Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Operators PDF
Uploaded by
Shineii0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views16 pagesComputer operators include arithmetic, relational, and logical operators that allow programmers to perform calculations and make comparisons in code. Arithmetic operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are used for mathematical expressions. Relational operators like greater than, less than, equal to are used to compare values. Logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT are used to connect conditional expressions. Operator precedence specifies the order that operators are evaluated.
Original Description:
Original Title
Computer Operators. pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComputer operators include arithmetic, relational, and logical operators that allow programmers to perform calculations and make comparisons in code. Arithmetic operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are used for mathematical expressions. Relational operators like greater than, less than, equal to are used to compare values. Logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT are used to connect conditional expressions. Operator precedence specifies the order that operators are evaluated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views16 pagesComputer Operators PDF
Uploaded by
ShineiiComputer operators include arithmetic, relational, and logical operators that allow programmers to perform calculations and make comparisons in code. Arithmetic operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are used for mathematical expressions. Relational operators like greater than, less than, equal to are used to compare values. Logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT are used to connect conditional expressions. Operator precedence specifies the order that operators are evaluated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Computer Operators
Arithmetic, Relational, & Logical Operators
Computer Operators:Processing data
For the programmer to instruct computers to
process mathematical computations and logical
operations, they would have to use symbols that
computer can understand.
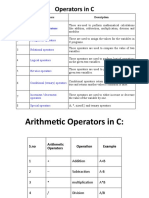
Computer Operators: Arithmetic
Arithmetic operators include operations such
as addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division, and modulo
Operation Symbol Example Explanation
Multiplication * A*B Multiply the value of Variable A to the value of
variable B
Division / X/Y Divide the value of variable X by the value of
variable Y
Addition + int1 + int2 Add the value of variable int1 to the value of variable
int2
Subtraction - A–B Subtract the value of Variable B to the value of
variable A
Modulo % num1 % num2 Returns the remainder of dividing the value of
variable num1 by the value of variable num2
Exponentiation ^ C^2 Multiply the value of variable C twice
examples
Mathematical Expression Computer Expression
• 3xy •3*x*y
• (x * x) + (y * y)
• X2 + y2
• X ^2 + y^2
• (3 * x) / (y*y*y)
• 3x/y3
• (3*x) / (y^3)
Computer Operators: Relational
a relational operator is used to test the
relation between two entities.
Operation Symbol Example Explanation
Greater than > A>B the value of Variable A is
greater than the value of
variable B
Less than < X<Y the value of variable X is less
than the value of variable Y
Equal to == int1 == int2 the value of variable int1 is
equal to the value of variable
int2
Not equal to != or <> net != gross the value of Variable net is not
equal to the value of variable
gross
Operation Symbol Example Explanation
Greater than >= pay1 >= pay2 the value of Variable pay1 is
or equal to greater than or equal to the
value of variable pay2
Less than <= age1 <= age2 the value of variable age1 is less
or equal to than or equal to the value of
variable age2
Assignment = X=5 assigns the value of its right-
operator hand operand to a variable x
a logical operator is a symbol or word used to
connect two or more expressions
such that the value of the compound expression
produced depends only on that of the original
expressions and on the meaning of the operator
Symbols Meaning explanation
&& AND both conditions should be TRUE
before the resulting data could be
TRUE, otherwise the resulting data will
be FALSE
|| OR if either of the two value is True
then the resulting data is True
otherwise, the resulting values is
FALSE
! NOT the other hand reverses the
value of the given
statement, a True will become
False and vice versa.
AND
both conditions should be
TRUE && TRUE TRUE
TRUE before the resulting
data could be TRUE
TRUE && FASLE FALSE
otherwise the resulting data
FALSE && TRUE FALSE
will be FALSE
FALSE && FALSE FALSE
OR
if either of the two value is
TRUE || TRUE TRUE
True then the resulting data is
True otherwise,
TRUE || FASLE TRUE
the resulting values is FALSE
FALSE || TRUE TRUE
FALSE || FALSE FALSE
the other hand reverses the
value of the given NOT
statement, ! TRUE FALSE
a True will become False and ! FALSE TRUE
vice versa.
