Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VILLAHERMOSA Tetanus Toxoid
Uploaded by
Jv Jore VillahermosaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VILLAHERMOSA Tetanus Toxoid
Uploaded by
Jv Jore VillahermosaCopyright:
Available Formats
TETANUS TOXOID
A Drug Study Presented to
The Faculty of Nursing Department
In Partial Fulfillment of
the Requirement in NCM – 209 RLE
OB ROTATION
Submitted to:
CHARMAINE A. OROCIO, RN
Clinical Instructor
Submitted by:
JV J. VILLAHERMOSA
BSN-2L – GROUP 5
April 26, 2021
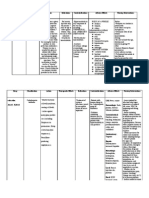
Generic Name Tetanus Toxoid
Brand Name 1. Bio-TT, TE Anatoxal Berna
Classification - Pharmacologic classification: Toxoid
- Therapeutic classification: Tetanus
Prophylaxis
- Tetanus bacterial vaccines.
Mode of Action Tetanus Toxoid induces active immunity to tetanus antigen by
stimulating the immune system to produce specific antitoxin.
Dose and Route Primary Immunization (Series of 3 doses)
- 0.5 mL of tetanus toxoid once followed by a second
dose after 4 to 8 weeks, the third dose is given t 6 to
12 months after the second dose.
Routine Booster Injection
- 0.5 mL IM of tetanus toxoid absorbed or 0.5 mL IM or
subcutaneously of tetanus toxoid given 10 years after
completion of primary immunization and every 10
years thereafter. If a dose is given sooner as part of
wound management, the next booster is not needed
for 10 years thereafter.
Pregnancy:
- If a pregnant woman has not previously been vaccinated, or
if her immunization status is unknown, she should receive two
(2) doses of a tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine (TT-CV) one
month apart.
- Second dose is given at least two weeks before delivery.
Two (2) doses protect against tetanus infection for 1–3 years
in most people.
- A third dose is recommended six months after the second
dose, which should extend protection to at least five years.
- Two further doses for women who are first vaccinated
against tetanus during pregnancy should be given after the
third dose, in the two subsequent years or during two
subsequent pregnancies.
- If a woman has had 1–4 doses of a TT-CV in the past, she
should receive one dose of a TT-CV during each
subsequent pregnancy to a total of five doses (five doses
protects throughout the childbearing years).
Indication - Tetanus toxoid vaccination is recommended for all pregnant
women depending on previous tetanus vaccination exposure,
to prevent maternal and neonatal mortality from tetanus.
- Prevention against tetanus in children and adults age 7
years and older.
- Tetanus toxoid is indicated for booster injection only for
persons 7 years old of age and older against tetanus.
Contraindication - Past anaphylaxis reaction to the tetanus toxoid
- Hypersensitivity
- Febrile illness and other acute infection
- Patient with low immune response
- Patient with immunoglobulin abnormalities
- Patient with thrombocytopenia or any coagulation disorder
- Neurologic disorders
- History of febrile seizures
Side Effect/Adverse Significant: Syncope.
Effect Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Lymphadenopathy.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea.
General disorders and administration site
conditions: Injection site reactions (e.g. pain, redness,
bruising, swelling, induration), fever, malaise, irritability.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Arthralgia,
myalgia.
Nervous system disorders: Neuritis, headache, dizziness.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash.
Vascular disorders: Hypotension.
Potentially Fatal: Anaphylactoid or hypersensitivity reactions.
Drug Interaction Some products that may interact with this vaccine are drugs
that weaken the immune system including cyclosporine,
tacrolimus, cancer chemotherapy, corticosteroids such
as prednisone, recent/planned vaccinations
(e.g., diphtheria/tetanus toxoids). Chloramphenicol,
corticosteroids, immunosuppressants may impair the
immune response to tetanus toxoid. Avoid concomitant
elective immunization.
