0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views6 pagesISI Exam Math Solutions
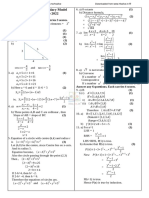
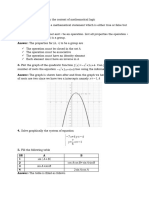
The document contains solutions to 8 math questions. Question 1 asks about the number of natural numbers less than 108 with a digit sum of 7. Question 2 asks about the number of positive integers less than 6300 not divisible by 3, 5, or 7. Question 3 involves showing the range of values a function can take. The remaining questions involve additional math problems and their solutions.
Uploaded by
Anindita D. MohantyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views6 pagesISI Exam Math Solutions
The document contains solutions to 8 math questions. Question 1 asks about the number of natural numbers less than 108 with a digit sum of 7. Question 2 asks about the number of positive integers less than 6300 not divisible by 3, 5, or 7. Question 3 involves showing the range of values a function can take. The remaining questions involve additional math problems and their solutions.
Uploaded by
Anindita D. MohantyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd