Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cfas
Uploaded by
Marianne Aguilar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesOriginal Title
cfas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesCfas
Uploaded by
Marianne AguilarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
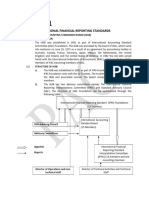
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
Accounting − effective from Dec. 1, 2016—14 board members,
− an information system designed to identify, of whom one is appointed as Chair and one as a
collect, measure, and communicate economic Vice-chair
information about a business entity (firm) to those − 5 year term, renewable for 3-5 years, term not
having an interest in the financial affairs of the exceeding 10 years
entity − to ensure broad int’l diversity, the constitution
requires:
User of financial information
• 4 members from the Asia/Oceana region
A. Primary users
- general purpose financial reports are • 4 from Europe
primarily directed • 4 from the America
1. Existing investors • 1 from Africa
2. Potential investors • 1 from any area, subject to nominating
3. Lenders overall geographical balance
4. Other creditors International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS)
B. Other users Foundation
- reports are not directed to them primarily
− predecessor was Int’l Accounting Standards
1. Employees – stability & profitability of the
Foundation (IASF)—Feb. 6, 2001
entity
− IFRS Foundation—Jul. 1, 2010
2. Customers – continuance of an entity
− independent not-for-profit organization and the
3. Gov’t and their agencies – allocation of
primary objective is to develop in the public
resources
interest, a single set of high quality ,
4. Public – substantial contribution to local
understandable, enforceable, and globally-
economy
accepted IFRS based on clearly articulated
Financial Accounting principles
− the information accumulation, processing and − IFRS standards are set by IFRS Foundation’s
communication system designed to satisfy the standards-setting body, the IASB
investment and credit decision-making
International Financial Reporting Interpretation
information needs of external users
Committee (IFRIC)
− focuses on developing FS
− assist the IASB by providing guidance on the
Financial Statements application and interpretation of IFRS
− principal output of a financial accounting − before Dec 2001, Standing Interpretations
Committee (SIC) was IASB’s interpretative body
− the means by which a company communicates its
− specified duties:
financial information to those outside the
• interpret the application of IASs and
organization
IFRSs, to provide timely guidance on
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) financial reporting issues not specifically
− independent group of experts with appropriate addressed in IASs and IFRSs, and
mix of recent practical experience in selling undertake other tasks at the request of the
accounting standards in preparing, auditing or IASB;
using financial reports and in accounting • carry out duties with regard to the IASBs
objective of working actively with
education
national standard setters to bring about
− founded on Apr. 1, 2001
convergence of national accounting
− successor of IASC standards;
− develops International Financial Reporting • publish, after clearance by the IASB,
Standards (IFRS) and promotes the use and draft Interpretations for public comment
application of these standards and consider comments made within a
reasonable period before finalizing a regulatory bodies and users of financial
interpretation statements
• report to the IASB and obtain its approval − replaced IC by ASC in 2000
for final interpretation
Philippine Regulatory Board of Accountancy
− comprise of 14 voting members, appointed by the
(PRBOA)
Trustees of the IFRS Foundation
− composition:
Financial Reporting Standards Council (FRSC) • 1 chairman, 6 members appointed by the
− established by PRC under the Implementing Pres.
Rules and Regulations of the Philippine • The board shall elect a Vice chairman
Accountancy Act of 2004 to assist the BOA in from among each member for a term of
carrying out its power and function to promulgate one year
accounting standards in the Phil. − qualifications:
− successor of ASC—created in Nov 1981 by • natural resident citizen
PICPA to establish GAAP in the Phil. • CPA with at least 10 year relevant
− composed of 15 members with a chairman who experience
had been or presently a senior accounting • good moral
practitioner in any of the scope of accounting • no pecuniary interest in any school
practice and 14 representative from − term office:
• 1 BSP • 3 years
• 1 BOA • any vacancy shall be filled up for the
• 1 BIR unexpired portion of the term only
• 1 COA • no person who has served 2 successive
• 1 FINEX (Financial, Executive and complete terms shall be eligible for
Professional Risks) reappointment until the lapse of 1 year
• 1 SEC • appointments to fill up an expired term is
• 2 NACPAE (National Association of not to be considered as a complete term
CPAs in Education) − powers and functions of the board:
• 2 ACPAPP (Association of CPAs in • prescribe and adopt the rules and
Public Practice) regulations necessary for carrying the
• 2 GACPA (Gov’t Association of CPA) provisions of the Phil. Accountancy Act
• 2 ACPACI (Association of CPAs in of 2004
Commerce and Industry • supervise the registration, licensure and
− monitors technical activities of the IASB and practice of accountancy in the Phil.
invites comments on exposure drafts of proposed • issue, suspend, revoke, reinstate the
IFRSs as these are issued by the IASB; adopted as certificate of registration for the practice
PFRSs when finalized of the accountancy profession
− similarly monitors issuances of the IFRIC of the • adopt an official seal
IASB, which it adopts as Phil. Interpretations— • prescribe and/or adopt a Code of Ethics
IFRIC, PFRSs and Phil. Interpretations—IFRIC for the practice of accountancy
approved for adaptation are submitted to the BOA
and PRC for approval Philippine Institute of Certified Public Accountants
(PICPA)
Philippine Interpretation Committee (PIC) − Section 30 of RA 9298 states that all registered
− formed by FRSC on Aug 2006 to assist the FRSC CPAs shall be united and integrated through their
in establishing and improving financial reporting membership in a one only registered and
standards in the Phil. accredited national professional organization of
− role—principally issue implementation guidance registered and licensed CPAs
on PFRSs − founded in 1929, accredited professional
− members are appointed by the FRSC and include organization (APO) of CPAs by PRC
accountants in public practice, the academe and − objectives:
• promote and maintain high professional Scope of Framework:
and ethical standards among accountants 1. OBJECTIVE AND GENERAL-PURPOSE
• advance the science of accounting FINANCIAL REPORTING
• develop and improve accountancy
education Overall Objective of Financial Reporting.
• encourage cordial relations among To provide financial information about the
accountants reporting entity that is useful to target in
• protect certificate of CPA granted by the making decisions about providing resources
Republic of the Philippines to the entity.
Specific Objectives of Financial Reporting
− 4 sectors of accountancy profession:
a. To provide information useful in making
• commerce & industry
decisions about providing resources to
• public practice
the entity
• government b. To provide information useful in
• education/academe assessing the prospects of future net cash
− four geographical groupings: flows to the entity
• Luzon c. To provide information about entity
• Visayas resources, claims and changes in
• Mindanao resources and claims
• NCR
Financial Position
Accreditation to Practice Public Accountancy
− information about the economic entity’s
− CPAs, firms and partnerships of CPAs engaged in
economic resources and the claims of a
the practice of public accountancy shall register
reporting entity at a particular moment in
with the PRC and the Board such registration to
time
be renewed every 3 years
Financial Performance
− single practitioners and partnerships for the
− level of income earned by the entity
practice of pubic accountancy shall be registered
through the efficient and effective use of
CPAs in the Phil.
