Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Synthesis Paper 11
Uploaded by
John Mark LaurioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Synthesis Paper 11
Uploaded by
John Mark LaurioCopyright:
Available Formats
John Mark Laurio
MAED-Science Education 1
SYNTHESIS PAPER
Confirmation, Falsification, Underdetermination
Unsatisfied with Hume's dilemma of increased expression, 20th-century thinkers devised
several additional primary theoretical issues to be solved by a rationalist ontology that underpins
the broad concepts and laws that characterize far too much medical medicine. Hempel's
contradictions of induction and Goodman's "new riddle of induction" are two examples of how
thoroughly possibly mired hypotheses would be. At least one major twentieth-century scholar,
Karl Popper, assumed he had to have a solution to an induction challenge. Matter of fact, he
believed that the entire trouble of finding data for a concept reflected a profound
misunderstanding of what the scientific method revolves around and how this all works. Oddly,
his initiative to hypothesize not just to failure to resolve the issue but also posed such a daunting
challenge to scientific inquiry that it spawned mobility that purely rejects that science is ruled by
knowledge, and perhaps even warns mankind's rationality.
Tries like Popper's to replace the queries of how the evidence supports theory with the
inquiry of whether it falsifies theory exacerbate the situation. For those who appear to revert to
the continual change of factors that can affect, as well as the threat to the world that monitoring,
experimentation, and data gathering may not be the primary means of controlling inquiry. In
other words, the challenges that epistemology faces have become more ferocious. This is
particularly true considering that these empirical science troubles have emerged and have been
considered seriously, primarily by pragmatists desiring to solidify their philosophy. Considering
the importance of bringing additional in either test of a concept, we can conclude that no major
scientific allegation fulfills expertise fa or test on its own. It does so only in the presence of other
theories, possibly a great amount of toner to derive some observational prediction to be tested
against the encounter, a subjective test in which expectations are not met cannot merely point
the finger of untruth at any of the theories, and adjustments in far more than one could be
comparable in resolving the overall set of assumptions to inspection. The option adjustments
are available to retain or keep improving obstinate big data when the size of the concept grows,
and it incorporates increasingly more dissimilar concepts. Are there two separate total
speculations of the planet, either equitable in substantiation, convenience, industry,
symmetrical, eloquence, mathematical function, or in any other extra marks of theory choosing,
at the never-to-be-reached "side of questioning" (when all statistics are in)? A favorable
response to the question could provide huge backing for an experimentalist profile of
speculations. Indeed, there appear to be no facts about the issue obtainable to an investigation
that can either of the two approaches. The amazing fact is that essentially turning is merely a
potential.
It rarely happens. This implies different possibilities. The very first solution, supported by
most theorists, is that assessment truly governs theoretical selection (otherwise, there might be
that much battle between theories and approaches than there has been); we have still not
reasoned the whole thing out until now. The second-best option is much more drastic, and it's
supported by a century of scholars, science experts, and a handful of intellectuals who dismiss
both the in-depth doctrines of coherent objectivism and its desires to underpin research quality.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Third Quarter Science 9: Content StandardDocument15 pagesThird Quarter Science 9: Content StandardJohn Mark Laurio92% (13)
- Management As An Art or ScienceDocument3 pagesManagement As An Art or ScienceYen-Naah Adams50% (2)
- 0262011816.MIT Press - Sunny Y. Auyang - Life, Mind in Everyday & Science, Cognitive - May.2009Document526 pages0262011816.MIT Press - Sunny Y. Auyang - Life, Mind in Everyday & Science, Cognitive - May.2009Branko NikolicNo ratings yet
- Carl Hempel - Problems and Changes in The Empiricist Criterion of MeaningDocument19 pagesCarl Hempel - Problems and Changes in The Empiricist Criterion of MeaningMilan VelkovskiNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesDocument14 pagesScience 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesJohn Mark Laurio100% (2)
- LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (1st Discussion)Document7 pagesLESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (1st Discussion)John Mark Laurio100% (8)
