Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkCopyright:
Available Formats
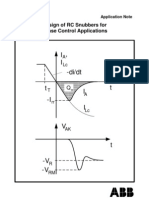
angles are also of interest.
First the overlap angle for α = 00 and when the delay angle just
permits the overlap to be over before the commutating voltage reaches 1800. The peak of ISC
occurs at this instant. This angle plus the time period required by the SCRs to complete their
turn-off process (refer: turn-off dynamics of SCR) is called the Margin Angle. Assuming zero
turn-off time,
μ m arg in − angle = − cos −1 (− 58.21 73.21) + 180 0
= 37.330
I SC 0 = 73.21sin( 2.π .50 − 90) + 73.21
0
μ 0 = cos −1 (58.21 73.21) + cos −1 (− 73.21 73.21)
0
= 37.33 0
The two angles are numerically equal as is evident from Fig. Example 20.1.
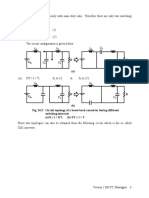
20.4 Three-phase converters
In a three phase six-pulse converter, the notches in the line voltage waveform are as shown in Fig
20.4. The triggering angle is α = 00 for the case illustrated. There are six notches per cycle.
While two of the notches reach down to zero volts, the four other have different magnitudes.
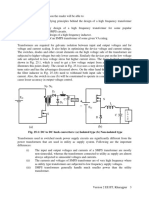
The three-phase converter, Fig. 20.1, has three inductances LS, each in series with each of
the three phases. They are the leakage inductances of the transformer, which may supply other
equipment of the plant too.
Fig. 20.4
The overlap time is dependent on the load current existing during the commutation period and
also the voltage behind the short circuit current. This commutating voltage magnitude is dictated
by the trigger angle. Thus for α = 00 this voltage is minimum. At α = 1800 too it would have
been very low if successful commutation had been possible. However, without any allowance for
an overlap time, the SCR current would just start to fall before it rises again. Note at α = 1800 the
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 7
You might also like
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document12 pagesL-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Venkatesh KarriNo ratings yet
- Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-II: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument11 pagesCommutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-II: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Thyristor PDFDocument10 pagesThyristor PDFMihir HembramNo ratings yet
- AN1003 Teccor ThyristorsDocument9 pagesAN1003 Teccor ThyristorsmtcquigNo ratings yet
- Phase Control Using SCR SDocument8 pagesPhase Control Using SCR StekellamerZ aka tekellamerNo ratings yet
- 5SYA 2020-02 Feb 08 Design of RC-CircuitsDocument14 pages5SYA 2020-02 Feb 08 Design of RC-Circuitsleo232No ratings yet
- BK 31212217Document6 pagesBK 31212217IJMERNo ratings yet
- IEC Exam 2023Document15 pagesIEC Exam 2023Phyo KoNo ratings yet
- By J. R. HILL, B.Sc. (Eng.), A. HUNT, B.Sc. (Eng.), W. J. JOYCE, B.SC, and D. H. TOMPSETT, B.Sc. (Eng-), Associate MembersDocument11 pagesBy J. R. HILL, B.Sc. (Eng.), A. HUNT, B.Sc. (Eng.), W. J. JOYCE, B.SC, and D. H. TOMPSETT, B.Sc. (Eng-), Associate MembersOgar OjugboNo ratings yet
- SFC Upgrade Modification For GT FensDocument3 pagesSFC Upgrade Modification For GT FensNima MoaddeliNo ratings yet
- SCR PDFDocument4 pagesSCR PDFKottamalai KaruppanNo ratings yet
- Switching Characteristics of ThyristorsDocument6 pagesSwitching Characteristics of ThyristorsPraveen Kumar NalliNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent - Relay Setting 3Document17 pagesOvercurrent - Relay Setting 3Shrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Thyristor CommutationsDocument41 pagesThyristor CommutationsRohan Bose100% (1)
- Unit-I 2Document22 pagesUnit-I 2Federico AldoNo ratings yet
- Cro Bar CalculationDocument2 pagesCro Bar CalculationRamakrishnan AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- Static Var CompensatorDocument23 pagesStatic Var CompensatorsetyawanNo ratings yet
- SCR ShareDocument5 pagesSCR ShareAsif HossainNo ratings yet
- Carga Inductiva Con TriacDocument11 pagesCarga Inductiva Con Triacanon_274509247No ratings yet
- Thyristor Commutation TechniquesDocument3 pagesThyristor Commutation Techniquesตะวันแดงปากน้ำโพNo ratings yet
- 2001jun15 Amd An2015Document8 pages2001jun15 Amd An2015Saurabh BhiseNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (18ELN14/18ELN24) - Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Module 2)Document5 pagesBasic Electronics (18ELN14/18ELN24) - Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Module 2)Shrishail BhatNo ratings yet
- Delayed Current Zeros Due To Out-Of-Phase SynchronizingDocument10 pagesDelayed Current Zeros Due To Out-Of-Phase SynchronizingRui TimóteoNo ratings yet
- L-4 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 6Document5 pagesL-4 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 6GagneNo ratings yet
- TEE3211 DrivesDocument126 pagesTEE3211 DrivesWebster Fungirai100% (1)
- Resonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperDocument5 pagesResonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperMukesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- (A) Time Graded (B) Current Graded (C) Combination of Time Graded and Current Graded SystemDocument31 pages(A) Time Graded (B) Current Graded (C) Combination of Time Graded and Current Graded SystemAnuja TipareNo ratings yet
- Static Var CompensatorDocument29 pagesStatic Var CompensatorCarlos Fabian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERDocument14 pagesAc Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERAAYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- SCR Half-Wave Rectifier ContDocument2 pagesSCR Half-Wave Rectifier ContArulBalaNo ratings yet
- FilterDocument8 pagesFilterVivek SanadhyaNo ratings yet
- Gate OscilatorDocument4 pagesGate OscilatorfjlpNo ratings yet
- SCR Switching Characteristics OR Dynamic CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesSCR Switching Characteristics OR Dynamic CharacteristicsVeeravasantharao BattulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRDocument2 pagesAssignment 2-3 For Industrial Electronics SCRPranjal GaurNo ratings yet
- Mitigation of The Transient Recovery Voltage On Generator Circuit Breaker During Generator Fed FaultsDocument4 pagesMitigation of The Transient Recovery Voltage On Generator Circuit Breaker During Generator Fed FaultsryreddyNo ratings yet
- U5 l35 Thyristor Commutation TechniquesDocument3 pagesU5 l35 Thyristor Commutation TechniqueskaushalNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Design of A Reversible Soft-Starter For An Induction Motor: Session 2533Document13 pagesDesign of A Reversible Soft-Starter For An Induction Motor: Session 2533Ersi AgoNo ratings yet
- SCR Power Control CircuitDocument8 pagesSCR Power Control CircuitRyan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- P. C. Sen - Principles of Electric Machines 2edDocument634 pagesP. C. Sen - Principles of Electric Machines 2edwilliancsm100% (1)
- Epc Module-5 (B) ThyristorsDocument16 pagesEpc Module-5 (B) Thyristorskaranphutane2254No ratings yet
- Impulse GeneratorDocument10 pagesImpulse GeneratorUdaya PushpakumaraNo ratings yet
- ThristerDocument63 pagesThristerPitchandi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- A Pulse TransformerDocument12 pagesA Pulse TransformerPooja Uchagaonkar100% (2)
- Ntrol Induction Motors by AC Voltage Controllers: N Nmo R o L LDocument10 pagesNtrol Induction Motors by AC Voltage Controllers: N Nmo R o L Lbond jamesNo ratings yet
- Experiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioDocument2 pagesExperiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioAnonymous ptCa270Uy2No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Selecting Trigger Circuits For Thyristors: Basic RequirementsDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Selecting Trigger Circuits For Thyristors: Basic RequirementsEngr Armghan ZafarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (B) Thyristor Commutation TechniquesDocument42 pagesModule 2 (B) Thyristor Commutation TechniquesK N DEEPSHINo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Question Model 1Document5 pagesPower Electronics Question Model 1sagarNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Power SourceDocument1 pageSingle Phase Power Sourceippon_osotoNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 2 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page2 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 1 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page1 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 1 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page1 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 2 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page2 L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet