Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bloom's Taxonomy: Three Learning Domains Explained
Uploaded by
gashu asmareOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bloom's Taxonomy: Three Learning Domains Explained
Uploaded by
gashu asmareCopyright:
Available Formats
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY: THREE LEARNING DOMAINS
1. Bloom’s Taxonomy - Cognitive Domain - (intellect - knowledge - 'think')
An adjusted model of Bloom's Taxonomy (1956) Cognitive Domain was produced by Anderson & Krathwhol in which the levels five and
six (synthesis & evaluation) were inverted and all the levels became verbs, suggesting that learning is an active process (Anderson &
Krathwohl, A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, 2001).
This is why you will see different versions of this Cognitive Domain model. While debate continues as to the order of levels five and six,
the revised version is gaining wider acceptance overall.
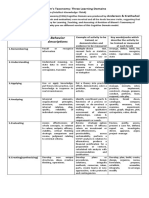
COGNITIVE DOMAIN
Examples of activity to be trained, or demonstration and 'Key words' (verbs which describe the activity
Category or 'level' Behavior descriptions
evidence to be measured to be trained or measured at each level)
Multiple-choice test, recount facts or statistics, recall a Arrange, define, describe, label, list, memorize,
1. Remembering Recall or recognize information
process, rules, definitions; quote law or procedure recognize, relate, reproduce, select, state
Explain, reiterate, reword, critique, classify,
Understand meaning, re-state data in Explain or interpret meaning from a given scenario or
summarize, illustrate, translate, review, report,
2. Understanding one's own words, interpret, statement, suggest treatment, reaction or solution to given
discuss, re-write, estimate, interpret, theorize,
extrapolate, translate problem, create examples or metaphors
paraphrase, reference, example
Use or apply knowledge, put theory Use, apply, discover, manage, execute, solve,
Put a theory into practical effect, demonstrate, solve a
3. Applying into practice, use knowledge in produce, implement, construct, change, prepare,
problem, manage an activity
response to real circumstances conduct, perform, react, respond, role-play
Interpret elements, organizational Identify constituent parts and functions of a process or Analyze, break down, catalogue, compare,
principles, structure, construction, concept, or de-construct a methodology or process, making quantify, measure, test, examine, experiment,
4. Analyzing
internal relationships; quality, qualitative assessment of elements, relationships, values and relate, graph, diagram, plot, extrapolate, value,
reliability of individual components effects; measure requirements or needs divide
Review strategic options or plans in terms of efficacy, return
Assess effectiveness of whole
on investment or cost-effectiveness, practicability; assess
concepts, in relation to values,
sustainability; perform a SWOT analysis in relation to Review, justify, assess, present a case for, defend,
outputs, efficacy, viability; critical
5. Evaluating alternatives; produce a financial justification for a report on, investigate, direct, appraise, argue,
thinking, strategic comparison and
proposition or venture, calculate the effects of a plan or project-manage
review; judgment relating to external
strategy; perform a detailed risk analysis with
criteria
recommendations and justifications
Develop new unique structures, Develop plans or procedures, design solutions, integrate Develop, plan, build, create, design, organize,
6. Creating systems, models, approaches, ideas; methods, resources, ideas, parts; create teams or new revise, formulate, propose, establish, assemble,
creative thinking, operations approaches, write protocols & contingencies integrate, re-arrange, modify
Injibara Poly Technic College Complied By Wondim Mihret Page 1
2. Bloom’s Taxonomy - Affective Domain - (emotions - attitude - 'feel')
Bloom's Taxonomy second domain, the Affective Domain, was detailed by Bloom, Krathwhol and Masia (1964, Taxonomy of
Educational Objectives: Vol. II, The Affective Domain. Bloom's theory advocates this structure and sequence for developing attitude -
also now commonly expressed in the modern field of personal development as 'beliefs'. As with the other domains, the Affective Domain
detail provides a framework for teaching, training, assessing and evaluating the effectiveness of training and lesson design and delivery,
and also the retention by and affect upon the learner or trainee.
AFFECTIVE DOMAIN
Examples of experience, or
demonstration and evidence to be 'Key words' (verbs which describe the activity to be
Category or 'level' Behavior descriptions
measured trained or measured at each level)
Listen to teacher or trainer, take interest
Open to experience, in session or learning experience, take Ask, listen, focus, attend, take part, discuss, acknowledge,
1. Receiving
willing to hear notes, turn up, make time for learning hear, be open to, retain, follow, concentrate, read, do, feel
experience, participate passively
Participate actively in group discussion,
active participation in activity, interest in React, respond, seek clarification, interpret, clarify, provide
React and participate
2. Responding outcomes, enthusiasm for action, other references and examples, contribute, question, present,
actively
question and probe ideas, suggest cite, become animated or excited, help team, write, perform
interpretation
Decide worth and relevance of ideas,
Attach values and express Argue, challenge, debate, refute, confront, justify, persuade,
3. Valuing experiences; accept or commit to
personal opinions criticize,
particular stance or action
4. Organizing or Reconcile internal Qualify and quantify personal views,
Build, develop, formulate, defend, modify, relate, prioritize,
Conceptualizing conflicts; develop value state personal position and reasons, state
reconcile, contrast, arrange, compare
Values system beliefs
5. Internalizing Adopt belief system and Self-reliant; behave consistently with
Act, display, influence, solve, practice,
Values philosophy personal value set
Injibara Poly Technic College Complied By Wondim Mihret Page 2
3. Bloom’s Taxonomy - Psychomotor Domain - (physical - skills - 'do')
The Psychomotor Domain was established to address skills development relating to the physical dimensions of accomplishing a task.
Because, 'motor' skills extend beyond the originally traditionally imagined manual and physical skills, always consider using this domain,
even if you think your environment is covered adequately by the Cognitive and Affective Domains. Whatever the situation, it is likely that
the Psychomotor Domain is significant.
PSYCHOMOTOR DOMAIN
Examples of activity or 'Key words' (verbs which describe the activity to
Category or 'level' Behavior descriptions demonstration and evidence to be be trained or measured at each level)
measured
Copy action of another; observe and Watch teacher or trainer and repeat Copy, follow, replicate, repeat, adhere, attempt,
1. Imitation reproduce, organize, sketch, duplicate
replicate action, process or activity
Reproduce activity from instruction Carry out task from written or verbal Re-create, build, perform, execute, implement,
2. Manipulation or memory instruction acquire, conduct, operate
Perform a task or activity with
Execute skill reliably, independent expertise and to high quality without
assistance or instruction; able to Demonstrate, complete, show, perfect, calibrate,
3. Precision of help, activity is quick, smooth,
demonstrate an activity to other control, achieve, accomplish, master, refine
and accurate
learners
Relate and combine associated Solve, adapt, combine, coordinate, revise, integrate,
Adapt and integrate expertise to
4. Articulation activities to develop methods to meet adapt, develop, formulate, modify, master
satisfy a new context or task
varying, novel requirements
Instinctive, effortless, unconscious
Define aim, approach and strategy for Construct, compose, create, design, specify, manage,
5. Naturalization mastery of activity and related skills
use of activities to meet strategic need invent, project-manage, originate
at strategic level
Injibara Poly Technic College Complied By Wondim Mihret Page 3
You might also like
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- IDS Bloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsDocument10 pagesIDS Bloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsSalsabila MilleniaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy All Three DomainsIno JohannisNo ratings yet
- Leading with Purpose The Guide to Becoming a Remarkable ChiefFrom EverandLeading with Purpose The Guide to Becoming a Remarkable ChiefNo ratings yet
- 03.blooms' Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument14 pages03.blooms' Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesThukten SherabNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TexanomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TexanomyMuhammad Wajahat Ali KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Authentic and Alternative Assessment MethodsDocument3 pagesAuthentic and Alternative Assessment MethodsVino€ H€rmosoNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument6 pagesBlooms TaxonomyPatrickNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Affective Psychomotor Knowledge Attitude Skills: Training Course For Instructors Handout 9Document6 pagesCognitive Affective Psychomotor Knowledge Attitude Skills: Training Course For Instructors Handout 9Conrad ManacapNo ratings yet
- The Learning Process Report WordDocument4 pagesThe Learning Process Report Wordreverson menorNo ratings yet
- Health Profession’s Education Assessment in Higher EdDocument7 pagesHealth Profession’s Education Assessment in Higher EdnajamaneelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document21 pagesLesson 3api-619738021100% (1)
- Module 3 Assessment of Student Learning 1Document4 pagesModule 3 Assessment of Student Learning 1Kim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy and Revised Version ExplainedDocument4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy and Revised Version Explainedjacqueline baeNo ratings yet
- Use Bloom's Taxonomy to Achieve Learning GoalsDocument61 pagesUse Bloom's Taxonomy to Achieve Learning GoalsSouvik DasNo ratings yet
- Bloom Taxonomy - Learning DomainsDocument8 pagesBloom Taxonomy - Learning DomainsrismaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotordeeeeeeeeedeeeeeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Home Assessment Resources BloomDocument11 pagesHome Assessment Resources BloomWidi AndewiNo ratings yet
- Ecb 2306 - 1Document22 pagesEcb 2306 - 1peterambrose009No ratings yet
- Improving Structure and Quality of Assessments: 3.1 Bloom's Taxonomy For Assessment DesignDocument5 pagesImproving Structure and Quality of Assessments: 3.1 Bloom's Taxonomy For Assessment DesignPragati ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bloom Revised Taxonomy 4. AnalyzeDocument1 pageBloom Revised Taxonomy 4. AnalyzeNURSABIRAH BINTI IDRISNo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of The Cognitive DomainDocument4 pagesTaxonomies of The Cognitive DomainRonel BorbonNo ratings yet
- Revised Blooms Taxonomy All DomainsDocument4 pagesRevised Blooms Taxonomy All DomainsRelampago CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningDocument6 pagesCognitive Domain: Cooperative LearningCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of LearningDocument19 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of Learningiq_mzj9892No ratings yet
- Category Examples Key Words (Verbs)Document5 pagesCategory Examples Key Words (Verbs)Christine Sheena Batican-BulalaNo ratings yet
- Domains of LearningDocument8 pagesDomains of LearningantonyNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4Document6 pagesTugas 4Widiayu SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Bloom Taxanomy DetailsDocument5 pagesBloom Taxanomy DetailsAsiraz InaliajNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Three Types of LearningDocument5 pagesUnderstanding the Three Types of LearningJonah A. RecioNo ratings yet
- REVISED BLOOM'S TAXONOMYDocument8 pagesREVISED BLOOM'S TAXONOMYIrmanda AmrihiNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of EducationDocument7 pagesTaxonomy of Educationasiyaasghar313No ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorsumonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan. 222Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan. 222Realm Daffodil SuquibNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain of BloomDocument1 pageCognitive Domain of BloomGavin FurukawaNo ratings yet
- Lesson II Instructional DecissionsDocument14 pagesLesson II Instructional DecissionsGreta SuNo ratings yet
- I-Plan Cot 2 GTCDocument6 pagesI-Plan Cot 2 GTCeyadcampNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Instructional Objectives and Learning Outcomes Handsout 1Document8 pagesLesson 3 Instructional Objectives and Learning Outcomes Handsout 1barcekylaNo ratings yet
- Iplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Qual Vs QuanDocument7 pagesIplan - DLP - Format - PR1 - Qual Vs Quanjenenn ann cacayanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's New Taxonomy-AndersonDocument8 pagesBloom's New Taxonomy-AndersonsamanzanaresNo ratings yet
- Teaching Higher Order ThinkingDocument16 pagesTeaching Higher Order ThinkingPee BaradasNo ratings yet
- 1. AssignmentsDocument25 pages1. AssignmentsMarvin IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain-Arlie G. FresnidoDocument29 pagesCognitive Domain-Arlie G. FresnidoArlie Gelua FresnidoNo ratings yet
- Blooms Domains 2Document9 pagesBlooms Domains 2Cherry-Ann C. OlajayNo ratings yet
- Bloom S-Taxonomy PDFDocument3 pagesBloom S-Taxonomy PDFjennifer paneloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEllorin RANo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document5 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Krizza Marie AtonNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of LearningDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of LearningXiena Rose BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Elucidate Concepts Through Definition, Explication and ClarificationDocument4 pagesElucidate Concepts Through Definition, Explication and ClarificationMa Lou100% (1)
- Blooms Taxonomy RevisedDocument8 pagesBlooms Taxonomy RevisedEmmylou Molito PesidasNo ratings yet
- CHANGES TO BLOOMs TAXONOMYDocument23 pagesCHANGES TO BLOOMs TAXONOMYMi Yu KeyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 12Document2 pagesLearning Task 12kenneth50% (6)
- Taxonomies of The Cognitive DomainDocument3 pagesTaxonomies of The Cognitive DomainRuth Salvatierra FuentesfinaNo ratings yet
- Learning Domains and Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesLearning Domains and Bloom's Taxonomyamber ariaNo ratings yet
- CS - RS12 Id e 2Document8 pagesCS - RS12 Id e 2Josua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningSheila Bliss J. Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument6 pagesBloom's TaxonomyJisiamar GeromoNo ratings yet
- Assisting Policy Development Client SupportDocument29 pagesAssisting Policy Development Client Supportgashu asmareNo ratings yet
- Apply OOPL SkillDocument109 pagesApply OOPL Skillgashu asmareNo ratings yet
- Applay General Work ExamDocument3 pagesApplay General Work Examgashu asmareNo ratings yet
- Contribute To The Development of Strategy ExamDocument4 pagesContribute To The Development of Strategy Examgashu asmareNo ratings yet
- Communication Competence: Competent CommunicatorDocument10 pagesCommunication Competence: Competent CommunicatorSeema HassanNo ratings yet
- Thomas Green: Power, Office Politics, and A Career in Crisis - 2095Document4 pagesThomas Green: Power, Office Politics, and A Career in Crisis - 2095Santu BiswaaNo ratings yet
- TPE 1 Artifact-Case StudyDocument13 pagesTPE 1 Artifact-Case StudyElyse HuescaNo ratings yet
- Coursebook EvaluationDocument32 pagesCoursebook EvaluationVindy Virgine GucciNo ratings yet
- FORMULAIC SPEECH - BukaprezentacjaDocument1 pageFORMULAIC SPEECH - BukaprezentacjasywuwojownikNo ratings yet
- Topic Iii: Human Relations: Effects On ManagementDocument39 pagesTopic Iii: Human Relations: Effects On ManagementDebbie May Ferolino Yelo-QuiandoNo ratings yet
- A Valid Evaluation of The Theory of Multiple Intelligences Is Not Yet PossibleDocument14 pagesA Valid Evaluation of The Theory of Multiple Intelligences Is Not Yet Possiblemikel torresNo ratings yet
- Communicative Approach focuses on language useDocument2 pagesCommunicative Approach focuses on language usevvikiNo ratings yet
- Course Module Educ 1 Week 4 Mrs. GarduqueDocument9 pagesCourse Module Educ 1 Week 4 Mrs. GarduqueRutchelle Pialago PolesticoNo ratings yet
- New Perspectives On Crafts and Health PromotionDocument8 pagesNew Perspectives On Crafts and Health PromotionAnne KirketerpNo ratings yet
- Review Colinizing EgyptDocument20 pagesReview Colinizing EgyptMichelle MatteiNo ratings yet
- Freud, Erickson, Piaget...Document21 pagesFreud, Erickson, Piaget...Kimberly Marie BayangNo ratings yet
- Speeches According To Methods of DeliveryDocument8 pagesSpeeches According To Methods of DeliveryAly SwiftNo ratings yet
- 博士学位-个人陈述 (Ph.D.-My Statement of Purpose)Document4 pages博士学位-个人陈述 (Ph.D.-My Statement of Purpose)Jeffery ChenNo ratings yet
- Behaviorist theories and theorists quizDocument2 pagesBehaviorist theories and theorists quizJoong Seo100% (1)
- Critical and Creative Thinking RelationshipDocument17 pagesCritical and Creative Thinking RelationshipAchmad Zultan MansurNo ratings yet
- Marta Ramírez Martínez Curriculum Vitae Fall 2019: PHD in Hispanic LinguisticsDocument9 pagesMarta Ramírez Martínez Curriculum Vitae Fall 2019: PHD in Hispanic Linguisticsapi-411824229No ratings yet
- Ambiguity: Lexical / SyntacticDocument20 pagesAmbiguity: Lexical / SyntacticIvan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- AnthropologyDocument8 pagesAnthropologyDanah RosalesNo ratings yet
- SIOP TrainingDocument14 pagesSIOP TrainingChris Prout100% (1)
- Foundations of Group BehaviorDocument22 pagesFoundations of Group Behaviorbondad daniel ryanNo ratings yet
- Neurofunctional TheoryDocument3 pagesNeurofunctional TheoryATHENA LOU PEPITONo ratings yet
- Portfolio Ece 260 Picture Book Evaluation FormDocument4 pagesPortfolio Ece 260 Picture Book Evaluation Formapi-548865153No ratings yet
- LANGUAGE SKILLS: SPEAKING, LISTENING, WRITING AND READINGDocument5 pagesLANGUAGE SKILLS: SPEAKING, LISTENING, WRITING AND READINGluis fernando RinconNo ratings yet
- 3rd MONTHLY ASSESSMENT - Trends, NetworkDocument6 pages3rd MONTHLY ASSESSMENT - Trends, NetworkEloisa Jane BituinNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Language Scaffolding Learning - Teaching English Language Learners in The Mainstream Classroom PDFDocument275 pagesScaffolding Language Scaffolding Learning - Teaching English Language Learners in The Mainstream Classroom PDFbursa buku100% (5)
- Impact of Think Aloud Protocol on TVL Learners' Reading ComprehensionDocument12 pagesImpact of Think Aloud Protocol on TVL Learners' Reading ComprehensionLESLIE MAGLALANGNo ratings yet
- Assignment Scaffold Template-1Document4 pagesAssignment Scaffold Template-1Everything FactsNo ratings yet
- Drama Performance Promotes Intercultural CompetenceDocument27 pagesDrama Performance Promotes Intercultural CompetenceMega Devega ArvianyNo ratings yet
- Individual Project Presentation RubricDocument1 pageIndividual Project Presentation RubricJohn Luis Masangkay Bantolino100% (1)