Order of Operation
Operator precedence specifies the order of
how operators are evaluated and performed
one after the other
X= 10 – 2 + 3 * (6 % 2)
X= 10 – 2 + 3 * (6 % 2)
X= 10 – 2 + 3 * 0
X= 10 – 2 + 3 * 0
X= 10 – 2 + 0
X= 10 – 2 + 0
X= 8 + 0
X= 8 + 0
X= 8
You might also like
- Day 2Document42 pagesDay 2khitcsec3No ratings yet
- 04 C OperatorsDocument12 pages04 C OperatorsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit III PDFDocument38 pagesUnit III PDFValentina JustinNo ratings yet
- C Plus Plus Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesC Plus Plus Cheat SheetAjay Chander R0% (1)
- C Programming Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesC Programming Cheat SheetAjay Chander R100% (1)
- Unit 3 (A)Document89 pagesUnit 3 (A)Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- 02 C++ OperatorsDocument15 pages02 C++ OperatorsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- DaminiDocument27 pagesDaminikiranjeet6283No ratings yet
- Robotics Training LNCHS 4Document18 pagesRobotics Training LNCHS 4Dan Jenniel CedeñoNo ratings yet
- ECE321 LEC PART5 - Control Structure - SelectionDocument19 pagesECE321 LEC PART5 - Control Structure - SelectionMohammed Mohsen Tadulan TawfiqNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Name: Prerna S. Mhatre Class: Sy - Bsc.ItDocument13 pagesDatabase Management System: Name: Prerna S. Mhatre Class: Sy - Bsc.ItPrerna Sanjivan MhatreNo ratings yet
- Basics of C Language - AdvancedDocument53 pagesBasics of C Language - AdvancedAugustine VineethNo ratings yet
- OperatorsDocument24 pagesOperatorsgopi chand mallelaNo ratings yet
- SQL 2Document11 pagesSQL 2Tiger KNo ratings yet
- JavaScript Day 1.pptx - 2Document35 pagesJavaScript Day 1.pptx - 2Aliaa TarekNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Revision of Basics of PythonDocument22 pagesCh01 Revision of Basics of PythonJaganNo ratings yet
- Operators in C: S.no Types of Operators DescriptionDocument23 pagesOperators in C: S.no Types of Operators Descriptiontemp SINGHNo ratings yet
- C Programming - Expressions TypesDocument6 pagesC Programming - Expressions TypesJazz VirakNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE BASICS Part 2Document5 pagesPROGRAMMING LANGUAGE BASICS Part 2Jay GaleNo ratings yet
- Various Data Types Available in Python.?Document5 pagesVarious Data Types Available in Python.?P.T.Lee CNCETNo ratings yet
- Operators in CDocument14 pagesOperators in Cabhiskarpokhrel999No ratings yet
- Programming 100927153217 Phpapp02Document33 pagesProgramming 100927153217 Phpapp02nanangsusetyoNo ratings yet
- Operators & ExpressionsDocument39 pagesOperators & ExpressionsPaksham Mahajan100% (1)
- Learning Scaffold Guided Practice 2Document4 pagesLearning Scaffold Guided Practice 2Abegail AmpongNo ratings yet
- 1 - Variable ConstantDocument19 pages1 - Variable ConstantMo SaNo ratings yet
- Learning Scaffold Guided Practice 1Document4 pagesLearning Scaffold Guided Practice 1Abegail AmpongNo ratings yet
- ch03 ExpressionsDocument36 pagesch03 ExpressionsVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document14 pagesLab 3Ibrahim KhanNo ratings yet
- Programming Lesson by SlidesgoDocument204 pagesProgramming Lesson by Slidesgogashaw mekonnenNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Operators in C ProgrammingDocument49 pagesLecture Notes Operators in C ProgrammingSandra LymoNo ratings yet
- Fortran95 LecturesDocument30 pagesFortran95 LecturesMd Alamin HaqueNo ratings yet
- PHP Data TypesDocument7 pagesPHP Data TypesnyaoroskitchenNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - HandoutsDocument30 pagesWeek 5 - HandoutsMaydelyn Joy LaudatoNo ratings yet
- Programming in C EssayDocument42 pagesProgramming in C EssayPRANAV CNo ratings yet
- Operators and Decision MakingDocument8 pagesOperators and Decision MakingShahid MandokhailNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic Operators1Document22 pages02 Basic Operators1the killerboyNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument24 pagesDecision MakingranaateeqNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesPython Cheat SheetShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Arduino - Basic ProgrammingDocument47 pagesArduino - Basic ProgrammingManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- Python UNIT-2Document43 pagesPython UNIT-2PrashanthNo ratings yet
- OperatorsDocument15 pagesOperatorsVraj Shah100% (1)
- Week 3Document6 pagesWeek 3Kaito KiddNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledAaron DumpNo ratings yet
- Programming Concepts Using C Language Subject Code: TBC 101 Unit-Ii Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA)Document20 pagesProgramming Concepts Using C Language Subject Code: TBC 101 Unit-Ii Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA)Gaurav boraNo ratings yet
