Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PST MLS Lesson 3
Uploaded by
seaynOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PST MLS Lesson 3
Uploaded by
seaynCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING STYLES
NOTE: This transes is strictly not for sale or reupload in MYERS-BRIGGS PERSONALITY INVENTORY
any site.
EXTROVERSION / INTROVERSION (SOCIAL ORIENTATION)
References:
Extroverts
o Alberg, J. et al. (1992). Educational approaches and
Likes talking with others and taking action
options for integrating students with disabilities: A decision
Prefers active learning and group activities and/or
tool. Research Triangle Institute. Research Triangle Park,
projects
NC.
o Dunn, R. (1984). Learning style: State of the science,
Introverts
Theory Into Practice. 23:1. 10-19. DOI:
Prefers others to do the talking
10.1080/00405848409543084
Prefers lectures and structured tasks
o Sana, E. et al. (2013). Teaching and Learning in the
Health Sciences. UP Diliman. Quezon City, Philippines. THINKING / FEELING (DECISION MAKING)
Thinkers
LEARNING STYLES
Likes to take objective approach
Learning styles refers to your most used style. Emphasizes on logic and analysis in their decision
3 ways information enters into the brain: Prefers objective feedbacks
Sight - those who learns by sight are referred to as Thrives when there is pressure to succeed
'Visual Learners'.
Hearing - those who learns by hearing are referred to Feelers
as 'Auditory Learners'. Prefers emotions to logic
Touch - those who learns by touch are referred to as Gives greater weight to the impact of relationships in
'Tactile (Kinesthetic) Learners'. their decisions
Prefers positive feedbacks and individual recognition
• Prefers to see the information such
as diagrams, pictures, cartoons, JUDGING / PERCEIVING (ACHIEVING GOALS)
demonstrations Judgers
• Pictures words and concepts they Prefers clearly defined strategies to achieve goals
hear as images May jump to closure too quickly
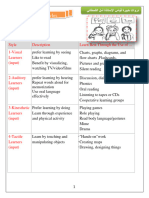
VISUAL
• Easily distracted in lectures with no Prefers orderliness, structures and deadlines
LEARNERS:
visual aids
“Let me see it”
• Overwhelmed with intense visuals Perceivers
accompanied by lectures Likes to consider all sides to a problem, sometimes
• Benefits from using charts, maps, risks for not completing their work
notes, and flashcards when Prefers spontaneity and flexibility
studying
DISCOVERING YOUR OWN LEARNING STYLE:
• Prefers to hear the information
Take a learning style test or think about your favorite class,
• Can absorb a lecture with little effort
what did they have in common? Did you like:
AUDITORY • May not need careful notes to learn
❖ Mastering facts
LEARNERS: • Often avoids eye contact in order to ❖ Discussion or working on your own
“Let me hear concentrate ❖ Lecture or working in pairs or with a group
it” • May read aloud to themselves ❖ Hands-on activities
• Likes background music when they Knowing your learning style, both your strengths and
study weaknesses, will help you study more effectively.
• Prefers touch as their primary mode
of taking in information How to build strengths across the learning style:
• During traditional lectures, they 1. Make the best use of your learning style
write out important facts 2. Work harder on skills that don’t come easily to
TACTILE OR • Create study sheets connected to you
KINESTHETIC vivid examples 3. Be flexible and adaptable, try new things and new
LEARNER: • Role playing can help them learn ways
“Let me and remember important ideas 4. Keep growing, don’t be easily satisfied
experience it” • May benefit by using manipulatives
(physical tools that engages • It is important to remember, no matter what your
students visually and physically with learning style is:
objects such as puzzles, coins, ❖ Be involved in class- participate
blocks, markers, etc.) ❖ Link classroom experience to the outside world
❖ Relate class concepts to your own life
❖ Ask questions and offer criticisms
❖ Stimulate further relevant discussions
❖ Don’t get distracted- stay “on task”
❖ Keep an open mind, there are many ideas beyond
your own
TUDTUD, SALVAÑA, LOVIANO | BSMT 1D & 1B 5
You might also like
- Learning Style & Learning TheoryDocument30 pagesLearning Style & Learning TheoryAgistha Novta100% (1)
- MPU 1223 - Learning StylesDocument23 pagesMPU 1223 - Learning StylesReen Zaza Zareen100% (1)
- Learning StylesDocument12 pagesLearning Stylesعبد الدايم عقاويNo ratings yet
- Natural, Habitual, and Preferred Way ofDocument3 pagesNatural, Habitual, and Preferred Way ofDinah DimagibaNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument19 pagesLearning Stylesvtay05No ratings yet
- PED05a Module-3 Nagares LucenaDocument11 pagesPED05a Module-3 Nagares LucenaCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument13 pagesLearning StylesJeffrey Roy Adlawan LopezNo ratings yet
- Instructional ApproachesDocument3 pagesInstructional Approachesapi-549234739No ratings yet
- Ebook: Preschool - 2Nd GradeDocument18 pagesEbook: Preschool - 2Nd GradeSueNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles and StrategiesDocument44 pagesLearning Styles and StrategiesDinar DiptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Foundation of Science Teaching and Learning: What To TeachDocument6 pagesLesson 1 Foundation of Science Teaching and Learning: What To TeachSambaikong D DaglokNo ratings yet
- NCM102j MODULE 4Document4 pagesNCM102j MODULE 4Jenny Ruth TubanNo ratings yet
- Learning & Development: Introduction To Training and LearningDocument115 pagesLearning & Development: Introduction To Training and LearningSoumya SulakheNo ratings yet
- Eseb3493 Learning Design: TOPIC 3 Learners' PersonalityDocument28 pagesEseb3493 Learning Design: TOPIC 3 Learners' PersonalitySEA ServerNo ratings yet
- LEARNING STYLES NotesDocument2 pagesLEARNING STYLES NotesFuentes, Kyla Diane C.No ratings yet
- Introduction To EducationDocument76 pagesIntroduction To EducationHina Kaynat100% (1)
- Learning Styles and PreferencesDocument5 pagesLearning Styles and Preferencesapi-3716467No ratings yet
- Engaging Students in Learning: Comprehensive Induction ProgramDocument18 pagesEngaging Students in Learning: Comprehensive Induction Programgotu123No ratings yet
- Week 34 Discovering Your Learning StylesDocument4 pagesWeek 34 Discovering Your Learning StylesAbegail BalloranNo ratings yet
- 7 e Instructional ModelDocument20 pages7 e Instructional ModelLuel Jay Viluan ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Learning How To LearnDocument36 pagesLearning How To LearnTiki MuchtarNo ratings yet
- Being The SupporteeacsDocument29 pagesBeing The Supporteeacsapi-467476025No ratings yet
- الاستراتيجيات الصحDocument13 pagesالاستراتيجيات الصحfaf22902No ratings yet
- Autism's Top 14 Areas of ConcernDocument2 pagesAutism's Top 14 Areas of Concernmefav7778520No ratings yet
- Tefl 2 BookDocument63 pagesTefl 2 BookSara TarawnehNo ratings yet
- Vrts112 PrelimDocument2 pagesVrts112 Prelimeli pascualNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles Report PDFDocument20 pagesLearning Styles Report PDFRolandNo ratings yet
- EduPsy Lecture 2Document25 pagesEduPsy Lecture 2Akbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Educator Fact SheetDocument2 pagesEducator Fact SheetJeremy JarviNo ratings yet
- Learners' StylesDocument39 pagesLearners' StylesFarah Zein EddinNo ratings yet
- Learning Style - 4 ExerciseDocument3 pagesLearning Style - 4 ExerciseHLANo ratings yet
- MET1 - Chapter 4 2023 Student TotalDocument30 pagesMET1 - Chapter 4 2023 Student TotalJuan Navarro TorresNo ratings yet
- Facilitators - Sian Giles Elizabeth PhillipsDocument12 pagesFacilitators - Sian Giles Elizabeth PhillipsKritika RamchurnNo ratings yet
- Teacher Learner CentredDocument74 pagesTeacher Learner CentredMohamed Fouad DriderNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The LearnerDocument25 pagesCharacteristics of The LearnerKaren Mae Señoron GarsutaNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning PDFDocument9 pagesAdult Learning PDFRain SmithNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument12 pagesLearning StylesSafaa Mohamed0% (1)
- Information Enters Your Brain Three Main Ways: Sight, Hearing and Touch, Which One You Use The Most Is Called Your Learning StyleDocument15 pagesInformation Enters Your Brain Three Main Ways: Sight, Hearing and Touch, Which One You Use The Most Is Called Your Learning StyleLieya AilurophilesNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Learning Learning Styles2 TransesDocument7 pages5 Types of Learning Learning Styles2 TransesDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Concept of LearningDocument37 pagesConcept of LearningNelyn Jill ObejeroNo ratings yet
- Altersadäquate Sprache - Study PackDocument8 pagesAltersadäquate Sprache - Study PackKaren Tatiana TORRES HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Effective Instructional TechniquesDocument36 pagesEffective Instructional TechniquesGladys Maer Jayme100% (2)
- Educational Psychology For TFL Students: Personality Factors Contributing To Second Language AcquisitionDocument23 pagesEducational Psychology For TFL Students: Personality Factors Contributing To Second Language AcquisitionZhanerke AbdirakhymNo ratings yet
- What Is It?: Foundations of Science Teaching and LearningDocument7 pagesWhat Is It?: Foundations of Science Teaching and LearningXylef Christiana Love YonsonNo ratings yet
- Styles and Multiple IntelligencesDocument17 pagesStyles and Multiple IntelligencesJane Agripa100% (1)
- Apst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies LogDocument2 pagesApst 3.3 Range of Teaching Strategies Logapi-525572712No ratings yet
- Learning Styles: Nanda Mitra-ItleDocument64 pagesLearning Styles: Nanda Mitra-ItleL.s. YanNo ratings yet
- Private TutoringDocument47 pagesPrivate TutoringHồ Hoàng Huy100% (2)
- Handout 0 Master Handout Adult Learning Principles Participant HandoutDocument29 pagesHandout 0 Master Handout Adult Learning Principles Participant Handoutinfo.cedugandaNo ratings yet
- Group Counseling - Study Skills 1 - CompressedDocument15 pagesGroup Counseling - Study Skills 1 - Compressedapi-663471551No ratings yet
- Learning Activities: From Assessment To Evaluation: in This ChapterDocument12 pagesLearning Activities: From Assessment To Evaluation: in This Chapternuzulul hidayahNo ratings yet
- Learning/ Thinking Styles and Multiple IntelligencesDocument32 pagesLearning/ Thinking Styles and Multiple IntelligencesginabonieveNo ratings yet
- TBM Lets Get TogetherDocument24 pagesTBM Lets Get TogetherDaisyNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction: "The More Senses or Modalities We Can Activate, The More Learning Will Take Place"Document1 pageDifferentiated Instruction: "The More Senses or Modalities We Can Activate, The More Learning Will Take Place"Mark Louie AguilarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Learning DisabilityDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Learning DisabilityAkuru GabrielNo ratings yet
- Build Skills To Learn Faster and Better According To NeuroscienceDocument94 pagesBuild Skills To Learn Faster and Better According To NeuroscienceHichem BsMNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-StylesDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-Stylesjonna delNo ratings yet
- Critical and Creative Thinking SkillsDocument84 pagesCritical and Creative Thinking SkillssharonNo ratings yet
- CLD 12Document3 pagesCLD 12Jeppy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dna FingerprintingDocument11 pagesDna FingerprintingseaynNo ratings yet
- Lec - 9 - Residential Occupational Recreational EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesLec - 9 - Residential Occupational Recreational EnvironmentsseaynNo ratings yet
- PST MLS Lesson 2Document2 pagesPST MLS Lesson 2seaynNo ratings yet
- PST MLS Lesson 1Document2 pagesPST MLS Lesson 1seaynNo ratings yet
- Probability and Inductive Argument - ELS101 - Manao - Pitan - FrigillanaDocument28 pagesProbability and Inductive Argument - ELS101 - Manao - Pitan - FrigillanaJim Paul ManaoNo ratings yet
- Research Project Memory Assignment 1Document5 pagesResearch Project Memory Assignment 1api-502417496No ratings yet
- What Is PsycholinguisticsDocument5 pagesWhat Is Psycholinguisticselsa safitriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Dev An Effective Business ModelDocument22 pagesLecture 6 - Dev An Effective Business ModelWasay HanifNo ratings yet
- Higher Stages of Human DevelopmentDocument93 pagesHigher Stages of Human Developmentmariaisabel armijoNo ratings yet
- CAPACIO Synthesis PaperDocument4 pagesCAPACIO Synthesis PaperLorreneil CapacioNo ratings yet
- 55 - 7 C'S of CommunicationDocument4 pages55 - 7 C'S of CommunicationPattyNo ratings yet
- Aubin. Seven-Step Palpation MethodDocument7 pagesAubin. Seven-Step Palpation MethodSofíaNo ratings yet
- PPT3 Constructivist Theory in Teaching Social StudiesDocument34 pagesPPT3 Constructivist Theory in Teaching Social StudiesJocelyn Caleza100% (1)
- Herbert Alexander SimonDocument7 pagesHerbert Alexander Simonsunny syNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Based On Behavioral ApproachDocument8 pagesLeadership: Based On Behavioral ApproachNaveen RajputNo ratings yet
- Historical Thinking ChartDocument1 pageHistorical Thinking ChartRofkar LarosNo ratings yet
- ED 219 - Theories and Principles in Educational Management Module 2Document7 pagesED 219 - Theories and Principles in Educational Management Module 2Raian DuranNo ratings yet
- Trinity Diploma Pre Interview TaskDocument3 pagesTrinity Diploma Pre Interview Taskviersieben100% (1)
- Personality DevelopmentDocument53 pagesPersonality Developmenthafsa ansariNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Background: Rizal College of Taal Taal, BatangasDocument6 pagesThe Problem and Its Background: Rizal College of Taal Taal, Batangasjaja salesNo ratings yet
- The Errors Analysis of Students' Grammatical Writing On Narrative TextDocument12 pagesThe Errors Analysis of Students' Grammatical Writing On Narrative Textadinda febiNo ratings yet
- Barton & Hamilton - Literacy PracticesDocument6 pagesBarton & Hamilton - Literacy PracticesJulio Neves PereiraNo ratings yet
- Deja Vu SpeechDocument2 pagesDeja Vu SpeechAruna Ranaweera50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Building The Foundation - PDF-WT - SummariesDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Building The Foundation - PDF-WT - SummariesReina DibNo ratings yet
- Effects of Dictogloss On Non-English Majored Undergraduates' Listening ComprehensionDocument12 pagesEffects of Dictogloss On Non-English Majored Undergraduates' Listening ComprehensionKimLoan VũNo ratings yet
- Mul Lex Rec in The Men Lex of Thi Lan UseDocument222 pagesMul Lex Rec in The Men Lex of Thi Lan UsefaustoQSNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language Tea Ching (CLT)Document51 pagesCommunicative Language Tea Ching (CLT)Mardhiyatun NisaNo ratings yet
- Content and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary SourcesDocument2 pagesContent and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary SourcesisidroNo ratings yet
- CrosswordDocument1 pageCrosswordCain FouardNo ratings yet
- The Power of The Mind The Whole Brain TheoryDocument11 pagesThe Power of The Mind The Whole Brain TheoryKenji AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Book 01 - Idea Units and Fluency PDFDocument47 pagesBook 01 - Idea Units and Fluency PDFChelladurai KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Ran-Ras Presentation FinalDocument19 pagesRan-Ras Presentation Finalapi-231978749100% (1)
- Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesProgram Studi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDevi Rafealia WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Semiotics of Translation in Ken KeseyDocument3 pagesSemiotics of Translation in Ken KeseyAlexandra MiereNo ratings yet