 Configuration Process (Bandwidth Notification)
When bandwidth notification is used, an egress maintenance end point (MEP) that matches
the MEP on the interconnected router must be created on the microwave equipment.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-7 Flowchart for Bandwidth Notification
Table 2-7 Process of configuring bandwidth notification
Step Operation Description
1 5.3.49 Creating an Required. Set parameters as follows:
MD l Set theMaintenance Domain Name
andMaintenance Domain Level consistently on
the microwave equipment and interconnected
router.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step Operation Description
2 5.3.50 Creating an Required. Set parameters as follows:
MA l SetMaintenance Domain Name to the
Maintenance Domain Nameconfigured in step 1.
l Set Maintenance Association Nameconsistently
on the microwave equipment and interconnected
router.
3 5.3.51 Creating an Required. Set parameters as follows:
MEP l SetMaintenance Association Name to
theMaintenance Association Name configured in
step 2.
l SetPort to a microwave port.
l Set VLAN IDto the VLAN ID configured on the
interconnected router.
l SetMEP ID to a unique value in a maintenance
association (MA).
l Set Direction to Egress.
4 5.3.65 Configuring Required. Set parameters as follows:
Bandwidth l Set Advertisement to Enable.
Notification
l Set Client Layer Level to be the same as that of
the MEP on the router, which is higher than or
equal to that of the local MEP.
2.8 Configuration Process (ERPS on a Single-ring
Network)
The key to configuring Ethernet ring protection switching (ERPS) for an Ethernet ring
network is creating Ethernet ring protection (ERP) instances. ERPS V1 or ERPS V2 can be
deployed on a single-ring network to protect Ethernet services. ERPS V1 is used as an
example here.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-8 Configuration procedure (ERPS on a single-ring network)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Table 2-8 Flow for configuring ERPS
Proc Operation Remarks
edur
e
1 5.3.13 Creating an ERPS Instance Required. Set parameters as follows:
l Set ERPS ID, East Port, West
Port, RPL Owner Ring Node
Flag, RPL Port, and Control
VLAN according to the network
plan.
l Pay attention to the following
when configuring RPL Owner
Ring Node Flag:
– An ERPS ring has only one
ring protection link (RPL)
owner node.
– In an ERPS V1 protection
instance, set RPL Owner
Ring Node Flag to RPL Port
for RPL owner nodes on the
ERPS ring and to None for
the non-RPL owner nodes.
l Set Control VLAN to a value
different from VLAN IDs of
Ethernet service packets.
2 Setting Protocol Parameters for an ERPS Required when you need to
Instance configure ERPS V1
Set Compatible_Version to ver1.
3 5.3.14 Setting Global ERPS Protocol Required. It is recommended that
Parameters you set parameters to default or
planned values.
2.9 Configuration Example (QinQ-based E-Line Services)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure QinQ-based E-Line
services according to network conditions.
2.9.1 Networking Diagram
The section describes the networking of NEs.
Configure QinQ-based E-Line services according to the requirements listed in Table 2-9.
Figure 2-9 shows the networking diagram.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Table 2-9 Service requirements
Requirement Description Requirement Satisfaction
Servic l Configure a port working in NE 4 and NE 2 provide electrical P&E ports for
e auto-negotiation mode for receiving services.
access receiving a channel of
capaci electrical GE signals from
ty NodeB 1.
l Configure a port working in
auto-negotiation mode for
receiving a channel of
electrical GE signals from
RAN 1.
Servic No
e
protec
tion
QinQ l Add the S-VLAN 100 label l Configure QinQ-based UNI-NNI services on
Servic to all service packets from NE4 and set the S-VLAN ID to 100. S-
e Node B 1 on NE4. VLAN IDs are used to separate services on
separa l Convert the S-VLAN ID of radio links.
tion 100 to the S-VLAN ID of l Configure QinQ-based UNI-UNI services on
200 for the packets from NE2. Set the S-VLAN ID to 100 and 200 for
NodeB 1 on NE2, to the GE(o) and the IF interface respectively,
prevent conflicts of the S- to implement S-VLAN switching.
VLAN ID with that of RAN
1.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-9 Networking diagram for QinQ-based E-Line services
2.9.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring QinQ-based E-Line services.
Data Preparation
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Procedure
Step 1 Delete an E-LAN service.
NOTE
For the RTN 320, RTN 380A or RTN 380H, no E-LAN service is configured by default. Therefore, the step
of deleting E-LAN services is not required for the RTN 320 or RTN 380H.
Step 2 Create a QinQ-based link on NE4 to carry the UNI-NNI E-Line services.
Step 3 Create QinQ-based link on NE3 and NE2 to carry the UNI-UNI E-Line services.
NE3 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
----End
2.10 Configuration Example (IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-
LAN Service)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based
E-LAN service based on network conditions.
2.10.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
An IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service needs to be configured according to the
requirements listed in Table 2-10. Figure 2-10 shows the networking diagram.
Table 2-10 Requirements
Requirement Description Requirement Satisfaction
Servic The transport network needs to NE4 and NE2 provide P&E electrical ports for
e implement backhaul for one service access.
access channel of GE electrical
capaci signals from RAN 1 and one
ty channel of GE electrical
signals from RAN 2. The port
working mode is auto-
negotiation.
Servic Not required. -
e
protec
tion
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Requirement Description Requirement Satisfaction
Servic l All service packets from l An IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN
e RAN 1 and RAN 2 are service is created on NE1 to NE4.
requir encapsulated with the S- l Packets from RAN1 are encapsulated with
ement VLAN ID 200 and S- the S-VLAN ID 200 at the P&E port of
s VLAN ID 100, NE2. Packets from RAN2 are encapsulated
respectively. with the S-VLAN ID 100 at the P&E port of
l Packets are forwarded NE4.
based on MAC addresses.
Figure 2-10 Networking diagram for an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service
NMS
RNC
LAN
switch
Regional
RAN 2 Backhaul
Network
GE(o) GE(o) P&E
P&E
P&E
NE4 NE3 NE2 NE1
RAN 1 Radio link Ethernet link
2.10.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN
service.
Data Preparation
Data Value in This Example Planning Guidelines
Tag Type S-Aware Set this parameter to S-
Aware for all IEEE 802.1ad
bridges.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Data Value in This Example Planning Guidelines
Ports mounted to a bridge See the following figure. -
l Set Encapsulation Type
to NULL for UNIs.
l Set Encapsulation Type
to QinQ for NNIs.
NMS
RNC
NNI: IF (SVLAN ID: 100) LAN
NNI: GE(o) (SVLAN ID: 100)
switch
NNI: GE(o) (SVLAN ID: 100) Regional
UNI: P&E (SVLAN ID: 100) UNI: P&E(SVLAN ID: 200) Backhaul
NNI: IF;(SVLAN ID: 100) NNI: IF (SVLAN ID: 100,200) Network
P&E GE(o) GE(o) P&E
RAN 2
P&E
NE4 NE3 NE2 NE1
UNI: P&E(SVLAN ID: 100,200)
NNI: IF (SVLAN ID: 100,200)
RAN 1 Radio link Ethernet link
Procedure
Step 1 Delete the existing E-LAN service.
NE2 is used as an example.
NOTE
The step of deleting E-LAN services is not required for the RTN 320, RTN 380A or RTN 380H.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 2 Configure an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service.
NE2 is used as an example.
----End
2.11 Configuration Example (MSTP)
This topic uses an example to describe how to plan and configure the MSTP according to the
conditions of the network.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support MSTP.
2.11.1 Networking Diagram
This topic describes the networking information about the NEs.
As shown in Figure 2-11, LAN switch 1 and LAN switch 2 are two Ethernet switches that run
the MSTP protocola. Suppose that NE1 to NE4 are RTN 380s.
After the port group is configured for NE1, NE1 runs the MSTP protocol together with LAN
switch 1 and LAN switch 2 on the access side, considering LAN switch 1 as the root. In this
manner, no loops will be generated on the network on the access side and the protection for
the network is realized.
NOTE
a: The RTN 380 supports only the MSTP that generates the CIST.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-11 Networking diagram
2.11.2 Configuration Process
This topic describes the procedure for the data configuration.
Data Planning
Figure 2-12 MSTP protocol parameters
NOTE
In this example, create an MSTP port group. The CIST parameters and bridge parameters uses the
default value.
Procedure
Step 1 Create an MSTP port group.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
----End
2.12 Configuration Example (QoS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure QoS based on network
conditions.
2.12.1 Networking Diagram
The section describes the networking of NEs.
The microwave network shown in Figure 2-13 has the following quality of service (QoS)
requirements:
l Different services including VoIP, video, and data services of the same NodeB are
identified by VLAN priority values. Each service requires a committed bandwidth.
l Use the WRED algorithm to first discard services with the bandwidth higher than the
limited bandwidth.
Figure 2-13 Networking diagram
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
2.12.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring quality of service (QoS).
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example Planning Guideline
DiffServ mapping Use the default DiffServ If the default DiffServ
mapping. mapping meets the
requirements, a new
DiffServ domain is not
required and consequently
networkwide QoS
configuration workload is
reduced.
Bandwidth limitation See Figure 2-14 Different types of services
of the same NodeB have
their bandwidths guaranteed
using bandwidth limitation.
Egress queue scheduling Figure 2-15 shows the -
policy queue scheduling policies
for the egress port.
Congestion avoidance In this example, the service -
WRED policy for egress
queues has an ID of 1 and is
named PW_WRED. For
details, see Figure 2-15
Figure 2-14 Bandwidth limitation
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-15 Queue scheduling policy and congestion avoidance
Procedure
Step 1 The default DiffServ mapping complies with the network planning requirements and therefore
does not need to be modified.
Step 2 Creat traffic classification
VoIP is used for example:
Step 3 Set the congestion management mode for egress queues.
EF is used for example:
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
----End
2.13 Configuration Example (HQoS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure HQoS according to
network conditions.
2.13.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
The microwave network shown in Figure 2-16 has the following hierarchical quality of
service (HQoS) requirements:
l Services on NodeB1 must be isolated from those on NodeB2, and the service bandwidth
must be guaranteed.
l Different services including VoIP, video, and data services from/to the same NodeB are
identified by VLAN priority. Each service requires a committed bandwidth.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-16 Networking diagram
2.13.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring hierarchical quality of service (HQoS).
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example Planning Guideline
DiffServ mapping Default DiffServ mapping If the mapping defined
for the default DiffServ
domain meets
requirements, creating
another DiffServ
domain is not required.
This minimizes the
workload for
configuring network-
wide QoS.
Bandwidth limitation See Figure 2-17. Bandwidth limitations
guarantee the
bandwidth for each
type of service on a
NodeB.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Item Value in This Example Planning Guideline
Egress queue scheduling In this example, the egress queue -
policy scheduling policy is SP+WRR,
as shown in Figure 2-18.
Congestion avoidance In this example, the service -
WRED policy for egress queues
is applied. The policy ID is 3 and
name is WRED. See Figure
2-18.
Figure 2-17 Bandwidth limitation
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-18 Queue scheduling policy and congestion avoidance
Procedure
Step 1 The default DiffServ mapping complies with the network planning requirements and therefore
does not need to be modified.
Step 2 Create WRR policies on NE1 and NE2.
The following uses NE1 as an example:
Step 3 Create service WRED policies on NE1 and NE2.
The following uses NE1 as an example:
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 56
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
----End
2.14 Configuration Example (Ethernet Service OAM)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure Ethernet service OAM based
on network conditions.
2.14.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
Figure 2-19 shows a radio network that transmits backhaul Ethernet services from the NodeB
to the RNC. The radio network is divided into VLANs. VLANs 100 to 109 process services
from the NodeB. After faults occur in VLAN 100, LT tests must be performed to identify the
faults.
The Ethernet service configurations on the NEs on the radio network are as follows:
l On NE1, the VLAN-based E-Line service from the NodeB to NE2 is named NE1toNE2,
with an ID of 1.
l On NE2, the VLAN-based E-Line service from NE1 to NE3 is named NE1toNE3, with
an ID of 1.
l On NE3, the VLAN-based E-Line service from NE2 to NE4 is named NE2toNE4, with
an ID of 1.
l On NE4, the VLAN-based E-Line service from NE3 to the RNC is named NE3toNE4,
with an ID of 1.
Figure 2-19 Networking diagram for Ethernet service OAM
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 57
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
2.14.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring Ethernet service OAM.
Data Preparation
Table 2-11 OAM plan information
Data Value in This Example Planning Guidelines
For the information about the -
maintenance domain (MD),
maintenance association (MA), and
maintenance points (MPs), see
OAM configuration information Figure 2-20.
LT test information In this example, an LT test is used
to verify OAM.
Other parameters Retain the default values.
Figure 2-20 OAM plan information
Service:1–NE1toNE2 Service:1–NE1toNE3 Service:1–NE2toNE4 Service : 1–NE3toNE4
NE1 NE2 NE3 NE4
IF P&E(GE1) IF
P&E IF IF P&E
P&E(GE1)
MEP1 MIP3 MIP4 MIP5 MIP6 MIP7 MIP8 MEP2
MD Name:MD1
MA Name:MA1
VLAN ID:100
Procedure
Step 1 Create an MD on NE1, NE2, NE3, and NE4.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 58
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 2 Create an MA on NE1, NE2, NE3, and NE4.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 3 Create maintenance association end points (MEPs) on NE1 and NE4.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 59
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 4 Create remote MEPs on NE1 and NE4.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 5 Create maintenance association intermediate points (MIPs) on NE1, NE2, NE3, and NE4.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 6 Start an LT test on NE1.
The LT test takes the MEP whose ID is 1 as the source end and the MEP whose ID is 2 as the
sink end.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 60
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
In normal cases, all the MPs on the link under an LT test respond to LTM frames. If any fault
occurs, locate the fault based on the test result.
l If LossRate in Detection Result is 0, the test is successful.
l If LossRate in Detection Result is not 0, the test has failed. The possible causes are as
follows.
Cause Troubleshooting Procedure
Connection time-out at the peer end Check whether services are interrupted in
the service path.
Packet loss Check whether service traffic is higher
than the transmission bandwidth.
Check the link for bit errors.
----End
2.15 Configuration Example (Ethernet Port OAM)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure Ethernet port OAM.
2.15.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
Ethernet port OAM focuses on the maintenance of point-to-point Ethernet links between two
sets of equipment that are directly connected to each other, but does not focus on specific
services. If equipment supports the IEEE 802.3ah OAM protocol, OAM auto-discovery is
performed after the IEEE 802.3ah OAM protocol is enabled on the interconnected ports. After
OAM auto-discovery is successful, you can perform OAM operations as required.
As shown in Figure 2-21, to monitor the performance of the GE link between NE1 and NE2,
enable Ethernet port OAM.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 61
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-21 Networking diagram for Ethernet port OAM
2.15.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring Ethernet port OAM. The configurations
on NE1 and NE2 are the same. This section uses the configuration on NE1 as an example.
Data Preparation
Table 2-12 OAM plan information
Data Value in This Example Planning Guidelines
Enable OAM auto-discovery for l Only the active end can initiate
NE1 and NE2 and set their an auto-discovery or remote
working modes to active. loopback. The OAM mode can
be set to active at both ends, or
active at one end and passive at
the other end. Note that the
OAM mode cannot be set to
passive at both ends.
l You do no need to enable OAM
auto-discovery in a local
OAM auto-discovery loopback detection test.
OAM operation In this example, the link The OAM error frame monitoring
performance monitoring function is threshold is a standard for OAM to
used to monitor bit errors on the check link performance. Generally,
link. The window values and the default value is used. You can
threshold values for link change the value according to the
performance events take default actual link status.
values.
Procedure
Step 1 Enable OAM auto-discovery for the P&E ports of NE1 and NE2.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 62
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 2 Enable link event notification for the P&E ports of NE1 and NE2.
NE1 is used as an example.
----End
2.16 Configuration Example (Bandwidth Notification)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure bandwidth notification based
on network conditions.
2.16.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
l A microwave link is configured between NE1 and NE2. NE2 is connected to a router.
l Bandwidth notification needs to be configured so that the router can be informed of air
interface bandwidth changes and perform the QoS function accordingly.
Figure 2-22 Networking diagram for bandwidth notification
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 63
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
2.16.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring bandwidth notification.
Data Preparation
Table 2-13 Data plan
Item Parameter Value
MD configuration Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Domain Level 4
MA configuration Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Relevant Service 1-NE1ToNE2
CC Test Transmit Period 1s
MEP configuration Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Board 1-DMC5
Port 1-DMC5-1(IF1)
VLAN 3
MEP ID 1
Direction Egress
CC Status Active
Client Layer Level 4
Bandwidth notification Maintenance Domain Name MD1
configuration
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 64
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Item Parameter Value
MEP ID 1
Advertisement Enable
Client Layer Level 7
Periodic Period
Periodic(s) 1
Hold Time(s) 0
NOTE
The table lists only microwave equipment configurations. For configurations of the interconnected
equipment, see the corresponding product documentation.
Procedure
Step 1 Create an MD.
NE2 is used as an example.
Step 2 Create an MA.
NE2 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 65
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 3 Create an MEP.
NE2 is used as an example.
Step 4 Configure bandwidth notification.
NE2 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 66
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
----End
2.17 Configuration Example (ERPS on a Single-ring
Network)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure Ethernet ring protection
switching (ERPS) for a single-ring network based on network conditions.
2.17.1 Networking Diagram
This topic describes the networking information about the NEs.
As shown in Figure 2-23, NE1, NE2, NE3, and NE4 construct a Hybrid microwave ring
network. The ERPS is configured to protect the Ethernet services on the ring network.
Generally, when a Hybrid microwave ring network is configured with the ERPS, the RPL
owner node (NE1) blocks the west RPL ports and all the services are transmitted through east
RPL ports. If a link on the ring network fails or an NE on the ring network becomes faulty,
NE1 enables the blocked west RPL ports so that the services can be transmitted through these
west RPL ports.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 67
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Figure 2-23 Networking diagram
2.17.2 Configuration Procedure
During the configuration, all other Ethernet ring protection switching (ERPS) parameters take
default values except the parameters whose values are already specified in the plan.
Data Preparation
Table 2-14 ERPS plan
Item Value in This Example
ERPS ID 1
East Port 1–MXUF4–1(IF)
West Port 1–MXUF4–5(GE(e))
ERP Ring Node Flag RPL Port
Flag Port 1–MXUF4–1(IF)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 68
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Item Value in This Example
Revertive Mode Revertive
Control VLAN 4093
Destination Node 01-19-A7-00-00-01
Loop Detect Enabled
Compatible_Version ver1
Hold-Off Time (ms) 0
WTR Time (mm:ss) 05:00
Guard Time (ms) 500
Packet Transmit Interval(s) 5
Entity Level 4
Procedure
Step 1 Create ERP instances.
NE1 is used as an example.
Step 2 Set protocol parameters for an ERPS instance.
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 69
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 2 Ethernet features
Step 3 Set global ERPS protocol parameters.
NE1 is used as an example.
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 70
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
3 Configuring Clock Features
About This Chapter
This topic provides hyperlinks to configuration processes and configuration examples of
various clock features.
3.1 Configuration Process(IEEE 1588v2)
This section describes the process of configuring the PTP clock attributes and IEEE 1588v2
attribute of IF ports.
3.2 Configuration Process (ITU-T G.8275.1)
If using the ITU-T G.8275.1 protocol to implement time synchronization, all NEs must work
in telecom boundary clock (T-BC) mode.
3.3 Configuration Example (Networkwide Time Synchronization)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure IEEE 1588v2 networkwide
time synchronization based on network conditions.
3.4 Configuration Example (Transparent Transmission of Time Signals)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure transparent transmission of
IEEE 1588v2 time signals based on network conditions.
3.5 Configuration Example (ITU-T G.8275.1)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure ITU-T G.8275.1-compliant
time synchronization based on network conditions.
3.1 Configuration Process(IEEE 1588v2)
This section describes the process of configuring the PTP clock attributes and IEEE 1588v2
attribute of IF ports.
l PTP clock attributes determine how the PTP clock of an NE works. PTP clock attributes
include the PTP NE attribute, system clock, port attribute, clock subnet, and BMC
algorithm parameters.
l PTP messages are transmitted as services when IEEE 1588v2 time signals are
transparently transmitted. Ethernet services must be configured correctly to guarantee
PTP message transmission.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 71
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Figure 3-1 Flowchart for configuring 1588v2
Time Synchronization Transparent Time Transmission
Required Start Start
Optical
Setting the PTP NE Attributes Setting the PTP NE Attributes
Creating a PTP Clock Port Querying or Modifying the
PTP System Time
Setting PTP Clock Port
Attributes Creating a PTP Clock Port
Setting Parameters for IEEE Setting PTP Clock Port
1588v2 Clock Packets Attributes
Configuring the Delay Offset Setting Parameters for IEEE
for Asymmetric Transmission 1588v2 Clock Packets
Between NEs
Configuring the Delay Offset
End for Asymmetric Transmission
Between NEs
Modifying the BMC Algorithm
Parameters for an NE Clock
Configuring Ethernet Services
End
Table 3-1 Process of configuring IEEE 1588v2 time synchronization
Operation Remarks
5.8.3 Setting the PTP NE Required.
Attributes
5.8.4 Creating a PTP Clock Port Required.
5.8.5 Setting PTP Clock Port Optional.
Attributes Every PTP port must have its attributes configured.
NOTE
Enable IEEE-1588 Timeslot is automatically enabled
after RTP ports are created. Therefore, it does not need to
be enabled separately.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 72
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Operation Remarks
5.8.6 Setting Parameters Clock Optional.
Packets Every PTP port must have its PTP message
parameters configured.
5.8.7 Configuring the Delay Offset Optional.
for Asymmetric Transmission
Between NEs
Table 3-2 Process of configuring transparent time transmission
Operation Remarks
5.8.3 Setting the PTP NE Required.
Attributes
5.8.1 Querying or Modifying the Required for the upstream NE of each microwave link
PTP System Time hop.
5.8.4 Creating a PTP Clock Port Required.
5.8.5 Setting PTP Clock Port Required.
Attributes Every PTP port must have its attributes configured.
NOTE
Enable IEEE-1588 Timeslot is automatically enabled after
RTP ports are created. Therefore, it does not need to be
enabled separately.
5.8.6 Setting Parameters Clock Optional.
Packets Every PTP port must have its PTP message
parameters configured.
5.8.7 Configuring the Delay Optional.
Offset for Asymmetric
Transmission Between NEs
5.8.8 Modifying the BMC Required for the Grandmaster clock NE.
Algorithm Parameters for an
NE Clock
Configuring Ethernet Services Required, when 1588v2 clock packets are the
independent service packets.
