Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 Summary
Uploaded by
Vy Bui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesChap 7 Intro BA
Original Title
Chapter 7 summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChap 7 Intro BA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesChapter 7 Summary
Uploaded by
Vy BuiChap 7 Intro BA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Describe the changes occurring today in the management function.
+ What does management look like today?
At one time, managers were called bosses, and their job consisted of tell-
ing people what to do, watching over them to be sure they did it, and rep-
rimanding those who didn’t. Many, if not most, managers still behave that
way. Today, however, some managers tend to be more progressive. For
example, they emphasize teams and team building; they create drop-in
centers, team spaces, and open work areas. They tend to guide, train, sup-
port, motivate, and coach employees rather than tell them what to do,
+ What reasons can you give to account for changes in management?
Leaders of Fortune 100 companies today tend to be younger, more of them
are female, and fewer of them were educated at elite universities. They
know that many of their employees know more about technology and
other practices than they do. Therefore, they tend to put more emphasis
on motivation, teamwork, and cooperation. Managers in the future are
likely to be assuming completely new roles in the firm. For one thing, they
will be taking a leadership role in adapting to climate change. Further,
they'll be doing more expansion overseas.
Gz Describe the four functions of management.
+ What are the primary functions of management?
The four primary functions are (1) planning, (2) organizing, (3) leading,
and (4) controlling.
+ How do you define each of these functions?
Planning includes anticipating trends and determining the best strategies
and tactics to achieve organizational goals and objectives. Organizing includes
designing the structure of the organization and creating conditions and
systems in which everyone and everything works together to achieve the
organization's goals and objectives. Leading means creating a vision for the
organization, and communicating, guiding, training, coaching, and moti-
vating others to achieve goals and objectives. Controlling means measuring
whether what actually occurs meets the organization's goals.
EGR ites te ering process and decision making tothe accomplishment of
‘company goals.
+ What's the difference between goals and objectives?
Goals are broad, long-term achievements that organizations aim to accom-
plish, whereas objectives are specific, short-term plans made to help reach
the goals.
+ What is a SWOT analysis?
Managers look at the strengths and weaknesses of the firm and the oppor-
tunities and threats facing it
+ What are the four types of planning, and how are they related to the orgat
zation’s goals and objectives?
‘rategic planning is broad, long-range planning that outlines the goals of
the organization, Tactical planning is specific, short-term planning that lists
organizational objectives. Operational planning is part of tactical planning
and sets specific timetables and standards. Contingency planning is developing
an alternative set of plans in case the first set doesn't work out.
203
204
PART2 Business Management: Empowering Employees to Satty Cust
+ What are the steps involved in decision making?
The six Ds of decision making are (1) define the situation; (2) describe
and collect needed information; (3) develop alternatives; (4) decide
which alternative is best; (5) do what is indicated (begin implementa-
tion); and (6) determine whether the decision was a good one, and fol-
low up
Describe the organizing function of management.
+ What are the three levels of management in the corporate hierarchy?
The three levels of management are (1) top management (highest level
consisting of the president and other key company executives who develop
strategic plans); (2) middle management (general managers, division man.
agers, and plant managers who are responsible for tactical planning and
controlling); and (3) supervisory management (first-line managers!
supervisors who evaluate workers’ daily performance),
+ What skills do managers need?
Managers must have three categories of skills: (1) technical skills (ability
to perform specific tasks such as selling products or developing software),
(2) human relations skills (ability to communicate and motivate), and (3)
conceptual skills (ability to see organizations as a whole and how all the
parts fit together).
+ Are these skills equally important at all management levels?
Managers at different levels need different skills. Top managers rely heav-
ily on human relations and conceptual skills and rarely use technical skills,
while first-line supervisors need strong technical and human relations
skills but use conceptual skills less often, Middle managers need to have a
balance of all three skills (see Figure 7.5).
Gz Explain the differences between
various leadership styles.
+ What's the difference between a manager and a leader?
A manager plans, organizes, and controls functions within an organiza-
tion. A leader has vision and inspires others to grasp that vision, estab-
lishes corporate values, emphasizes corporate ethics, and doesn't fear
change.
+ Describe the various leadership styles.
Figure 7.6 shows a continuum of leadership styles ranging from boss-
cemtere:
+ Which leadership style is best?
The most effective leadership style depends on the people being led and the
situation, The challenge of the future will be to empower self-managed teams.
+ What does empowerment mean?
Empowerment means giving employees the authority and responsibility
to respond quickly to customer requests. Enabling is giving workers the
education and tools they need to assume their new decision-making
powers.
+ What is knowledge management?
Knowledge management is finding the right information, keeping the
information in a readily accessible place, and making the information
known to everyone in the firm,
Management endLeadership CHAPTER
‘Summarize the five steps ofthe control function of management.
+ What are the five steps of the control function?
Controlling incorporates (1) setting clear standards, (2) monitoring and
recording performance, (3) comparing performance with plans and stan-
dards, (4) communicating results and deviations to employees, and (5)
providing positive feedback for a job well done and taking corrective
action if necessary.
+ What qualities must standards possess to measure performance results?
Standards must be specific, attainable, and measurable.
205
autocratic leadership 137
brainstorming 192
conceptual skills 194
contingency
planning 191
controlling 188
decision making 192
‘enabling 199
‘external customers 202
free-rein leadership 198
goals 189
human relations
skills 194
internal customers 202
knowledge
management 199
leading 188
‘management 187
middle management 194
mission statement 189
objectives 189
‘operational planning 190
‘organizing 188
participative (democratic)
leadership 198
planning 188
PMI 192
problem solving 132
staffing 195
strategic planning “90
sy
management 194
‘wot
analysis 189
tactical planning 190
technical skills 194
‘top management 193
transparency 196
vision 189
‘Many students say they would like to be a manager someday, Here are some
‘questions to get you started thinking like a manager:
1, Would you like to work for a large firm or a small business? Private or
public? In an office or out in the field? Give your reasons for each answer.
2. What kind of leader would you be? Do you have evidence to show that?
3. Do you see any problems with a participative (democratic) leadership style?
Can you see a manager getting frustrated when he or she can' control others?
4, Can someone who's trained to give orders (like a military sergeant) be
retrained to be a participative leader? How? What problems may emerge?
Key: © Team 4 Analytic A Communication @ Technology
1, Allocate time to do some career planning with a SWOT analysis of your A.
present situation. Choose one career you are interested in and answer the
following questions: What does the marketplace for your chosen carcer
developing workplace skills
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 9 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 9 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 5 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 8 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Education IdeasDocument4 pagesEducation IdeasVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 P1Document24 pagesLecture03 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 P1Document29 pagesLecture02 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
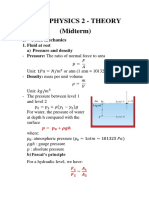
- Note Physics 2 - Theory (Midterm) : I. Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesNote Physics 2 - Theory (Midterm) : I. Fluid MechanicsVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 P1Document25 pagesLecture01 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet