Professional Documents
Culture Documents
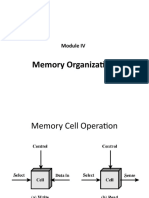
What Is Interleaved Memory
What Is Interleaved Memory
Uploaded by
Asha DurafeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Interleaved Memory
What Is Interleaved Memory
Uploaded by
Asha DurafeCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Interleaved Memory?
It is a technique for compensating the relatively slow speed of DRAM (Dynamic RAM). In this
technique, the main memory is divided into memory banks which can be accessed individually
without any dependency on the other.
For example: If we have 4 memory banks(4-way Interleaved memory), with each containing
256 bytes, then, the Block Oriented scheme(no interleaving), will assign virtual address 0 to 255
to the first bank, 256 to 511 to the second bank. But in Interleaved memory, virtual address 0
will be with the first bank, 1 with the second memory bank, 2 with the third bank and 3 with the
fourt, and then 4 with the first memory bank again.
Hence, CPU can access alternate sections immediately without waiting for memory to be cached.
There are multiple memory banks which take turns for supply of data.
Memory interleaving is a technique for increasing memory speed. It is a process that makes the
system more efficient, fast and reliable.
For example: If we have 4 memory banks(4-way Interleaved memory), with each containing
256 bytes, then, the Block Oriented scheme(no interleaving), will assign virtual address 0 to 255
to the first bank, 256 to 511 to the second bank. But in Interleaved memory, virtual address 0
will be with the first bank, 1 with the second memory bank, 2 with the third bank and 3 with the
fourt, and then 4 with the first memory bank again.
Hence, CPU can access alternate sections immediately without waiting for memory to be cached.
There are multiple memory banks which take turns for supply of data.
Memory interleaving is a technique for increasing memory speed. It is a process that makes the
system more efficient, fast and reliable.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Module 5.3Document39 pagesModule 5.3Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- ELX 702: Power Electronics: Asha Durafe, Asst. ProfessorDocument15 pagesELX 702: Power Electronics: Asha Durafe, Asst. ProfessorAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- IA2 Notes DLCADocument6 pagesIA2 Notes DLCAAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Restoring DivisionDocument5 pagesRestoring DivisionAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Document6 pagesPower Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Inverter - NEWDocument51 pagesLecture 2 - Inverter - NEWAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Cache Memory LevelsDocument2 pagesCache Memory LevelsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Patent Enforcement OptionsDocument1 pagePatent Enforcement OptionsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- ELX 702: Power Electronics: Asha Durafe, Asst. ProfessorDocument11 pagesELX 702: Power Electronics: Asha Durafe, Asst. ProfessorAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- The Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsDocument6 pagesThe Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Power BJT & MOSFETDocument7 pagesPower BJT & MOSFETAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Inverter - NEWDocument51 pagesLecture 2 - Inverter - NEWAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Intellectual Property (IP) Relates To E-CommerceDocument1 pageUnderstanding How Intellectual Property (IP) Relates To E-CommerceAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Project Report007Document57 pagesProject Report007Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Types of Patent InfringementDocument2 pagesTypes of Patent InfringementAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Indian Patent Law and US LawDocument1 pageDifference Between Indian Patent Law and US LawAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Project Budget-2Document1 pageProject Budget-2Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Experiment Iv Silicon-Controlled RectifierDocument8 pagesExperiment Iv Silicon-Controlled RectifierAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- #1 e Scan ProtectedDocument1 page#1 e Scan ProtectedAsha DurafeNo ratings yet