1588v2 packets are transparently transmitted as
independent service packets. Ethernet services need to
be created to transmit them. You can create E-Line or
E-LAN services based on the network topology. If
VLAN IDs are configured for PTP packets, ensure the
packets can be forwarded correctly.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 73
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Table 3-3 Planning principles for important parameters
Parameter Plan
NE clock type l If only one PTP port is required, set NE Clock Type to OC.
l If the NE is used for networkwide synchronization and multiple
PTP ports are required, set NE Clock Type to BC.
l If IEEE 1588v2 time signals need to be transparently transmitted
only between Ethernet ports, set this parameter to TC.
l If IEEE 1588v2 time signals need to be transparently transmitted
across a microwave link, set NE Clock Type to TC+BC.
l If both time synchronization and transparent transmission of
IEEE 1588v2 time signals are required, set NE Clock Type to
TC+BC.
PTP time Time synchronization can be achieved only when PTP Time
adjustment Adjustment is set to Enabled.
Default: Enabled.
PTP clock port l When NE Clock Type is set to OC, only one PTP port can be
attributes created.
l When NE Clock Type is set to BC, multiple PTP ports working
in BC mode can be created.
l When Work Mode is TC, the Ethernet port can be created as a
PTP port whose working mode is TC.
l When NE Clock Type is set to TC+BC, multiple PTP ports can
be created. In this case, Clock Type of an IF port is always BC
and cannot be changed. Clock Type of an Ethernet port can be
set to TC or BC. A TC port transparently transmits IEEE 1588v2
time messages, and a BC port obtains time synchronization or
externally provides time through IEEE 1588v2 time messages.
For PTP ports whose Work Mode is BC, it is recommended that
Port Status be set to Master+Slave. In this manner, the master-
slave synchronization hierarchy of the PTP network is determined by
the BMC algorithm.
The VLAN IDs of PTP packets must be different from the VLAN
IDs of service packets and inband DCN packets.
PTP Packets l P/E Mode specifies the delay measurement mode of a port. An
Parameters Ethernet port supports the E2E/P2P mode, and an IF port
supports the P2P mode.
l Set the PTP message transmission period. Keep the default value
if it is not planned.
l When NE Clock Type is set to TC or Clock Type of PTP port is
set to TC, the PTP message transmission period cannot be set.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 74
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Parameter Plan
The Delay Offset l When the delays in the receive and transmission directions of a
for Asymmetric PTP link are not equal, set Cable Transmitting Distance to
Transmission compensate for the time difference.
Between NEs l Measure the time difference between an NE and the reference
time source, or the cable length difference between the
transmission direction and the receive direction.
Clock subnet IEEE 1588v2 time synchronization is only applied to the PTP
equipment within the same clock subnet. When a physical PSN
needs to be divided into several clock domains, clock subnets need
to be configured.
l When Clock Type is set to OC or BC, it is recommended that
this parameter take the default value, that is, clock domain ID
being 0.
l When Work Mode is TC+BC, it is recommended that the clock
subnet ID of the NE is different from the ID of the clock subnet
transparently transmitting 1588v2 packets.
l When Clock Type is set to TC, a clock subnet is not required
and cannot be configured.
PTP clock source It is recommended that you set PTP Clock Source Priority 2 to 1
priority and retain the default values for other parameters.
3.2 Configuration Process (ITU-T G.8275.1)
If using the ITU-T G.8275.1 protocol to implement time synchronization, all NEs must work
in telecom boundary clock (T-BC) mode.
l PTP clock attributes determine how the PTP clock of an NE works. PTP clock attributes
include the PTP NE attribute, system clock, port attribute, clock subnet, and BMC
algorithm parameters.
l PTP messages are transmitted as services when G.8275.1 time signals are transparently
transmitted. Ethernet services must be configured correctly to guarantee PTP message
transmission.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 75
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Figure 3-2 Flowchart for configuring G.8275.1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 76
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Table 3-4 Process of configuring G.8275.1 time synchronization
Operation Remarks
5.8.2 Configuring the PTP Profile Required.
NOTE
Set PTP Profile to G.8275.1.
5.8.1 Querying or Modifying the Optional.
PTP System Time l Set the PTP system clock for an NE only
when the NE functions as the grandmaster
clock and uses the local real-time clock as a
timescale.
On the live network, a PTP system clock is
introduced from an external time device.
Manually configuring a PTP system clock is
often for the function test purpose.
l If time calibration is enabled, a system clock
is automatically synchronized with external
time signals or a PTP time source.
5.8.4 Creating a PTP Clock Port Required.
l Only a PTP port can transmit, receive, and
process PTP packets, thereby obtaining and
providing time synchronization information.
l An FE, GE, or IF port can be configured as a
PTP port.
l Multiple PTP ports can be configured on an
NE that works in T-BC mode.
5.8.5 Setting PTP Clock Port Required.
Attributes l Set Not Slave to Disabled.
l It is advised to retain the default values for the
other parameters.
Local Priority indicates the local priority of a
clock source. If this parameter is incorrectly
configured, clock tracing may be incorrect or
even a clock loop is formed. This parameter
can be modified only according to a proper
plan.
NOTE
Enable IEEE-1588 Timeslot is automatically enabled
after RTP ports are created. Therefore, it does not need
to be enabled separately.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 77
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Operation Remarks
5.8.6 Setting Parameters Clock Required.
Packets l It is advised to retain the default values of
PTP packet parameters.
l If necessary, modify PTP packet parameters
according to the network plan and ensure that
they are consistently configured for
interconnected PTP ports.
l If using the ITU-T G.8275.1 protocol, an
Ethernet port supports only the E2E mode. an
IF port supports only the P2P mode.
5.8.7 Configuring the Delay Offset Optional.
for Asymmetric Transmission l When propagation delay of a PTP link in the
Between NEs transmit direction is different from that in the
receive direction, set parameters on Cable
Transmitting Warp parameters to
compensate for the time difference.
l Measure the time difference between an NE
and the reference time source, or the cable
length difference between the transmit
direction and the receive direction. Then,
compensate for the propagation delay on the
cables at associated ports, at both ends of the
PTP link.
l Set Warp Direction. The value Positive
indicates that the receive link distance is
longer than the transmit link distance (that is,
the transmission time over the receive link is
longer than that over the transmit link, and
therefore the PTP time on the slave NE is later
than that on the master NE). The value
Negative indicates that the receive link
distance is shorter than the transmit link
distance (that is, the transmission time over
the receive link is shorter than that over the
transmit link, and therefore the PTP time on
the slave NE is earlier than that on the master
NE).
l Compensation for propagation asymmetry
takes effect only for slave ports.
3.3 Configuration Example (Networkwide Time
Synchronization)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure IEEE 1588v2 networkwide
time synchronization based on network conditions.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 78
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
3.3.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
On the mobile backhaul network as shown in Figure 3-3, the OptiX RTN equipment provides
NodeB 1 and NodeB 2 with service backhaul links, frequency synchronization signals, and
time synchronization signals. The service requirements are as follows:
l At the central site, the BITS provides time signals to the RNC through the 1PPS+ToD
port, and distributes PTP time synchronization information through the FE/GE port.
l The local backhaul network is a network-wide synchronized PTP network.
l The OptiX RTN equipment works in BC mode, achieving PTP time synchronization
with the local backhaul network. The OptiX RTN equipment achieves physical-layer
clock synchronization over microwave or synchronous Ethernet.
l NodeB 1 and NodeB 2 support the IEEE 1588v2 protocol in order to achieve time
synchronization through PTP messages or clock synchronization through synchronous
Ethernet.
Figure 3-3 Networking diagram of IEEE 1588v2 clock
3.3.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring IEEE 1588v2 networkwide time
synchronization.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 79
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Data Planning
Figure 3-4 Diagram of parameter configuration for networkwide IEEE 1588v2 time
synchronization
NOTE
l NE1 is used as an example to describe the parameter plan. The parameter plans for other NEs are
similar.
l "-" indicates that a parameter does not need to be set.
NOTE
NE1 is used as an example. The configuration on other NEs is similar.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the PTP NE attributes for NE1.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 80
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Step 2 Create PTP clock ports, which include IF, P&E and GE(e).
Step 3 Set PTP clock port attributes.
Step 4 Set parameters for IEEE 1588v2 clock packets.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 81
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
----End
3.4 Configuration Example (Transparent Transmission of
Time Signals)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure transparent transmission of
IEEE 1588v2 time signals based on network conditions.
3.4.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
As shown in Figure 3-5, the RTN NEs need to transparently transmit time synchronization
signals from RNCs to NodeBs.
Figure 3-5 Networking diagram of IEEE 1588v2
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 82
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
3.4.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring transparent transmission of IEEE 1588v2
time signals.
Data Planning
This example describes only the PTP service plan for the RTN equipment.
To apply the IEEE 1588v2 transparent transmission, properly plan the PTP clock attributes
and Ethernet services to guarantee PTP message transmission.
Figure 3-6 Diagram of parameter configuration for networkwide IEEE 1588v2 time
synchronization
NOTE
NE1 is used as an example. The configuration on other NEs is similar.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the PTP NE attributes for NE1.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 83
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Step 2 Create PTP clock ports, which include IF and P&E ports.
Step 3 Set PTP clock port attributes.
Step 4 Set P/E Mode to E2E for P&E port.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 84
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Step 5 To configure Ethernet services for PTP messages, see the Configuration Guide. Set the
service VLAN ID to 200.
----End
3.5 Configuration Example (ITU-T G.8275.1)
This section provides an example of how to plan and configure ITU-T G.8275.1-compliant
time synchronization based on network conditions.
3.5.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
On the mobile backhaul network as shown in Figure 3-7, the OptiX RTN equipment provides
NodeB 1 and NodeB 2 with service backhaul links, frequency synchronization signals, and
time synchronization signals. Wherein,
l At the central site, a BITS provides the RNC with time signals through a 1PPS+TOD
port and distributes PTP time synchronization information through a FE/GE port.
l The local backhaul network uses ITU-T G.8275 to implement network-wide PTP time
synchronization.
l The OptiX RTN equipment works in T-BC mode to synchronize with the local backhaul
network and implement PTP time synchronization. The OptiX RTN equipment
implements physical-layer clock synchronization over microwave or synchronous
Ethernet.
l NodeB 1 and NodeB 2 support ITU-T G.8275.1. They implement time synchronization
through PTP packets and frequency synchronization through synchronous Ethernet.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 85
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Figure 3-7 Networking diagram for ITU-T G.8257.1-compliant time synchronization
3.5.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring ITU-T G.8257.1-compliant time
synchronization.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 86
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Data Preparation
Figure 3-8 Diagram of parameter configuration for networkwide G.8275.1 time
synchronization
NOTE
l NE2 is used as an example to describe the parameter plan. The parameter plans for other NEs are
similar.
l "-" indicates that a parameter does not need to be set.
NOTE
NE2 is used as an example. The configuration on other NEs is similar.
Context
Configure NE2 as follows:
1. Set PTP Profile to G.8275.1.
2. Set the microwave, GE1(e), and P&E ports to PTP ports.
3. Configure PTP port attributes according to the following table.
Parameter Value
Step Mode Single step
Reference Clock FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Source No
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 87
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Parameter Value
Not Slave Disabled
Local Priority 128
4. Set PTP packet parameters for PTP ports on an NE in T-BC mode according to the
following table.
Parameter Value
IF Port GE1(e) Port P&E Port
P/E Mode P2P E2E E2E
SYNC Packet 64/1024 8/1024 8/1024
Period(s)
DELAY Packet - 128/1024 128/1024
Period(s)
PDELAY Packet 128/1024 - –
Period(s)
ANNOUNCE 128/1024 128/1024 128/1024
Packet Period(s)
Procedure
Step 1 Specify the PTP profile.
Step 2 Create a PTP clock port.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 88
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
Step 3 Configure the PTP port attributes.
Step 4 Set PTP packet packets.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 89
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 3 Configuring Clock Features
NOTE
An IF port supports the P2P mode and an Ethernet port supports the E2E mode.
PTP packet parameters must be consistently set for interconnected PTP ports. It is advised to retain the
default values for the PTP packet parameters.
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 90
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
About This Chapter
This topic provides hyperlinks to configuration processes and configuration examples of
various MPLS/PWE3.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support MPLS/PWE3 Features.
4.1 Configuration Process (MPLS Tunnel)
The configuration method is the same as that for MPLS tunnels over common NNIs.
4.2 Configuration Process (Configuring ETH PWE3 Services)
ETH PWE3 services are available in E-Line services carried by PWs, E-Aggr services carried
by PWs, and E-LAN services (VPLS) carried by PWs.
4.3 Configuration Procedure (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)
The OAM configurations for MPLS APS are different from those for LSP long-term
monitoring.
4.4 Configuration Procedure (LSP Ping/Traceroute)
The configuration procedure of LSP ping/traceroute contains only one configuration task.
4.5 Configuration Procedure (MPLS APS)
When MPLS APS is configured, OAM is configured simultaneously.
4.6 Configuration Procedure (PW OAM_Y.1711)
The OAM configurations of PW APS are different from those of the PW long-term
monitoring.
4.7 Configuration Process (PW Ping/Traceroute)
The configuration process of LSP ping/traceroute contains only one configuration task.
4.8 Configuration Process (PW APS/PW FPS)
You need to configure PW OAM when configuring PW APS/PW FPS.
4.9 Configuration Process (MPLS-TP OAM)
Set MEG IDs/MP IDs before using MPLS-TP OAM functions. If MEG IDs/MP IDs are set to
be IP-based, an NE can automatically generate MEG IDs/MP IDs and no configuration is
required.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 91
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4.10 Configuration Example (MPLS Tunnels with No Protection)
This example assumes that the network topology and microwave links have been configured.
4.11 Configuration Example (E-Line Services Carried by PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure E-Line services carried by
PWE3 according to network conditions.
4.12 Configuration Example (E-LAN Services Carried by PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure E-LAN services carried
by PWE3 according to network conditions.
4.13 Configuration Example (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS OAM (Y.1711) for
long-term LSP monitoring according to network conditions.
4.14 Configuration Example (LSP Ping/Traceroute)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure LSP ping/traceroute
according to network conditions.
4.15 Configuration Example (MPLS APS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS APS according to
network conditions.
4.16 Configuration Example (PW OAM_Y.1711)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW OAM (Y.1711) for
long-term PW monitoring according to network conditions.
4.17 Configuration Example (PW Ping/Traceroute)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW ping/traceroute
according to network conditions.
4.18 Configuration Example (PW APS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW APS according to
network conditions.
4.19 Configuration Example (PW FPS)
This configuration example describes how to configure PW FPS for RTN devices when the
RTN devices form a Mixed VPN with CX devices.
4.20 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for Tunnels)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS-TP tunnel OAM
according to network conditions.
4.21 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS-TP PW OAM
according to network conditions.
4.1 Configuration Process (MPLS Tunnel)
The configuration method is the same as that for MPLS tunnels over common NNIs.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 92
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-1 Configuration flowchart (MPLS tunnel)
The configuration process is described as follows.
Table 4-1 Process of setting MPLS port attributes (not using VLAN sub-interfaces)
Operation Description
Setting 5.3.1 Setting the Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
attributes of Basic Attributes l For ports to be used, set Enable Port to Enabled.
Ethernet for an Ethernet
ports Port l Set Port Mode to Layer 3.
l For Ethernet ports that are connected to external
equipment, set Working Mode to the same value
as that of the external equipment (generally, the
working mode of the external equipment is auto-
negotiation). For Ethernet ports used for
connection within the network, set Working Mode
to Auto-negotiation.
l Set Max Frame Length (byte) according to the
service packet length.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 93
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Operation Description
5.3.9 Required when the flow control function is enabled on
Configuring the external equipment to which the Ethernet port is
Flow Control for connected. Set the major parameters as follows:
an Ethernet Port l When the external equipment uses the non-auto-
negotiation flow control function, set Non-
Autonegotiation Flow Control Mode to Enable
Symmetric Flow Control.
l When the external equipment uses the auto-
negotiation flow control function, set Auto-
Negotiation Flow Control Mode to Enable
Symmetric Flow Control.
5.3.3 Setting Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
Layer 3 l For ports to be used, set Enable Tunnel to
Attributes of Enabled.
Ethernet Ports
NOTE
If LAG protection is configured for the MPLS ports, set
Enable Tunnel on the main port to Enabled, and set
Enable Tunnel on the slave port to Disabled (the default
value).
l Set Specify IP Address to Manually.
NOTE
If LAG protection is configured for the MPLS ports, set
Specify IP Address on the main port to Manually, and
set Specify IP Address on the slave port to Unspecified.
l Set IP Address of each port according to the plan.
The IP addresses of different ports on the NE must
be in different network segments, but the IP
addresses of the ports at both ends of the MPLS
tunnel must be in the same network segment.
5.3.4 Setting the Optional.
Advanced l To enable the function of triggering switching by
Attributes of bit errors, set Enable Switching Triggered by Bit
Ethernet Ports ErrortoEnabled and set Switching Mode
Triggered by Bit Error (SF by default) according
to the plan.
l To enable the bit error detection function, set
Enable Bit Error Detection to Enabled and
setEXC Threshold for Packet Loss at Port and
SD Threshold for Packet Loss at Port according
to the plan.
Setting 5.3.1 Setting the Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
attributes of Basic Attributes Set Port Mode to Layer 3.
IF_ETH for an Ethernet
portsa Port
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 94
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Operation Description
5.3.7 Setting the Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
L3 Attributes for l For ports to be used, set Enable Tunnel to
Microwave Ports Enabled.
l Set Specify IP Address and IP Address according
to the plan. The IP addresses of different ports on
the NE must be in different network segments, but
the IP addresses of the ports at both ends of the
MPLS tunnel must be in the same network
segment.
5.3.8 Setting the Optional.
Advanced
Attributes of
Microwave Ports
NOTE
a:For a microwave link for which 1+1 protection or link aggregation group (LAG) is configured, set
parameters only for the main IF_ETH port. The following operations described in this section are also
applicable only to the main port.
Table 4-2 Process of configuring MPLS ports (using VLAN sub-interfaces)
Operation Description
Setting 5.3.1 Setting the Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
attributes of Basic Attributes l For ports to be used, set Enable Port to Enabled.
Ethernet for an Ethernet
ports Port l Set Port Mode to Layer Mix.
l For Ethernet ports that are connected to external
equipment, set Working Mode to the same value
as that of the external equipment (generally, the
working mode of the external equipment is auto-
negotiation). For Ethernet ports used for
connection within the network, set Working Mode
to Auto-negotiation.
l Set Max Frame Length (byte) according to the
service packet length.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 95
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Operation Description
5.3.9 Required when the flow control function is enabled on
Configuring the external equipment to which the Ethernet port is
Flow Control for connected. Set the major parameters as follows:
an Ethernet Port l When the external equipment uses the non-auto-
negotiation flow control function, set Non-
Autonegotiation Flow Control Mode to Enable
Symmetric Flow Control.
l When the external equipment uses the auto-
negotiation flow control function, set Auto-
Negotiation Flow Control Mode to Enable
Symmetric Flow Control.
5.3.3 Setting Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
Layer 3 l Set IP Address for each port according to the plan.
Attributes of The IP addresses of different ports on the NE must
Ethernet Ports be in different network segments, but the IP
addresses of the ports at both ends of the MPLS
tunnel must be in the same network segment.
l For ports to be used, set Enable Tunnel to
Enabled.
5.3.4 Setting the Optional.
Advanced l To enable the function of triggering switching by
Attributes of bit errors, set Enable Switching Triggered by Bit
Ethernet Ports ErrortoEnabled and set Switching Mode
Triggered by Bit Error (SF by default) according
to the plan.
l To enable the bit error detection function, set
Enable Bit Error Detection to Enabled and
setEXC Threshold for Packet Loss at Port and
SD Threshold for Packet Loss at Port according
to the plan.
Setting 5.3.1 Setting the Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
attributes of Basic Attributes Set Port Mode to Layer Mix.
IF_ETH for an Ethernet
portsa Port
5.3.3 Setting Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
Layer 3 l Set IP Address for each port according to the plan.
Attributes of The IP addresses of different ports on the NE must
Ethernet Ports be in different network segments, but the IP
addresses of the ports at both ends of the MPLS
tunnel must be in the same network segment.
l For ports to be used, set Enable Tunnel to
Enabled.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 96
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Operation Description
5.3.8 Setting the Optional.
Advanced
Attributes of
Microwave Ports
NOTE
a:For a microwave link for which 1+1 protection or link aggregation group (LAG) is configured, set
parameters only for the main IF_ETH port. The following operations described in this section are also
applicable only to the main port.
Table 4-3 Process of Configuring LAG on Ethernet ports
Operation Description
5.3.11 Creating Required if LAG protection is configured for Ethernet ports. Set the
a LAG parameters as follows:
l Set LAG Type to the same value as that at the opposite end.
Generally, set LAG Type to Static at both ends.
l Set Load Sharing to the same value as that at the opposite end. It is
recommended that you set Load Sharing to Non-Sharing at both
ends, if the LAG is configured only to provide protection. It is
recommended that you set Load Sharing to Sharing at both ends, if
the LAG is configured to increase the bandwidth.
l Set Revertive Mode to the same value as that at the opposite end.
l It is recommended that the main and slave ports take the same
settings at both ends. In this case, you can set System Priority as
required. It is recommended that this parameter take its default value.
This parameter is valid only to static LAGs.
l Set the Main Port and Selected Standby Ports according to the
network plan. It is recommended that the same main and slave ports
are used for the LAGs at both ends.
5.3.12 Setting Optional.
LAG It is recommended that you set Load Sharing Hash Algorithm to the
Parameters default value Automatic.
Table 4-4 Process of configuring an MPLS tunnel
Operation Description
5.4.2 Setting Basic MPLS Required.
Attributes
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 97
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Operation Description
Configuring 5.4.5 Creating a Required if you need to configure a unidirectional
MPLS Unidirectional MPLS tunnel.
Tunnel MPLS Tunnel Set the parameters according to the plan.
5.4.6 Creating a Required if you need to configure a bidirectional
Bidirectional MPLS tunnel.
MPLS Tunnel Set the parameters according to the plan.
5.4.1 Creating ARP Static Required when the dynamic ARP protocol cannot
Entries obtain the next-hop MAC address (for example, when
traversing an L2 network). Set the major parameters as
follows:
l ARP List IP Address: Set this parameter to the IP
address of the next-hop port.
l ARP List MAC: Set this parameter to the MAC
address of the next-hop port.
Table 4-5 Configuring MPLS APS
Operation Description
5.5.1 Creating an Required when you need to configure MPLS tunnels with MPLS
MPLS APS AP protection.
Protection Group
Table 4-6 Configuring QoS
Operation Description
2.4 Configuration Optional.
Process (QoS/HQoS)
4.2 Configuration Process (Configuring ETH PWE3
Services)
ETH PWE3 services are available in E-Line services carried by PWs, E-Aggr services carried
by PWs, and E-LAN services (VPLS) carried by PWs.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 98
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Flowchart
Figure 4-2 Flowchart for configuring E-Line services carried by PWs
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 99
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-3 Flowchart for configuring E-LAN services carried by PWs
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 100
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-4 Flowchart for configuring E-Aggr services carried by PWs
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 101
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Configuring Ethernet Ports
Table 4-7 Configuring Ethernet ports
Operation Remarks
5.3.1 Setting the Basic Attributes for an Required if UNIs are Ethernet ports. Basic
Ethernet Port attributes include the port mode,
encapsulation type, and maximum frame
length.
5.3.2 Setting the Layer 2 Attributes of Required if UNIs are Ethernet ports. Layer
Ethernet Ports 2 attributes of Ethernet ports define link-
layer information, including TAG attributes
and port attributes.
5.3.4 Setting the Advanced Attributes of Required when you need to enable the port
Ethernet Ports self-loop test function, the automatic
loopback shutdown function, or the
broadcast packet suppression function.
Configuring IF_ETH Ports
Table 4-8 Configuring IF_ETH ports
Operation Remarks
5.3.5 Setting the Basic Attributes of Required if UNIs are IF_ETH ports. Basic
microwave Ports attributes of an IF_ETH port specify the
basic information, including the port mode
and encapsulation mode.
5.3.6 Setting the L2 Attributes for Required if UNIs are IF_ETH ports. Layer 2
Microwave Ports attributes of the IF_ETH port specify link-
layer information, including the TAG
attribute and QinQ type domain.
Creating a LAG for Ethernet Ports
Table 4-9 Configuring a LAG
Operation Remarks
5.3.11 Creating a LAG Required if the LAG function needs to be
used for an FE/GE port.
5.3.12 Setting LAG Parameters Optional.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 102
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
NOTE
For an Ethernet link for which a LAG is configured, configure parameters only for the main port. The
following operations described in this section are also applicable to the main port only.
Configuring ETH PWE3 Services
Table 4-10 Configuring ETH PWE3 Services
Operation Remarks
Configuring E-Line Services Configuring E-Line Required.
Carried by PWs. Services Carried by PWs
5.6.2 Creating an MS-PW Required for an S-PE.
Configuring E-LAN Configuring E-LAN Optional.
Services Carried by PWs. Services Carried by PWs Perform this operation to
change the T-PID value of
the S-VLAN tag carried in
PW-carried QinQ services.
4.12 Configuration Required.
Example (E-LAN Services NOTE
Carried by PWs) On a packet switched network
(PSN), if Ethernet services
carried on PEs are end-to-end
services from one UNI to a
PW, configure the Ethernet
services as E-Line services
carried by PWs on a per-NE
basis.
5.6.2 Creating an MS-PW Required for an S-PE.
Configuring PW Protection
For details about how to configure PW protection, see Configuration Process (PW APS/PW
FPS) of the Feature Description.
Configuring QoS
For details about the QoS configuration procedure, see2.4 Configuration Process (QoS/
HQoS).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 103
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Verifying Ethernet Services
Table 4-11 Verifying Ethernet services
Operation Remarks
5.6.4 Performing a PW Ping Test Required.
You can perform a PW ping test to verify
the service connectivity.
4.3 Configuration Procedure (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)
The OAM configurations for MPLS APS are different from those for LSP long-term
monitoring.
NOTE
This section describes only the OAM configurations for LSP long-term monitoring. The OAM
parameters for MPLS APS are configured during MPLS APS configuration.
Figure 4-5 Configuration procedure (MPLS OAM ITU-T Y.1711)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 104
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-12 Flow for configuring MPLS OAM (ITU-T Y.1711)
Procedure Operation Remarks
1 5.4.4 Required if the tunnel OAM does not comply with Y.1711.
Changing Change the tunnel OAM to be compliant with Y.1711 (the
the MPLS default setting).
Tunnel/PW
OAM
Standard
2 5.4.8 Setting Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
MPLS l Set OAM Status to Enabled on the ingress and egress
OAM (Y. nodes of an LSP to be tested.
1711)
Parameters l For a unidirectional tunnel, it is advisable to set
Detection Packet Type of the ingress node of the LSP
to be tested to CV; for a bidirectional tunnel, it is
advisable to set Detection Mode of the ingress and
egress nodes of the LSP to be tested to CV.
l It is advisable to set Detection Mode of the egress node
of the LSP to be tested to Adaptive.
l For a unidirectional tunnel, Reverse Tunnel needs to be
configured.
l It is advisable to set SD Threshold(%) and SF
Threshold(%) to the default value (0).
NOTE
If there are special requirements for the packet detection period, it
is advisable to set Detection Packet Type to FFD and set Packet
Detection Interval (ms) as required.
3 5.4.9 Optional.
Enabling/ Select Enable FDI.
Disabling
FDI
4.4 Configuration Procedure (LSP Ping/Traceroute)
The configuration procedure of LSP ping/traceroute contains only one configuration task.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 105
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-6 Configuration procedure (LSP Ping/Traceroute)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 106
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-13 Flow for configuring LSP ping
Step Operation Description
1 5.4.12 Performing an Required. Regarding an MPLS tunnel, perform the
LSP Ping Test operation on the required LSP on the ingress node.
Set the major parameters as follows:
l Set Packet Count to the default value.
l Set Packet Length and EXP Value as
required.
l Set Response Mode based on the tunnel
direction and the support capability of the
egress node:
– If the tunnel is bidirectional and the egress
node supports the reverse channel response,
set Response Mode to Application
Control Channel.
– If the tunnel is bidirectional and the egress
node does not support the reverse channel
response but supports DCN channel
response by using IP protocols, set
Response Mode to IPv4 UDP Response.
– If the tunnel is unidirectional and the egress
node supports DCN channel response by
using IP protocols, set Response Mode to
IPv4 UDP Response.
– In other cases, set Response Mode to No
Response.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 107
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-14 Flow for configuring LSP traceroute
Step Operation Description
1 5.4.13 Performing an Required. Regarding an MPLS tunnel, perform the
LSP Traceroute Test operation on the required LSP on the ingress node.
Set the major parameters as follows:
l Set Packet Count to the default value.
l Set Packet Length and EXP Value as
required.
l Set Response Mode based on the tunnel
direction and the support capability of the
egress node:
– If the tunnel is bidirectional and the egress
node supports the reverse channel response,
set Response Mode to Application
Control Channel.
– If the tunnel is bidirectional and the egress
node does not support the reverse channel
response but supports DCN channel
response by using IP protocols, set
Response Mode to IPv4 UDP Response.
– If the tunnel is unidirectional and the egress
node supports DCN channel response by
using IP protocols, set Response Mode to
IPv4 UDP Response.
– In other cases, set Response Mode to No
Response.
4.5 Configuration Procedure (MPLS APS)
When MPLS APS is configured, OAM is configured simultaneously.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 108
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-7 Configuration procedure (MPLS APS)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 109
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-15 Flow for configuring MPLS APS
Proce Operation Remarks
dure
1 5.4.4 Changing the MPLS Required.
Tunnel/PW OAM Standard l If MPLS OAM (Y1.711) is used to
detect faults for MPLS APS, change
tunnel OAM to be compliant with
Y.1711 (the default setting).
l If MPLS-TP tunnel OAM is used to
detect faults for MPLS APS, change
tunnel OAM to be compliant with
Y.1731.
2 5.4.8 Setting MPLS OAM (Y.1711) Required if MPLS OAM (Y.1711) is
Parameters used to check the availability of a
tunnel. Set the major parameters as
follows:
l Set OAM Status on the ingress/
egress node of the required tunnel to
Enabled.
l Regarding a unidirectional tunnel,
set Detection Packet Type of the
ingress node of the required tunnel
to FFD; regarding a bidirectional
tunnel, set Detection Packet Type
of the ingress/egress node to FFD.
It is recommended that you set
Packet Detection Interval(ms) to
3.3 ms. If this parameter of an
MPLS tunnel exceeds 3.3 ms, set
the packet transmission interval to a
value greater than the delay.
l It is recommended that you set
Detection Mode of the ingress node
to Auto-Sensing.
l Regarding a unidirectional tunnel,
set Reverse Tunnel ID.
l It is recommended that you set SD
Threshold(%) and SF
Threshold(%) to 0 (default value).
NOTE
If Packet Detection Interval(ms) needs to
be set as required, set Detection Packet
Type to FFD.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 110
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Proce Operation Remarks
dure
MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM Required if MPLS-TP tunnel OAM is
used to check the availability of an
MPLS tunnel. Set the parameters as
follows:
l Set OAM Status to Enabled.
l If the MPLS tunnels involve only
Huawei equipment that supports IP-
based MPLS-TP OAM, it is
recommended that you set MEG ID
Type to IP Based, to avoid
planning MEG IDs, MP IDs, RMEP
IDs, and MIPs.
l If some MPLS-TP OAM
components cannot be set to IP
Based or have special requirements,
it is recommended that you set
MEG ID Type to ICC Based. In
this case, plan MEGs and MPs
according to the following
principles:
– All MPs on an MPLS tunnel
must belong to the same MEG.
Each MPLS tunnel must belong
to a unique MEG.
– Each MEG of an operator must
have a unique name and the
MEG parameters for all NEs in
the MEG must be set
consistently.
– Each MP in an MEG must have
a unique MP ID.
l Set MEG Level to 7.
l Detection Mode can be set only for
ingress nodes on bidirectional
tunnels and egress nodes. Generally,
it is recommended that you set this
parameter to the default value
Adaptive.
l It is recommended that you set SD
Threshold (%) and SF Threshold
(%) to the default value 0.
l If an NE is the S-PE of an MS-PW
and alarms triggered by PW faults
caused by MPLS tunnel faults need
to be suppressed, set AIS Status to
Enabled.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 111
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Proce Operation Remarks
dure
l If the MPLS-TP OAM CC function
is used to trigger MPLS APS, it is
recommended that you set CC
Packet Interval (ms) to 3.3 ms. If
the frame delay variation on a
tunnel exceeds 3.3 ms, set the CCM
transmit interval to a value greater
than the frame delay variation. If the
MPLS-TP OAM CC function is
used for only continuity check, it is
recommended that you set CC
Packet Interval (ms) to the default
value 1000. This parameter is valid
for only egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels and ingress
nodes.
l It is recommended that you set CC
Packet Priority to 7 to ensure that
CC packets are forwarded with
priority. This parameter is valid for
only egress nodes on bidirectional
tunnels and ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that you set LM
Packet Mode to Standard.
3 5.4.9 Enabling/Disabling FDI Optional.
Enable FDI is enabled by default.
Therefore, the FDI packet is
transmitted to the downstream when
the port detects a fault. Then, switching
will be performed on the egress node
after the FDI packet arrives at the
egress node.
4 5.3.4 Setting the Advanced Optional.
Attributes of Ethernet Ports l To enable the function of triggering
switching by bit errors, set Enable
Switching Triggered by Bit Error
to Enabled and set Switching
Mode Triggered by Bit Error (SF
by default) according to the plan.
l To enable the bit error detection
function, set Enable Bit Error
Detection to Enabled and set EXC
Threshold for Packet Loss at Port
and SD Threshold for Packet Loss
at Port according to the plan.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 112
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Proce Operation Remarks
dure
5 5.5.1 Creating an MPLS APS Required. The parameters of the ingress
Protection Group node and egress node must be set to the
same values. Set the major parameters
as follows:
l Set Protection Type to 1:1.
l Set Switching Mode to Dual-
Ended.
l Set Working Ingress Tunnel ID
and Working Egress Tunnel ID for
the working tunnel according to the
planning information.
NOTE
Regarding a bidirectional tunnel,
Working Ingress Tunnel ID and
Protection Ingress Tunnel ID need to
be set, but Working Egress Tunnel ID
and Protection Egress Tunnel ID do
not need to be set.
l Set Protection Ingress Tunnel ID
and Protection Egress Tunnel ID
for the protection tunnel according
to the network planning.
l It is recommended that you set
Revertive Mode to Revertive.
l It is recommended that you set
WTR Time (min) to 5.
l It is recommended that you set
Hold-off Time (100 ms) to 0.
l Set Protocol Status to Disabled.
5 5.5.4 Enabling/Disabling MPLS APS After the ingress node and egress node
Protection are configured, set Protocol Status of
the APS protection groups on the two
nodes to Enabled.
4.6 Configuration Procedure (PW OAM_Y.1711)
The OAM configurations of PW APS are different from those of the PW long-term
monitoring.
NOTE
This section describes only the OAM configurations for PW long-term monitoring. The OAM
parameters for PW APS are configured during PW APS Configuration.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 113
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-8 Configuration procedure (PW OAM ITU-T Y.1711)
Table 4-16 Flow for configuring PW OAM (Y.1711)
Step Operation Description
1 5.4.4 Required if PW OAM is not compliant with Y.1711.
Changing Change PW OAM to be compliant with Y.1711 (the default
the MPLS setting).
Tunnel/PW
OAM
Standard
2 5.6.3 Setting Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
PW OAM l Set OAM Status of the required PW to Enabled.
(Y.1711)
Parameters l Set Detection Packet Type of the required PW to CV.
l Set Detection Mode of the required PW to Auto-
Sensing.
NOTE
If Packet Detection Interval(ms) needs to be set as required, set
Detection Packet Type to FFD.
4.7 Configuration Process (PW Ping/Traceroute)
The configuration process of LSP ping/traceroute contains only one configuration task.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 114
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Flowchart
Figure 4-9 shows the flowchart for configuring PW ping.
Figure 4-9 Flowchart for configuring PW ping
Figure 4-10 shows the flowchart for configuring PW traceroute.
Figure 4-10 Flowchart for configuring PW traceroute
Process
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support PW ping or traceroute.
NOTICE
Prior to PW ping/traceroute operations, set the control channel types of VCCV to the same at
both ends. Otherwise, PW ping/traceroute operations will fail.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 115
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-17 Flow for configuring PW ping
Ste Operation Description
p
1 5.6.4 Performing a PW Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
Ping Test l Set Packet Count and EXP Value to the default
values.
l Set Packet Length as required.
l Set Response Mode based on the support capability
of the remote PE:
– If the remote PE supports the reverse channel
response, set Response Mode to Application
Control Channel.
– If the remote PE does not support the reverse
channel response but supports DCN channel
response by using IP protocols, set Response
Mode to IPv4 UDP Response.
– In other cases, set No Response.
Table 4-18 Flow for configuring PW traceroute
Ste Operation Description
p
1 5.6.5 Required. Set the major parameters as follows:
Performing a l Set Packet Length as required.
PW Traceroute
Test l Set EXP Value to the default value.
l Set Response Mode based on the support capability of the
remote PE:
– If the remote PE supports the reverse channel response,
set Response Mode to Application Control Channel.
– If the remote PE does not support the reverse channel
response but supports DCN channel response by using IP
protocols, set Response Mode to IPv4 UDP Response.
– In other cases, set Response Mode to No Response.
4.8 Configuration Process (PW APS/PW FPS)
You need to configure PW OAM when configuring PW APS/PW FPS.
Flowchart
Figure 4-11 shows the flowchart for configuring PW APS.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 116
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-11 Flowchart for configuring PW APS
Figure 4-12 shows the flowchart for configuring PW FPS.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 117
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-12 Flowchart for configuring PW FPS
Process
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support PW APS or PW FPS.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 118
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-19 Process of configuring PW APS
S Operation Remarks
t
e
p
1 Configuring Global OAM Required.
Parameters l If PW OAM (Y.1711) is used to detect faults for
PW APS, change PW OAM to be compliant with
Y.1711 (the default setting).
l If MPLS-TP PW OAM is used to detect faults for
PW APS, change PW OAM to be compliant with
Y.1731.
2 5.7.1 Creating a PW APS Required.
Protection Group Select one PWE3 service from the required ones to
create a PW APS protection group.
l Set the major parameters in the General
AttributesPW tab as follows.
– Set PW Incoming Label and PW Outgoing
Label according to the planning information.
l Set the major parameters in the Protect Group tab
as follows.
– Set Protection Group ID to a protection group
ID that is planned.
– Set Enabling Status to Disabled.
– Set Revertive Mode to Revertive.
– Set Switchover Restoration Time (min) to 5.
– Set Switchover Delay Time (100 ms) to 0.
l Set the major parameters in the PW OAM tab as
follows.
– Set Detection Mode to Auto-Sensing.
– Set Detection Packet Type to FFD.
– Set Packet Detection Interval(ms) to 3.3.
– Set Transmitted PW ID according to the
planning information.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 119
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
S Operation Remarks
t
e
p
5.6.6 Configuring MEP Required if MPLS-TP PW OAM is used to check the
Parameters for MPLS-TP availability of an MPLS tunnel. Set the parameters as
PW OAM follows:
l Set OAM Status to Enabled.
l If the PWs involve only Huawei equipment that
supports IP-based MPLS-TP OAM, it is
recommended that you set MEG ID Type to IP
Based, to avoid planning MEG IDs, MP IDs,
RMEP IDs, and MIPs.
l If some MPLS-TP PW OAM components cannot
be set to IP Based or have special requirements, it
is recommended that you set MEG ID Type to
ICC Based. In this case, plan MEGs and MPs
according to the following principles:
– All MPs on a PW must belong to the same
MEG. Each PW must belong to a unique MEG.
– Each MEG of an operator must have a unique
name and the MEG parameters for all NEs in
the MEG must be set consistently.
– Each MP in an MEG must have a unique MP
ID.
l Set MEG Level to 7.
l Detection Mode can be set only for a T-PE.
Generally, it is recommended that you set this
parameter to the default value Adaptive.
l It is recommended that you set SD Threshold (%)
and SF Threshold (%) to the default value 0.
l Set GAL Enable Status to the default value
Disabled if MPLS-TP PW OAM is implemented
on PWE3 services whose control words are
enabled. In other cases, set GAL Enable Status to
Enabled and set GAL Mode according to the plan.
When GAL Mode is set to RFC5586, the GAL is
13. When GAL Mode is set to Y.1711, the GAL is
14.
l For an MS-PW, LSR ID to be Received and PW
ID to be Received need to be manually specified.
l If the MPLS-TP PW OAM CC function is used to
trigger PW APS, it is recommended that you set
CC Packet Interval (ms) to 3.3 ms. If the frame
delay variation on a tunnel exceeds 3.3 ms, set the
CCM transmit interval to a value greater than the
frame delay variation. If the MPLS-TP PW OAM
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 120
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
S Operation Remarks
t
e
p
CC function is used for only continuity check, it is
recommended that you set CC Packet Interval
(ms) to the default value 1000. This parameter is
valid for only egress nodes on bidirectional tunnels
and ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that you set CC Packet
Priority to 7 to ensure that CC packets are
forwarded with priority. This parameter is valid for
only egress nodes on bidirectional tunnels and
ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that you set LM Packet Mode
to Standard.
3 5.7.3 Configuring Slave Optional.
Protection Pairs of PW APS Create slave protection pairs for the other PWE3
services that need to be bound to the PW APS
protection group.
Set Protection Group ID of the slave protection pairs
to a protection group ID that is planned.
4 5.7.6 Enabling/Disabling PW Required.
APS Protection In the Protect Group tab, set Enabling Status to
Enabled for the APS protection groups on the two
nodes.
Table 4-20 Process of configuring PW FPS
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.4.3 Configuring Global OAM Required.
Parameters l If PW OAM (Y.1711) is used to
detect faults for PW APS, change
PW OAM to be compliant with
Y.1711 (the default setting).
l If MPLS-TP PW OAM is used to
detect faults for PW APS, change
PW OAM to be compliant with
Y.1731.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 121
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
2 5.7.2 Creating a PW FPS Required.
Protection Group Select one PWE3 service from the
required ones to create a PW APS
protection group.
l Set the major parameters in the
General AttributesPW tab as
follows.
– Set PW Incoming Label and
PW Outgoing Label
according to the planning
information.
l Set the major parameters in the
Protect Group tab as follows.
– Set Protection Group ID to a
protection group ID that is
planned.
– Set Enabling Status to
Disabled.
– Set Revertive Mode to
Revertive.
– Set Switchover Restoration
Time (min) to 5.
– Set Switchover Delay Time
(100 ms) to 0.
l Set the major parameters in the
PW OAM tab as follows.
– Set Detection Mode to Auto-
Sensing.
– Set Detection Packet Type to
FFD.
– Set Packet Detection
Interval(ms) to 3.3.
– Set Transmitted PW ID
according to the planning
information.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 122
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
5.6.6 Configuring MEP Required if MPLS-TP PW OAM is
Parameters for MPLS-TP PW used to check the availability of an
OAM MPLS tunnel. Set the parameters as
follows:
l Set OAM Status to Enabled.
l If the PWs involve only Huawei
equipment that supports IP-based
MPLS-TP OAM, it is
recommended that you set MEG
ID Type to IP Based, to avoid
planning MEG IDs, MP IDs,
RMEP IDs, and MIPs.
l If some MPLS-TP PW OAM
components cannot be set to IP
Based or have special
requirements, it is recommended
that you set MEG ID Type to
ICC Based. In this case, plan
MEGs and MPs according to the
following principles:
– All MPs on a PW must
belong to the same MEG.
Each PW must belong to a
unique MEG.
– Each MEG of an operator
must have a unique name and
the MEG parameters for all
NEs in the MEG must be set
consistently.
– Each MP in an MEG must
have a unique MP ID.
l Set MEG Level to 7.
l Detection Mode can be set only
for a T-PE. Generally, it is
recommended that you set this
parameter to the default value
Adaptive.
l It is recommended that you set
SD Threshold (%) and SF
Threshold (%) to the default
value 0.
l Set GAL Enable Status to the
default value Disabled if MPLS-
TP PW OAM is implemented on
PWE3 services whose control
words are enabled. In other
cases, set GAL Enable Status to
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 123
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
Enabled and set GAL Mode
according to the plan. When
GAL Mode is set to RFC5586,
the GAL is 13. When GAL
Mode is set to Y.1711, the GAL
is 14.
l For an MS-PW, LSR ID to be
Received and PW ID to be
Received need to be manually
specified.
l If the MPLS-TP PW OAM CC
function is used to trigger PW
APS, it is recommended that you
set CC Packet Interval (ms) to
3.3 ms. If the frame delay
variation on a tunnel exceeds 3.3
ms, set the CCM transmit
interval to a value greater than
the frame delay variation. If the
MPLS-TP PW OAM CC
function is used for only
continuity check, it is
recommended that you set CC
Packet Interval (ms) to the
default value 1000. This
parameter is valid for only egress
nodes on bidirectional tunnels
and ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that you set
CC Packet Priority to 7 to
ensure that CC packets are
forwarded with priority. This
parameter is valid for only egress
nodes on bidirectional tunnels
and ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that you set
LM Packet Mode to Standard.
3 5.7.3 Configuring Slave Protection Optional.
Pairs of PW APS Create slave protection pairs for the
other PWE3 services that need to be
bound to the PW APS protection
group.
Set Protection Group ID of the
slave protection pairs to a protection
group ID that is planned.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 124
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
4 5.7.6 Enabling/Disabling PW APS Required.
Protection In the Protect Group tab, set
Enabling Status to Enabled for the
APS protection groups on the two
nodes.
