Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mod. 3 - Chemical Formulae
Uploaded by
Nerio Bogoni JrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mod. 3 - Chemical Formulae
Uploaded by
Nerio Bogoni JrCopyright:
Available Formats
Concise Course in Brewing Technology
Supplementary Course Content Information
Date Created: August 23, 2005
Module # # 3
Title of Module Basic Biochemistry
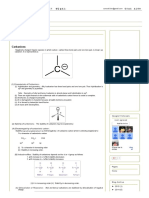
Question: If esters are a combination of an organic alcohol and an organic acid, shouldn't there be an -OH group
in the chemical formula?
Answer: It is difficult to show chemical formulas in a word document but I will try.
R1-CH2OH (an alcohol) joins with R2- COOH (an organic acid – note that one of the oxygen atoms is actually
double bonded to the carbon atom) and they form R1 CH2OOC-R2 plus H2O. The thing to note is that water has
been liberated from the joining of these 2 compounds and hence the –OH group you were referring to is actually in
the water molecule. Pictorially an ester molecule looks like this:
You should also be aware that in biochemical formulas the use of the capital R refers to some side chain of an
organic molecule.
Question: Page 8 of the biochem video shows a protein chain and a blow up of an amino acid. It says to note the
double bond to the -COOH group but shows a single bond.
Answer: Biochemists use simplified ways to talk about molecules. So when you see the combination “–COOH” ,
one of these 2 oxygen atoms is actually double bonded to the carbon. You will just have to accept this way the
biochemists communicate. I know it is tough. The good news is you do not need to know details about molecular
structure to be a good brewer.
Question: Also, how do the A.A's. bond? In the R- group? I'm not seeing the recurring NCC.
Answer: In my lecture I referred to the polymerization of the amino acids as a nitrogen atom joining to the carbon
atom of another amino acid.
This picture is a deeper explanation of how that “saw-tooth” looking chain of a.a.’s is
joined between the nitrogen atoms and the carbon atoms.
Question: Page 22 of the biochemistry module, talks about lipids as saturated and un-saturated. What does this
mean?
Answer: In organic chemistry, saturation refers to an organic compound having the maximum amount of hydrogen
atoms possible: i.e., no double bonds or when every carbon atom in a hydrocarbon chain is attached to two
hydrogen atoms. Another way to state this is that each carbon atom has associated with it only single bonds and all
are occupied by hydrogen atoms.
A saturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there are no double bonds between the carbon atoms of the fatty acid
chain (hence, it is fully saturated with hydrogen atoms).
As per the notes in the module, fatty acids have both positive and negative qualities in brewing. Oxidation of fatty
acids (i.e., the addition of oxygen atoms) can lead to negative flavour qualities in beer. In general in the step after
kettle boiling, we separate flocculated clumps of coagulated protein and polyphenols from the hot wort and in so
doing also remove a lot of fatty acids at the same time. It is considered good brewing practice to make sure that the
clarity of the wort going intro the fermenter is as clear as possible to minimize flavour deterioration.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellDocument14 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellEma FatimahNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of The Pillar College-Cauayan Reina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School Tallungan, Reina Mercedes, IsabelaDocument9 pagesOur Lady of The Pillar College-Cauayan Reina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School Tallungan, Reina Mercedes, IsabelaLena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes: Lecture Notes in Inorganic Chemistry 1 Acids and BasesDocument10 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes: Lecture Notes in Inorganic Chemistry 1 Acids and Basessarah meneseNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To HydrocarbonsDocument56 pages1 - Introduction To HydrocarbonsPaul NderebaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesPhysical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions Manualthoabangt69100% (30)
- Protein FoldingDocument32 pagesProtein Folding9374 DIVYATA PATILNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules, Polymers & PocDocument127 pagesBiomolecules, Polymers & PocDebasish goudaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11Document10 pagesChemistry 11catalystgrowthNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations AnswersDocument1 pageBalancing Chemical Equations AnswersSeema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument10 pagesLab ManualozlemNo ratings yet
- 9701 w09 QP 12Document6 pages9701 w09 QP 12FahmiAlziePutraNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1017 Shapes of Molecules ANSDocument4 pagesChemsheets AS 1017 Shapes of Molecules ANSDecklinNo ratings yet
- 2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisDocument5 pages2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisVenu KavetiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesChapter 14 BiomoleculesJaanvi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Piccs 2012 PDFDocument1,614 pagesPiccs 2012 PDFAnnabelle GuilingNo ratings yet
- Chem Salt PractDocument5 pagesChem Salt PractSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Sal de ZeiseDocument5 pagesSal de ZeiseValeria BelénNo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Chemistry MGDocument22 pages2023 HSC Chemistry MGazizi5916No ratings yet
- 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFDocument4 pages1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFshahbazhu006No ratings yet
- 2007-2016 NSEC QuestionsDocument18 pages2007-2016 NSEC Questionsshravan trialNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its Compound.1Document10 pagesHydrogen and Its Compound.1abhishekNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Document16 pagesSalt Analysis (Answer) (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Carbanion PDFDocument4 pagesChemistry - Carbanion PDFSung-Eun Kim0% (1)
- Trial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Document8 pagesTrial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Chan Yek FungNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument38 pagesInorganic ChemistryAnubhav Sinha100% (1)
- HC DPP Ak 2 PDFDocument6 pagesHC DPP Ak 2 PDFJannaki PvNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A Sudah FinalDocument20 pagesLampiran A Sudah FinalBayu Handika PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Orange IiDocument6 pagesOrange IiDini KartikaNo ratings yet
- Language of Chemistry1Document31 pagesLanguage of Chemistry1Divya MishraNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life (Biomolecules)Document24 pagesThe Chemistry of Life (Biomolecules)Mam Jay MeeNo ratings yet