its resources
− Certificate shall be issued to CPAs in public
practice only upon showing, that such registrant Accrual Accounting
has acquired a minimum of 3 years meaningful
− depicts the effects of the transactions and
experience in any areas of public practice
other events and circumstances on an
including taxation
entity’s economic resources and claims in
Conceptual Framework the periods in which those effects occur
− sets out fundamental concepts of financial even if the resulting cash receipts and
reporting that guide the IASB in developing IFRS payments occur in a different period
− helps to ensure that the standards are conceptually Accrual Cash Basis
consistent and that similar transactions are treated Revenue earned collected
the same way, so as to provide useful information Expense incurred paid
− assists companies in developing accounting
policies when no IFRS applies to a particular
transaction, and more broadly, helps stakeholders 2. QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF
USEFUL INFORMATION
to understand and interpret the standards
A. Fundamental
− does not override any specific IFRS
• content or substance
− should the IASB decide to issue a new or revised
1. Relevance
pronouncement that is in conflict with the
- capacity if the information to
framework, the IASB will highlight the fact and
influence a decision
explain the reasons for the departure in the basis
a. predictive value – used
for conclusions
to predict future outcome
b. feedback Affect all items in the FS
(confirmatory) value – • Materiality – an item is material if
used to confirm or correct its omission or misstatements could
earlier expectations influence economic decisions
• Cost-benefit – the cost of processing
information should not exceed the
2. Faithful Representation benefits to be derived from it
- actual effect of transactions 3. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND THE
shall be properly accounted REPORTING ENTITY
for and reported in the FS Financial Statements
a. completeness – adequate − particular form of financial reports that
or full disclosure of all provide information about the reporting
necessary information entity’s assets, liabilities, equity, income
b. neutrality – fairness and and expenses
freedom from bias Types:
c. free from error – no a. consolidated – parent and
inaccuracies and subsidiaries
omissions b. unconsolidated – parent only
B. Enhancing c. combines fs – two or more not all
• presentation or form linked by a parent-subsidiary
1. Comparability relationship
- information can be compared
Complete Set of Financial Statements
with similar information
1. Statement of Financial Position
about other entities and with
2. Statement of Profit or Loss and Other
similar information about the
Comprehensive Income
same entity for another
3. Statement of Changes in Equity
period or date
4. Statement of Cash Flows
2. Understandability
5. Notes to Financial Statements
- classifying, characterizing
and presenting information
4. ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
clearly and concisely makes
• quantitative information reported in
it understandable.
the statement of financial position
3. Verifiability
and income statement
- implies consensus
a. assets - present economic
- financial information
resource controlled by the entity
supported by evidence is
as a result of past events
verifiable
b. liabilities - present obligation of
- means that different
an entity to transfer an economic
knowledgeable and
resource as a result of past events
independent observers could
c. equity - residual interest in the
reach consensus, although not
assets of the entity after
necessarily complete
deducting all of the liabilities
agreement, that a particular
d. income - increases in assets or
depiction is a faithful
decreases in liabilities that result
representation
in increases in equity, other than
4. Timeliness
those relating to contributions
- means information is
from equity holders
available to decision-makers
e. expense - decreases in assets or
in time to be capable of
increases in liabilities that result
influencing their decisions.
in decreases in equity, other than
Constraints
those relating to distributions to consideration paid and
equity holders transaction cost
5. RECOGNITION & DERECOGNITION 7. PRESENTATION AND DISCLOSURE
Recognition − communication tools
• process of capturing for inclusion in − reporting entity communicates
the financial statements an item that information about its assets, liabilities,
meets the definition of an asset, equity, income and expenses by
liability, equity, income or expense presenting and disclosing information in
Derecognition the financial statements
• removal of all or part of a recognized a. focusing on presentation and
asset or liability from the statement of disclosure objectives and principles
financial position rather than focusing on rules
• normally occurs when an item no b. classifying information in a manner
longer meets the definition of an asset that grouped similar items and
or a liability separates dissimilar items; and
• for an asset when the entity losses c. aggregating information in such way
control of all or part of the recognized that it is not obscured either by
asset unnecessary detail or excessive
• for a liability when an entity no aggregation
longer has a present obligation for all
or part of the recognized liability 8. CONCEPTS OF CAPITAL AND
6. MEASUREMENT CAPITAL MAINTENANCE
• quantifying in monetary terms the Concept of Capital
elements in the financial statements 1. Financial Concept of Capital
a. historical cost • Adopted by most entities
- original acquisition cost of an • Capital is synonymous with the net
asset is the cost incurred in assets or equity of the entity.
acquiring or creating the asset • Adopted if the users of FS are
comprising the consideration primarily concerned with the
paid plus transaction cost maintenance of nominal invested
- entry price or entry value to capital or the purchasing power of
acquire an asset or to incur a invested capital
liability 2. Physical Concept of Capital
b. current value • Capital is regarded as the productive
• fair value - price that capacity of the entity based on, for
would be received to sell example, units of output per day.
an asset • If the main concern of users is with
• value in use - present
the operating capability of the entity,
value of the cash flows
a physical capital should be used.
