Professional Documents
Culture Documents
My Papers
Uploaded by
esraa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesOriginal Title
my papers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesMy Papers
Uploaded by
esraaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
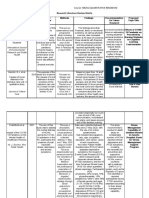
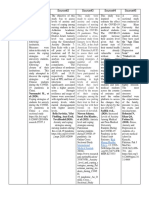
author year of publication country purpose of study
to measure the anxiety and depression among
Bazmi Inam[7] 2007 Saudi Arabia 1st 2nd and 3rd year students using
anxiety and estimate its correlation with
questionarre.
Shao et al[8] 2020 China
family function, social
to estimate the risk support
factors that and
leadcoping
to increase
Tabalipa et al[9] 2015 Brazil to provide
anxiety anda depression
clear insight
inabout
medicaldepression
students.that
Zang et al[10] 2019 China experienced by chinese medical students, and
to assess the
evidance baseanxiety
basis. and depression among
Bertani at el[11] 2020 Italy
italian medical student by using
to estimate the prevalence rate ofHAD scale.
4th, 5th and
Elsawy et al[12] 2020 Egypt to investigate the sociodermographic factors
6th medical students in Alexandria.
Shawahna et al[13] 2020 Palestine and its relation to depressive and anxiety
to assess the rates of depression and anxiety
symptoms.
Kumar et al[14] 2019 Pakistan
among finalwhether
to estimate year medical student.
final examinations affect
Thiemann et al[15] 2020 UK to study the depression, burnout and other risk
males or females more.
Pokhrel et al[16] 2020 Nepal factors among medical students and residents
exhausion and depersonalization with
Ernst et al[17] 2021 Switzerland of aNepalese medical school.
symptoms of depression of Swiss medical
number of
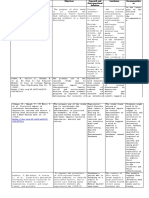
ose of study mental problem Assessment tool conclusion/result
iety and depression among patients
Depression and 288 male,105 the prevalence of anxiety in female
ar students using AKUADS students
te its correlation with anxiety
depression and Social Support female
2057 medical is higher with
in 1stfinancial
year. burden, bad
relationship
not physicians andtheir
with thoselovers
whoandfelt
cial support
factors that and
leadcoping
to increase anxiety
depression and Rating Scale and student
(BDI) family, less sleep quality and who
nsight
sion inabout
medicaldepression
students.that depression, anxiety,
anxiety BDI, ,SDS,
(BAI) 262 pushed by their parents, while
30,817 Chinese or suicidal ideation
depression increasesbetween
in thosechinese
whom
nese medical students, and suicidal ideation, CESD,PHQ-9,SCL-
medical students medical students, and there is no
s.y and depression among anddepression and
eating disorders (HADS),90.PID-5-BF 459
combined anxiety-depressive
dent by using like womenweregender, not having
valence rate ofHAD scale.
4th, 5th and anxiety symptoms reported.
ociodermographic factors Depression BDI-II 390 someone to talk to under pressure,
ts in Alexandria. depression and had minimal depression, and quarter
epressive and anxiety BDI-II, BAI 425 stressful life conditions,
of depression and anxiety anxiety
Depression, of the sample
higher in public hadcollege
mild tostudents
moderate
DASS-21 450
medical student.
r final examinations affect Anxiety, and Stress
depression and because of too many
anxiety increases factors
during finalinclude
exams
sion, burnout and other risk Depression, HADS 446 burnout was more prevalnt in
more. anxiety and mostly occure in females.
ical students and residents anxiety, and HADS, CBI, MSSQ 651 residents, whereas medical students
ersonalization
cal school. with Burnout, depression
burnout occure in women
have more anxietywith
and 23 median
depression.
PHQ-9, GAD-7 574
ssion of Swiss medical and anxiety age, with correlations between
types of
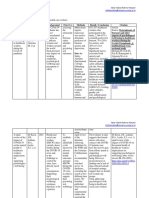
conclusion/result studies
prevalence of anxiety in female Cross sectional
dents with
higher in 1stfinancial
year. burden, bad study.
Cross sectional
ationship
physicians andtheir
with thoselovers
whoandfelt study.
Cross sectional
mily, less sleep quality
hed by their parents, whileand who
suicidal ideation study.
pression increasesbetween
in thosechinese
whom Cross sectional
dical students, and
mbined anxiety-depressivethere is no study.
Cross sectional
e womenwere
mptoms gender, not having
reported. study.
Cross sectional
meone to talk to under pressure, cross-sectional
dessful
minimal depression, and quarter study.
life conditions, observational
he sample
her in publichadcollege
mild tostudents
moderate observational
design
ause increases
of too many factors a multicentre
xiety during finalinclude
exams study
nout was more prevalnt in cross-sectional
d mostly occure in females. Crossstudy
sectional
idents, whereas medical students
study.
veure in women
more anxietywith
and 23 median
depression. Cross sectional
, with correlations between study.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068631/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32321593/
https://www.scielo.br/j/rbem/a/dhNzFb9S8G57t9fVKmyF85f/?format=pdf&lang=en
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31045774/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33349727/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33402990/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32429889/
https://www.cureus.com/articles/18501-depression-anxiety-and-stress-among-final-year-medical-students
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7181528/
https://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12888-020-02645-6.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022395621005562
You might also like
- NR201 ReportDocument10 pagesNR201 ReportSeradallab Ch RishNo ratings yet
- The Negative Emotional States of DepressionDocument22 pagesThe Negative Emotional States of DepressionKeith OlfindoNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Stress and Happiness Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicDocument7 pagesThe Relationship Between Stress and Happiness Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Academic Performance and Depression Risk Among Nursing StudentsDocument23 pagesRelationship Between Academic Performance and Depression Risk Among Nursing StudentsIosif CadeNo ratings yet
- The Mediating Role of Self Compassion and Repetitive Negat - 2023 - PersonalityDocument6 pagesThe Mediating Role of Self Compassion and Repetitive Negat - 2023 - PersonalitymarfuNo ratings yet
- Jvme 0116-006rDocument13 pagesJvme 0116-006rDhanang Prawira NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Assessing stress levels and sources among college studentsDocument5 pagesAssessing stress levels and sources among college studentsmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- The Negative Emotional States of Depression Anxiety and StressDocument22 pagesThe Negative Emotional States of Depression Anxiety and Stressangelojames comelioNo ratings yet
- Collage pr1Document5 pagesCollage pr1Maria Carmina Beroin VegaNo ratings yet
- Literature Matrix 2Document5 pagesLiterature Matrix 2Sweety KurnNo ratings yet
- Correlates and Predictors of Resilience Among Baccalaureate Nursing StudentsDocument5 pagesCorrelates and Predictors of Resilience Among Baccalaureate Nursing StudentsRicardoNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Emotional Intelligence of Senior High School Students: A Correlational StudyDocument6 pagesMental Health and Emotional Intelligence of Senior High School Students: A Correlational StudyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Amidst The Online Learning Modality: The Social Support and Its Relationship To The Anxiety of Senior High School StudentsDocument5 pagesAmidst The Online Learning Modality: The Social Support and Its Relationship To The Anxiety of Senior High School StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Personality, cognitive flexibility, and motivation among medical professionalsDocument12 pagesPersonality, cognitive flexibility, and motivation among medical professionalsBishal.P 1830401No ratings yet
- JPSP 2022 038Document14 pagesJPSP 2022 038Kimberly NogaloNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Happiness and Depression Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicDocument6 pagesThe Relationship Between Happiness and Depression Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effects_of_COVID-19_stress_proximity_and_adverse_cDocument13 pagesEffects_of_COVID-19_stress_proximity_and_adverse_cKrishnapriya T SNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Mental Health Status of Children and Adolescents in ChinaDocument7 pagesAn Investigation of Mental Health Status of Children and Adolescents in ChinaCECILIA BELEN FIERRO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Problems Faced by Healthcare WorkersDocument14 pagesMental Health Problems Faced by Healthcare WorkersRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- Exploring links between career anxiety, well-being and self-efficacyDocument14 pagesExploring links between career anxiety, well-being and self-efficacycandra ditiaNo ratings yet
- Antecedents of Psychological Empowerment and The Impact On Nurses BurnoutDocument11 pagesAntecedents of Psychological Empowerment and The Impact On Nurses BurnoutClaudia MoksidyNo ratings yet
- School Based Depression and Anxiety Prevention Programs - 2021 - Clinical PsychDocument24 pagesSchool Based Depression and Anxiety Prevention Programs - 2021 - Clinical PsychFlor De LisNo ratings yet
- Research in Developmental DisabilitiesDocument15 pagesResearch in Developmental DisabilitiesSonny TehNo ratings yet
- Afrontamiento CovidDocument5 pagesAfrontamiento Covidsofia valloryNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2022 Father AssetsDocument8 pagesZhang 2022 Father AssetsXiaoying ZhangNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Peer Pressure and Mental Well-Being Among Senior High School StudentsDocument9 pagesThe Correlation Between Peer Pressure and Mental Well-Being Among Senior High School StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Lecturas Complementarias T. DepresionDocument53 pagesLecturas Complementarias T. DepresionmariajosecazorlaNo ratings yet
- Depresi 1Document24 pagesDepresi 1dhikaNo ratings yet
- Children and Youth Services ReviewDocument7 pagesChildren and Youth Services ReviewNiLa AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Hussong2021 Article CopingAndMentalHealthInEarlyAdDocument11 pagesHussong2021 Article CopingAndMentalHealthInEarlyAdXiadani VillasanaNo ratings yet
- CovidDocument7 pagesCovidRise KingdomsNo ratings yet
- Short Journal ComparisonDocument13 pagesShort Journal ComparisonKlinik Anjani IINo ratings yet
- PM Is The Key: Perceived Stress and Mental Health As The KEY Indicator of Wellbeing of Selected College Online Students in The Philippines During COVID-19 PandemicDocument13 pagesPM Is The Key: Perceived Stress and Mental Health As The KEY Indicator of Wellbeing of Selected College Online Students in The Philippines During COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Loneliness, College Belongingness, Subjective Vitality, and Psychological Adjustment During Coronavirus PandemicDocument15 pagesLoneliness, College Belongingness, Subjective Vitality, and Psychological Adjustment During Coronavirus PandemicHazel PotterNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Literacy, Level of Stressful Experiences and Coping Strategies of Elementary School TeachersDocument15 pagesMental Health Literacy, Level of Stressful Experiences and Coping Strategies of Elementary School TeachersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- BPD and Employment 1Document11 pagesBPD and Employment 1Leonard AmundsonNo ratings yet
- Hussong Et Al., 2021Document11 pagesHussong Et Al., 2021Edgardo ToroNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Issues Among Health Care Workers During The COVID-19 Pandemic A Study From IndiaDocument6 pagesMental Health Issues Among Health Care Workers During The COVID-19 Pandemic A Study From IndiaYingying XuNo ratings yet
- Open Folder Approved StudiesDocument15 pagesOpen Folder Approved Studiesjustineflorendo879No ratings yet
- TP - Online - For Transition-Age YouthDocument8 pagesTP - Online - For Transition-Age YouthFabiana MartinsNo ratings yet
- Group 7 PRDocument10 pagesGroup 7 PRPol Vince Bernard SalisiNo ratings yet
- 79-Main Text-571-1-10-20220508Document10 pages79-Main Text-571-1-10-20220508ateng FangirlNo ratings yet
- Children and Youth Services Review: Wenxin Xu, Wei Shen, Shen WangDocument8 pagesChildren and Youth Services Review: Wenxin Xu, Wei Shen, Shen WangLucia LopezNo ratings yet
- Source#1 Source#2 Source#3 Source#4 Source#5: Nurunnabi M., Et Al (2020)Document4 pagesSource#1 Source#2 Source#3 Source#4 Source#5: Nurunnabi M., Et Al (2020)RekimNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies of Teachers Amid COVID-19 PandemicDocument14 pagesCoping Strategies of Teachers Amid COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Predict That Financial or Family Support Has A Positive Effect On Mental Health and It Can RelieveDocument5 pagesPredict That Financial or Family Support Has A Positive Effect On Mental Health and It Can RelieveGil GameshNo ratings yet
- Work Values and Stress Levels of Selected Displaced Filipino Workers of COVID-19 PandemicDocument9 pagesWork Values and Stress Levels of Selected Displaced Filipino Workers of COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effects of Depression On Learning CompetencyDocument50 pagesEffects of Depression On Learning CompetencySam AlerozaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Research: Letter To The EditorDocument3 pagesPsychiatry Research: Letter To The EditorGeorge ApostolNo ratings yet
- Amidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: The Relationship of Burnout and Depression Among College StudentsDocument6 pagesAmidst The COVID-19 Pandemic: The Relationship of Burnout and Depression Among College StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Happiness and Stress Among Senior High School Students From Public Schools Amidst Online LearningDocument4 pagesThe Relationship Between Happiness and Stress Among Senior High School Students From Public Schools Amidst Online LearningPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effort-Reward Imbalance and Burnout Among Nurses of Community General Hospital in San Pablo CityDocument11 pagesEffort-Reward Imbalance and Burnout Among Nurses of Community General Hospital in San Pablo CityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Depression, Anxiety and Stress Among Nursing Students in Sri LankaDocument13 pagesDepression, Anxiety and Stress Among Nursing Students in Sri LankaJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Academic Stress and Depression of Chinese Adolescents in Junior High SchoolsDocument6 pagesAcademic Stress and Depression of Chinese Adolescents in Junior High SchoolsnurulaqilahizzatiNo ratings yet
- guan2021Document10 pagesguan2021lulixbeNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty, and Fear and Anxiety Among COVID-19 Vaccinated Filipinos in Rizal Province:Basis For ProgramDocument10 pagesUncertainty, and Fear and Anxiety Among COVID-19 Vaccinated Filipinos in Rizal Province:Basis For ProgramPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Overlap Between Burnout and Depression Through A Different LensDocument7 pagesThe Overlap Between Burnout and Depression Through A Different LensNess LiendoNo ratings yet
- Child Family Social Work - 2022 - Rahmani - Caregiver or Care Receiver Adolescents Experience of Caregiving To A ParentDocument10 pagesChild Family Social Work - 2022 - Rahmani - Caregiver or Care Receiver Adolescents Experience of Caregiving To A ParentLuz Maria RojasNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Social Support and Depression Among Senior High School Students in The Midst of Online Learning ModalityDocument8 pagesThe Relationship Between Social Support and Depression Among Senior High School Students in The Midst of Online Learning ModalityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Identifying Perinatal Depression and Anxiety: Evidence-based Practice in Screening, Psychosocial Assessment and ManagementFrom EverandIdentifying Perinatal Depression and Anxiety: Evidence-based Practice in Screening, Psychosocial Assessment and ManagementJeannette MilgromNo ratings yet
- Top 1000 (2022)Document100 pagesTop 1000 (2022)esraaNo ratings yet
- CIBNP Research Training Program Syllabus GuideDocument12 pagesCIBNP Research Training Program Syllabus GuideesraaNo ratings yet
- (DK How Things Work) DK - How Business Works - The Facts Visually Explained-DK (2022)Document354 pages(DK How Things Work) DK - How Business Works - The Facts Visually Explained-DK (2022)esraa100% (6)
- Posselt, Julie R - Inside Graduate Admissions - Merit, Diversity, and Faculty Gatekeeping-Harvard University Press (2016)Document263 pagesPosselt, Julie R - Inside Graduate Admissions - Merit, Diversity, and Faculty Gatekeeping-Harvard University Press (2016)esraaNo ratings yet
- Mastering the Graduate School Statement of PurposeDocument68 pagesMastering the Graduate School Statement of PurposeesraaNo ratings yet
- Get Into Grad School Checklist - Self Made MillennialDocument3 pagesGet Into Grad School Checklist - Self Made MillennialesraaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 WordsDocument16 pagesGroup 2 WordsYuria SatomiNo ratings yet
- Number Word Noun Verb Adjective: ProdigalDocument15 pagesNumber Word Noun Verb Adjective: Prodigalymt1123No ratings yet
- Group 4 WordsDocument20 pagesGroup 4 WordsesraaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric ComorbidityDocument13 pagesPsychiatric ComorbidityMarcelo Santos SoledadeNo ratings yet
- PCORI Methodology Standards Curriculum Research Questions 3Document13 pagesPCORI Methodology Standards Curriculum Research Questions 3Krizele Acu PagalananNo ratings yet
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University College of Nursing students' mental health assessmentDocument7 pagesDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University College of Nursing students' mental health assessmentEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Mcmi Iii Report JamilDocument8 pagesMcmi Iii Report Jamilshubhangi kapoor100% (1)
- Family Health Care Nursing Theory Practice and Research 6th Edition Kaakinen Test BankDocument10 pagesFamily Health Care Nursing Theory Practice and Research 6th Edition Kaakinen Test Bankgarycampbell23081997gzw100% (31)
- Psychiartry NotesDocument38 pagesPsychiartry NotesAlthea Lujille PinazoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Society and Human Behavior 16th Edition Hart Test BankDocument12 pagesDrugs Society and Human Behavior 16th Edition Hart Test Bankmichelleortizpxnzkycmbw100% (28)
- (Timothy A. Brown, David H. Barlow) Anxiety and Related Disorders Interview Schedule For DSM-5Document30 pages(Timothy A. Brown, David H. Barlow) Anxiety and Related Disorders Interview Schedule For DSM-5calintwf60% (10)
- The Goodnewspaper - The Mental Health EditionDocument22 pagesThe Goodnewspaper - The Mental Health EditiondubitNo ratings yet
- Rosh ReviewDocument125 pagesRosh ReviewPrince Du100% (2)
- Effects of social media on mental health of Catanauan studentsDocument12 pagesEffects of social media on mental health of Catanauan studentsAdrianPaul ArtiolaNo ratings yet
- PTSD Test PDFDocument8 pagesPTSD Test PDFLady A MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- DAY ONE Introductory Workshop Handouts 1.2018Document28 pagesDAY ONE Introductory Workshop Handouts 1.2018decomoraes4275No ratings yet
- RPMC ACEs Questionnaire and Patient HandoutApr2019Document2 pagesRPMC ACEs Questionnaire and Patient HandoutApr2019Tuấn KhangNo ratings yet
- SuicideDocument9 pagesSuicideJana Marie CorpuzNo ratings yet
- American Psychological Association Study: Mental Illness and Crime Not Typically LinkedDocument12 pagesAmerican Psychological Association Study: Mental Illness and Crime Not Typically LinkedkuimbaeNo ratings yet
- Reading Module 2023Document29 pagesReading Module 2023Badrut Tamam Hikmawan Fauzi (Tamam)No ratings yet
- Healing Architecture Daylight in Hospital Design-LibreDocument9 pagesHealing Architecture Daylight in Hospital Design-LibreAdita RianNo ratings yet
- Domain Diagnosa Gizi-Intake 2013-4Document58 pagesDomain Diagnosa Gizi-Intake 2013-4Ilmi Dewi A100% (1)
- Mental Disorders Due To A General Medical ConditionDocument145 pagesMental Disorders Due To A General Medical ConditionKaye NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy and Mental Health - Research PaperDocument14 pagesMusic Therapy and Mental Health - Research Paperapi-550020034100% (1)
- Building Resistance To Stress and AgingDocument378 pagesBuilding Resistance To Stress and Agingdoc_oz3298No ratings yet
- Evidence Table WorksheetDocument16 pagesEvidence Table Worksheetapi-282223043No ratings yet
- Depression ProjectDocument56 pagesDepression Projectbrian samNo ratings yet
- Conduct and Behavior ProblemsDocument165 pagesConduct and Behavior Problemsnao100% (4)
- Somatoform DisordersDocument88 pagesSomatoform DisordersGothanda RamanNo ratings yet
- GERONTOLOGICAL NURSING Editable 1Document20 pagesGERONTOLOGICAL NURSING Editable 1kesNo ratings yet
- Frances, A. (2010) - Opening Pandora's Box - The 19 Worst Sugestiones For DSM 5Document10 pagesFrances, A. (2010) - Opening Pandora's Box - The 19 Worst Sugestiones For DSM 5A100% (1)
- July 2006, Vol 51, Supplement 2: Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Anxiety DisordersDocument92 pagesJuly 2006, Vol 51, Supplement 2: Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Anxiety DisordersSendruc OvidiuNo ratings yet
- School Lunches Take Unhealthy Turn as Kraft Heinz Junk Food AddedDocument8 pagesSchool Lunches Take Unhealthy Turn as Kraft Heinz Junk Food AddedRocco LamponeNo ratings yet