Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCERT Lab Manual - Verifying (A+b+c) 2
Uploaded by
Pranav Reddy SathiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Lab Manual - Verifying (A+b+c) 2
Uploaded by
Pranav Reddy SathiCopyright:
Available Formats
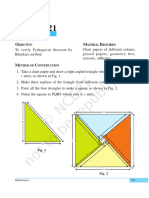
Activity 6
OBJECTIVE MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity : Hardboard, adhesive, coloured
papers, white paper.
(a+b+c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Take a hardboard of a convenient size and paste a white paper on it.
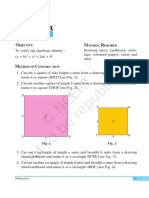
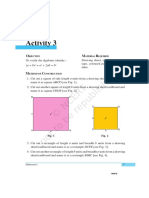
2. Cut out a square of side a units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 1].
3. Cut out a square of side b units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 2].
4. Cut out a square of side c units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 3].
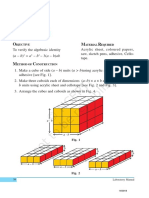
5. Cut out two rectangles of dimensions a× b, two rectangles of dimensions
b × c and two rectangles of dimensions c × a square units from a coloured
paper [see Fig. 4].
Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Mathematics 25
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 25 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
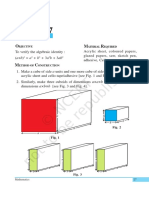
6. Arrange the squares and rectangles on
the hardboard as shown in Fig. 5.
DEMONSTRATION
From the arrangement of squares and
rectangles in Fig. 5, a square ABCD is
obtained whose side is (a+b+c) units.
Area of square ABCD = (a+b+c)2 .
Therefore, (a+b+c) 2 = sum of all the
squares and rectangles shown in Fig. 1 to
Fig. 4. Fig. 5
= a2 + ab + ac + ab + b2 + bc + ac + bc + c2
= a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............., c = ..............,
So, a2 = .............., b2 = .............., c2= .............., ab= ..............,
bc= .............., ca = .............., 2ab = .............., 2bc = ..............,
2ca= .............., a+b+c = .............., (a+b+c)2 = ..............,
Therefore, (a+b+c)2 = a2 + b2 +c2 +2ab + 2bc + 2ca
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. simiplification/factorisation of algebraic expressions
2. calculating the square of a number expressed as a sum of three convenient
numbers.
26 Laboratory Manual
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 26 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
You might also like
- Birthday Baseball Parabola PDFDocument2 pagesBirthday Baseball Parabola PDFjessicarrudolph80% (5)
- MathsDocument6 pagesMathsHema sripriyaNo ratings yet
- Activity 6: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument2 pagesActivity 6: Bjective Aterial EquiredMalati MauryaNo ratings yet
- Activities 6Document2 pagesActivities 6Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- OISDJFIOJWEFDocument3 pagesOISDJFIOJWEFPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activities Class 9Document22 pagesLab Activities Class 9vidya jayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Activities 5Document3 pagesActivities 5Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument3 pagesActivity 3: Bjective Aterial EquiredMalati MauryaNo ratings yet
- Lelm 403Document33 pagesLelm 403yutika1803No ratings yet
- Activity 1: Objective Material RequiredDocument3 pagesActivity 1: Objective Material Requirednd hrdNo ratings yet
- Lelm 402Document22 pagesLelm 402For JunkNo ratings yet
- Activities 8Document3 pagesActivities 8Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- SMK ST Michael, Penampang: Examinations 3 2008Document16 pagesSMK ST Michael, Penampang: Examinations 3 2008tinamicNo ratings yet
- Activities 4Document2 pagesActivities 4lolmao12No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMohamed AnsaryNo ratings yet
- Maths Activity Class 3 8 Part3Document49 pagesMaths Activity Class 3 8 Part3jaya_sassiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Activity 1 To 10 in EnglishDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Activity 1 To 10 in EnglishManya ElhanceNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 p2 RevisionDocument6 pagesGrade 10 p2 RevisionShivaranjali VirasamiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Projects Manual - Class 9-10 - Module 3Document33 pagesCBSE Maths Projects Manual - Class 9-10 - Module 3msujoyNo ratings yet
- Lelm 406Document29 pagesLelm 406tamannavikram83No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Maths Previous Year Question Paper 2014Document7 pagesICSE Class 10 Maths Previous Year Question Paper 2014royaljm1432No ratings yet
- Term-2 - Grade 8 Math Mock Paper-2Document2 pagesTerm-2 - Grade 8 Math Mock Paper-2bhagatNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4008/2Document12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4008/2Humphrey MunzvekureNo ratings yet
- Maths 1 Test 2 AY2021 Sem1 Main Paper V2Document6 pagesMaths 1 Test 2 AY2021 Sem1 Main Paper V2HAZENo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument8 pagesAdditional MathematicsSwordfighterXNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths Paper 2-Mock 2023 FinalDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Maths Paper 2-Mock 2023 Finallucksonmumba88No ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 21Document20 pages4024 w11 QP 21SyedMaazAliNo ratings yet
- Stage 8 End of Unit 14 WorksheetDocument4 pagesStage 8 End of Unit 14 WorksheetDeena100% (1)
- Activity 11: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument12 pagesActivity 11: Bjective Aterial Equiredharshitcreations3704No ratings yet
- Term 3 MathematicsDocument10 pagesTerm 3 Mathematicsmilk GangNo ratings yet
- April 9 OnlineDocument3 pagesApril 9 OnlineMalik MuneebNo ratings yet
- Practice 5 - 2021 A-Levels P4 (Sample Report)Document20 pagesPractice 5 - 2021 A-Levels P4 (Sample Report)zavairling05No ratings yet
- Grade 10 p2 RevisionDocument8 pagesGrade 10 p2 RevisionShivaranjali VirasamiNo ratings yet
- Asm 96085Document6 pagesAsm 96085p5jp29697cNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 22Document24 pages4024 w11 QP 22Hamza NawazNo ratings yet
- Icse-Question-Paper Solved Maths 2014Document7 pagesIcse-Question-Paper Solved Maths 2014Faisal GheyasNo ratings yet
- Question Paper gr10 Math 1 Copy Both SidedDocument5 pagesQuestion Paper gr10 Math 1 Copy Both SidedfarzinahammedNo ratings yet
- 0581 w14 QP 32 PDFDocument16 pages0581 w14 QP 32 PDFCorinSaputraNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Medians of A Triangle Are ConcurrentDocument5 pagesActivity 1: Medians of A Triangle Are ConcurrentDr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Class - X, KISA Maths Preparatory Exam Question PaperDocument6 pagesClass - X, KISA Maths Preparatory Exam Question Paperbindyasri16No ratings yet
- Activity Maths 01Document5 pagesActivity Maths 01Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths Paper 2 Model AnswersDocument18 pagesIGCSE Maths Paper 2 Model AnswersraksnghNo ratings yet
- IGCSEDocument9 pagesIGCSEBalasubramaniam GauthamanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 MathDocument12 pagesGrade 9 MathTrevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- 0606 w09 QP 2Document8 pages0606 w09 QP 2Sochima NwobiaNo ratings yet
- 4024 s08 QP 1Document16 pages4024 s08 QP 1Melvyn MardamootooNo ratings yet
- G9 Maths Mock P2Document15 pagesG9 Maths Mock P2lucksonmumba88No ratings yet
- Form 4: Chapter 2: Quadratic Expressions and EquationsDocument2 pagesForm 4: Chapter 2: Quadratic Expressions and EquationsYue TengNo ratings yet
- 0580 m15 QP 42 PDFDocument16 pages0580 m15 QP 42 PDFNamanNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 November 2006Document12 pagesMaths Paper 2 November 2006TadiwaNo ratings yet
- 4037 s07 QP 1Document8 pages4037 s07 QP 1MamunNo ratings yet
- Fatsch-MOCK 2022-P1Document10 pagesFatsch-MOCK 2022-P1Tahpehs PhiriNo ratings yet
- Summative Test IGCSE 2 PDFDocument6 pagesSummative Test IGCSE 2 PDFFatima FarooqNo ratings yet
- 4024 s15 QP 22Document24 pages4024 s15 QP 22Kevin AarasingheNo ratings yet
- G9 Mock MathDocument10 pagesG9 Mock Mathlucksonmumba88No ratings yet
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsFrom EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Grade 6 To 8 GCSE QP The ExtinctsDocument7 pagesGrade 6 To 8 GCSE QP The ExtinctsPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- It So Happened (Grade 8) Mizoram EditionDocument110 pagesIt So Happened (Grade 8) Mizoram EditionPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar LinkDocument1 pageNCERT Exemplar LinkPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- The Monty Hall ProblemDocument1 pageThe Monty Hall ProblemPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Set, Relation and FunctionDocument2 pagesMathematics: Set, Relation and FunctionRamNagalNo ratings yet
- Beginning and Intermediate Algebra 6th Edition Lial Solutions ManualDocument90 pagesBeginning and Intermediate Algebra 6th Edition Lial Solutions ManualJamesWolfefsgr100% (46)
- Jacobian Matrix and Determinant: F: R R X F (X) F JDocument8 pagesJacobian Matrix and Determinant: F: R R X F (X) F Jdan shenNo ratings yet
- BYJUS Class 10 NCERT Examplar Solutions Ch-4Document10 pagesBYJUS Class 10 NCERT Examplar Solutions Ch-4Vicky28 Indhu10No ratings yet
- Puerto National High School: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Division of Cagayan de Oro CityDocument2 pagesPuerto National High School: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Division of Cagayan de Oro CityJaylor GaridoNo ratings yet
- Algebra II Review Worksheet Show All Work!!!Document2 pagesAlgebra II Review Worksheet Show All Work!!!kcarveyNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Equivalent Forms of Hensel's LemmaDocument28 pages9.1 Equivalent Forms of Hensel's Lemmamoesiom22No ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument17 pagesUnit IIfaraazhabeebNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Number Theory Notes Anwar KhanDocument110 pagesAlgebraic Number Theory Notes Anwar KhanAmeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Mat1014 SyDocument1 pageMat1014 SyJoeseNo ratings yet
- Assignment 15Document2 pagesAssignment 15api-261755710No ratings yet
- IOQM Question PaperDocument4 pagesIOQM Question PaperParshveer JainNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE Linear AlgebraDocument6 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE Linear AlgebraMBIEDA NGOMEGNI FRANK GAETANNo ratings yet
- Interpolation: Presented by Parkhe Ravindra AmbadasDocument12 pagesInterpolation: Presented by Parkhe Ravindra AmbadasRavi ParkheNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9 (MAN-001)Document4 pagesAssignment 9 (MAN-001)vrm8000No ratings yet
- 4A01 FS 01eDocument31 pages4A01 FS 01eTerence LuiNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane Part 1 CH4Document26 pagesMotion in A Plane Part 1 CH4Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 1 Module EditedDocument8 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 1 Module EditedB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.No ratings yet
- Abel-Ruffini TheoremDocument5 pagesAbel-Ruffini TheoremRafih YahyaNo ratings yet
- 1 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument124 pages1 Algebraic ExpressionsAngelika Kristi-Ana ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Aph Theory Morphisms, Monoids and Matrices, Knauer, de Gruyter, 2011 PDFDocument325 pagesAph Theory Morphisms, Monoids and Matrices, Knauer, de Gruyter, 2011 PDFviyerod100% (4)
- BCH CodesDocument11 pagesBCH CodesAmol AmollNo ratings yet
- კომბინატორიკაDocument8 pagesკომბინატორიკაanimehub.shoppNo ratings yet
- Math30.CA U1l1 PolynomialFunctionsDocument20 pagesMath30.CA U1l1 PolynomialFunctionsUnozxcv Doszxc100% (1)
- Notes On Complex Numbers: Math 170: Ideas in Mathematics (Section 002)Document5 pagesNotes On Complex Numbers: Math 170: Ideas in Mathematics (Section 002)Ardit ZotajNo ratings yet
- Positive Grassmannian, Lectures by A. PostnikovDocument82 pagesPositive Grassmannian, Lectures by A. PostnikovpepeqfNo ratings yet
- Clifford AlgebrasDocument228 pagesClifford Algebrasjoseamh6906224780% (5)
- The Factor & Remainder TheoremDocument6 pagesThe Factor & Remainder TheoremwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Absolute Value and Operations On Integers: Learning Activity SheetDocument5 pagesAbsolute Value and Operations On Integers: Learning Activity Sheetlourdes amitNo ratings yet