4.9 Configuration Process (MPLS-TP OAM)
Set MEG IDs/MP IDs before using MPLS-TP OAM functions. If MEG IDs/MP IDs are set to
be IP-based, an NE can automatically generate MEG IDs/MP IDs and no configuration is
required.
Figure 4-13 provides the process of configuring MPLS-TP OAM.
Figure 4-13 MPLS-TP OAM configuration process
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 125
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-21 Configuring basic attributes for MPLS-TP OAM
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.4.3 Configuring Global Required. Set parameters as
OAM Parameters follows:
l Set Carrier ID
according to the network
plan if MPLS-TP OAM
uses the ICC-based
format. Carrier ID must
be set to the same value
for all NEs on a network.
l Set Port AIS Status to
Enabled if you want to
suppress alarms triggered
by MPLS tunnel faults
that are caused by port
faults.
l When AC link failures
must be notified to its
peer end in real time, set
CSF Status to Enabled.
l Channel Type must be
set to the same value for
all NEs on a network. It
is recommended that you
set this parameter to the
default value.
2 5.4.4 Changing the MPLS Required.
Tunnel/PW OAM Change the OAM standard
Standard to Y.1731 for a tunnel/PW
that requires the MPLS-TP
OAM functions. By default,
OAM complies with Y.1711.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 126
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-22 Configuring MPLS-TP tunnel OAM
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.4.14 Configuring MEP Required for ingress/egress
Parameters for MPLS-TP nodes. Set parameters as
Tunnel OAM follows:
l Set OAM Status to
Enabled.
l If the MPLS tunnels
involve only Huawei
equipment that supports
IP-based MPLS-TP
OAM, it is recommended
that you set MEG ID
Type to IP Based, to
avoid planning MEG
IDs, MP IDs, RMEP
IDs, and MIPs.
l If some MPLS-TP OAM
components cannot be
set to IP Based or have
special requirements, it is
recommended that you
set MEG ID Type to
ICC Based. In this case,
plan MEGs and MPs
according to the
following principles:
– All MPs on an MPLS
tunnel must belong to
the same MEG. Each
MPLS tunnel must
belong to a unique
MEG.
– Each MEG of an
operator must have a
unique name and the
MEG parameters for
all NEs in the MEG
must be set
consistently.
– Each MP in an MEG
must have a unique
MP ID.
l Set MEG Level to 7.
l Detection Mode can be
set only for ingress nodes
on bidirectional tunnels
and egress nodes.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 127
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
Generally, it is
recommended that you
set this parameter to the
default value Adaptive.
l It is recommended that
you set SD Threshold
(%) and SF Threshold
(%) to the default value
0.
l If an NE is the S-PE of
an MS-PW and alarms
triggered by PW faults
caused by MPLS tunnel
faults need to be
suppressed, set AIS
Status to Enabled.
l If the MPLS-TP OAM
CC function is used to
trigger MPLS APS, it is
recommended that you
set CC Packet Interval
(ms) to 3.3 ms. If the
frame delay variation on
a tunnel exceeds 3.3 ms,
set the CCM transmit
interval to a value greater
than the frame delay
variation. If the MPLS-
TP OAM CC function is
used for only continuity
check, it is recommended
that you set CC Packet
Interval (ms) to the
default value 1000. This
parameter is valid for
only egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels and
ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that
you set CC Packet
Priority to 7 to ensure
that CC packets are
forwarded with priority.
This parameter is valid
for only egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels and
ingress nodes.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 128
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
l It is recommended that
you set LM Packet
Mode to Standard.
2 5.4.14 Configuring MEP If the value of MEG ID
Parameters for MPLS-TP Type is not IP Based and
Tunnel OAM LT tests need to be
performed, configure an
MIP creation task for every
transmit node. Set
parameters as follows:
l It is recommended that
you set MEG ID Type
to ICC Based.
l All MIPs and MEPs on
an MPLS tunnel must
belong to the same MEG
and have the same MEG
ID.
l Each MP on an MPLS
tunnel must have a
unique MP ID.
3 5.4.16 Starting a CC Test If MPLS-TP tunnel OAM is
of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM used to check the continuity
of MPLS APS or the CC
function is used to monitor
the connectivity of a tunnel
in real time, start a CC test
on egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels or
ingress nodes.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 129
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
5.4.17 Starting an LB Test To perform LB tests, start an
of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM LB test on egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels or
ingress nodes. Set
parameters as follows:
l If Node Type is set to
MIP, set TTL correctly
according to the number
of hops between the
MEP and the MIP. If
Node Type is set to
MEP, set TTL to a value
greater than or equal to
the number of hops
between the MIP and the
remote MEP. It is
recommended that you
set TTL to the default
value.
l Set Remote MEP/MIP
ID or IP Address
according to the
termination node of an
LB/LT test. If MEG ID
Type is set to IP Based
for the termination node,
set Remote MEP/MIP
ID or IP Address to the
LSR ID of the
termination node. If
MEG ID Type is set to
ICC Based for the
termination node, set
Remote MEP/MIP ID
or IP Address to the MP
ID of the termination
node.
l It is recommended that
you set Packet Count,
Packet Priority,
Transmit Interval (ms),
and Packet Length to
their default values.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 130
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
5.4.18 Starting an LT Test Perform this task when you
Provided by MPLS-TP need to perform an LT test.
Tunnel OAM Set parameters as follows:
It is recommended that you
retain the default values for
Packet Sending Interval,
Packet Sending Priority,
and Length of Sending
Packet.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
5.4.19 Testing the Delay Perform this task when you
and Delay Variation of an need to query the delay and
MPLS Tunnel delay variation.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
5.4.20 Setting the LCK Perform this task when you
Status of MPLS-TP need to lock the MPLS
Tunnel OAM tunnel.
Set Lock Status to Lock.
5.4.21 Starting a TST Test Perform this task when you
Provided by MPLS-TP need to test the packet loss
Tunnel OAM situation.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 131
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-23 Configuring MPLS-TP PW OAM
Step Operation Remarks
1 5.6.6 Configuring MEP Required for the T-PE. Set
Parameters for MPLS-TP parameters as follows:
PW OAM l Set OAM Status to
Enabled.
l If the PWs involve only
Huawei equipment that
supports IP-based
MPLS-TP OAM, it is
recommended that you
set MEG ID Type to IP
Based, to avoid planning
MEG IDs, MP IDs,
RMEP IDs, and MIPs.
l If some MPLS-TP PW
OAM components
cannot be set to IP
Based or have special
requirements, it is
recommended that you
set MEG ID Type to
ICC Based. In this case,
plan MEGs and MPs
according to the
following principles:
– All MPs on a PW
must belong to the
same MEG. Each PW
must belong to a
unique MEG.
– Each MEG of an
operator must have a
unique name and the
MEG parameters for
all NEs in the MEG
must be set
consistently.
– Each MP in an MEG
must have a unique
MP ID.
l Set MEG Level to 7.
l Detection Mode can be
set only for a T-PE.
Generally, it is
recommended that you
set this parameter to the
default value Adaptive.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 132
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
l It is recommended that
you set SD Threshold
(%) and SF Threshold
(%) to the default value
0.
l Set GAL Enable Status
to the default value
Disabled if MPLS-TP
PW OAM is
implemented on PWE3
services whose control
words are enabled. In
other cases, set GAL
Enable Status to
Enabled and set GAL
Mode according to the
plan. When GAL Mode
is set to RFC5586, the
GAL is 13. When GAL
Mode is set to Y.1711,
the GAL is 14.
l For an MS-PW, LSR ID
to be Received and PW
ID to be Received need
to be manually specified.
l If the MPLS-TP PW
OAM CC function is
used to trigger PW APS,
it is recommended that
you set CC Packet
Interval (ms) to 3.3 ms.
If the frame delay
variation on a tunnel
exceeds 3.3 ms, set the
CCM transmit interval to
a value greater than the
frame delay variation. If
the MPLS-TP PW OAM
CC function is used for
only continuity check, it
is recommended that you
set CC Packet Interval
(ms) to the default value
1000. This parameter is
valid for only egress
nodes on bidirectional
tunnels and ingress
nodes.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 133
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
l It is recommended that
you set CC Packet
Priority to 7 to ensure
that CC packets are
forwarded with priority.
This parameter is valid
for only egress nodes on
bidirectional tunnels and
ingress nodes.
l It is recommended that
you set LM Packet
Mode to Standard.
2 5.6.7 Creating MIPs of If the value of MEG ID
MPLS-TP PW OAM Type is not IP Based and
LT tests need to be
performed, configure an
MIP creation task for every
S-PE. Set parameters as
follows:
l It is recommended that
you set MEG ID Type
to ICC Based.
l All MIPs and MEPs on a
PW must belong to the
same MEG and they
have the same MEG ID.
l Each MP on a PW must
have a unique MP ID.
3 5.6.8 Starting a CC Test of If MPLS-TP PW OAM is
MPLS-TP PW OAM used to check the continuity
of PW APS or the CC
function is used to monitor
the connectivity of a PW in
real time, start a CC test on
each T-PE.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 134
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
5.6.9 Starting an LB Test To perform LB tests, start an
of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM LB test on a T-PE. Set
parameters as follows:
l If Node Type is set to
MIP, set TTL correctly
according to the number
of hops between the
MEP and the MIP. If
Node Type is set to
MEP, set TTL to a value
greater than or equal to
the number of hops
between the MIP and the
remote MEP. It is
recommended that you
set TTL to the default
value.
l Set Remote MEP/MIP
ID or IP Address
according to the
termination node of an
LB/LT test. If MEG ID
Type is set to IP Based
for the termination node,
set Remote MEP/MIP
ID or IP Address to the
LSR ID of the
termination node. If
MEG ID Type is set to
ICC Based for the
termination node, set
Remote MEP/MIP ID
or IP Address to the MP
ID of the termination
node.
l It is recommended that
you set Packet Count,
Packet Priority,
Transmit Interval (ms),
and Packet Length to
their default values.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 135
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step Operation Remarks
5.6.10 Starting an LT Test Perform this task when you
Provided by MPLS-TP need to perform an LT test.
Tunnel OAM Set parameters as follows:
It is recommended that you
retain the default values for
Packet Sending Interval,
Packet Sending Priority,
and Length of Sending
Packet.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
5.6.11 Testing the Packet Perform this task when you
Loss Ratio, Delay, and need to query the packet
Delay Variation of a PW loss ratio, delay, and delay
variation.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
5.6.12 Setting the LCK Perform this task when you
Status of MPLS-TP PW need to lock the PW.
OAM Set Lock Status to Lock.
5.6.13 Starting a TST Test Perform this task when you
of MPLS-TP PW OAM need to test the packet loss
situation.
NOTE
This task is supported only
when the configuration is
performed in end-to-end mode
on the U2000.
4.10 Configuration Example (MPLS Tunnels with No
Protection)
This example assumes that the network topology and microwave links have been configured.
4.10.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
Configure MPLS tunnels according to the requirements listed in Table 4-24. The networking
diagram is shown in Figure 4-14.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 136
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Table 4-24 Service requirements
Requirement Description Requirement Satisfaction
Servic Bidirectional MPLS tunnels -
e need to be configured between
requir NE1 and NE4.
ement
Figure 4-14 Networking diagram
4.10.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring MPLS tunnels.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example
Specify IP Address Manually
IP Address 46.1.64.1
Sink Node 130.0.0.2
Tunnel Type E-LSP
Procedure
Step 1 Set MPLS port attributes.
NE2 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 137
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step 2 Set Basic MPLS Attributes
NE2 is used as an example.
Step 3 Create an MPLS Tunnel.
Create a Unidirectional MPLS Tunnel on NE2 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 138
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.11 Configuration Example (E-Line Services Carried by
PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure E-Line services carried by
PWE3 according to network conditions.
4.11.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
Ethernet services from BTSs need to be converged to an RNC through PWs, based on MPLS
tunnel configuration. The specific service requirements are as follows:
l Ethernet services from BTS33 are received by NE7 and need to be transmitted to the
RNC.
l The information about the tunnels between NE7 and NE1 is as follows:
– A bidirectional tunnel (ID: 1502) with no protection is available between NE7 and
NE4
– A bidirectional tunnel (ID: 1501) with protection is available between NE4 and
NE1.
– Ethernet services from BTSs are carried by PWs on the two tunnels, and PW labels
and tunnel labels are swapped on NE32.
l Ethernet services from all BTSs have been configured with VLAN priorities based on
the service types The transmission network provides end-to-end QoS control based on
the VLAN priorities.
l NE1's GE ports, which are connected to the RNC, need to be protected by a link
aggregation group (LAG).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 139
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-15 Networking diagram
4.11.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring E-Line services carried by PWs.
Context
Configure E-Line services carried by PWs according to the following table.
Parameter Value
Service ID 123
Service Name service_1
Direction UNI-NNI
Source VLANs 100
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 140
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.12 Configuration Example (E-LAN Services Carried by
PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure E-LAN services carried
by PWE3 according to network conditions.
4.12.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking of NEs.
Ethernet services from BTSs need to be converged to an RNC through PWs, based on MPLS
tunnel configuration. The specific service requirements are as follows:
l Ethernet services from BTS33 are received by NE7 and need to be transmitted to the
RNC.
l The information about the tunnels between NE7 and NE1 is as follows:
– A bidirectional tunnel (ID: 1502) with no protection is available between NE7 and
NE4
– A bidirectional tunnel (ID: 1501) with protection is available between NE4 and
NE1.
– Ethernet services from BTSs are carried by PWs on the two tunnels, and PW labels
and tunnel labels are swapped on NE32.
l Ethernet services from all BTSs have been configured with VLAN priorities based on
the service types The transmission network provides end-to-end QoS control based on
the VLAN priorities.
l NE1's GE ports, which are connected to the RNC, need to be protected by a link
aggregation group (LAG).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 141
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-16 Networking diagram
4.12.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring E-LAN services carried by PWs.
Context
Configure E-LAN services carried by PWs according to the following table.
Parameter Value
Service ID 1
Service Name ELAN_1
Tag Type S-Aware
Self-Learning MAC Address Enabled
MAC Address Learning Mode IVL
Protection Type Unprotected
VLAN Filtering Table 100–300
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 142
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.13 Configuration Example (MPLS OAM_Y.1711)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS OAM (Y.1711) for
long-term LSP monitoring according to network conditions.
NOTE
An OptiX RTN 380 housing the SHUF3 board does not support MPLS OAM.
4.13.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
On a PSN shown in Figure 4-17, CV packets are used to continuously test the connectivity of
the bidirectional MPLS tunnel (ID = 1501) between NE1 and NE3.
Figure 4-17 Network diagram of the MPLS OAM (Y.1711) function
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 143
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4.13.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring MPLS OAM (Y.1711).
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example
OAM Status Enabled
Detection Packet Type CV
Detection Mode Adaptive
SD Threshold(%) 0
SF Threshold(%) 0
Procedure
Step 1
NE1 is used as an example.
----End
4.14 Configuration Example (LSP Ping/Traceroute)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure LSP ping/traceroute
according to network conditions.
NOTE
This example describes the application of LSP Ping. The application of LSP Traceroute is similar, and
therefore is not described.
An OptiX RTN 380 housing the SHUF3 board does not support LSP Ping/Traceroute.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 144
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4.14.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
On a PSN as shown in Figure 4-18, LSP ping is used to test the connectivity of a bidirectional
tunnel (ID = 1501) between NE1 and NE3.
Figure 4-18 Network diagram of the LSP ping function
4.14.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring LSP ping.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example
Detection Packet LSP Ping
EXP Value 7
TTL 255
Transmit Interval (10 ms) 100
Packet Length 100
Response Timeout Period (10 ms) 300
Response Mode IPv4 UDP Response
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 145
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.15 Configuration Example (MPLS APS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS APS according to
network conditions.
4.15.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
As shown in Figure 4-19, in a packet switching network, two bidirectional tunnels are
configured in MPLS APS protection between NE1 and NE4 to improve reliability. Y.1711-
compliant MPLS-TP OAM is used to check the MPLS tunnel availability.
Figure 4-19 Network diagram of MPLS APS
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 146
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4.15.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring MPLS APS.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example
Set MPLS OAM OAM Status Enabled
(ITU-T Y.1711)
parameters. Detection Packet Type CV
Detection Mode Adaptive
SD Threshold(%) 0
SF Threshold(%) 0
Create an MPLS Protection Type 1:1
APS protection
group. Switching Mode Dual-Ended
Working Ingress Tunnel ID 1502
Protection Ingress Tunnel ID 1501
Revertive Mode Revertive
WTR Time (min) 3
Hold-Off Time (100 ms) 0
Protocol Status Disabled
Procedure
Step 1 Set MPLS OAM (ITU-T Y.1711) parameters.
Working tunnel 1501 on NE1 is used as an example:
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 147
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step 2 Create an MPLS APS protection group.
NE1 is used as an example:
Step 3 Enable the MPLS APS protection protocol.
NE1 is used as an example:
----End
4.16 Configuration Example (PW OAM_Y.1711)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW OAM (Y.1711) for
long-term PW monitoring according to network conditions.
NOTE
An OptiX RTN 380 housing the SHUF3 board does not support MPLS OAM.
4.16.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 148
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
On a PSN shown in Figure 4-20, CV packets in the PW OAM (Y.1711) mechanism are used
to continuously test the connectivity of the PW between NE1 and NE3.
Figure 4-20 Network diagram of the PW OAM (Y.1711) function
4.16.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring PW OAM (Y.1711).
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example
OAM Status Enabled
Detection Mode Adaptive
Detection Packet Type CV
SD Threshold(%) 0
SF Threshold(%) 0
Procedure
Step 1
NE1 is used as an example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 149
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.17 Configuration Example (PW Ping/Traceroute)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW ping/traceroute
according to network conditions.
NOTE
The RTN 380 equipped with an SHUF3 board does not support Y.1711-compliant PW OAM.
4.17.1 Network Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
On a PSN as shown in Figure 4-21, PW ping is used to test the connectivity of a PW between
NE1 and NE3.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 150
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-21 Network diagram of the PW ping function
4.17.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring PW ping.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Example Planning Principle
Packet test PW ping The PW ping function is
used to check PW
connectivity, instead of
locating a fault.
Packet length 64 (short packet test) PWPWs transmit packets of
1400 (long packet test) variable lengths. Set the test
packets to different lengths
to verify the connectivity of
a PW when it transmits
short and long packets.
Response mode Application control channel NE3 can respond to PW
ping/traceroute request
packets through the reverse
tunnel. Therefore, set the
response mode to
application control channel
when a test is initiated at
NE1.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 151
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Procedure
Step 1
----End
4.18 Configuration Example (PW APS)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure PW APS according to
network conditions.
NOTE
The RTN 380 equipped with an SHUF3 board does not support PW APS.
4.18.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
In Figure 4-22, NE1 is an OptiX RTN 300 NE. PW APS is configured for NE1 to achieve
RNC dual-homing. PW OAM (Y.1711) is used to check the availability of PWs.
Figure 4-22 Network diagram of PW APS
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 152
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
NOTE
In this figure, the working tunnel is the tunnel that carries the working PW, and the protection tunnel is
the tunnel that carries the protection PW. MPLS APS is not configured between the two tunnels.
The service requirements are as follows:
l A working tunnel is configured with an ID of 1501, and a protection tunnel is configured
with an ID of 1502.
l Three unprotected PWE3 services are created on the working tunnel. Table 4-25
provides the service planning information.
l To save resources, only one PWE3 service is configured into a PW APS protection
group. The other two services are configured into its slave protection pairs. This means
that the two services will be switched if the PWE3 service in the PW APS protection
group is switched.
Table 4-25 Planning information about PW APS
Parameter Ethernet Service
Service ID 202 203
Protection type PW APS protection Slave protection pair
4.18.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring PW APS.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Planning
Example Principle
Basic attributes Detection packet FFD -
type
detection mode Adaptive
Information about the protection PW See the following Disable the protocol
figure. before you configure
the protection PW.
MPLS APS Protocol status Enabled -
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 153
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Procedure
Step 1 The following describes how to create a PW APS protection group on NE1.
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 154
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
4.19 Configuration Example (PW FPS)
This configuration example describes how to configure PW FPS for RTN devices when the
RTN devices form a Mixed VPN with CX devices.
NOTE
The RTN 380 equipped with an SHUF3 board does not support PW FPS.
4.19.1 Networking Diagram
On the network, the OptiX RTN 300 NEs are configured with PW FPS to implement dual-
homing protection of services.
In Figure 4-23, NE1 is an OptiX RTN 900 NE. PW FPS is configured for NE1 to achieve
RNC dual-homing. Y.1731-compliant MPLS-TP OAM is used to check the PW availability.
Figure 4-23 Networking diagram of PW FPS
NOTE
A working tunnel is configured with an ID of 201, and a protection tunnel is configured with an ID of
801.
In the figure, the working tunnel bears the working PW and the protection tunnel bears the protection
tunnel. The two tunnels are not in one MPLS APS protection group.
4.19.2 Configuration Procedure
A PW FPS protection group needs to be created and the ARP entry dually-transmitting and
buffering needs to be enabled.
Data Preparation
Item Value in This Planning
Example Principle
Information about PW ID 2 -
the protection PW
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 155
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Item Value in This Planning
Example Principle
PW Incoming Label 83
PW Outgoing Label 17
Information about Packet Detection 3.3 -
MPLS-TP OAM Interval(ms)
GAL Enable Status Enabled
ARP Dual Feed Enabled -
Procedure
Step 1 The following describes how to configure a PW FPS protection group on NE1.
----End
4.20 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for Tunnels)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS-TP tunnel OAM
according to network conditions.
NOTE
The RTN 380e or The RTN 380 equipped with an SHUF3 board does not support MPLS-TP OAM.
4.20.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
On a PSN shown in Figure 4-24, two LB tests must be performed to locate the fault on the
bidirectional MPLS tunnel (ID = 1501) between NE1 and NE3.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 156
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-24 Networking diagram for MPLS-TP tunnel OAM
4.20.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring data.
Procedure
Step 1 Change the OAM standard to Y.1731.
Step 2 Set global OAM parameters.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 157
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step 3 Configure MEP parameters for MPLS-TP tunnel OAM.
Step 4 Start a CC test of MPLS-TP tunnel OAM.
Step 5 Start an LB test of MPLS-TP tunnel OAM.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 158
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
4.21 Configuration Example (MPLS-TP OAM for PWs)
This section uses an example to describe how to plan and configure MPLS-TP PW OAM
according to network conditions.
NOTE
The RTN 380 equipped with an SHUF3 board does not support MPLS-TP OAM.
4.21.1 Networking Diagram
This section describes the networking information about the NEs.
On a PSN shown in Figure 4-25, LB tests are used to test the connectivity of the PW between
NE1 and NE3.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 159
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Figure 4-25 Networking diagram for MPLS-TP PW OAM
4.21.2 Configuration Procedure
This section describes the procedure for configuring data.