- SHS (QUARTER 2) Earth and Life Science DLPDocument3 pagesSHS (QUARTER 2) Earth and Life Science DLPJohn Mark Laurio100% (1)
- LT 3 Research Methods in Agribusiness and Value ChainDocument72 pagesLT 3 Research Methods in Agribusiness and Value Chainoliyaad Habtaamuu100% (4)
- Agar Blocks Lab ReportDocument3 pagesAgar Blocks Lab Reportanon_537322746No ratings yet
- Complexity TheoryDocument24 pagesComplexity TheoryPranav KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology in Political ScienceDocument222 pagesResearch Methodology in Political Sciencejaseme7579100% (1)
- Thomas M. Haladyna - Developing and Validating Multiple-Choice Test Items-Routledge (2004) PDFDocument319 pagesThomas M. Haladyna - Developing and Validating Multiple-Choice Test Items-Routledge (2004) PDFmuffin8980% (5)
- Laurio Task 1Document2 pagesLaurio Task 1John Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Laurio Task 6Document21 pagesLaurio Task 6John Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Research Culture of The Junior and Senior High Schools in The ProvinceDocument3 pagesResearch Culture of The Junior and Senior High Schools in The ProvinceJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Mastrace QR Code Registration - City of MasbateDocument5 pagesMastrace QR Code Registration - City of MasbateJohn Mark Laurio84% (45)
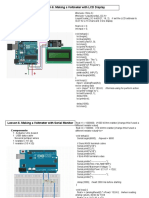
- Lesson 6. Making A Voltmeter With LCD Display: ComponentsDocument2 pagesLesson 6. Making A Voltmeter With LCD Display: ComponentsJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Ipcrf Development PlanDocument1 pageIpcrf Development PlanJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Understanding TyphoonsDocument32 pagesUnit 7 Understanding TyphoonsJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Earthquake and FaultsDocument33 pagesUnit 6 Earthquake and FaultsJohn Mark LaurioNo ratings yet
- Coyne. Wicked Problems RevisitedDocument13 pagesCoyne. Wicked Problems RevisitedLuiza Graça M P FelmanNo ratings yet
- Science Writing Sample 7th GradeDocument4 pagesScience Writing Sample 7th Gradeapi-217459968No ratings yet
- Geometry of Thought (Abstract)Document1 pageGeometry of Thought (Abstract)Peter Rulon-Miller100% (1)
- Development of Learner LanguageDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Learner LanguageRonalie JameloNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Using Diamond Model: Pritam DeyDocument8 pagesProblem Solving Using Diamond Model: Pritam Deymm62810No ratings yet
- Action Research Model Jack WhiteheadDocument10 pagesAction Research Model Jack WhiteheadWanfadzleen WannoryuhaidiNo ratings yet
- Contingency & Path Goal TheoryDocument4 pagesContingency & Path Goal TheoryArun Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Determinism VS. Free Will: Philo0 01 Ms - Jhohanah R. Bediones DPRO Olivarez CollegeDocument20 pagesDeterminism VS. Free Will: Philo0 01 Ms - Jhohanah R. Bediones DPRO Olivarez CollegeCd LeonorNo ratings yet
- Potts 1965Document3 pagesPotts 1965Erik Novak RizoNo ratings yet
- Linking N&P Char To OutcomeDocument2 pagesLinking N&P Char To OutcomeAira FrancescaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Existing Turnover Intention TheoriesDocument8 pagesA Review of Existing Turnover Intention TheoriesMayorNo ratings yet
- Probability and Inductive Argument - ELS101 - Manao - Pitan - FrigillanaDocument28 pagesProbability and Inductive Argument - ELS101 - Manao - Pitan - FrigillanaJim Paul ManaoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Marxism Reading ListDocument3 pagesAnalytical Marxism Reading ListAllen Sigal0% (1)
- 4cog1 041150794 Tma1Document13 pages4cog1 041150794 Tma1Rajalingam RamanNo ratings yet
- Asme b31 2 PDFDocument71 pagesAsme b31 2 PDFRamon NievesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Division of Taguig and Pateros Taguig National High School First Quarter Pretest Practical Research 2 A.Y. 2020-2021Document5 pagesDepartment of Education Division of Taguig and Pateros Taguig National High School First Quarter Pretest Practical Research 2 A.Y. 2020-2021Sherla PerenaNo ratings yet
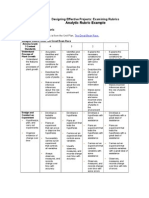
- Analytic RubricDocument3 pagesAnalytic RubricHelinar Kryxera100% (2)
- 01 - Research PhylosophyDocument22 pages01 - Research PhylosophygitaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Knowledge Wisdom and OpinionDocument11 pagesLESSON 4 Knowledge Wisdom and OpinionEdward BelenNo ratings yet
- Van Fraassen's Constructive Empiricism, Symmetry Requirements and Scientific Realism Michel GhinsDocument16 pagesVan Fraassen's Constructive Empiricism, Symmetry Requirements and Scientific Realism Michel GhinsDavy PedroNo ratings yet
- Investigation - Dominance MatricesDocument4 pagesInvestigation - Dominance MatricesGopal BotadraNo ratings yet
- A Short Biography of Albert EinsteinDocument2 pagesA Short Biography of Albert EinsteinHalimatus Sa'diyah100% (3)