Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths
Uploaded by
Hema sripriyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths
Uploaded by
Hema sripriyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 3
OBJECTIVE MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity : Drawing sheet, cardboard, cello-
tape, coloured papers, cutter and
(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
ruler.
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
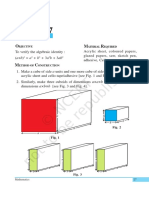
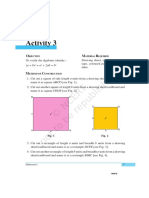
1. Cut out a square of side length a units from a drawing sheet/cardboard and
name it as square ABCD [see Fig. 1].
2. Cut out another square of length b units from a drawing sheet/cardboard and
name it as square CHGF [see Fig. 2].
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
3. Cut out a rectangle of length a units and breadth b units from a drawing
sheet/cardbaord and name it as a rectangle DCFE [see Fig. 3].
4. Cut out another rectangle of length b units and breadth a units from a drawing
sheet/cardboard and name it as a rectangle BIHC [see Fig. 4].
Mathematics 17
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 17 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
Fig. 3 Fig. 4
5. Total area of these four cut-out figures
= Area of square ABCD + Area of square CHGF + Area of rectangle DCFE
+ Area of rectangle BIHC
= a2 + b2 + ab + ba = a2 + b2 + 2ab.
6. Join the four quadrilaterals using cello-tape as shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 5
18 Laboratory Manual
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 18 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
Clearly, AIGE is a square of side (a + b). Therefore, its area is (a + b)2. The
combined area of the constituent units = a2 + b2 + ab + ab = a2 + b2 + 2ab.
Hence, the algebraic identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............. (a+b) = ..............,
So, a2 = .............. b2 = .............., ab = ..............
(a+b)2 = .............., 2ab = ..............
Therefore, (a+b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 .
The identity may be verified by taking different values of a and b.
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating the square of a number expressed as the sum of two convenient
numbers.
2. simplifications/factorisation of some algebraic expressions.
Mathematics 19
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 19 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
Activity 7
OBJECTIVE MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity : Acrylic sheet, coloured papers,
glazed papers, saw, sketch pen,
(a+b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2
adhesive, Cello-tape.
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
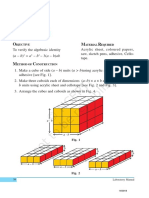
1. Make a cube of side a units and one more cube of side b units (b < a), using
acrylic sheet and cello-tape/adhesive [see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2].
2. Similarly, make three cuboids of dimensions a×a×b and three cuboids of
dimensions a×b×b [see Fig. 3 and Fig. 4].
Fig. 2
Fig. 1
Fig. 3
Mathematics 27
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 27 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
Fig. 4
3. Arrange the cubes and cuboids as shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 5
28 Laboratory Manual
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 28 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
DEMONSTRATION
Volume of the cube of side a = a×a×a = a3, volume of the cube of side b = b3
Volume of the cuboid of dimensions a×a×b = a2b, volume of three such cuboids
= 3a2b
Volume of the cuboid of dimensions a×b×b = ab2, volume of three such cuboids
= 3ab2
Solid figure obtained in Fig. 5 is a cube of side (a + b)
Its volume = (a + b)3
Therefore, (a+b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2
Here, volume is in cubic units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = ............., a3 = ..............,
So, a3 = .............., b3 = ............., a2b = .............., 3a2b= ..............,
ab2 = .............., 3ab2 = .............., (a+b)3 = ..............,
Therefore, (a+b)3 = a3 + b3 +3a2b + 3ab2
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating cube of a number expressed as the sum of two convenient
numbers
2. simplification and factorisation of algebraic expressions.
Mathematics 29
Lab manual IX (setting on 21-05-09) 1_10.pmd 29 28-May-2019, 12:43 PM
You might also like
- OISDJFIOJWEFDocument3 pagesOISDJFIOJWEFPranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Lab Manual - Verifying (A+b+c) 2Document2 pagesNCERT Lab Manual - Verifying (A+b+c) 2Pranav Reddy SathiNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument3 pagesActivity 3: Bjective Aterial EquiredMalati MauryaNo ratings yet
- Activities 5Document3 pagesActivities 5Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab Activities Class 9Document22 pagesLab Activities Class 9vidya jayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Activity 6: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument2 pagesActivity 6: Bjective Aterial EquiredMalati MauryaNo ratings yet
- Activities 6Document2 pagesActivities 6Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Activities 8Document3 pagesActivities 8Partha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Activities 4Document2 pagesActivities 4lolmao12No ratings yet
- Activity 1: Objective Material RequiredDocument3 pagesActivity 1: Objective Material Requirednd hrdNo ratings yet
- Lelm 403Document33 pagesLelm 403yutika1803No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Activity 1 To 10 in EnglishDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Activity 1 To 10 in EnglishManya ElhanceNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 p2 RevisionDocument8 pagesGrade 10 p2 RevisionShivaranjali VirasamiNo ratings yet
- Maths Activity Class 3 8 Part3Document49 pagesMaths Activity Class 3 8 Part3jaya_sassiNo ratings yet
- Lelm 402Document22 pagesLelm 402For JunkNo ratings yet
- Activity 11: Bjective Aterial EquiredDocument12 pagesActivity 11: Bjective Aterial Equiredharshitcreations3704No ratings yet
- CLASS 9 Maths Lab ACTIVITY 1Document4 pagesCLASS 9 Maths Lab ACTIVITY 1Manish RathoreNo ratings yet
- Activities 23Document2 pagesActivities 23lolmao12No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMohamed AnsaryNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Projects Manual - Class 9-10 - Module 3Document33 pagesCBSE Maths Projects Manual - Class 9-10 - Module 3msujoyNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Maths Previous Year Question Paper 2014Document7 pagesICSE Class 10 Maths Previous Year Question Paper 2014royaljm1432No ratings yet
- Chapter - Activity Plus in Mathematics 9 PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - Activity Plus in Mathematics 9 PDFAstha YadavNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Medians of A Triangle Are ConcurrentDocument5 pagesActivity 1: Medians of A Triangle Are ConcurrentDr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Activity Maths 01Document5 pagesActivity Maths 01Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 p2 RevisionDocument6 pagesGrade 10 p2 RevisionShivaranjali VirasamiNo ratings yet
- 2017-18 Grade 9 Term I MathematicsDocument3 pages2017-18 Grade 9 Term I MathematicsHitanshu JainNo ratings yet
- Icse-Question-Paper Solved Maths 2014Document7 pagesIcse-Question-Paper Solved Maths 2014Faisal GheyasNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Mathematics Board Question Paper 2014: (Two and A Half Hours)Document37 pagesICSE Board Class X Mathematics Board Question Paper 2014: (Two and A Half Hours)DEBASIS SAHOO0% (1)
- ICSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper 2019 - ICSE-Class-9-Maths-Sample-Paper-2019Document7 pagesICSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper 2019 - ICSE-Class-9-Maths-Sample-Paper-2019misatok775No ratings yet
- Activity 5 and 10Document5 pagesActivity 5 and 10IsseiNo ratings yet
- Icse Class 10 Maths Mock Sample Question Paper 2Document5 pagesIcse Class 10 Maths Mock Sample Question Paper 2Debayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- CISCE - GRADE 8 - Mathematics - SAMPLE PAPER - QP - AY 22-23Document9 pagesCISCE - GRADE 8 - Mathematics - SAMPLE PAPER - QP - AY 22-23Harry mate100% (1)
- 3rd HFS Thane ICSE10 Maths Prel-1 2020-21-UnprotectedDocument5 pages3rd HFS Thane ICSE10 Maths Prel-1 2020-21-Unprotecteddinesh lalwaniNo ratings yet
- Term-2 - Grade 8 Math Mock Paper-2Document2 pagesTerm-2 - Grade 8 Math Mock Paper-2bhagatNo ratings yet
- Practice 5 - 2021 A-Levels P4 (Sample Report)Document20 pagesPractice 5 - 2021 A-Levels P4 (Sample Report)zavairling05No ratings yet
- G9 Mock MathDocument10 pagesG9 Mock Mathlucksonmumba88No ratings yet
- Sulit 3472/2Document3 pagesSulit 3472/2Saya MenangNo ratings yet
- Lelm 406Document29 pagesLelm 406tamannavikram83No ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 November 2006Document12 pagesMaths Paper 2 November 2006TadiwaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Unit 1 Practice AssessmentDocument4 pagesAlgebra Unit 1 Practice AssessmentGeorge SabaNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Maths Prelim I Set A 1Document26 pagesX ICSE Maths Prelim I Set A 1robins2007No ratings yet
- Class - X, KISA Maths Preparatory Exam Question PaperDocument6 pagesClass - X, KISA Maths Preparatory Exam Question Paperbindyasri16No ratings yet
- IGCSEDocument9 pagesIGCSEBalasubramaniam GauthamanNo ratings yet
- Alg3 & Trig2 - Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesAlg3 & Trig2 - Practice QuestionsAbdullah NHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Mathematics 9794/01Document4 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Mathematics 9794/01Rushil MohabeerNo ratings yet
- X P4 - FinalDocument18 pagesX P4 - FinalWates SoluNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 June 2000Document12 pagesMaths Paper 2 June 2000Tinashe KamusaireNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Document16 pagesIGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Arturo PizarroNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationBoxNo ratings yet
- Maths-F3-P2 .Document14 pagesMaths-F3-P2 .okoth billNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument8 pagesAdditional MathematicsSwordfighterXNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4008/2Document12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Mathematics 4008/2Humphrey MunzvekureNo ratings yet
- SMK ST Michael, Penampang: Examinations 3 2008Document16 pagesSMK ST Michael, Penampang: Examinations 3 2008tinamicNo ratings yet
- Maths: (Two and A Half Hours)Document6 pagesMaths: (Two and A Half Hours)parthNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 June 2001Document11 pagesMaths Paper 2 June 2001Shelin FarmerNo ratings yet
- NameDocument10 pagesNameapi-19562657No ratings yet
- 2011 Math Counts Chapter Competition SolutionsDocument11 pages2011 Math Counts Chapter Competition SolutionsJoel EspelienNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument7 pagesQuadrilateralsTrisha DasNo ratings yet
- 203030004Document88 pages203030004Vinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Upper Primary Division Round 2Document7 pagesInstructions:: Upper Primary Division Round 2Lê Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- PRMO 2018 Answer SolutionsDocument9 pagesPRMO 2018 Answer SolutionsPrashantNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For Igcse Mathematics 0580 FinalDocument23 pagesRevision Checklist For Igcse Mathematics 0580 FinalAshfaNo ratings yet
- Math Kangaroo 2003: Level of Grades 5 - 6Document5 pagesMath Kangaroo 2003: Level of Grades 5 - 6Vasilis KoutsoubasNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Revision Sheet 2Document8 pagesGrade 7 Revision Sheet 2esivaks2000100% (1)
- P4 ISMC 2019 Questions W AnswersDocument8 pagesP4 ISMC 2019 Questions W AnswersAileen Mimery100% (1)
- MensurationDocument143 pagesMensurationshubh9190100% (1)
- Math Homework Module8Document17 pagesMath Homework Module8Valerie Yenshaw100% (1)
- GR 7 ASSET WORKSHEET HWDocument6 pagesGR 7 ASSET WORKSHEET HWSharon BijuNo ratings yet
- SLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aDocument7 pagesSLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aErica BecariNo ratings yet
- Mensuration and Practical GeometryDocument12 pagesMensuration and Practical Geometrydocuments unaisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 9 Monty The Artist CLILDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 9 Monty The Artist CLILDaryl DelavinNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci Numbers and The Golden RatioDocument94 pagesFibonacci Numbers and The Golden RatioAslanNo ratings yet
- QP Odisha Ntse Stage 1 2020-21 MatDocument18 pagesQP Odisha Ntse Stage 1 2020-21 MatPrakash PrakashNo ratings yet
- Math - January 2022 QP 2FDocument28 pagesMath - January 2022 QP 2FLing JaiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 LAS Quarter 3Document91 pagesMathematics 9 LAS Quarter 3Jake Padua94% (33)
- 3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9Document4 pages3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9sweetheart barrion43% (7)
- Math Ira 2019 OralsDocument6 pagesMath Ira 2019 OralsGil Deon BasaNo ratings yet
- Counting - Meng, Guan (WS, 2002)Document123 pagesCounting - Meng, Guan (WS, 2002)SANJIVsharma65No ratings yet
- Triangles: TLE Grade 7 Learning Activity SheetDocument3 pagesTriangles: TLE Grade 7 Learning Activity SheetAshly RoderosNo ratings yet
- MTAP Grade 3 QuestionnairesDocument35 pagesMTAP Grade 3 QuestionnairesRoselyn TubogNo ratings yet
- 3Q W2 Special-Parallelograms Version2Document57 pages3Q W2 Special-Parallelograms Version2Layar ArianneNo ratings yet
- Application of Spiral Principles in Ulam S Spiral To Smooth Flow and Reduce Hesitation in Internet MessagingDocument10 pagesApplication of Spiral Principles in Ulam S Spiral To Smooth Flow and Reduce Hesitation in Internet MessagingGary GabrielNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Intso - Mtso - Viii Class - WS-4Document2 pagesGeometry - Intso - Mtso - Viii Class - WS-4Gurrapu SudhaNo ratings yet
- Za M 1659888207 Grade 6 Maths Exam Paper November - Ver - 3Document23 pagesZa M 1659888207 Grade 6 Maths Exam Paper November - Ver - 3HeshaniNo ratings yet
- Cbjemaco 06Document11 pagesCbjemaco 06Babitha VimalNo ratings yet