Procedure
Step 1 Change the OAM standard to Y.1731.
Step 2 Set global OAM parameters.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 160
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
Step 3 Configure MEP parameters for MPLS-TP PW OAM.
Step 4 Start a CC test of MPLS-TP PW OAM.
Step 5 Start an LB test of MPLS-TP PW OAM.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 161
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 4 Configuring MPLS/PWE3 Features
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 162
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5 Task Collection
About This Chapter
This task collection contains all the network management system (NMS) operation tasks
related to the product features.
5.1 Network Management Features
This section provides links to operations related to the network management features.
5.2 Managing Microwave Links
Before you configure a microwave link between two microwave sites, configure information
about the microwave link.
5.3 Ethernet Services and Features
This section provides links to operations of configuring Ethernet features.
5.4 Managing MPLS Tunnels
Managing MPLS tunnels include managing MPLS OAM functions.
5.5 Managing MPLS APS Protection Groups
MPLS APS is the commonest protection mode for MPLS tunnels.
5.6 Managing PWs
All types of PWE3 services are carried by PWs.
5.7 Managing a PW APS/PW FPS Protection Group
PW APS and PW FPS are two modes for protecting PWs.
5.8 Managing the IEEE 1588v2 Clock
This section provides hyperlinks to 1588v2 configuration operations.
5.1 Network Management Features
This section provides links to operations related to the network management features.
5.1.1 Creating an NE by Using the Search Method
The U2000 can find all NEs that communicate with a specific gateway NE by using the IP
address of the gateway NE, the network segment of the gateway NE IP address, or the NSAP
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 163
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
addresses. In addition, the U2000 can create the NEs that are found in batches. Compared
with the method of manually creating NEs, this search method creates NEs faster and more
reliably.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The network management system (NMS) is communicating with NEs properly.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
This task can also be performed on the Web LCT, but the steps are different from those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Creates an NE by using the search method.
l Creates an NE by using the NE Search method (only on the Web LCT) if the NE is the
gateway NE and belongs to the same network segment as the NMS server.
Procedure
Step 1 Create an NE by using the search method (U2000).
Step 2 Create an NE by using the NE Search method (Web LCT).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 164
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.2 Creating an NE Manually
If you create NEs manually, you can create them one by one instead of in batches.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The network management system (NMS) is properly communicating with the NE to be
created.
l If the NE to be created is a non-gateway NE, the corresponding gateway NE has been
created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
If new NEs are created manually on the Web LCT:
l SSL is recommended for communication with NEs. Set the port number to 5432 and perform the
following steps to replace the SSL certificate:
l Delete the WebLCT\conf\certificate directory on the Web LCT.
l Copy the server\etc\ssl\nemanager\default directory on the U2000 to the path WebLCT\conf on the
Web LCT. Rename default to certificate. Note that the installation path on the Web LCT should not
contain Chinese characters, spaces, or special characters.
l Restart the Web LCT.
l Install the SSL certificate to the NE using the U2000. For details, see the Security Configuration
Maintenance & Hardening.
Context
The following procedure creates NE1 manually.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 165
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1 Creating an NE manually
----End
5.1.3 Changing an NE ID
Change the NE ID according to the engineering plan to ensure that each NE ID is unique.
This task does not interrupt services.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure changes an NE ID to the planned value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
New ID 1
New Extended ID 9
After changing the NE ID, you need to relog in to the NE.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 166
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1 Changing an NE ID
----End
5.1.4 Changing an NE Name
For easier identification of an NE in Main Topology, name the NE according to its
geographical location or the device to which it is connected.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure changes an NE name to the planned value listed in the following
table.
Parameter Value
Name NE1
Procedure
Step 1 Changing an NE Name
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 167
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.5 Synchronizing NE Time
If NE time is synchronized with the time on the NMS or NTP server, the time when an alarm
or abnormal event occurs can be recorded accurately.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The time zone and time have been set correctly on the PC or server running the NMS
software if the NE time needs to be synchronized with the NMS time.
l The time on the NTP server has been set correctly and the NTP is running properly if the
NE time needs to be synchronized with the NTP server time.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Synchronizes the NE time with the NMS time according to the parameter value listed in
the following table.
Table 5-1 NE time synchronization parameter
Parameter Value
Synchronous Mode NM
l Synchronizes the NE time with the NTP server time according to the parameter values
listed in the following tables.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 168
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Table 5-2 NE time synchronization parameters
Parameter Value
Synchronous Mode Standard NTP
Standard NTP Authentication Disabled
Table 5-3 Parameters of the standard NTP server
Parameter Value
Standard NTP Server Flag NE ID
Standard NTP Server 9-16
Standard NTP Server Key 0
Procedure
Step 1 Synchronize the NE time with the NMS time.
Step 2 Synchronize the NE time with the NTP server time.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 169
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.6 Synchronizing NE Time with Local Time
If daylight saving time (DST) is used in the area where an NE is located, you need to
synchronize the NE time with the local time.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
This task can also be performed on the Web LCT, but the procedure is different from that on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure synchronizes the NE time with the local time according to the
parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Time Zone (U2000) (UTC+01:00)-Central European Time
(Europe/Berlin)
Time Zone (Web LCT) (GMT+08:00)-China Standard Time (PRC)
DST Selected
Start Rule Week
End Rule Week
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 170
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.7 Configuring a Standard NTP Key
An NTP key needs to be configured if an NE synchronizes time with the NTP server and if
the NE needs to be authenticated by the NTP server.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
l Synchronous Mode is set to Standard NTP, and Standard NTP Authentication is set
to Enabled.
l The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is running properly. The NTP identity authentication
has been enabled on the NTP server.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
For the Web LCT, this operation is completed in the procedure of 5.1.5 Synchronizing NE Time.
Context
The following procedure sets a standard NTP key according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Key ID 1024
Password 123456
Trusted Yes
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 171
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.8 Setting NE Communication Parameters
NE communication parameters include the NE IP address, extended ID, gateway IP address,
subnet mask, and NSAP address.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
If multiple parameters need to be set, click Apply after setting each parameter.
NOTE
l Do not use the default IP address of an NE to access the public network (for example, Internet).
l The default IP address of an NE is a temporary address and is only used for the DCN plug-and-play of the
NE. Users must modify the default IP address in a timely manner.
Context
The following procedure sets the IP address and subnet mask of an NE to the planned values
listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 172
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
IP Address 10.0.0.1
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Connection Mode Common+Security SSL
NOTE
When Connection Mode is set to Common +
Security SSL for gateway NEs, it is
recommended that you set Connection Mode to
Security SSL for the NMS.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.9 Configuring DCCs
To meet the requirements for managing a complex network, you must set the channel type,
protocol type, and status of data communications channels (DCCs) according to the network
plan.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 173
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure changes the DCC protocol to TCP/IP.
Parameter Value
Enabled/Disabled Enabled (default value)
Protocol Type TCP/IP(default value)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.10 Setting the VLAN ID and Bandwidth for an Inband DCN
The VLAN ID used by an inband data communication network (DCN) must be different from
the VLAN ID used by services. The bandwidth of an inband DCN must meet the
requirements of the transmission network for managing messages.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the VLAN ID and bandwidth to the planned values listed in the
following table for an inband DCN.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 174
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
VLAN ID 4094
Bandwidth(Kbit/s) 512Kbit/s
Procedure
Step 1 Setting the VLAN ID and Bandwidth for an Inband DCN
----End
5.1.11 Configuring the Priorities of Inband DCN Packets
By performing this task, you can set the VLAN priorities and differentiated services code
point (DSCP) values carried by inband data communication network (DCN) packets.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the VLAN priority and DSCP value carried by inband DCN
packets to the planned values listed in the following table.
Packet Type Priority
VLAN CS6
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 175
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Packet Type Priority
DSCP BE (default value)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.12 Setting a Port for an Inband DCN
By performing this task, you can set the inband data communication network (DCN) status
and inband DCN protocol stack type for an inband DCN port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Sets the inband DCN protocol stack to the IP protocol stack for thwo Ethernet ports.
Parameter P&E GE(o)
Enabled Status Disabled Enabled (default value)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 176
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter P&E GE(o)
Protocol Type IP(default value) IP(default value)
l Change the inband DCN status for a microwave port.
Parameter IF
Enabled Status Enabled (default value)
Protocol Type IP(default value)
Procedure
Step 1 Change the inband DCN protocol stack for an Ethernet port.
Step 2 Change the inband DCN status for a microwave port.
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 177
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.1.13 Configuring Access Control
When an NE is connected to the network management system (NMS) using an Ethernet
service port, you must configure access control.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
NOTE
l Do not use the default IP address of an access control interface to access the public network (for example,
Internet).
l The default IP address is a temporary address and is only used for the DCN plug-and-play of the NE.
Users must modify the default IP address in a timely manner.
Context
The following procedure configures the access control function for the port P&E according to
the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Enabled Status Enabled (default value)
IP Address 10.0.0.1
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Procedure
Step 1 Configuring Access Control
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 178
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.14 Creating a Static IP Route
When dynamic routes fail to meet planning requirements, you must create static IP routes
manually.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a static IP route according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Destination Address 10.2.0.100
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.255
Gateway 10.0.0.2
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 179
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.15 Setting OSPF Protocol Parameters
When the OptiX RTN equipment is interconnected with third-party equipment, routing
protocol interaction works properly after you set Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol
parameters of the OptiX RTN equipment based on related requirements of the third-party
equipment.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures OSPF parameters according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Area 0.0.0.1
OSPF Status Enabled
Static route Enabled
LAN Interface Disabled
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 180
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.16 Creating an OSPF Area
If an NE functions as an area border router (ABR), you must create the non-backbone area to
which the ABR belongs.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area according to the
planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
ID 0.0.0.1
IP Address 129.11.0.0
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Authentication Type none
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 181
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Automatic Route Aggregation Enabled
Stub Type NON-STUB
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.17 Configuring the Network Information of an ABR
By performing this task, you can add or modify the network information of an area border
router (ABR).
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Modifies the network information about the backbone Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
area according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 182
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
IP Address 129.9.0.0
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
l Adds the network information about a non-backbone OSPF area according to the
planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
IP Address 129.10.0.0
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Procedure
Step 1 Modify the network information about the backbone OSPF area.
Step 2 Add the network information about a non-backbone OSPF area.
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 183
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.1.18 Creating a Manual Route Aggregation Group
An NE supports a maximum of eight manual route aggregation groups.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a manual route aggregation group according to the planned
parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
IP Address 129.11.0.0
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 184
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.1.19 Configuring Port IP Addresses for an ABR
If a port on an area border router (ABR) does not belong to the backbone area, you must
configure an IP address for this port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Sets a port IP address for the data communications channel (DCC) at a microwave port.
Parameter Value
Enabled/Disabled Enabled (default value)
Protocol Type IP (default value)
IP Address 129.9.0.10
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
l Sets a port IP address for the inband data communication network (DCN) channel at the
Ethernet port GE1.
Parameter Value
Enabled/Disabled Enabled (default value)
Protocol Type IP (default value)
IP Address 129.9.0.11
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Procedure
Step 1 Set a port IP address for the DCC channel at a microwave port.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 185
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Set a port IP address for the inband DCN channel at the Ethernet port P&E.
----End
5.1.20 Configuring the OSPF Authentication Type
NEs added into an OSPF area can be authenticated in MD5 mode or using a simple password.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 186
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l Changes the authentication type for area 0.0.0.1.
Table 5-4 Authentication Type
Parameter Value
Authentication Type MD5
l Sets the passwords used for a data communication network (DCN) port when different
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) authentication types are used.
Table 5-5 Authentication Password
Port Type Authentication Authentication MD5 Key
Type Password
LAN MD5 abc123 16
DCC none (default - -
value)
Procedure
Step 1 Change the authentication type for an area.
Step 2 Set the passwords used for a DCN port when different OSPF authentication types are used.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 187
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.21 Enabling the Proxy ARP
The proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) enables NEs in the same network segment but
different domains to communicate with one another.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure enables the proxy ARP function for NE1 (gateway NE) shown in the
following figure. By performing this operation, the network management system (NMS) gains
direct access to NE2.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 188
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.22 Enabling/Disabling the RSTP Protocol When the L2 DCN
Solution Is Used
The RSTP protocol improves stability of an L2 DCN.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 189
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure enables the RSTP protocol when the L2 DCN solution is used.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.23 Querying IP Routes
By querying IP routes, you can check whether the IP data communication network (DCN)
solution and inband DCN solution are configured correctly and whether NEs properly
communicate with one another.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure checks whether the NE IP routes and parameters are properly
planned.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 190
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.24 Verifying the Connectivity of an IP DCN Network
You can perform a ping or traceroute test to verify the connectivity between two NEs on an IP
DCN network.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Checks the connectivity between two NEs on an IP DCN network by performing a ping
test.
l Checks the connectivity between two NEs on an IP DCN network by performing a
traceroute test.
Procedure
Step 1 Check the connectivity by performing a ping test.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 191
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Check the connectivity by performing a traceroute test.
----End
5.1.25 Setting SNMP Communication Parameters
This section describes how to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
parameters for an NE that functions as an SNMP agent. This SNMP agent uses these
parameters to communicate with the SNMP server.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 192
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Precautions
l The SNMP version, read/write permissions, and community name planned for the OptiX
RTN 380 must be the same as those for the SNMP server.
l NMS IP Address can be set to 0.0.0.0 if all SNMP servers are allowed to access an NE.
Such configuration may cause security risks. Therefore, exercise caution when you set
NMS IP Address to 0.0.0.0.
Context
The following procedure sets SNMP parameters according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
SNMP IP Address 10.0.0.106
Read/Write permissions Reading and writing
Report SDH performance Trap Report
Report data performance Trap Report
Report Alarm Trap Report
Port 162
Read community name RTN300_Read01
Write community name RTN300_Write01
Trap community name RTN300_Trap01
Trap version SNMPV2C
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 193
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.1.26 Configuring the Active and Standby Gateway NEs
This section describes how to configure the active and standby gateway NEs on a DCN
network, which can improve network reliability.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
The Web LCT does not support this operation.
Context
The following procedure configures the standby gateway NE for NE(9-40838) according to
the planned parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Standby gateway NE NE1
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.27 Configuring an Electrical Interface for Ethernet Services as
an Ethernet Network Management Interface
This section describes how to configure an electrical interface for Ethernet services as the
Ethernet network management interface.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 194
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.28 Configuring the Ethernet NMS Port on an NE
By default, an NE can connect to the network management system (NMS) or another NE
through its Ethernet NMS port. The Ethernet NMS port works in auto-negotiation mode.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l It is recommended that the LCT connects to an NE through an Ethernet port.
l If you need to use the LCT to initialize an NE or download software, connect the LCT to
the NE through an Ethernet port.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 195
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure enables the Ethernet NMS port of an NE and sets its working mode
to Auto-Negotiation.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.29 Configuring Security Management Parameters for the
WLAN Module
By default, WLAN is enabled on an NE.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps set the SSID and access password for the WLAN module according to
the planned values listed in the following table.
NOTE
l The default WLAN password is Modify_123.
l If the account for logging in to the NE is admin or above, you can set a new password without verifying
the old password.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 196
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
SSID wifi_300
Password wifitest_123
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.30 Configuring the Port IP Address of the WLAN Module
The default port IP address is 192.168.1.1 and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures the port IP address of the WLAN module according to
the planned parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
IP Address 192.168.10.1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 197
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.31 Configuring DHCP for the WLAN Module
By default, DHCP is enabled on an NE to automatically allocate an IP address to the LCT
connected through WLAN.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps enable DHCP on an NE.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 198
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.32 Configuring Channels for the WLAN Module
By default, the Auto mode is selected for the WLAN access channel.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps configure channels for the WLAN module.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 199
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.33 Enabling WLAN Whitelist
WLAN Whitelist protects NEs against access from unauthorized addresses.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps enable WLAN Whitelist.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 200
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.34 Configuring WLAN Whitelist
When WLAN Whitelist is not enabled on the U2000, you can configure MAC addresses of
NEs that are allowed to access the U2000.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps configure WLAN Whitelist.
Parameter Value
Mac address 2E-3D-1A-CE-38–2F
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 201
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.35 Configuring LLDP
When an RTN NE and a base station are directly connected or connected through a PI, the
LLDP function can be enabled for them so that they can query basic information about each
other.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets LLDP parameters according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Mode Transmit&Receive
VLAN 100
VLAN Priority 0
Multicast Mode Nearest Bridge
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 202
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.1.36 Querying Information About an RTN NE's Neighboring
Base Stations Based on LLDP
The U2000 can query information about all base stations that set up LLDP neighbor
relationships with an RTN NE.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure query LLDP Neighbor Relationship.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 203
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.37 Generating a Pair of Public and Private Keys
This section describes how to operate the U2000 to generate public and private key pairs. The
private key must be backed up and kept safe.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
The Web LCT does not support this operation.
Context
The following steps generate a pair of public and private keys.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 204
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.1.38 Configuring NE Anti-Theft
Two anti-theft policies are available to RTN NEs: configuration control and service control.
By default, the configuration control policy is used.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
A pair of public and private keys have been generated.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Before using the Web LCT to configure this operation, you must import the generated RSA Key and Public
Key by U2000.
Context
Item Value in This Example
Anti-theft State Enabled
Control Policy Configuration
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 205
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.2 Managing Microwave Links
Before you configure a microwave link between two microwave sites, configure information
about the microwave link.
5.2.1 Configuring Microwave Link Data
Configure microwave link data before aligning antennas.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l If microwave links are created for the first time, automatic frequency selection is
disabled by default when you are configuring microwave link data. This can prevent
automatic operating frequency switching from affecting antenna alignment.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Background Information
The network planning has been completed. Suppose that the planned parameter values are as
follows:
Parameter Value
Mode Master
TDD Timeslot Ratio 2:1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 206
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Frequency Range China (59000-64000)
Link ID 1
Opposite Ne Name NE2
Distance between two NEs of a hop 100
microwave link
Tx Power 3.0 (Only 3.0 is supported.)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.2.2 Setting the Maximum Transmit Power and Power
Thresholds
This section describes how to set the maximum transmit power and power thresholds.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 207
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure sets the maximum transmit power for an NE according to the
planned parameter value listed in the following table.
NOTE
The method for setting power thresholds is the same as that for setting the maximum transmit power.
Parameter Value
Maximum Transmit Power 10 dBm
Procedure
Step 1
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this task.
----End
5.2.3 Enabling/Disabling AM Booster
Enabling AM Booster can increase the maximum transmit power in modulation scheme of
full AM capacity.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The AM function has been enabled.
NOTE
Only the RTN 380 support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 208
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets AM Booster Status to Enabled.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.2.4 Configuring Ethernet Frame Header Compression and Error
Frame Discarding at an Air Interface
This section describes how to configure Ethernet frame header compression and error frame
discarding at an air interface.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 380H and RTN 380A does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures a microwave port according to the parameter values
listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 209
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
1-MXUF4-1 (IF)
Speed transmission at L2 Enabled
Speed transmission at L3 Enabled
NOTE
If Ethernet frame header compression is enabled, set the preceding two parameters to Enabled to compress
Layer 2 frame headers and IP frame headers.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3 Ethernet Services and Features
This section provides links to operations of configuring Ethernet features.
5.3.1 Setting the Basic Attributes for an Ethernet Port
The basic attributes of an Ethernet port define physical-layer information, such as the port
mode, encapsulation type, and maximum frame length.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 210
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
The procedures performed on the Web LCT and U2000 are the same. In addition, the procedure performed on
the Web LCT can configure basic attributes for microwave ports.
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for a P&E port according to the parameter
value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
1-MXUF4-2 (P&E)
Working Mode 100M Full-Duplex
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.2 Setting the Layer 2 Attributes of Ethernet Ports
Ethernet port Layer 2 attributes define link-layer information.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The Ethernet board must be added on the NE Panel.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 211
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.3 Setting Layer 3 Attributes of Ethernet Ports
The Layer 3 attributes of Ethernet ports define the relevant information used for carrying
MPLS tunnels, such as MPLS tunnel statuses and Ethernet port IP addresses.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
l Port Mode of Ethernet ports are set to Layer 3.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support this operation.
Context
The following procedure sets the Layer 3 Attributes of Ethernet Ports according to the
parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Specify IP Address Manually
IP Address 46.1.64.1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 212
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.4 Setting the Advanced Attributes of Ethernet Ports
You can configure MAC/PHY layer loopbacks, check the port rates, and configure loopback
detection and broadcast packet suppression functions by setting related Ethernet advanced
attributes.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 213
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.5 Setting the Basic Attributes of microwave Ports
microwave port attributes specify the basic information, including the port mode and
encapsulation mode.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for microwave port according to the
parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Name IF
Port Mode Layer 2
Encapsulation Type 802.1Q
Traffic Policing Status Enabled
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 214
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.6 Setting the L2 Attributes for Microwave Ports
The Layer 2 attributes of microwave ports specify the relevant information about the link
layer, including the tag attribute and QinQ type domain.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
An IF board has been added on the NE Panel.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps configure the basic attributes for microwave ports according to the
following parameter settings.
Parameter Value
Tag Tag Aware
Default VLAN ID 1
VLAN Priority 0
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 215
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.7 Setting the L3 Attributes for Microwave Ports
The Layer 3 attributes of microwave ports specify the relevant information used for carrying
MPLS tunnels, such as the tunnel enable status and IP address.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
An IF board has been added on the NE Panel.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support this operation.
Context
The following steps configure the basic attributes for microwave ports according to the
following parameter settings.
Parameter Value
Enable Tunnel Enable
Specify IP Address Manually
IP Address 46.1.64.9
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 216
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.8 Setting the Advanced Attributes of Microwave Ports
You can configure MAC/PHY layer loopbacks, check the port rates, and configure loopback
detection and broadcast packet suppression functions by setting related advanced attributes for
microwave ports. You can also configure the P&E power supply status and port bit error
detection functions through this operation.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
An IF board has been added on the NE Panel.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps configure the basic attributes for microwave ports according to the
following parameter settings.
Parameter Value
L2 Frame Header Compression Disable
L3 Frame Header Compression Disable
Loopback Check Disable
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 217
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Loopback Port Block Disable
Broadcast Packet Suppression Disable
Broadcast Packet Suppression Threshold(%) 25
Enable Switching Triggered by Bit Error Disable
Switching Mode Triggered by Bit Error SF
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.9 Configuring Flow Control for an Ethernet Port
After flow control is enabled, an Ethernet port sends a pause frame to instruct the peer end to
stop sending Ethernet packets for a specific period of time if congestion occurs on the link.
Then the link congestion is eliminated.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 218
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure configures flow control for a P&E port according to the planned
parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
1-MXUF4-2 (P&E)
Auto-Negotiation Flow Control Mode Enable Symmetric Flow Control
Non-Autonegotiation Flow Control Mode Disabled
NOTE
Enable flow control for ports connected to external equipment only when the external equipment uses the
flow control function. Normally, the function is not required.
NOTE
RTN 380H does not support Symmetric Flow Control.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.10 Creating VLAN Sub-Interfaces
When LSPs need to traverse a Layer 2 network or be transmitted together with Native
Ethernet services, you need to create VLAN sub-interfaces.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Port Mode has been set to Layer Mix for Ethernet boards and IF boards.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 219
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380H does not support this operation.
Context
The following steps configure the basic attributes for VLAN sub-interfaces according to the
following parameter settings.
Parameter Value
Port 1
Name VLAN_port1
Associated Board 1–MXUF4
Associated Port 1–MXUF4–(IF)
VLAN 200
Specify IP Address Manually
IP Address 46.1.64.1
IP Mask 255.255.255.252
Enable Tunnel Enable
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 220
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.3.11 Creating a LAG
If the bandwidth or availability of the Ethernet link between two NEs needs to be improved,
create a link aggregation group (LAG).
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Create a non-load sharing LAG to protect the Ethernet link from a UNI-side equipment
to an NE, according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter NE
LAG No. Assign Automatically
LAG Name LAG
LAG Type Static (default value)
Load Sharing Non-Sharing
LAG Priority 32768 (default value)
Packet Receive Timeout Period Long period
Main Ports P&E
Standby Ports GE(e)
l Create a load sharing LAG to increase Ethernet bandwidth of Ethernet links, according
to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter NE
LAG No. Assign Automatically
LAG Name LAG
LAG Type Static (default value)
Load Sharing Sharing
LAG Priority 32768 (default value)
Packet Receive Timeout Period Long period
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 221
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter NE
LAG Min Active Link Threshold 2
Main Ports P&E
Standby Ports COMBO
GE(o)
l Create a LAG for configuring 1+1 protection according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter NE
LAG No. Assign Automatically (default value).
LAG type Static (default value)
Load sharing type Non-load sharing (default value)
LAG priority 32768 (default value)
Main port P&E
Procedure
Step 1 Create a non-load sharing LAG.
Step 2 Create a load sharing LAG.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 222
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 3 Create a LAG for configuring 1+1 protection.
----End
5.3.12 Setting LAG Parameters
Link aggregation group (LAG) parameters include Port Priority and System Load Sharing
Hash Algorithm.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 223
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure sets LAG parameters according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Port Priority 32768 (default value)
System Load Sharing Hash Algorithm Source and Destination MACs
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.13 Creating an ERPS Instance
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) is configured by creating ERPS instances.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l Ethernet boards and IF boards have been added in NE Panel.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
The following steps create an ERPS instance according to the planned parameter values listed
in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 224
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
ERPS ID 1
East Port 1–MXUF4-1
West Port 1–MXUF4-5
ERP Ring Node Flag RPL Port
Flag Port 1–MXUF4-1
Revertive Mode Revertive
Control VLAN 4093
Loop Detect Enabled
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.14 Setting Global ERPS Protocol Parameters
Configured global ERPS protocol parameters take effect to all ERPS instances.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The ERPS protection instance must be created.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 225
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following steps configure parameters for the ERPS protocol according to the planned
values listed in the following figure.
Parameter Value
Hold-Off Time (ms) 0
WTR Time (mm:ss) 05:00
Guard Time (ms) 500
Packet Transmit Interval(s) 5
Entity Level 4
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.15 Setting ERPS Protocol Parameters
The Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) protocol parameters include the hold-off
time, WTR time, and guard time.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An Ethernet ring protection (ERP) instance has been created.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 226
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets ERPS protocol parameters according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
WTR time (mm:ss) 10:00
NOTE
Set ERPS protocol parameters according to the network plan. The default values are recommended.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.16 Creating a Virtual Channel VLAN Forwarding Table
You need to create a virtual channel VLAN forwarding table on an interconnection node.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l A multi-ring ERPS instance has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 227
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
l A virtual channel VLAN forwarding table needs to be created only for sub-rings. The
sub-rings need to be associated with corresponding major rings.
l Virtual Channel Status must have been enabled and Virtual Channel VLANs must
have been correctly set for the major ring by Setting Protocol Parameters for an ERPS
Instance.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.17 Setting Parameters for Switching Upon Multiple Failures
This section describes how to set parameters to minimize segmentation on an ERPS-protected
network after multiple failures occur.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
l Understand the network topology and properly configure parameters for switching upon
multiple failures to ensure that proper switching can be triggered on an ERPS sub-ring.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 228
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Otherwise, normal services may be interrupted. For details about the switching principles
for minimization of segmentation, see Feature Description.
l It is advised to configure a bound MEP for an interconnection node sub-ring port when
the network is normal.
l Modify Interconnected Node and Multi-point Failure only after multiple failures
occur. Restore the two parameters to default values immediately after faults are rectified.
Context
The example in the procedure will accomplish the following objectives:
Parameter Value
Hold-Off Time(ms) 100
Guard Time(ms) 3000
Entity Level 4
Interconnected Node None
Packet Transmit Interval(s) 5
Bound MEP -
Multi-point Failure Disable
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.18 Performing an External ERPS Switchover
This section describes how to perform an external ERPS switchover.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 229
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.19 Creating an Ethernet Service for Transmitting L2 Protocol
Packets
An Ethernet service for transmitting L2 protocol packets can transmit L2 protocol packets
from the source to the sink as high-priority packets with the PHB of CS7.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-Line services or 802.1q-based E-LAN services have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 230
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure creates an E-Line service and an E-LAN service for transmitting
LACP packets as shown in the following figure.
GE1(P&E)
LACP packet
IF
Ethernet Service LACP packet
Procedure
Step 1 Create an E-Line service to transmit L2 protocol packets.
Step 2 Create an E-LAN service to transmit L2 protocol packets.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 231
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.20 Configuring a VLAN Forwarding Table
A VLAN forwarding table enables VLAN ID swapping at the source or sink end of an E-Line
service.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-Line services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures a VLAN forwarding table to implement VLAN swapping
for an E-Line service.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 232
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
GE1(P&E)
VLAN ID=100,300 E-Line
IF
VLAN ID=200,400
E-Line Service Information Table VLAN Forwarding Table
Source Source Sink Sink Source Source Sink Sink
Interface VLAN ID Interface VLAN ID Interface VLAN ID Interface VLAN ID
P&E 100 IF 200
P&E 100 IF 200
IF 200 P&E 100
P&E 300 IF 400
P&E 300 IF 400
IF 400 P&E 300
NOTE
l A VLAN forwarding table entry implements only unidirectional VLAN swapping. For bidirectional
VLAN swapping, you need to configure two VLAN forwarding table entries.
l After a service is created, the U2000 automatically configures a VLAN forwarding table. If there are
multiple source and end VLAN IDs, the VLAN forwarding table automatically configured by the U2000
may be inconsistent with the plan. In this case, you need to configure a new VLAN forwarding table.
l Only the U2000 supports automatic configuration of the VLAN forwarding table. On the Web LCT, the
VLAN forwarding table must be manually configured.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.21 Configuring a QinQ Link
QinQ link configuration is the prerequisite for configuring a QinQ-based Ethernet line (E-
Line) service.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 233
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l On associated ports, the Encapsulation Type is set to QinQ.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures a QinQ link according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
QinQ Link ID 1
Port IF
S-VLAN ID 100
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.22 Configuring an E-Line Service Carried by QinQ
This section describes how to configure an Ethernet line (E-Line) service carried by QinQ.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 234
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l For NNI ports of UNI-NNI service, Encapsulation Type has been set to QinQ.
l The source port and sink port of the E-Line service carried by QinQ cannot be used for
the E-LAN port.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The following procedure creates an E-Line service carried by QinQ shown in the following
figure.
Figure 5-1 UNI-NNI Service
Figure 5-2 UNI-UNI(QinQ Port to QinQ Port) Service
Procedure
Step 1 Configure a UNI-NNI E-line service
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 235
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Configure a UNI-UNI service from a QinQ port to a QinQ port.
----End
5.3.23 Configuring an IEEE 802.1ad Bridge-based E-LAN Service
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An Ethernet board has been added on the NE Panel.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The following procedure configures an IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN service according
to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 236
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Tag Type S-Aware
Ports mounted to a bridge P&E port: NULL (S-VLAN: 200)
GE(o) port: QinQ (S-VLAN: 100)
IF port: QinQ (S-VLAN: 100, 200)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.24 Configuring a Split Horizon Group
Ports mounted to the same split horizon group cannot forward packets to each other.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-LAN services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a split horizon group for E-LAN services so that the ports
GE1 and GE2 cannot forward packets to each other.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 237
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
GE1(P&E)
(Auto-Negotiation)
IF
GE2(COMBO)
(Auto-Negotiation)
Bridge
Split horizon group
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.25 Creating a Static MAC Address Entry
By creating static MAC address entries, you can ensure that NEs with specific MAC
addresses are not affected after the MAC addresses are aged out. In addition, static MAC
address entries ensure that E-LAN services are applicable to NEs that receive but not transmit
packets.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-LAN services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 238
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure adds a static MAC address entry with the parameters listed in the
following table for an E-LAN service.
Parameter Value
VLAN ID 100
MAC Address 00–09–09–09–58–01
Egress Interface GE1 (P&E)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.26 Creating a Blacklist MAC Address Entry
This section describes how to create blacklist MAC address entries to prevent NEs with
specific MAC addresses from receiving/transmitting E-LAN services.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-LAN services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 239
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure adds a blacklist MAC address entry with the parameters listed in the
following table for an E-LAN service.
Parameter Value
VLAN ID 100
MAC Address 00–08–09–09–57–07
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.27 Managing a Dynamic MAC Address Table
By performing this task, you can set the entry aging parameter, or query or clear the entries in
a dynamic MAC address table.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l E-LAN services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 240
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure sets the aging time to 10 minutes for a dynamic MAC address entry.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.28 Creating an MSTP Port Group
If an NE needs to run MSTP with a user network, you must create an MSTP port group and
add NE ports that are connected to the user network into this port group. All ports in the port
group are involved in calculation of the spanning tree of the user network.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 don't support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an MSTP port group for NE1. This group includes the GE(e)
and P&E ports.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 241
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.29 Setting MSTP Bridge Parameters
MSTP bridge parameters include the bridge parameters and the parameters of each port
mounted to the bridge.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets MSTP bridge parameters. The default values are retained for
these parameters.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 242
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.30 Setting CIST Parameters
This section describes how to set CIST parameters, including the bridge priority, port priority,
and path cost.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
NOTE
The RTN 360 does not support this operation.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the port path cost to 200000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 243
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.31 Deleting an E-LAN Service
When an Ethernet local area network (E-LAN) service is not used, you need to delete the
service to release Ethernet resources.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An E-LAN service has been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure deletes the E-LAN service whose ID is 1.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 244
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.32 Modifying the Mapping for a DS Domain
This section describes how to modify the mapping between packet priorities and per-hop
behaviors (PHBs) in the ingress or egress direction of a Differentiated Services (DS) domain.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
OptiX RTN 380 has a default DS domain whose Mapping Relation ID is 1 and Mapping
Relation Name is default map. The default DS domain can be modified but cannot be
deleted. Other DS domains can be deleted or modified.
The following procedure modifies the mappings for a DS domain according to the planned
values listed in the following table.
The following table describes parameters on the Inbound Mapping Relationship tab.
CVLAN/SVLAN MPLS EXP IP DSCP PHB
Default value Default value 0-7 BE
8-15 AF11
16-23 AF21
24-31 AF31
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 245
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
CVLAN/SVLAN MPLS EXP IP DSCP PHB
32-39 AF41
40-47 EF
48-55 CS6
56-63 CS7
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.33 Changing the Ports Applied to a DS Domain and Their
Trusted Packet Types
This section describes how to set the packet type trusted by a port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure changes the packet types trusted by the Ethernet ports and
microwave port to the planned value listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 246
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Packet Type
IF cvlan
Procedure
Step 1 Delete a port that uses the DS domain.
Step 2 Add a port that uses the DS domain.
Step 3 Change the packet type trusted by the port.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 247
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.34 Enabling/Disabling DSCP Demapping at an Egress Port
If DSCP-based Diffserv is enabled and if you do not want the DSCP values to be changed by
demapping at egress ports, you can disable DSCP demapping.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets Egress DSCP Mapping Status to Disabled.
The following procedure sets Egress DSCP Mapping Status to Enable.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 248
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.35 Setting Egress Queue Scheduling Policies
This section describes how to set queue scheduling policies for an egress port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures queue scheduling policies for a microwave port
according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Grooming Policy After Reloading
CS7 SP
CS6 SP
EF SP
AF4 SP
AF3 WRR(weight=25)
AF2 WRR(weight=25)
AF1 WRR(weight=25)
BE WRR(weight=25)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 249
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.36 Configuring a Flow Based on the Port Policy
This section describes how to configure ACL, CAR for a service flow, map the service flow
to a specified priority queue, and configure CAR for a port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
NOTE
l Configuring CAR for a port and mapping a service flow to a specified priority queue are mutually
exclusive for a port.
l If Match Value is set to 0, this task enables you to configure CAR for a port. If Match Value is set
to a non-zero value, this task enables you to map a flow that complies with traffic classification
matching rules to a specified priority queue.
The following procedure:
l Configures CAR for a port.
Parameter Value
Traffic Classification ID 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 250
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Port GE(o)
Match Type CVLAN ID
Match Value 0
CoS AF1
Bandwidth Limit Enable
CIR (kbit/s) 102400
PIR (kbit/s) 204800
CBS (byte) 128000
PBS (byte) 256000
Yellow packet processing mode pass
l Map a flow that complies with traffic classification matching rules to EF priority queue.
Parameter Value
Traffic Classification ID 1
Port P&E
Match Type CVLAN ID
Match Value 100
CoS EF
Procedure
Step 1 Configure CAR for a port.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 251
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Map a flow that complies with traffic classification matching rules to EF priority queue.
----End
5.3.37 Configuring Port Shaping
This section describes how to configure traffic shaping for an egress port.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures port shaping for the Ethernet port GE(o) according to the
planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Bandwidth Limit Enabled
PIR (kbit/s) 512
PBS (kbit/s) 512
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 252
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.38 Setting Traffic Shaping for Egress Queues
This section describes how to set traffic shaping for an egress queue.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets traffic shaping for an egress queue (AF4) at a microwave port
according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Bandwidth Limit Enabled
PIR (kbit/s) 512
PBS (kbit/s) 512
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 253
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.39 Setting the Congestion Management Mode for Egress
Queues
This section describes how to set the congestion management mode for an egress queue.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the congestion management mode for an egress queue at a P&E
port according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 254
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Paramete Congesti WRED Configuration
r on
Manage ID Name Upper Lower Discard
ment Threshol Threshol Ratio (%)
Mode d (%) d (%)
CS7 Tail drop - - - - -
CS6 (default)
AF4
AF3
AF2
AF1
BE
EF WRED Auto- WRED1 90 (red) 75 (red) 100
assign 90 75 (default
(yellow) (yellow) value)
100 90 (green)
(green)
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.40 Creating a Service WRED Policy
This section describes how to create a service WRED policy.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 255
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a service WRED policy according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Policy ID 3
Policy name WRED
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.41 Configuring a V-UNI Egress Policy
This section describes how to create queue scheduling and shaping policies for V-UNI egress
queues, and specify WRR and discarding policies.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 256
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures a V-UNI egress policy according to the planned
parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Policy ID 1
Policy Name policy
WRR Scheduling Policy 102–WRR
Table 5-6 CoS configurations
Co Groom Bandw CIR PIR CBS PBS Tail Service
S ing idth (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/ Drop WRED
Policy Limitat s) Thresho Policy
After ion ld (256
Reload kbit/s)
ing
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
7 d
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
6 d
EF SP Enabled 20032 20032 — — / 3–
WRED
AF WRR Enabled — 30016 — — / 3–
4 WRED
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
3 d
AF WRR Enabled — 30016 — — / 3–
2 WRED
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
1 d
BE SP Disable — — — — — —
d
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 257
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.42 Configuring a V-UNI Group
This section describes how to create a V-UNI group and set bandwidth limitations for the
group.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures a V-UNI group according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
V-UNI Group ID 1
V-UNI Group Type Egress
CIR (kbit/s) 20032
CBS (kbit/s) 20032
PIR (kbit/s) 30016
PBS (kbit/s) 30016
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 258
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.43 Creating a PW Policy
This section describes how to create PW policies, including scheduling, shaping, packet
dropping, and WRR policies for PW queues.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support this operation.
Data Preparation
The following procedure creates a PW policy according to the planned parameter values listed
in the following table.
Parameter Value
Policy ID 1
Policy Name test1
WRR Scheduling Policy 1–WRR Default Scheduling
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 259
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Table 5-7 PW Configurations
Co Groom Bandw CIR(kb PIR(kb CBS(k PBS( Tail Service
S ing idth it/s) it/s) bit/s) kbit/ Drop WRED
Policy Limitat s) Thresho Policy
After ion ld (256
Reload kbit/s)
ing
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
7 d
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
6 d
EF SP Enabled NO — — — — —
limit
AF WRR Enabled — — — — — —
4
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
3 d
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
2 d
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
1 d
BE SP Disable — — — — — —
d
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 260
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.3.44 Configuring a QinQ Policy
This section describes how to create queue scheduling and shaping policies for QinQ queues,
and specify WRR and discarding policies.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a QinQ policy according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Policy ID 1
Policy Name policy
WRR Scheduling Policy 102–WRR
Table 5-8 CoS configurations
Co Groom Bandw CIR PIR CBS PBS Tail Service
S ing idth (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/ Drop WRED
Policy Limitat s) Thresho Policy
After ion ld (256
Reload kbit/s)
ing
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
7 d
CS SP Disable — — — — — —
6 d
EF SP Enabled 20032 20032 — — / 3–
WRED
AF WRR Enabled — 30016 — — / 3–
4 WRED
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
3 d
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 261
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Co Groom Bandw CIR PIR CBS PBS Tail Service
S ing idth (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/s) (kbit/ Drop WRED
Policy Limitat s) Thresho Policy
After ion ld (256
Reload kbit/s)
ing
AF WRR Enabled — 30016 — — / 3–
2 WRED
AF WRR Disable — — — — — —
1 d
BE SP Disable — — — — — —
d
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.45 Applying Policies
This section describes how to apply QinQ or V-UNI egress policies to services.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 262
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure applies a QinQ link policy according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Policy 1
Procedure
Step 1 Apply a V-UNI egress policy.
Step 2 Apply a QinQ link policy.
----End
5.3.46 Configuring Bandwidth Limitation for MPLS Tunnels
This section describes how to configure bandwidth limitation for MPLS tunnels.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 263
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MPLS tunnel has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support this operation.
Data Preparation
Parameter Value
CIR(Kbit/s) 100000
Other parameters the default values.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.47 Configuring Bandwidth Limitation for PWs
This section describes how to configure bandwidth limitation for PWs carrying ETH PWE3
services.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 264
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l An ETH PWE3 service has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support this operation.
Data Preparation
Parameter Value
CIR(Kbit/s) 64
CBS(bytes) 64
PIR(Kbit/s) 64
PBS(bytes) 64
Other parameters the default values.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.48 Configuring QinQ Link Bandwidth Limitations
This section describes how to configure QinQ link bandwidth limitations for QinQ services.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 265
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure configures QinQ link bandwidth limitations according to the
planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Bandwidth limitation Enabled
CIR (kbit/s) 5000
PIR (kbit/s) 5000
Policy 1
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.49 Creating an MD
A maintenance domain (MD) defines the range and level of the Ethernet OAM. MDs of
different ranges and levels can provide users with differentiated OAM services.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 266
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an MD according to the planned parameter values listed in
the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Domain Level 4
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.50 Creating an MA
A maintenance domain (MD) can be divided into several independent maintenance
associations (MAs). After creating MAs, you can associate specific Ethernet services with
MAs, which facilitates Ethernet OAM operations.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 267
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MD has been created.
l An Ethernet service has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an MA according to the planned parameter values listed in
the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name default
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Relevant Service auto_configuration
CC Test Transmit Period 1s
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 268
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.3.51 Creating an MEP
MEPs initiate and terminate all Ethernet OAM packets. After creating MEPs, you can check
the Ethernet link between MEPs in the same MA by performing OAM operations.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MA has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an MEP at a P&E port according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name default
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Port 1-MXUF4-2(P&E)
VLAN 100
MP ID 1
Direction Ingress
CC Status Active
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 269
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.52 Creating a Remote MEP in an MA
To ensure that an MEP can respond to the OAM operations initiated by the other MEPs in the
same MA, you need to set the other MEPs to be the remote MEPs of this MEP.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MA has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates a remote MEP at an Ethernet port according to the planned
parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name default
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Remote Maintenance Point ID 2
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 270
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.53 Creating an MIP
An MIP can only respond to specific OAM packets. By creating MIPs, you can divide the
Ethernet link between two MEPs in the same maintenance association (MA) into several
segments, thereby facilitating the Ethernet link checking.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MA has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure creates an MIP at an IF port according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Port 1-MXUF4-1(IF)
MP ID 3
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 271
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.54 Performing a CC Test
A continuity check (CC) test checks the status of a unidirectional link automatically and
periodically. If a CC test started at the source end finds that the link is faulty, the sink reports
the corresponding alarm.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The source and sink maintenance association end points (MEPs) in the same
maintenance association have been created.
l The remote MEPs have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
l Only an MEP can start a CC test and function as the receive or respond end in the test.
l During a CC check, the source MEP constructs and transmits continuity check message
(CCM) packets periodically. After receiving the CCM packets from the source MEP, the
sink MEP directly enables the CC function. If the sink MEP fails to receive the CCM
packets from the source MEP within the specified period (3.5 times the transmission
interval), it reports an alarm automatically.
l A CC test does not affect services.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 272
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure performs a CC test.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.55 Performing an LB Test
A loopback (LB) test enables you to check the bidirectional connectivity between the source
and sink maintenance association end points (MEPs) in the same maintenance association
(MA).
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The source and sink MEPs in the same maintenance associations have been created.
l The remote MEPs have been created.
l The continuity check (CC) function has been enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
l Only an MEP can initiate an LB test and function as the receive end in the test.
l During an LB test, the source MEP constructs and transmits loopback message (LBM)
frames and starts the timer. If the sink MEP receives the LBM frames, it sends loopback
reply (LBR) frames back to the source MEP. This indicates that the loopback is
successful. If the source MEP timer expires, the loopback has failed.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 273
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l An LB test does not affect services.
Context
The following procedure performs an LB test according to the planned parameter values listed
in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Source Maintenance Point ID 1
Destination Maintenance Point ID 2
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.56 Performing an LT Test
Based on the loopback (LB) test, the link trace (LT) test further improves the capability to
locate faults. A faulty network segment can be located based on maintenance association
intermediate points (MIPs) through only one test.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The source and sink maintenance association end points (MEPs) in the same
maintenance association (MA) have been created.
l The remote MEPs have been created.
l The continuity check (CC) function has been enabled.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 274
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
l Only an MEP can initiate an LT test and work as the receive end in the test.
l During an LT test, the source MEP constructs and transmits link trace message (LTM)
frames and starts the timer. All the MPs that receive the LTM frames respond with link
trace reply (LTR) frames. According to the LTR frames, you can determine all the MIPs
long the path from the source MEP to the sink MEP.
l An LT test does not affect services.
Context
The following procedure performs an LT test according to the planned parameter values listed
in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Association Name MA1
Source Maintenance Point ID 1
Destination Maintenance Point ID 2
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 275
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.3.57 Activating AIS
After a fault is detected by an MP on which the alarm indication signal (AIS) function is
activated, the MP sends an AIS packet to inform a higher-level MP of the fault information.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l Source and sink MEPs in the same MD have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure activates the AIS function.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.58 Checking the Packet Loss Ratio, Delay, or Delay Variation
of Ethernet Services
The ETH OAM function allows you to check the packet loss ratio, delay, or delay variation of
Ethernet services without affecting the Ethernet services.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 276
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l Native E-Line services that are transmitted based on ports and VLAN IDs have been
created.
l Source and sink MEPs in the same MD have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Precautions
Statistics on the packet loss ratio, delay, or delay variation can be collected for Ethernet
services on the RTN 300 on a per-NE basis or in an end-to-end manner.
Context
The following procedure:
l Checks the real-time performance statistics of Ethernet ports (on a per-NE basis).
l Checks the packet loss of Ethernet services using an LM test (in an end-to-end manner).
Procedure
Step 1 Check the real-time performance statistics of Ethernet ports (on a per-NE basis).
Step 2 Checks the packet loss of Ethernet services using an LM test (in an end-to-end manner).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 277
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.59 Enabling OAM Auto-discovery
OAM auto-discovery is the basis for implementing IEEE 802.3ah-compliant OAM. After
successful OAM auto-discovery, the equipment automatically monitors the faults and
performance of links.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
OAM auto-discovery is achieved based on auto-negotiation between the local and peer
equipment. If the negotiation fails, the local equipment reports an alarm. After successful
OAM auto-discovery, the link performance is monitored according to the error frame
threshold. You can set the error frame threshold on the NMS.
Context
The following procedure enables AOM auto-discovery according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Port 1-MXUF4-2(P&E)
Enable OAM Protocol Enabled
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 278
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
OAM Working Mode Active
Procedure
Step 1 Enable OAM auto-discovery.
----End
5.3.60 Enabling Link Event Notification
After link event notification is enabled on the local equipment, it notifies the peer equipment
if the OAM detects a link fault and link performance event.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The OAM auto-discovery operation has been performed successfully on the equipment
at both ends.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure enables link event notification for a P&E port.
Procedure
Step 1 Enable link event notification.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 279
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.3.61 Changing the OAM Error Frame Monitoring Threshold
The OAM error frame monitoring threshold is a standard for OAM to check link performance.
Generally, the default value is used. You can change the value according to the actual link
status.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
After the OAM auto-discovery operation is successful, link event notification is enabled and
the monitoring time and error frame monitoring threshold are set at the local end. If the local
equipment detects a link event in the receive direction, it notifies the peer equipment of the
link event. If link event notification is also enabled on the peer equipment, the peer equipment
notifies the local equipment when detecting a link event. The local equipment then reports the
corresponding alarm.
Context
The following procedure changes the OAM error frame monitoring threshold according to the
planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Error Frame Monitor Window (ms) 1000 (default value)
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 280
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Error Frame Monitor Threshold (frames) 1 (default value)
Error Frame Period Window(frames) 8928000
Error Frame Period Threshold(frames) 1 (default value)
Error Frame Second Window(s) 60 (default value)
Error Frame Second Threshold(s) 1 (default value)
Procedure
Step 1 Change the error frame monitoring threshold.
----End
5.3.62 Performing a Remote Loopback
After the Ethernet port on the local equipment sends data to the port on the peer equipment,
the local end can request the peer end to return the data.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The OAM auto-discovery operation has been performed successfully on the equipment
at both ends.
l OAM Working Mode has been set to Active on the equipment that will initiate a
loopback.
l The equipment that will respond to the loopback supports the remote loopback function.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 281
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Precautions
l If a port is capable of responding to loopbacks, it enters the loopback responding state
and reports a loopback responding alarm after receiving the command of enabling the
remote loopback function sent from the peer OAM port. The equipment that initiates the
loopback enters the loopback initiation state and reports a loopback initiation alarm.
l Generally, after the remote loopback function is enabled, service packets, except for
OAMPDU packets and data communication network (DCN) packets, are looped back at
the peer end.
l After using the remote loopback function to locate a fault and test link performance, you
must disable the remote loopback function at the end where the loopback is initiated and
recover services. Then the reported alarms are automatically cleared.
Context
The following procedure performs a remote loopback on a microwave port.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.63 Enabling Local Loopback Detection
After enabling local loopback detection on an Ethernet port, you can check the loopback of
the port and the loopbacks between the port and other Ethernet ports on the same board.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The Ethernet port that will use the local loopback detection function has been enabled.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 282
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure enables local loopback detection for the Ethernet port GE1.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.64 Configuring LPT
After link-state pass through (LPT) is configured, Ethernet ports correlated with microwave
links can be disabled automatically in the case of a microwave link fault.RTN 300 supports
simplified LPT.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The following procedure configures LPT according to the planned parameter values listed in
the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 283
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Convergence Port IF
Access Port P&E
NOTE
The RTN 380A does not support this operation.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.3.65 Configuring Bandwidth Notification
This section describes how to configure bandwidth notification. Bandwidth notification
monitors air-interface bandwidth changes and informs the peer router of the changes.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An egress MEP has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Background
l Bandwidth notification can be configured only on an egress MEP.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 284
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l Bandwidth notification packets do not affect services.
The following step configures bandwidth notification according to the planned parameter
values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Maintenance Domain Name MD1
Maintenance Association Name MA1
MEP ID 1
Advertisement Enable
Client Layer Level 7
Periodic Period
Periodic (s) 1
Hold Time (s) 0
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4 Managing MPLS Tunnels
Managing MPLS tunnels include managing MPLS OAM functions.
NOTE
The RTN 380H and RTN 380A does not support MPLS/PWE3.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 285
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.4.1 Creating ARP Static Entries
This topic describes how to create ARP entries that are not aged.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for ARP Static Entries according to the
parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
ARP List IP Address 1.1.1.12
ARP List MAC 00–10–5C-D6–BF-AC
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.2 Setting Basic MPLS Attributes
This topic describes how to set basic MPLS attributes, including the LSR ID and the global
label space.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 286
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.3 Configuring Global OAM Parameters
Once being configured for an NE, global OAM parameters take effect to all tunnels and PWs
on the NE.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure Configuring Global OAM according to the planned parameter values
listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 287
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Carrier ID 111
Port AIS Status Disabled
Channel Type 7F FA
CSF Status Enabled
Ping/Tracert Socket Port Status Enabled
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.4 Changing the MPLS Tunnel/PW OAM Standard
The default MPLS Tunnel/PW OAM standard is Y.1711.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l Tunnels/PWs have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 288
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.5 Creating a Unidirectional MPLS Tunnel
When creating a unidirectional MPLS tunnel, you need to manually create an MPLS tunnel in
the reverse direction.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The port attributes are set correctly.
l The LSR ID of each NE is set correctly.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Data Preparation
Table 5-9 MPLS tunnel planning data
Parameter Value
Sink Node 130.0.0.2
Tunnel Type E-LSP
Other parameters You can retain the default values in this example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 289
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Figure 5-3 MPLS tunnel planning data
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.6 Creating a Bidirectional MPLS Tunnel
During creation of a bidirectional MPLS tunnel, both the forward and reverse tunnels are
created.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The port attributes have been correctly configured.
l The LSR ID of each NE has been correctly configured.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 290
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Data Preparation
Table 5-10 MPLS tunnel planning data
Parameter Value
Sink Node 130.0.0.2
Tunnel Type E-LSP
Other parameters You can retain the default values in this example.
Figure 5-4 MPLS tunnel planning data
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 291
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.7 Deleting MPLS Tunnels
If a tunnel is no longer used, you can delete it to free the corresponding transmission
resources.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l An MPLS tunnel is configured correctly and is no longer used to transmit services.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 292
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.8 Setting MPLS OAM (Y.1711) Parameters
This section describes how to set MPLS OAM (Y.1711) parameters for MPLS tunnel
availability test.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS tunnels are created and enabled.
l Node Type is set to Ingress or Egress for tunnels.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 293
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.9 Enabling/Disabling FDI
When MPLS OAM (Y.1711) is used to detect MPLS APS, enable the FDI function for an NE
to decrease the MPLS APS switching time.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS tunnels are created and enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 294
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.10 Starting/Stopping CV/FFD Detection for MPLS Tunnels
Before enabling CV/FD detection, you need to set MPLS OAM (Y.1711) parameters.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
The MPLS OAM (Y.1711) function has been enabled and related parameters have been
configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 295
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
l For unidirectional tunnels, this operation task can be performed only for a tunnel whose Node Type
is Ingress.
l For bidirectional tunnels, this operation task cannot be performed if Node Type is Transit.
l After the MPLS OAM (Y.1711) function is enabled, CV/FFD detection is enabled by default.
NOTE
l You can select more than one tunnel at a time by pressing and holding down the Ctrl key.
l Alternatively, you can select the required tunnel, right-click the tunnel, and then select Start
CV/FFD or Stop CV/FFD from the drop-down list.
----End
5.4.11 Clearing OAM Configuration Data for MPLS Tunnel OAM
(Y.1711)
This topic describes how to restart MPLS OAM detection by clearing MPLS OAM (Y.1711)
configuration data.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS OAM (Y.1711) detection function has been enabled.
l The tunnel is not configured in any protection group.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 296
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.4.12 Performing an LSP Ping Test
This topic describes how to detect whether an MPLS tunnel is available.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.13 Performing an LSP Traceroute Test
You can detect fault points on an MPLS tunnel by performing LSP traceroute tests.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 297
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.14 Configuring MEP Parameters for MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
To use MPLS-TP tunnel OAM to test whether an MPLS tunnel is available, you need to
configure MEP parameters on the ingress and egress nodes of the MPLS tunnel.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS tunnel has been configured, with its ingress/egress node as an MEP.
l The MPLS-TP tunnel OAM standard has been changed to Y.1731.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 298
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.15 Creating MIPs of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
This section describes how to add MIPs of MPLS-TP tunnel OAM at transit nodes.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS tunnel has been created and the newly created MIP node is a transit node.
l The MPLS-TP tunnel OAM standard has been changed to Y.1731.
l Global OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Data Preparation
Table 5-11 MIP planning data
Parameter Value
Tunnel 1501
MEG ID Type ICC Based
MEG ID 111
MIP ID 101
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 299
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.16 Starting a CC Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
After you start a CC test, unidirectional tunnel connectivity is periodically detected. If the link
is fault after the CC test is started at the source MEP, the sink MEP reports the corresponding
alarms.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled and OAM parameters have been
configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 300
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.17 Starting an LB Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
During a loopback (LB) test, you can check the bidirectional connectivity between the source
MEP and the sink MEP or an MIP.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source MEP and the sink
MEP/MIP and OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Data Preparation
Table 5-12 LB test planning data
Parameter Value
Node Type MEP
Remote MEP/MIP ID Or IP Address 46.1.64.19
Transmit Interval 1s
Other parameters You can retain the default values in this example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 301
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.18 Starting an LT Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
This section describes how to start a link trace (LT) test provided by MPLS-TP tunnel OAM.
Based on LB tests, LT tests further improve the fault location capability. To be specific, a
faulty network segment can be located upon one LT test.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source and sink MPs and OAM
parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Background
An LT test provided by MPLS-TP tunnel OAM can be started only in end-to-end
configuration mode.
Data Preparation
Table 5-13 LT test planning data
Parameter Value
Packet Sending Interval 100 ms
Packet Sending Priority 7
Other parameters You can retain the default values in this example.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 302
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.19 Testing the Delay and Delay Variation of an MPLS Tunnel
This section describes how to test the delay and delay variation of an MPLS tunnel.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source and sink MPs and OAM
parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Background Information
This task is supported only when the configuration is performed in end-to-end mode on the
U2000.
NOTE
l It is recommended that you measure the performance of MPLS tunnels deployed in end-to-end manner by
performing the preceding procedure.
l To perform performance measurement for an MPLS tunnel in the NE Explorer, select the desired MPLS
tunnel, right-click, and choose Performance Statistics Management from the shortcut menu. In the
displayed dialog box, create the corresponding monitoring instance. Note that the PE at both ends must be
configured with the corresponding performance monitoring instance for this MPLS tunnel. Otherwise,
errors occur during performance measurement.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 303
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.4.20 Setting the LCK Status of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
Perform this task to lock an MPLS tunnel and suppress alarms on PWs carried by the tunnel.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled and OAM parameters have been
configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 304
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.4.21 Starting a TST Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
RTN supports testing the packet loss on an MPLS tunnel.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source MP and the sink MP and
OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Background Information
l This task is supported only when the configuration is performed in end-to-end mode on
the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 305
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.5 Managing MPLS APS Protection Groups
MPLS APS is the commonest protection mode for MPLS tunnels.
NOTE
The RTN 380H and RTN 380A does not support MPLS/PWE3.
5.5.1 Creating an MPLS APS Protection Group
An MPLS APS protection group needs to be configured if a service carried by an MPLS
tunnel needs to be protected.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The working and protection MPLS tunnels have been created.
l MPLS OAM as been enabled for both working and protection MPLS tunnel in the
protection group.
l The protection tunnel cannot carry extra services.
l PW APS protection is not configured for the service.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Background
MPLS OAM needs to be enabled for working and protection tunnels. The detection packets
used by MPLS OAM are FFD packets. FFD packets are usually sent at an interval of 3.3 ms.
If the packet transmission delay time of an MPLS tunnel exceeds 3.3 ms, the transmission
interval of FFD packets needs to be a value greater than the delay time.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 306
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.5.2 Querying MPLS APS Status
You can know current information about MPLS APS by querying MPLS APS status on the
NMS.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS APS protection group has been created.
l The MPLS APS protocol has been enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 307
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.5.3 Triggering MPLS APS Switching
This topic describes how to trigger external PW APS switching.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS APS protection group has been created.
l The MPLS APS protocol has been enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 308
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.5.4 Enabling/Disabling MPLS APS Protection
If you first stop the MPLS APS protection protocol and then start it, the MPLS APS
protection protocol is restored to its initial state.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS APS protection group has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 309
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.6 Managing PWs
All types of PWE3 services are carried by PWs.
NOTE
The RTN 380H and RTN 380A does not support MPLS/PWE3.
5.6.1 Querying Information and Running Status of PWs
This topic describes how to query information and running status of PWs.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
PW-carried services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 310
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.6.2 Creating an MS-PW
This topic describes how to configure cross-connections for front-end and rear-end PWs at an
S-PE node and create an MS-PW.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for MS-PW according to the parameter value
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Forward PW Backward PW
ID 1
Name eth01
MTU(bytes) -
Service Type Ethernet Service
PW ID 1501 1502
PW Siganling Type Static Static
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 311
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Forward PW Backward PW
PW Type Ethernet Ethernet
PW Incoming Label 1501 1502
PW Outgoing Label 1501 1502
Tunnel Type MPLS MPLS
Ingress Tunnel 1501(NE1) 1502(NE3)
Egress Tunnel 1503(NE2) 1502(NE3)
Configuration Qos parameters
Parameter Value
Bandwidth Limit Disabled Disabled
Policy 1(eth01) 2(eth02)
Configuration the PW advanced parameters
Parameter Value
Control Word Not in use
Control Channel Type Alert Label
VCCV Verification Mode Ping
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 312
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.6.3 Setting PW OAM (Y.1711) Parameters
This topic describes how to set PW OAM (Y.1711) parameters for PW availability test.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l PW-carried services have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 313
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.6.4 Performing a PW Ping Test
This section describes how to detect whether a PW is available.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l A PW has been created and enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following table provides parameters and their values for performing a PW ping test.
Parameter Value
Packet Count 3
EXP Value 7
TTL 255
Transmit Interval (10 ms) 100
Packet Length 100
Response Timeout Period (10 ms) 300
Response Mode IPv4 UDP Response
Peer PW ID 100
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 314
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Peer IP 131.0.0.2
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.5 Performing a PW Traceroute Test
You can detect fault points on an MS-PW by performing PW traceroute tests.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l A PW has been created and enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following table provides parameters and their values for performing a PW traceroute test.
Parameter Value
EXP Value 7
TTL 255
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 315
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Packet Length 100
Response Timeout Period (10 ms) 300
Response Mode IPv4 UDP Response
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.6 Configuring MEP Parameters for MPLS-TP PW OAM
To use MPLS-TP PW OAM to test whether a PW is available, you need to configure MEP
parameters on the T-PE of the PW.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The PW has been configured, with its T-PE as an MEP.
l The MPLS-TP PW OAM standard has been changed to Y.1731.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following table provides MEP parameters and their values for configuring MPLS-TP PW
OAM.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 316
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
OAM Status Disabled
MEG ID Type IP Based
MEG Level 7
CC Packet Priority 7
CC Packet Interval 1S
Lock Status Unlock
SD Threshold(%) 0
SF Threshold(%) 0
GAL Enable Status Disabled
LM Packet Mode Standard Mode
GAL Mode RFC5586
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.7 Creating MIPs of MPLS-TP PW OAM
This section describes how to add MIPs of MPLS-TP PW OAM at S-PE nodes.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MS-PW has been created and the newly created MIP node is an S-PE node.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 317
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
l The MPLS-TP PW OAM standard has been changed to Y.1731.
l Global OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following table provides parameters and their values for creating MIPs of MPLS-TP PW
OAM.
Parameter Value
MS PW 41
MEG ID Type ICC Based
MEG ID 123
MIP ID 321
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.8 Starting a CC Test of MPLS-TP PW OAM
After you start a CC test, unidirectional PW connectivity is periodically detected. If the link is
fault after the CC test is started at the source MEP, the sink MEP reports the corresponding
alarm.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 318
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The MPLS-TP PW OAM has been enabled and OAM parameters have been configured
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.9 Starting an LB Test of MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
During a loopback (LB) test, you can check the bidirectional connectivity between the source
MEP and the sink MEP or an MIP.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source MEP and the sink
MEP/MIP and OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 319
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
preparation
Parameter Value
Node Type MEP
Remote MEP/MIP ID Or IP Address 46.1.64.19
Packet Count 3
Packet Priority 7
TTL 225
Transmit Interval 1
Packet Length 128
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.10 Starting an LT Test Provided by MPLS-TP Tunnel OAM
This section describes how to start a link trace (LT) test provided by MPLS-TP tunnel OAM.
Based on LB tests, LT tests further improve the fault location capability. To be specific, a
faulty network segment can be located upon one LT test.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
MPLS-TP tunnel OAM has been enabled for both the source and sink MPs and OAM
parameters have been configured.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 320
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for LT Test according to the parameter value
listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Interrupt Service Do Not Interrupt
Packet Sending Intervat 3.3ms
Packet Sending Priority 225
Transport Code Type Null signal without CRC-32
Protocal Format Huawei mode
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.11 Testing the Packet Loss Ratio, Delay, and Delay Variation
of a PW
This section describes how to query the packet loss ratio, delay, and delay variation of a PW.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS-TP PW OAM has been enabled for both the source and sink MPs and OAM
parameters have been configured.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 321
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Background Information
This task is supported only when the configuration is performed in end-to-end mode on the
U2000.
NOTE
l It is recommended that you measure the performance of PW deployed in end-to-end manner by
performing the preceding procedure.
l To perform performance measurement for an PW in the NE Explorer, select the desired PW, right-click,
and choose Performance Statistics Management from the shortcut menu. In the displayed dialog box,
create the corresponding monitoring instance. Note that the PE at both ends must be configured with the
corresponding performance monitoring instance for this PW. Otherwise, errors occur during performance
measurement.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.12 Setting the LCK Status of MPLS-TP PW OAM
Perform this task to lock a PW and suppress alarms at the customer layer carried by the PW.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
The MPLS-TP PW OAM has been enabled and OAM parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 322
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.6.13 Starting a TST Test of MPLS-TP PW OAM
OptiX RTN 380 supports testing the packet loss on a PW.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
MPLS-TP PW OAM has been enabled for both the source MP and the sink MP and OAM
parameters have been configured.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for TST Test according to the parameter
value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
Interrupt Service Do Not Interrupt
Packet Sending Intervat 3.3ms
Packet Sending Priority 225
Transport Code Type Null signal without CRC-32
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 323
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
Protocal Format Huawei mode
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.7 Managing a PW APS/PW FPS Protection Group
PW APS and PW FPS are two modes for protecting PWs.
NOTE
The RTN 380H and RTN 380A does not support MPLS/PWE3.
5.7.1 Creating a PW APS Protection Group
If MPLS APS cannot be configured to protect a PW-carried service, you can configure PW
APS to protect the service.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS APS protection is not configured for the service.
l The tunnel carrying the working and protection PWs has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 324
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
PW OAM needs to be enabled for the working and protection PWs of a PW APS protection
group. The detection packets used by PW OAM are FFD packets. FFD packets are usually
sent at an interval of 3.3 ms. If the packet transmission delay time of a PW exceeds 3.3 ms,
the transmission interval of FFD packets needs to be a value greater than the delay time.
You can create a PW APS protection group during initial service configuration or after service
configuration.
l During initial service configuration, set Protection Type to PW APS, create the working
and protection PWs, use the PWs to configure a PW APS protection group.
l If services are already configured, create the PW APS protection group in the Protection
Group tab page.
l For SS-PWs and MS-PWs, configuration of the PW APS protection group needs to be
done on both source NE and sink NE.
NOTE
l This topic describes how to configure PW APS after services are configured.
l This topic uses a PW-carried E-Line service as an example to describe how to configure PW APS
protection. The methods of configuring PW APS protection for other types of service are similar.
Parameters for Creating a PW APS Protection Group
The following table provides parameters and their values for creating a PW APS protection
group.
Parameter Value
PW ID 2
PW Incoming Label 83
PW Outgoing Label 17
Ingress Tunnel 1520
Protection Group ID 2
Enabling Status Disabled
Revertive Mode Revertive
Switchover WTR Time (min) 1
Switchover Hold-Off Time (100 ms) 0
Detection Mode FFD
Detection Packet Type 3.3
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 325
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.7.2 Creating a PW FPS Protection Group
In a Mixed VPN solution, a PW FPS protection group needs to be configured for NEs
functioning as CSGs, to achieving dual-homing to ASGs.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l MPLS FPS protection is not configured for the service.
l The tunnels carrying the working and protection PWs have been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the similar to those on the U2000.