that an entity expects to
derive from the use of an
asset and from the
ultimate disposal
• fulfillment value -
present value of cash that
an entity expects to
transfer in paying or
settling a liability
• current cost - cost of an
equivalent asset at the
measurement date
comprising the
Concepts of capital maintenance
Capital maintenance – means that net
income occurs only after the capital used
from the beginning of the period is
maintained
1. Financial capital maintenance concept
− invested money or invested
purchasing power, capital is
synonymous with net assets or
equity of the entity
− traditional concept based on
historical cost and adopted by
most entities
− net assets—excess of total assets
over total liabilities
2. Physical capital maintenance
− quantitative measure of the
physical productive capacity to
produce goods and services
− physical productive capacity—
units of output per day or
physical capacity of productive
assets to produce goods and
services
− productive assets—measured at
current cost rather than historical
cost
− productive assets—include
inventories and PPE
The Accounting Cycle
1. Identification of events to be recorded
2. Transactions are recorded in journal
3. Entries ported to the ledger
4. Preparation of trial balance
5. Preparation of worksheet with adjusting entries
6. Preparation of financial statements
7. Adjusting entries are journalized & posted
8. Closing entries are journalized & posted
9. Preparation of post-closing trial balance
10. Reversing entries are journalized & posted
You might also like
- IFRS Simplified: A fast and easy-to-understand overview of the new International Financial Reporting StandardsFrom EverandIFRS Simplified: A fast and easy-to-understand overview of the new International Financial Reporting StandardsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Group 1Document8 pagesGroup 1Jason Leur BernabeNo ratings yet
- Development of Financial Reporting Framework, Standard-Setting Bodies and Regulation of The Accountancy ProfessionDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Financial Reporting Framework, Standard-Setting Bodies and Regulation of The Accountancy ProfessionJUST KINGNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 (January 16, 2023)Document10 pagesModule 1 and 2 (January 16, 2023)The Brain Dump PHNo ratings yet
- BABE1 Reviewer 1Document13 pagesBABE1 Reviewer 1James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- OBE ReviewerDocument14 pagesOBE Reviewerhermione grangerNo ratings yet
- Cfas Reviewer PDF Free PDFDocument6 pagesCfas Reviewer PDF Free PDFDonghyuk LeeNo ratings yet
- Cfas ReviewerDocument6 pagesCfas ReviewerJedi Duenas100% (2)
- CFAS.100 - Diagnostic Test Part 1Document4 pagesCFAS.100 - Diagnostic Test Part 1Mika MolinaNo ratings yet
- Week 01 - 02 - Module 02 - Financial Reporting StandardsDocument21 pagesWeek 01 - 02 - Module 02 - Financial Reporting Standards지마리No ratings yet
- ACYFAR NOTES Standard Setting IAS 1 Conceptual FrameworkDocument34 pagesACYFAR NOTES Standard Setting IAS 1 Conceptual FrameworkFritzey Faye RomeronaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document7 pagesLesson 1Ira Charisse BurlaosNo ratings yet
- B S A 2 - 1 Pup Binan CampusDocument292 pagesB S A 2 - 1 Pup Binan CampusGUNDA, NICOLE ANNE T.No ratings yet
- LS 1 - ACCOUNTING AND ITS ENVIRONMENT Part 3Document51 pagesLS 1 - ACCOUNTING AND ITS ENVIRONMENT Part 3Danielle Angel MalanaNo ratings yet
- Cfas ReviewerDocument2 pagesCfas ReviewerElaine Ü LubianoNo ratings yet
- Acyfar 1 NotesDocument7 pagesAcyfar 1 Noteskate santosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document11 pagesLesson 1shadowlord468No ratings yet
- Notes in CFASDocument5 pagesNotes in CFASJohn Raymond MarzanNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting Lam LauDocument21 pagesFinancial Reporting Lam LauElmiImiartiPurbaNo ratings yet
- CFAS Part 1Document3 pagesCFAS Part 1AINAH SALEHA MIMBALAWAGNo ratings yet
- 6 Evolution of Accounting Standards SummarizedDocument5 pages6 Evolution of Accounting Standards SummarizedLorraine Joy TioxonNo ratings yet
- 1 Ifrs Ias 1-AccaDocument265 pages1 Ifrs Ias 1-AccaSabrina Aeni100% (1)
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: OutlineDocument6 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: OutlineMichael TorresNo ratings yet
- Acca - Chapter 1-9 SummaryDocument5 pagesAcca - Chapter 1-9 SummaryBianca Alexa SacabonNo ratings yet
- ACCA - Chapter 1-4Document5 pagesACCA - Chapter 1-4Bianca Alexa SacabonNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Theory and Practice Vol 1Document1 pageFinancial Accounting Theory and Practice Vol 1Jessa BasarteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Framework and RegulationDocument13 pagesModule 1 - Framework and RegulationLuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 10 NotesAyaan Ahaan Malik-WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (CFAS) - Chapter 1-13Document26 pagesReviewer (CFAS) - Chapter 1-13pilingat23-1851No ratings yet
- The Environment of Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument12 pagesThe Environment of Financial Accounting and ReportingJi Baltazar100% (1)
- Standard Setting BodiesDocument3 pagesStandard Setting Bodiesshe lacks wordsNo ratings yet
- FRSCDocument8 pagesFRSCKrystyn MyrhyllNo ratings yet
- Philippine and International Accounting Standard-Setting OrganizationsDocument6 pagesPhilippine and International Accounting Standard-Setting OrganizationsChocobetternotNo ratings yet
- FAR 2 CF 01 - Overview of AccountingDocument2 pagesFAR 2 CF 01 - Overview of AccountingCatherine CaleroNo ratings yet
- CFAS Part 2Document5 pagesCFAS Part 2AINAH SALEHA MIMBALAWAGNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 IFRS Foundation and The IASBDocument22 pagesUnit - 1 IFRS Foundation and The IASBSanthosh SanthuNo ratings yet
- Development of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard-Setting BodiesDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Financial Reporting Framework and Standard-Setting BodiesJosua PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument11 pagesOverviewangel ciiiNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Chapter 2Document9 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting Chapter 2BlueBladeNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework Accounting SystemDocument13 pagesConceptual Framework Accounting SystemYes ChannelNo ratings yet
- Cfas Chapter 1Document6 pagesCfas Chapter 1Mack Jigo DiazNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting Standards Council PDF FreeDocument6 pagesFinancial Reporting Standards Council PDF Freelana del reyNo ratings yet
- Quiz NotesDocument4 pagesQuiz NotesJacqueline OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework & Accounting StandardsDocument4 pagesConceptual Framework & Accounting StandardsEila PNo ratings yet
- Notes ActDocument3 pagesNotes ActNathaniel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Information in The Preparation and Presentation of StatementsDocument4 pagesInformation in The Preparation and Presentation of StatementsLucille Rose MamburaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To IFRSDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To IFRSBahader AliNo ratings yet
- (Own Notes) Chapter 1 The Conceptual FrameworkDocument2 pages(Own Notes) Chapter 1 The Conceptual Frameworkling shareNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 - Accounting Standards Setting Bodies PrinDocument34 pagesMateri 1 - Accounting Standards Setting Bodies Prinannisah nsa20No ratings yet
- The CPA ProfessionDocument50 pagesThe CPA ProfessionKarina Barretto AgnesNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Preface To PFRSsDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Preface To PFRSsKaren CaelNo ratings yet
- The Environment of Financial Accounting and Reporting IasbDocument7 pagesThe Environment of Financial Accounting and Reporting IasbvhuusbcNo ratings yet
- Ae3 Ae6 ReviewDocument7 pagesAe3 Ae6 ReviewvhuusbcNo ratings yet
- 01 Overview of Accounting PDFDocument18 pages01 Overview of Accounting PDFEdogawa SherlockNo ratings yet
- 2 Accounting Standards Setting BodyDocument6 pages2 Accounting Standards Setting BodycristiancelerianNo ratings yet
- FAR 001 Conceptual FrameworkDocument4 pagesFAR 001 Conceptual FrameworkdreianyanmaraNo ratings yet
- AcFn 511-Ch II Ppt-LK-2020 - Part One-2Document110 pagesAcFn 511-Ch II Ppt-LK-2020 - Part One-2Chilot YihuneNo ratings yet
- Toa q1 Rev p1Document17 pagesToa q1 Rev p1Ivy MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Print - Purnima Advertising AgencyDocument25 pagesPrint - Purnima Advertising AgencyPrashant Janardhan PandeyNo ratings yet
- An Outsourcing Challenge by Schneider ElectricDocument4 pagesAn Outsourcing Challenge by Schneider ElectricAbinesan SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- ECON 1012 - Market Power, RevisedDocument63 pagesECON 1012 - Market Power, RevisedTami GayleNo ratings yet
- CTR-GM - General & Management (0.11)Document9 pagesCTR-GM - General & Management (0.11)Elias EliasNo ratings yet
- AUDIT OF CashDocument24 pagesAUDIT OF CashMr.AccntngNo ratings yet
- RCC Title IIDocument19 pagesRCC Title IITanya Mia PerezNo ratings yet
- ICT Investment Opportunities in Myanmar (U Ye Yint Win)Document32 pagesICT Investment Opportunities in Myanmar (U Ye Yint Win)Mark CookNo ratings yet
- Sarthee Consultancy - Corporate PresentationDocument11 pagesSarthee Consultancy - Corporate PresentationSarthee ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Performance Health CheckDocument2 pagesPerformance Health CheckRavi Theja SolletiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem 1Document1 pagePractice Problem 1Desree Gale0% (2)
- Lecture Note 3 - Globalization and Role of MNCSDocument64 pagesLecture Note 3 - Globalization and Role of MNCSgydoiNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Labor and Organizational Management by Edris AbdellaDocument14 pagesAssignment of Labor and Organizational Management by Edris AbdellaEdris Abdella NuureNo ratings yet
- Pert PPT PresentationDocument13 pagesPert PPT PresentationDhanjay Das100% (2)
- A Summer Internship Project Report ON "Online Ordering Business"Document35 pagesA Summer Internship Project Report ON "Online Ordering Business"Ankur Guglani50% (2)
- Consignment Agreement (Panjang)Document3 pagesConsignment Agreement (Panjang)Izzat SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Transfer PricingDocument14 pagesTransfer PricingDiana Rose BassigNo ratings yet
- Lean IT Enabling and Sustaining Your Lean TransformationDocument2 pagesLean IT Enabling and Sustaining Your Lean TransformationHitalor20No ratings yet
- Ayan Chakravarty BrandwagonDocument5 pagesAyan Chakravarty BrandwagonAyan ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Oct 2011: Qualitative Evaluation To Determine The Necessity of Step 1 of The Goodwill Impairment TestDocument3 pagesOct 2011: Qualitative Evaluation To Determine The Necessity of Step 1 of The Goodwill Impairment TestSingerLewakNo ratings yet
- The Financial Planning ProcessDocument8 pagesThe Financial Planning ProcessFerline Mae Fuene100% (1)
- Creating A Functional Process Control Configuration in HFMDocument3 pagesCreating A Functional Process Control Configuration in HFMDeva Raj0% (1)
- The Pitch Canvas© Explained - V3 - 1Document1 pageThe Pitch Canvas© Explained - V3 - 1AABBCCNo ratings yet
- 10 Practice Problems Monopoly Price DiscrimDocument12 pages10 Practice Problems Monopoly Price Discrimphineas12345678910ferbNo ratings yet
- Vishwa Brochure All FINALDocument11 pagesVishwa Brochure All FINALpooh1992No ratings yet
- FIFPro (2016) 1st FIFPro Global Employment Report. Top FindingsDocument36 pagesFIFPro (2016) 1st FIFPro Global Employment Report. Top FindingsRMADVNo ratings yet
- Milliman Mission, VissionDocument2 pagesMilliman Mission, VissionVaishnavi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- CSI1241 Assignment 1 1Document3 pagesCSI1241 Assignment 1 1Nik Yusof Nik FaridNo ratings yet
- 003 SHORT QUIZ - Professional Practice, Standards, and Quality Control System - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovDocument2 pages003 SHORT QUIZ - Professional Practice, Standards, and Quality Control System - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovMarilou PanisalesNo ratings yet
- Vineet Tandon: Senior Management ProfessionalDocument2 pagesVineet Tandon: Senior Management ProfessionalsalmanNo ratings yet
- Sales TerritoriesDocument20 pagesSales TerritoriesKrishna_Gupta_9757No ratings yet