- (C++) Lec 2 Basic Elements of C++Document38 pages(C++) Lec 2 Basic Elements of C++Ibrahim Elmorsy Maintenance - 3397No ratings yet
- Week4 CombineDocument80 pagesWeek4 CombineraleyNo ratings yet
- Operators and HierarchyDocument39 pagesOperators and Hierarchypco000No ratings yet
- Operators in C LanguageDocument41 pagesOperators in C LanguageTathagat TripathyNo ratings yet
- PL/SQLDocument66 pagesPL/SQLMahesh IndlaNo ratings yet
- 03 C Part3Document32 pages03 C Part3zam T MudaNo ratings yet
- Python 2 - Basic OperatorsDocument105 pagesPython 2 - Basic OperatorsAlassan saineNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 - Lecture5 - Arithmetic Expressions and Data ConversionDocument27 pagesCh. 2 - Lecture5 - Arithmetic Expressions and Data Conversionelio salibaNo ratings yet
- Each Operator in C Has A Precedence Level Related To It, Which Determines How An Expression Involving More Than One Operator Is EvaluatedDocument9 pagesEach Operator in C Has A Precedence Level Related To It, Which Determines How An Expression Involving More Than One Operator Is EvaluatedSushant PathakNo ratings yet
- PLSQPDocument84 pagesPLSQPMahesh IndlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document20 pagesLecture 7Muneeb AshrafNo ratings yet
- PythonmaterialtkgDocument30 pagesPythonmaterialtkgJana SNo ratings yet
- UNIT5 - PLSQL Introduction 1Document110 pagesUNIT5 - PLSQL Introduction 1Anish KumarNo ratings yet
- Operators in JavaDocument10 pagesOperators in JavaVani MittalNo ratings yet
- Intro To Python ProgrammingDocument4 pagesIntro To Python Programmingyahia farouqNo ratings yet
- Master Syllabus Fix TOM-JAN2019-BOED PDFDocument4 pagesMaster Syllabus Fix TOM-JAN2019-BOED PDFBogiNo ratings yet
- Ev 3 Solar StationDocument52 pagesEv 3 Solar Stationavira0002No ratings yet
- Why Slabs Curl - Part1Document6 pagesWhy Slabs Curl - Part1Tim LinNo ratings yet
- New Maths Frameworking: Matches The Revised KS3 FrameworkDocument232 pagesNew Maths Frameworking: Matches The Revised KS3 FrameworkMerihane Naguib100% (2)
- Sketched Symbol Recognition Using Zernike MomentsDocument11 pagesSketched Symbol Recognition Using Zernike MomentsmailforspamNo ratings yet
- The Machine Stops - The New YorkerDocument8 pagesThe Machine Stops - The New YorkermalvinaNo ratings yet
- FCOE Directory 2015-16Document196 pagesFCOE Directory 2015-16Cheryl WestNo ratings yet
- r121 Auto Cash App ErdDocument2 pagesr121 Auto Cash App ErdLam TranNo ratings yet
- Third-Party LogisticsDocument16 pagesThird-Party Logisticsdeepshetty100% (1)
- SwatiDocument23 pagesSwatiShashankNo ratings yet
- 03 Task Performance 1 - ARG - MMW - RelevoDocument4 pages03 Task Performance 1 - ARG - MMW - Relevocessarine relevoNo ratings yet
- Glor - Io Wall HackDocument889 pagesGlor - Io Wall HackAnonymous z3tLNO0TqH50% (8)
- Reflection Week 3 - The Sensible ThingDocument3 pagesReflection Week 3 - The Sensible Thingtho truongNo ratings yet
- VT 300dDocument3 pagesVT 300dAndrei IulianNo ratings yet
- 07 Test ADocument24 pages07 Test ARashmin ShetNo ratings yet
- 7 ODE 2nd Order v2Document3 pages7 ODE 2nd Order v2Agung GuskaNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1 - Problem SolvingDocument3 pagesWorkshop 1 - Problem SolvingADRIANA CATHERIN AGUILAR LEMUSNo ratings yet
- Anam CVDocument2 pagesAnam CVAnam AslamNo ratings yet
- Data ModelingDocument98 pagesData ModelingparthascNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFDocument6 pagesSolutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFMichael Christian BaysauliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three SpeechDocument12 pagesChapter Three SpeechAlex GetachewNo ratings yet
- Flexible Vision Software SetupDocument12 pagesFlexible Vision Software SetupAnonymous 1vMe99XL7INo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 2Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 2Ûdây RäjpütNo ratings yet
- Bcpp6e TB Ch01Document32 pagesBcpp6e TB Ch01tnguyen194No ratings yet
- X16 42552VS2010UltimTrial1Document2 pagesX16 42552VS2010UltimTrial1An LcNo ratings yet
- MusixtexDocument121 pagesMusixtexmoretaleNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics ExcerptDocument49 pagesMasteringPhysics ExcerptFrancy Anne RiccioNo ratings yet
- American Association For Medical Transcription 100 Sycamore Avenue, Modesto, CA 95354-0550 - 800-982-2182Document5 pagesAmerican Association For Medical Transcription 100 Sycamore Avenue, Modesto, CA 95354-0550 - 800-982-2182JijoNo ratings yet
- #4 Nov.7-11, 2016 DLLDocument3 pages#4 Nov.7-11, 2016 DLLRoselyn MyerNo ratings yet
- Bridge Embankment FailuresDocument13 pagesBridge Embankment Failuresirmreza68No ratings yet