Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Summary
Uploaded by
Vy Bui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesChap 8 Intro BA
Original Title
Chapter 8 summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChap 8 Intro BA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesChapter 8 Summary
Uploaded by
Vy BuiChap 8 Intro BA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
‘Sructurng Orgenttations for Todays Challenges CHAPTER'S 233
The informal
organization is the
‘system that develops as
employees meet and
form relationships. The
‘grapevine, the unofficial
flow of information
among employees, is
the nerve center of the
informal organization.
How does the informal
organization affect the
ret eneremet
As effective as the informal organization may be in creating group coop-
eration, it can still be equally powerful in resisting management directives.
Employees may form unions, go on strike together, and generally disrupt
operations. Learning to create the right corporate culture and work within the
informal organization is thus a key to managerial success.”*
eum.
+ What is an inverted organization?
+ Why do organizations outsource functions?
+ What is organizational culture?
‘atin the basi pines of organization management.
+ What is happening today to American businesses?
They are adjusting to changing markets. That is a normal function in a
capitalist economy. There will be big winners, like Google and Facebook,
and big losers as well. The key to success is remaining flexible and adapt-
ing to the changing times.
+ What are the principles of organization management?
Structuring an organization means devising a division of labor (some-
times resulting in specialization), setting up teams or departments, and
assigning responsibility and authority. It includes allocating resources
(such as funds), assigning specific tasks, and establishing procedures for
accomplishing the organizational objectives. Managers also have to make
ethical decisions about how to treat workers.
234
PARTS Business Management Empowering Employee to Setisty Customers
Cr ‘Compare the organizational theories of Fayol and Weber.
+ What were Fayo!'s basic principles?
Fayol introduced principles such as unity of command, hierarchy of
authority, division of labor, subordination of individual interests to the gen-
eral interest, authority, clear communication channels, order, and equity.
+ What principles did Weber add?
Weber added principles of bureaucracy such as job descriptions, written
rules and decision guidelines, consistent procedures, and staffing and pro.
motions based on qualifications.
PRED Evaluate the choices managers make in structuring organizations.
+ What are the four major choices in structuring organizations?
Choices to make in structuring and restructuring organizations cover (1)
centralization versus decentralization, (2) breadth of span of control, (3) tall
versus flat organization structures, and (4) type of departmentalization.
+ What are the latest trends in structuring?
Departments are often replaced or supplemented by matrix organizations
and cross-functional teams that decentralize authority, The span of con-
trol becomes larger as employees become self-directed. Another trend is to
eliminate managers and flatten organizations.
ce Contrast thé
+ What are the two major organizational models?
‘wo traditional forms of organization are (1) line organizations and
(2) line-and-staff organizations. A line organization has clearly defined
responsibility and authority, is easy to understand, and provides each
worker with only one supervisor. The expert advice of staff assistants in a
line-and-staff organization helps in areas such as safety, quality control,
computer technology, human resource management, and investing.
+ What are the key alternatives to the major organizational models?
Matrix organizations assign people to projects temporarily and encour-
age interorganizational cooperation and teamwork. Cross-functional
self-managed teams have all the benefits of the matrix style and are long
term,
various organizational model
EERD eertitytne benetits of ntertirm cooperation and coordination
+ What are the major concepts involved in interfirm communications?
Networking uses communications technology and other means to link
organizations and allow them to work together on common objectives.
A virtual corporation is a networked organization of replaceable firms that
join and leave as needed. Benchmarking tells firms how their performance
measures up to that of their competitors in specific functions. The com-
pany may then outsource to companies that perform its weaker functions
more effectively and efficiently. The functions that are left are the firm's
core competencies
+ What is an inverted organization?
An inverted organization places employees at the top of the hierarchy;
managers are at the bottom to train and assist employees.
‘Structuring Organizations or Today's Ch
curren 235
CEE Soe or opinion ctr canta bnenes aap are
+ What is organizational culture?
Organizational (or corporate) culture consists of the widely shared values
within an organization that foster unity and cooperation to achieve com-
mon goals.
+ Whatis the difference between the formal and informal organization of a firm?
The formal organization details lines of responsibility, authority, and po
tion. It’s the structure shown on organization charts. The informal organi
zation is the system that develops spontaneously as employees meet and
form cliques, relationships, and lines of authority outside the formal orga-
nization. It’s the human side of the organization. The informal organiza-
tion is an invaluable managerial asset that often promotes harmony among
workers and establishes the corporate culture. As effective as the informal
organization may be in creating group cooperation, it can still be equally
powerful in resisting management directives.
err
benchmarking 228 economies of scale 214 networking 226
bureaucracy 217 flat organization organization (or
centralized authority 218 structure 219 corporate) culture 231
chain of command 26 formal organization 232 organizational
core competencies 229 hierarchy 2'6 chart 216
cross-functional self- Informal organization 232 real time 227
managed teams 226 inverted restructuring 230
decentralized ‘organization 230 span of control 219
‘authority 218 line organization 223 _staff personnel 223
departmentalization 220 line personnel 223, tall organization
digital natives 229 matrix organization 224 structure 219
virtual corporation 227
Now that you have learned some of the basic principles of organization, pause
and think about where you have already applied such concepts yourself or
when you have been part of an organization that did.
1. Did you find a division of labor necessary and helpful?
2. Were you assigned specific tasks or left on your own to decide what to do?
3. Were promotions based strictly on qualifications, as Weber suggested?
What other factors may have been considered?
4, What problems seem to emerge when an organization gets larger?
5. What organizational changes might you recommend to the auto compa-
nies? The airline industry?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 9 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 9 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 5 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 7 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 SummaryVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Education IdeasDocument4 pagesEducation IdeasVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 P1Document24 pagesLecture03 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 P1Document29 pagesLecture02 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
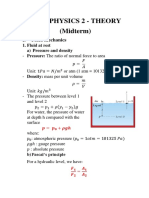
- Note Physics 2 - Theory (Midterm) : I. Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesNote Physics 2 - Theory (Midterm) : I. Fluid MechanicsVy BuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 P1Document25 pagesLecture01 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet