Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-Styles
Uploaded by
jonna delOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-Styles
Uploaded by
jonna delCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Styles
Memletic Learning Style Model
Learning Styles/Cognitive
● Recognizes that each of us prefers
Styles
to learn in different ways.
➔ The habitual manner in which learners
receive and perceive information,
process it, understand it, value it, store
it, and recall it.
➔ The way a person processes,
internalizes studies, interprets, and
changes new and challenging
materials.
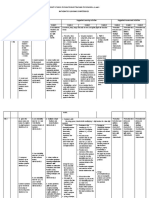
Learning Style Other Term Description Area of the Brain
Responsible
Visual Spatial ➔ Prefers using pictures, ● Occipital lobes
images, graphs, charts, and parietal
logic puzzles, and lobes
spatial understanding
Aural Auditory-Musical ➔ Prefers using sound ● Temporal lobe
and music Right (music)
Verbal Linguistic ➔ Prefers using words, ● Temporal and
both in speech and in frontal lobes
writing
Physical Kinesthetic ➔ Prefers using body, ● Cerebellum and
hands, and sense of motor cortex
touch
Logical Mathematical ➔ Prefers using logic, ● Left parietal
reasoning, and systems lobes
Social Interpersonal ➔ Prefers to learn in ● Frontal and
groups or with other temporal lobes
people and limbic
system
Solitary Intrapersonal ➔ Prefers to work alone ● Frontal and
and use self-study temporal lobes
and limbic
system
Dunn and Dunn Learning Style Model
● Most people can learn, and each individual has his own unique ways of mastering new
and difficult subject matter.
Strand Examples
Environmental Some people study in a cool and quiet room, while others cannot focus
unless they have music playing
Emotional Some people work best when motivated and encouraged, while some feel
motivated when assigned to lead and assume responsibility
Sociological A number of people need to work alone when tackling a new and difficult
subject, while others learn best when working with colleagues
Physiological Some people prefer to study at night, accomplishing more in a quiet
environment; still others find it easier to complete tasks in the morning as
a part of the daily routine.
Psychological Global learners prefer to work in an environment with soft lighting and
informal seating. Analytic learners prefer to work in an environment with
bright lighting and formal seating.
Kolb’s Learning Style ● Finally, the person actively experiments
with actions to test them out.
● depicts learning as 4 stage cycle
● The four-stage learning cycle are:
beginning with an intermediate
○ Concrete experience
concrete experience during which the
○ Reflective observation
person makes observations and
○ Abstract conceptualization
reflections
○ Active experimentation
● Then the person develops an abstract
theory from which he or she develops
ideas on how to proceed.
Creative/Diverger Learners
Are imaginative.
They have an open mind to new ideas
and offer multiple perspectives.
They value brainstorming with a group
although they often listen and observe
sharing their own ideas.
They rely on concrete examples to
learn, and trust their own feelings when
making decisions.
They excel in imagination and
awareness of meaning.
Kolb then hypothesized that learners
They are feeling oriented and people
need for abilities to be effective: oriented and like working in groups.
1. Concrete Experience (CE)
Intellectual/Assimilator Learners
abilities:
- Leaning from actual experience Are organized, logical and precise.
2. Reflective Observation (RO) They like to learn from lectures,
abilities: reading, and contemplation.
- Learning by observing others They find facts, ideas, and information
3. Abstract Conceptualization (AC) fascinating and challenging to people
abilities: and emotions.
- Creating theories to explain what is More scientific than artistic.
seen Their strengths are in inductive
4. Active Experimentation (AE) reasoning, creating theoretical models
abilities: and integrating ideas
- Using theories to solve problems. They prefer playing with ideas to
Social/Accomodator Learners actively and applying it
They are more concerned with ideas
Are leaders
than with people.
They learn best by analyzing and
solving a problem as a group using Practical/Converger Learners
their own intuition and information from Are both thinkers and doers.
other people rather than from books They are those who learn through
and lectures. experimentation, seeking out new
They look for new experiences; often ideas, and discovering practical
take risks and employ hands-on applications for them.
methods to accomplish their goals. They can focus intently on selected
They actively accomplish things, often subjects.
using trial-and-error methods to solve They favor technical challenges to
problems. interpersonal matters.
They may be impatient with other They are goal-oriented and make
people and act on intuition and are a decisions easily.
risk taker.
They are good at decision making and
problem solving and like dealing with
technical work rather than
interpersonal relationships.
Matching Learning Styles to
Instructions
Some studies have shown increased
levels of student achievement when
learners with a strong preference for a
certain style were matched with a
similar teaching or testing style.
Some studies have shown more
student satisfaction when the teacher
matches the student’s learning style,
but some have not.
You might also like
- The Power of The MindDocument77 pagesThe Power of The MindJM Favis Corteza100% (1)
- Multiple Intelligences and Learning Thinking StylesDocument17 pagesMultiple Intelligences and Learning Thinking StylesMaribel Nitor LopezNo ratings yet
- Kolb's Theory of Experiential LearningDocument13 pagesKolb's Theory of Experiential LearningPiyush AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Brain Framing: Instructional Planning with the Brain in MindFrom EverandBrain Framing: Instructional Planning with the Brain in MindNo ratings yet
- SPED203 ADocument56 pagesSPED203 ACharityNo ratings yet
- Job EvaluationDocument4 pagesJob EvaluationAdithya RamNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Teaching and LearningDocument28 pagesThe Elements of Teaching and LearningMicheleNo ratings yet
- Etic111 Prelim Act 2-Case-Study-1Document2 pagesEtic111 Prelim Act 2-Case-Study-1jonna del100% (2)
- Decision-Making and Policy AnalysisDocument19 pagesDecision-Making and Policy AnalysisThoughts and More ThoughtsNo ratings yet
- Case Study2 PDFDocument2 pagesCase Study2 PDFedmarT100% (1)
- Kolbs Experiential Theory of LearningDocument20 pagesKolbs Experiential Theory of LearningEldho SabuNo ratings yet
- Counting - Meng, Guan (WS, 2002)Document123 pagesCounting - Meng, Guan (WS, 2002)SANJIVsharma65No ratings yet
- The Learning Styles Learning StylesDocument4 pagesThe Learning Styles Learning StylesMARY JEANINA ALBANo ratings yet
- Value Engineering IntroductionDocument78 pagesValue Engineering IntroductionSudha100% (2)
- Developing Level of Interest of Grade Learners of City Central Elementary School in Relation To Problem Solving Activities in MathematicsDocument2 pagesDeveloping Level of Interest of Grade Learners of City Central Elementary School in Relation To Problem Solving Activities in MathematicsFrances Marie Z. CieloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EducationDocument76 pagesIntroduction To EducationHina Kaynat100% (1)
- Learning StylesDocument18 pagesLearning StylesVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Learners: Deep LearningDocument3 pagesLearners: Deep LearningPauline Bautista100% (1)
- الاستراتيجيات الصحDocument13 pagesالاستراتيجيات الصحfaf22902No ratings yet
- English - PrelimDocument3 pagesEnglish - Prelimhuangsil0gNo ratings yet
- PED05a Module-3 Nagares LucenaDocument11 pagesPED05a Module-3 Nagares LucenaCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument3 pagesLearning StylesClarice EspinaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Pertemuan Pertama-Bab 2Document12 pages2.0 Pertemuan Pertama-Bab 2nazi akmarNo ratings yet
- Students, Teachers, and TextbookDocument31 pagesStudents, Teachers, and TextbookzyanmktsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document5 pagesChapter 1 & 2tyrasyaaNo ratings yet
- Eseb3493 Learning Design: TOPIC 3 Learners' PersonalityDocument28 pagesEseb3493 Learning Design: TOPIC 3 Learners' PersonalitySEA ServerNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Learning Learning Styles2 TransesDocument7 pages5 Types of Learning Learning Styles2 TransesDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- PST MLS Lesson 3Document1 pagePST MLS Lesson 3seaynNo ratings yet
- LEARNING STYLES NotesDocument2 pagesLEARNING STYLES NotesFuentes, Kyla Diane C.No ratings yet
- Study Skills 1stDocument81 pagesStudy Skills 1stalifahime62No ratings yet
- Learning Thinking StylesDocument21 pagesLearning Thinking StylesRHEANNE OSEANo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching 1 Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 1 Reviewer PDFBrian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching 1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 1 ReviewerVen Gelist TanoNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument19 pagesLearning Stylesvtay05No ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching 1Document7 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 1Irish De VeraNo ratings yet
- Active Learning in ClassicsDocument31 pagesActive Learning in Classicsgemma monderoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Faci LearningDocument7 pagesModule 5 Faci LearningZandro EbioNo ratings yet
- The Learning Styles: - Remedios H. Fernando, RN MANDocument54 pagesThe Learning Styles: - Remedios H. Fernando, RN MANfleur harrisonNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument19 pagesLearning Stylesclarissa renoloNo ratings yet
- Navotas Polytechnic College: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument6 pagesNavotas Polytechnic College: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingLeilalyn NicolasNo ratings yet
- 7 e Instructional ModelDocument20 pages7 e Instructional ModelLuel Jay Viluan ValmoresNo ratings yet
- Natural, Habitual, and Preferred Way ofDocument3 pagesNatural, Habitual, and Preferred Way ofDinah DimagibaNo ratings yet
- Instructional ApproachesDocument3 pagesInstructional Approachesapi-549234739No ratings yet
- Learning How To LearnDocument36 pagesLearning How To LearnTiki MuchtarNo ratings yet
- Health Education Chapter 56Document9 pagesHealth Education Chapter 56Danica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Durable LearningDocument67 pagesDurable LearningThabiseng Nqobile MolefeNo ratings yet
- Educ 12. Module 2 2024Document16 pagesEduc 12. Module 2 2024Angel Dwayne GenovesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study Skills and MethodsDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Study Skills and Methodsganiasma758No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Module 5Document36 pagesLesson Plan Module 5Ellah Mae FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning TheoryDocument52 pagesCognitive Learning TheoryJellz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Module in Educ 6a Facilitating-Learner Centered Teaching: Web: EmailDocument7 pagesModule in Educ 6a Facilitating-Learner Centered Teaching: Web: EmailyoonglespianoNo ratings yet
- Teacher Learner CentredDocument74 pagesTeacher Learner CentredMohamed Fouad DriderNo ratings yet
- Tefl 2 BookDocument63 pagesTefl 2 BookSara TarawnehNo ratings yet
- Teaching and LearningDocument20 pagesTeaching and LearningFrances Bea AbaradoNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Answer Sheets: IDocument3 pagesModule 9 Answer Sheets: ILyca MamantarNo ratings yet
- Elements of TeacheingDocument44 pagesElements of TeacheingKim MatiasNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 11Document5 pagesKelompok 11SunAlfiNo ratings yet
- Basic EducationDocument3 pagesBasic EducationKristine KayeNo ratings yet
- Week 3-Learning Styles and StudyingDocument35 pagesWeek 3-Learning Styles and StudyingMwaniki WilNo ratings yet
- Self Managed LearningDocument34 pagesSelf Managed LearningGayan Laknatha AriyarathnaNo ratings yet
- Mind Styles: Anthony GregorcDocument39 pagesMind Styles: Anthony GregorckarlaNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument13 pagesLearning StylesJeffrey Roy Adlawan LopezNo ratings yet
- Learning Thinking Styles and Multiple IntelligencesDocument4 pagesLearning Thinking Styles and Multiple IntelligencesHsu Sandi AungNo ratings yet
- Learners' StylesDocument39 pagesLearners' StylesFarah Zein EddinNo ratings yet
- EDCS 101 ReviewerDocument8 pagesEDCS 101 ReviewerAnonymous e3ftpCnYzyNo ratings yet
- Faci Module5 Learning Styles & Mutiple IntlligenceDocument22 pagesFaci Module5 Learning Styles & Mutiple IntlligenceClaire Dacles100% (3)
- Learning StylesDocument24 pagesLearning StylesBlessy QuimnoNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation: I. Textual Narrative or Textual PresentationDocument11 pagesData Presentation: I. Textual Narrative or Textual Presentationjonna delNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-StylesDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 4-Learning-Stylesjonna delNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 2 Roles & Function of A TeacherDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 2 Roles & Function of A Teacherjonna delNo ratings yet
- Bioe211 Prelim Lec 3.1-Health-IndicatorsDocument7 pagesBioe211 Prelim Lec 3.1-Health-Indicatorsjonna delNo ratings yet
- Bioe211 Prelim Lec 1.3-Principles-Of-SamplingDocument3 pagesBioe211 Prelim Lec 1.3-Principles-Of-Samplingjonna delNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Critical ReadingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Critical Readingjonna delNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 3-Learning-TheoriesDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 3-Learning-Theoriesjonna delNo ratings yet
- The Nature of The Text: What Questions Should Be Asked? Academic & Non-Academic TextsDocument2 pagesThe Nature of The Text: What Questions Should Be Asked? Academic & Non-Academic Textsjonna delNo ratings yet
- CRWT111 - Prelim - Lec - 3 Steps in Critical ReadingDocument2 pagesCRWT111 - Prelim - Lec - 3 Steps in Critical Readingjonna delNo ratings yet
- CRWT111 Prelim Lec 4-Reading-StrategiesDocument2 pagesCRWT111 Prelim Lec 4-Reading-Strategiesjonna delNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 3-Learning-TheoriesDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 3-Learning-Theoriesjonna delNo ratings yet
- Etic111 Prelim Act 1-What-Is-GoodDocument2 pagesEtic111 Prelim Act 1-What-Is-Goodjonna delNo ratings yet
- Pstm221 Prelim Lec 2 Roles & Function of A TeacherDocument4 pagesPstm221 Prelim Lec 2 Roles & Function of A Teacherjonna delNo ratings yet
- Complete Capstone ProjectDocument42 pagesComplete Capstone Projectapi-547581651No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship & Creativity - Sirsanath BanerjeeDocument36 pagesEntrepreneurship & Creativity - Sirsanath BanerjeeSirsanath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Santhosh Internship MainDocument69 pagesSanthosh Internship MainGaayatri Devi SNo ratings yet
- ADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Document20 pagesADEC - Al Manhal International Private School 2015 2016Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Ealing Connexions CV Guide and TemplateDocument17 pagesEaling Connexions CV Guide and Templateanwer_zakiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Basic PQ ToolsDocument136 pagesModule 5 - Basic PQ Toolsdhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Bat WebQuest ChangesDocument3 pagesBat WebQuest ChangessbeckmyersNo ratings yet
- Personal Philosophy of Special EducationDocument5 pagesPersonal Philosophy of Special Educationapi-307137290No ratings yet
- Report Comments Semester 1 2022Document10 pagesReport Comments Semester 1 2022api-658503315No ratings yet
- Yielding The Lightning Bolt of CreativityDocument8 pagesYielding The Lightning Bolt of CreativityGary GabrielNo ratings yet
- RPH Math Year 4Document13 pagesRPH Math Year 4Haslinda Mohd JamilNo ratings yet
- Note Guidance and CounselingDocument21 pagesNote Guidance and CounselingHAnif KHairNo ratings yet
- 6.how To Improve Metacognition in Learmers Mental HealthDocument23 pages6.how To Improve Metacognition in Learmers Mental HealthStephenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1.1: Problem SolvingDocument13 pagesTutorial 1.1: Problem SolvingveshiniNo ratings yet
- ORSC 201 - Organizational Behavior - Faiza Ali 2Document7 pagesORSC 201 - Organizational Behavior - Faiza Ali 2Dania AmjadNo ratings yet
- Productivity and Leadership SkillsDocument22 pagesProductivity and Leadership SkillsDan Jezreel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Project Report - Training and Development of EmployeesDocument17 pagesProject Report - Training and Development of EmployeesPraveen Kumar R BNo ratings yet
- Hero of Alexandria's Mechanical Geometry: Karin TybjergDocument28 pagesHero of Alexandria's Mechanical Geometry: Karin TybjergNițceValiNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Methodology of Operations ResearchDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Methodology of Operations Researchankitoye0% (1)
- Math GR 456 1st To 4th Quarter MG BowDocument84 pagesMath GR 456 1st To 4th Quarter MG Bowapi-359551623100% (2)
- Creative Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesCreative Problem SolvingwriterlakshmivNo ratings yet
- Let's Be Friends: Elementary CurriculumDocument48 pagesLet's Be Friends: Elementary CurriculumAnonymous Zljo0HNo ratings yet
- Notes On Heuristics in Problem SolvingDocument104 pagesNotes On Heuristics in Problem SolvingrjeceNo ratings yet
- What Is Problem Based Learning?Document5 pagesWhat Is Problem Based Learning?ArifPadillahNo ratings yet
- Comparing Frameworks For "21 Century Skills"Document16 pagesComparing Frameworks For "21 Century Skills"Elga HaryNo ratings yet