Context
Enable MPLS-TP OAM for both the working and protection PWs in the PW FPS protection
group. The packet transmission interval is often set to 3.3 ms for the enabled MPLS-TP
OAM. If the packet transmitting delay jitter in a PW exceeds 3.3 ms, set the packet
transmission interval to a value greater than the delay.
PW APS protection groups can be created when services are initially configured or after
services are configured.
l During initial service configuration, set Protection Type to PW APS, create the working
and protection PWs, use the PWs to configure a PW FPS protection group.
l If services are already configured, create the PW FPS protection group on the Protect
Group tab page.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 326
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
NOTE
l This topic only describes how to configure PW FPS after services are configured.
l A PW-carried E-Line service is used as an example to describe how to configure PW FPS protection. The
methods of configuring PW FPS protection for other types of service are similar.
Parameters for Creating a PW FPS Protection Group
The following table provides parameters and their values for creating a PW FPS protection
group.
Parameter Value
PW ID 2
PW Incoming Label 83
PW Outgoing Label 17
Ingress Tunnel 1520
Protection Group ID 2
Enabling Status Disabled
Revertive Mode Revertive
Switchover WTR Time (min) 1
Switchover Hold-Off Time (100 ms) 0
Detection Mode FFD
Detection Packet Type 3.3
Procedure
Step 1
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 327
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
5.7.3 Configuring Slave Protection Pairs of PW APS
During PW APS switching, the PWs in the slave protection pair are also switched.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The mapping between a slave protection pair and a PW APS protection group has been
specified.
l MPLS APS protection is not configured for the service.
l The tunnel carrying the working and protection PWs has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Background Information
The slave protection pairs are bound with a PW APS protection group. You can create a slave
protection pair during initial service configuration or after service configuration.
l During initial service configuration, set Protection Type to Slave Protection Pair,
create the working and protection PWs, use the PWs to configure a slave protection pair.
l If services are already configured, create the slave protection pair in the Protection
Group tab page.
l For SS-PWs and MS-PWs, binding of a slave protection pair to a PW APS protection
group requires that the slave protection pair is added on both the source NE and sink NE.
NOTE
l This topic describes how to configure a slave protection pair after services are configured.
l This topic uses a PW-carried E-Line service as an example to describe how to configure a slave protection
pair. The methods of configuring slave protection pairs for other types of service are similar.
Context
The following procedure sets the basic attributes for Protection Pairs of PW APS according to
the parameter value listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
PW ID 140
PW Signaling Type Static
PW Incoming Label 83
PW Outgoing Label 17
Ingress Tunnel 1521
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 328
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.7.4 Querying PW APS/PW FPS Status
You can know current information about a PW APS/PW FPS protection group by querying
PW APS/PW FPS status on the NMS.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
The PW APS/PW FPS protection group has been created.
The PW APS/PW FPS protocol has been enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 329
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.7.5 Triggering PW APS/PW FPS Switching
This topic describes how to trigger an external PW APS/PW FPS switching.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
The PW APS/PW FPS protection group has been created.
The PW APS/PW FPS protocol has been enabled.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 330
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.7.6 Enabling/Disabling PW APS Protection
If you first stop the PW APS protection protocol and then start it, the PW APS protection
protocol is restored to its initial state.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The PW APS protection group has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 331
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.8 Managing the IEEE 1588v2 Clock
This section provides hyperlinks to 1588v2 configuration operations.
5.8.1 Querying or Modifying the PTP System Time
If the IEEE 1588v2 protocol is used for time synchronization, identical Precision Time
Protocol (PTP) system time is displayed on all NEs. If the PTP system time of the primary
time source in the clock subnet is changed, the PTP system time of other NEs on the clock
subnet changes accordingly.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l The PTP time synchronization function has been enabled (this function is enabled by
default).
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure changes the PTP system time to November 07, 2013.
NOTE
In practice, in an IEEE 1588v2 clock synchronization solution, the basic PTP system time of a network is
provided by the GPS and does not need to be changed manually. This task is mainly performed for
commissioning and verifying the IEEE 1588v2 time synchronization.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 332
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Procedure
Step 1
----End
5.8.2 Configuring the PTP Profile
Configure an IEEE 1588v2 or ITU-T G.8257.1 profile for an NE as required. All NEs in a
clock domain must use the same PTP profile.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE administrator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 333
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.8.3 Setting the PTP NE Attributes
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) NE attributes include the working mode, multicast packet
transmission mode, and time calibration function.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Changes the NE clock type to TC+BC for transparent clock transmission.
l Changes the NE clock type to BC for networkwide time synchronization.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the PTP NE attributes (TC+BC mode).
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 334
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Set the PTP NE attributes (BC mode).
----End
5.8.4 Creating a PTP Clock Port
A Precision Time Protocol (PTP) clock port transmits or receives PTP packets.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l NE Clock Type has been set.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 335
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Context
The following procedure:
l Configures the microwave port, P&E port, and GE(e) port as PTP ports.
Procedure
Step 1 Configure the microwave port, P&E port, and GE(e) port as PTP ports.
----End
5.8.5 Setting PTP Clock Port Attributes
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) clock port attributes include the VLAN ID and encapsulation
format carried in the PTP packets transmitted or received at a port and the reference clock
source.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l NE Clock Type has been set.
l A PTP port has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Sets PTP port attributes for an NE whose clock type is TC+BC, according to the planned
parameter values listed in the following table.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 336
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
P&E Port
Clock Type TC
Step Mode Single step
PTP Packet VLAN 100
PTP Packet Encapsulation PTP ETH
Format
NOTE
l If an Ethernet port is connected to a device in another clock domain, set Clock Type to TC.
l If clock signals are transparently transmitted through a TC port with services, it is
recommended that you set PTP Packet VLAN to the VLAN ID of a service, so that PTP
packets of another clock domain are transmitted as service packets in this clock domain.
l Sets PTP port attributes for an NE whose clock type is boundary clock (BC), according
to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Parameter
IF Port P&E Port GE(e) Port
Step Mode Single step Single step Single step
PTP Packet VLAN 100 100 100
PTP Packet PTP ETH PTP ETH PTP ETH
Encapsulation
Format
Port Status MASTER+SLAVE SLAVE MASTER+SLAVE
Procedure
Step 1 Set attributes for a PTP port on an NE whose clock type is TC+BC.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 337
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Step 2 Set attributes for a PTP port on an NE whose clock type is BC.
----End
5.8.6 Setting Parameters Clock Packets
Parameters clock packets include the P/E mode, packet transmission period, and announce
packet timeout coefficient.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l NE Clock Type has been set.
l A Precision Time Protocol (PTP) port has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure:
l Sets the P/E mode to E2E for the P&E port on an NE whose clock type is TC+BC.
l Configures ITU-T G.8275.1 packet parameters for the PTP ports on an NE whose clock
type is BC according to the planned parameter values listed in the following table.
Parameter Value
IF port P&E port GE(e) port
P/E Mode P2P E2E E2E
Delay Packet - 128/1024 128/1024
Frequency
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 338
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
Parameter Value
IF port P&E port GE(e) port
Pdelay Packet 128/1024 - –
Frequency
Announce Packet 128/1024 128/1024 128/1024
Frequency
NOTE
l If a microwave port is a PTP port, it is recommended that you set all IEEE 1588v2 clock packet
parameters to their default values.
l If the clock type of an Ethernet port is boundary clock (BC), set IEEE 1588v2 clock packet
parameters consistently for the Ethernet port and interconnected equipment.
Procedure
Step 1 Set packet parameters for P&E port on an NE whose clock type is TC+BC.
Step 2 Set packet parameters for PTP ports on an NE whose clock type is BC.
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 339
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.8.7 Configuring the Delay Offset for Asymmetric Transmission
Between NEs
The task is used to compensate for the delay that results from asymmetric transmission
between NEs.
Prerequisites
l You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
l NE Clock Type has been set.
l A PTP port has been created.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure compensates for -3 ns for a P&E port.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 340
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
5.8.8 Modifying the BMC Algorithm Parameters for an NE Clock
When the internal clock of an NE is used as a best master clock (BMC) source, you can
modify the BMC algorithm parameters for the internal clock of the NE.
Prerequisites
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
NOTE
Web LCT also supports this operation and the steps are the same as those on the U2000.
Context
The following procedure changes PTP Clock Source Priority 2 to 1 for the BMC algorithm
of the NE1 clock.
NOTE
It is recommended that you set PTP Clock Source Priority 2 to 1 and retain the default values for other
parameters.
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 341
OptiX RTN 300 Radio Transmission System
Feature Configuration Guide 5 Task Collection
----End
Issue 01 (2018-07-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 342
You might also like
- Information Technology Risk Management in Enterprise Environments: A Review of Industry Practices and a Practical Guide to Risk Management TeamsFrom EverandInformation Technology Risk Management in Enterprise Environments: A Review of Industry Practices and a Practical Guide to Risk Management TeamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RTN 310 Commissioning and Configuration Guide 01Document326 pagesRTN 310 Commissioning and Configuration Guide 01Daniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- RTN 320 V100R009C00 Product Description 02 PDFDocument227 pagesRTN 320 V100R009C00 Product Description 02 PDFLima Anjos AnjosNo ratings yet
- RTN 380 V100R007C10 Maintenance Guide 03 PDFDocument436 pagesRTN 380 V100R007C10 Maintenance Guide 03 PDFAbo Hodhaifa100% (1)
- RTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Feature Description 02 PDFDocument289 pagesRTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Feature Description 02 PDFSaeed Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- Commissioning and Configuration Guide: Optix RTN 380 Radio Transmission System V100R001C10Document624 pagesCommissioning and Configuration Guide: Optix RTN 380 Radio Transmission System V100R001C10SOS INFORMATIQUENo ratings yet
- RTN 900 V100R009C10 Configuration Guide 02Document2,047 pagesRTN 900 V100R009C10 Configuration Guide 02Hossein HosseinpourNo ratings yet
- Manual Do Produto 980Document471 pagesManual Do Produto 980imeldoNo ratings yet
- RTN 980 V100R009C10 Maintenance Guide 02 PDFDocument1,400 pagesRTN 980 V100R009C10 Maintenance Guide 02 PDFHogr RgohNo ratings yet
- Users Manual RTN360Document88 pagesUsers Manual RTN360peperimeNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R003C03 Configuration Guide 04 (U2000)Document2,188 pagesRTN 950 V100R003C03 Configuration Guide 04 (U2000)Alvaro Avila SanchezNo ratings yet
- Optix RTN 320 OAU 2A Product DescriptionDocument176 pagesOptix RTN 320 OAU 2A Product DescriptionRaziel VelazquezNo ratings yet
- RTN 380 V100R001C10 Maintenance Guide 02Document308 pagesRTN 380 V100R001C10 Maintenance Guide 02Abo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- Users Manual 2436274Document98 pagesUsers Manual 2436274Ahmed Abd El HamedNo ratings yet
- RTN 320 V100R007C10 OAU 2A Product Description 02 (20170315)Document185 pagesRTN 320 V100R007C10 OAU 2A Product Description 02 (20170315)jorge luis diaz perez0% (1)
- RTN980 IduDocument198 pagesRTN980 IduJhannoSJY MuñozNo ratings yet
- RTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Maintenance Guide 02 PDFDocument443 pagesRTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Maintenance Guide 02 PDFSaeed Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R011C00 User Guide For North America 02 PDFDocument108 pagesRTN 950 V100R011C00 User Guide For North America 02 PDFOmer KhalidNo ratings yet
- RTN 950A V100R007C10 Product Description 02 PDFDocument243 pagesRTN 950A V100R007C10 Product Description 02 PDFmarko caballeroNo ratings yet
- MA5603T Product DescriptionDocument68 pagesMA5603T Product DescriptionHibiki KwoaHuiNo ratings yet
- RTN 900 V100R020C00 Feature Configuration Guide 02Document1,819 pagesRTN 900 V100R020C00 Feature Configuration Guide 02robelmoura100% (2)
- RTN 950 V100R010C00 IDU Hardware DescriptionDocument559 pagesRTN 950 V100R010C00 IDU Hardware DescriptionPietro GallinaNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R010C00 Maintenance Guide 02Document1,398 pagesRTN 950 V100R010C00 Maintenance Guide 02thawdewaiNo ratings yet
- Nar Ont 1 GbpsDocument49 pagesNar Ont 1 GbpsCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R009C00 Product Description 02Document275 pagesRTN 950 V100R009C00 Product Description 02Ernesto TalaveraNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R003C03 Maintenance Guide 05 (U2000)Document834 pagesRTN 950 V100R003C03 Maintenance Guide 05 (U2000)Alvaro Avila Sanchez100% (1)
- RTN 950A Product DescriptionDocument217 pagesRTN 950A Product DescriptionMarco VirgilioNo ratings yet
- OptiX RTN 905 1E - 2E Radio Transmission System V100R007C10. Commissioning Guide. Issue 02 Date HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.Document188 pagesOptiX RTN 905 1E - 2E Radio Transmission System V100R007C10. Commissioning Guide. Issue 02 Date HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.JuanNo ratings yet
- TP48200A-DX12A1 Outdoor Power System User ManualDocument62 pagesTP48200A-DX12A1 Outdoor Power System User ManualSimon Bustamante CondoriNo ratings yet
- RTN 905 1E&2E V100R009C00 MaintenanceGuide 02Document943 pagesRTN 905 1E&2E V100R009C00 MaintenanceGuide 02aricomen100% (1)
- OSN8800 V100R011C00 ConfigDocument3,213 pagesOSN8800 V100R011C00 ConfigThiago Andrade RangelNo ratings yet
- RTN 905 1E&2E V100R007C10 Feature Description 02 PDFDocument937 pagesRTN 905 1E&2E V100R007C10 Feature Description 02 PDFRoDo TJNo ratings yet
- RTN 950A V100R008C10 Commissioning Guide 02Document214 pagesRTN 950A V100R008C10 Commissioning Guide 02Marco VirgilioNo ratings yet
- MTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System Installation Guide Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Document62 pagesMTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System Installation Guide Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Влад Толчеев100% (1)
- RTN 950A V100R011C10 IDU Hardware Description 02 PDFDocument531 pagesRTN 950A V100R011C10 IDU Hardware Description 02 PDFricardo mielnikNo ratings yet
- OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transport System V10Document526 pagesOptiX RTN 950 Radio Transport System V10balalouseNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R010C00 Commissioning Guide 02Document218 pagesRTN 950 V100R010C00 Commissioning Guide 02Anonymous 8RFzObvNo ratings yet
- SCC800-S1 SmartSite Management System V100R003C10 Installation GuideDocument190 pagesSCC800-S1 SmartSite Management System V100R003C10 Installation GuidetaufiqNo ratings yet
- ECC800 Data Center Controller V100R002C10 User ManualDocument278 pagesECC800 Data Center Controller V100R002C10 User Manualhadi permanaNo ratings yet
- RTN 950A V100R009C10 Product DescriptionDocument265 pagesRTN 950A V100R009C10 Product DescriptionAnonymous sV02Ggn4TONo ratings yet
- ISitePower Integrated Smart Site V100R001C00 User Manual (ICC1000-A1-E1)Document181 pagesISitePower Integrated Smart Site V100R001C00 User Manual (ICC1000-A1-E1)rudi amsyahNo ratings yet
- OptiX PTN 960 V100R007C10 Installation Guide 02Document186 pagesOptiX PTN 960 V100R007C10 Installation Guide 02Naser KhoshbakhtNo ratings yet
- EA5800 Hardware Description 05Document178 pagesEA5800 Hardware Description 05arez99No ratings yet
- RTN 980 V100R006C10 IDU Hardware Description 01Document410 pagesRTN 980 V100R006C10 IDU Hardware Description 01MicogenNo ratings yet
- JUPITER - (3000K, 6000K, 9000K) - H1 Smart Transformer Station User ManualDocument46 pagesJUPITER - (3000K, 6000K, 9000K) - H1 Smart Transformer Station User ManualandrescastroencinaNo ratings yet
- RTN 950A V100R005C01 IDU Hardware Description 03Document344 pagesRTN 950A V100R005C01 IDU Hardware Description 03Paul Joseph MsambilaNo ratings yet
- RTN950 DSDocument741 pagesRTN950 DSHassir Tajan NieblesNo ratings yet
- ETP48200-C5D6 Embedded Power User Manual (Flexible Configuration)Document114 pagesETP48200-C5D6 Embedded Power User Manual (Flexible Configuration)David ChokaniNo ratings yet
- Rectificador HW Etp48400-C9a2 v500r001 User Manual 01Document88 pagesRectificador HW Etp48400-C9a2 v500r001 User Manual 01Sergio rock eo eoxvNo ratings yet
- MA5801 Hardware Description 03Document69 pagesMA5801 Hardware Description 03Alexander Pischulin100% (1)
- RTN 900 V100R019C00 MIMO User Guide 02Document81 pagesRTN 900 V100R019C00 MIMO User Guide 02Christopher AiyapiNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R009C00 Commissioning Guide 02 PDFDocument224 pagesRTN 950 V100R009C00 Commissioning Guide 02 PDFFajar BalidoNo ratings yet
- NCE V100R018C10 Command Reference (Restricted) 01-CDocument266 pagesNCE V100R018C10 Command Reference (Restricted) 01-CyugNo ratings yet
- F01T100 (ETP4860) Product DescriptionDocument101 pagesF01T100 (ETP4860) Product DescriptionHoa Viet LuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Pdfsam - CX600 V800R007C00 Hardware Description 02 - 1 - 5Document99 pages1 - Pdfsam - CX600 V800R007C00 Hardware Description 02 - 1 - 5josé martínezNo ratings yet
- ISitePower Integrated Smart Site V100R001C00 Installation Guide (ICC1000-A1-E1)Document203 pagesISitePower Integrated Smart Site V100R001C00 Installation Guide (ICC1000-A1-E1)Typical PhillipsNo ratings yet
- 380AX (P&E Option)Document136 pages380AX (P&E Option)Electronica Sandro Soto HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Northbound TL1 Interface User Guide PDFDocument3,820 pagesNorthbound TL1 Interface User Guide PDFnpc_nicoNo ratings yet
- Safe and Secure Cyber-Physical Systems and Internet-of-Things SystemsFrom EverandSafe and Secure Cyber-Physical Systems and Internet-of-Things SystemsNo ratings yet
- RTN 380 V100R001C10 Maintenance Guide 02Document308 pagesRTN 380 V100R001C10 Maintenance Guide 02Abo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- InternalFiber CAH Ngaous (FOADM)Document1 pageInternalFiber CAH Ngaous (FOADM)Abo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- FiberConnectionDiagram - 05002 BSC BarikaDocument4 pagesFiberConnectionDiagram - 05002 BSC BarikaAbo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- FiberConnectionDiagram - 05615 SeganaDocument1 pageFiberConnectionDiagram - 05615 SeganaAbo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- InternalFiber Hamada (FOADM)Document1 pageInternalFiber Hamada (FOADM)Abo HodhaifaNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 PDFDocument4 pagesEasa Part 66 PDFAhsan Malik25% (4)
- BRKDCT 2218Document93 pagesBRKDCT 2218Surya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- TCP Ports Used by AppleDocument5 pagesTCP Ports Used by Applesergio vieiraNo ratings yet
- s15 QP 12Document16 pagess15 QP 12ahmed ramadanNo ratings yet
- The 2000s, Bob BatchelorDocument260 pagesThe 2000s, Bob BatchelorRaluca Elena SuciuNo ratings yet
- R310.2 Support Software Change NoticeDocument166 pagesR310.2 Support Software Change Noticethanh_cdt01No ratings yet
- KAS Visual Seven - KAS AstrologyDocument3 pagesKAS Visual Seven - KAS AstrologyGauriGanNo ratings yet
- Lora FabianDocument7 pagesLora FabianAKSHATHAVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- Soal Lks It Networking Support 20121Document5 pagesSoal Lks It Networking Support 20121Hendi RuhandiNo ratings yet
- Rainfall Runoff Library User Guide v1.0.5 (GP)Document110 pagesRainfall Runoff Library User Guide v1.0.5 (GP)Joselle RuizNo ratings yet
- I. Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Underlined PartDocument4 pagesI. Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Underlined PartNguyen HưngNo ratings yet
- Visual Web Developer 2005 Express EditionDocument244 pagesVisual Web Developer 2005 Express EditionGeña GonzalesNo ratings yet
- TVman Home User Manual enDocument16 pagesTVman Home User Manual enros56100% (1)
- The Impact of Web Page Text-Background Colour Combinations On Readability, Retention, Aesthetics and Behavioural IntentionDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Web Page Text-Background Colour Combinations On Readability, Retention, Aesthetics and Behavioural IntentionDayaNo ratings yet
- HUANG - Design and Implementation of An Open Source NB-IoT eNB-Chin-Ya HuangDocument34 pagesHUANG - Design and Implementation of An Open Source NB-IoT eNB-Chin-Ya HuangÖzer DenizNo ratings yet
- P2P Life CycleDocument72 pagesP2P Life CycleRahul PatkiNo ratings yet
- Manual - Layer-3 MPLS VPN Example - MikroTik WikiDocument5 pagesManual - Layer-3 MPLS VPN Example - MikroTik WikiCarlos Henrique TrentiniNo ratings yet
- Guibone, Brandon D. GE10A (Final Exam)Document1 pageGuibone, Brandon D. GE10A (Final Exam)Angel DiiNo ratings yet
- YouTube - Diante Da Cruz - Aline BarrosDocument3 pagesYouTube - Diante Da Cruz - Aline Barrosanon-791816No ratings yet
- Goo ReaderDocument8 pagesGoo ReaderYasas Ravin KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- IS3167 10.0 Security Issues in The Digital EnvironmentDocument32 pagesIS3167 10.0 Security Issues in The Digital EnvironmentcookieproductorNo ratings yet
- Grievance Redressal SystemDocument3 pagesGrievance Redressal Systemvvincent58No ratings yet
- 10 DOLLE Online Reputation Management PDFDocument11 pages10 DOLLE Online Reputation Management PDFJuliana 97No ratings yet
- KhalidDocument4 pagesKhalidKhalid RobinNo ratings yet
- B2 UNIT 5 Test StandardDocument8 pagesB2 UNIT 5 Test StandardMichael BoichukNo ratings yet
- Skype For Business Worksheet Module 1Document7 pagesSkype For Business Worksheet Module 1Ahmad JundiNo ratings yet
- 24.1.4 Lab - Implement Flexible Netflow - ILMDocument22 pages24.1.4 Lab - Implement Flexible Netflow - ILMTRYST CHAMANo ratings yet
- The Product Description of Smartax Mt880 Adsl2+ Cpe: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument16 pagesThe Product Description of Smartax Mt880 Adsl2+ Cpe: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDSamuelNo ratings yet
- SAD Report ActivityDocument2 pagesSAD Report Activityeverchan18No ratings yet
- 3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 InstructionsDocument3 pages3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 Instructionsrugun silitongaNo ratings yet