Nursing - Observe the 12 rights in giving the medication
Responsibilities - Postpone immunization if patient has acute illnesses.
- Determine the date of last tetanus toxoid
immunization.
- Monitor vital signs
- Allow the patient to lie down to prevent vomiting
- Shake well the vial before withdrawing each dose.
- Monitor patient for hypersensitivity reactions,
seizures, and injection site reactions.
- Educate the patient to increase fluid intake to prevent
dehydration
- It isn’t known whether tetanus toxoid appears in
breast milk. Use cautiously in breast-feeding women.
- Educate patient that pain and tenderness in the
injection site may occur
- Inform patient of possible adverse reactions.
- Encourage patient to report distressing adverse
reactions.
- Instruct to avoid extraneous activities
- Although there’s no evidence of teratogenicity, it’s
recommended that administration be deferred until
second trimester.
- Tell patient that immunization requires a series of
injections. Stress the importance of keeping
scheduled appointments for subsequent doses.
- Inform the patient of the importance of completing the
immunization series, unless a contraindication to
further immunization exists.
Reference
Drugs (2020). Tetanus Toxoid (Adsorbed). Retrieved from
https://www.drugs.com/cdi/tetanus-toxoid-adsorbed.html
FDA (n.d). Tetanus Toxoid – Bio-TT. Retrieved December 2, 2020 from
https://ww2.fda.gov.ph/index.php/consumers-corner/registered-drugs-2/528377-BR-663
Global Library of Women’s Medicine (n.d). Tetanus toxoid, absorbed. Retrieved
December 2, 2020 from
https://www.glowm.com/resources/glowm/cd/pages/drugs/t017.html
Mayo Clinic (2020). Tetanus Toxoid (Intramuscular Route, Injection Route). Retrieved
December 2, 2020 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/tetanus-toxoid-
intramuscular-route-injection-route/description/drg-20066243
Omudhome, O. (2019). Tetanus Toxoid Injection (Tetanus Toxoid Absorbed) Retrieved
December 2, 2020 from https://www.medicinenet.com/tetanus_toxoid-
injection/article.htm
Rabadi, T., Brady M. (2020). Tetanus Toxoid. Retrieved December 2, 2020 from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557415/
WHO (2018). WHO recommendation on tetanus toxoid vaccination for pregnant women.
Retrieved December 9, 2020 from https://extranet.who.int/rhl/topics/preconception-
pregnancy-childbirth-and-postpartum-care/antenatal-care/who-recommendation-
tetanus-toxoid-vaccination-pregnant-women
You might also like
- TetanusDocument2 pagesTetanusmegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersFrom EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Toxoid For Booster Use Only: (Not Recommended For Primary Immunization)Document5 pagesTetanus Toxoid For Booster Use Only: (Not Recommended For Primary Immunization)Ade PurnaNo ratings yet
- AIP BP Tetanus PEPDocument3 pagesAIP BP Tetanus PEPSatrio WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersFrom EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On TetanusDocument2 pagesGuidelines On Tetanusich4_28No ratings yet
- Tetanus Questions Part A-CDocument17 pagesTetanus Questions Part A-CAira CatubayNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Immunization GuidelinesDocument6 pagesTetanus Immunization GuidelinesNataliaMaedyNo ratings yet
- Tetraxim APIDocument2 pagesTetraxim APIFinesse ClassesNo ratings yet
- DIPHTHERIADocument6 pagesDIPHTHERIAblack_knight118No ratings yet
- TetraximDocument5 pagesTetraximkemalahmadNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument18 pagesTetanusRohan TejaNo ratings yet
- Reading - 4 2Document22 pagesReading - 4 2nurdalynarakama1994No ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY TetanustoxoidDocument2 pagesDRUGSTUDY TetanustoxoidMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet TetanusDocument4 pagesFact Sheet TetanusSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Pentaxim-Pi-Sg Pen 0118 Spc0914Document10 pagesPentaxim-Pi-Sg Pen 0118 Spc0914walkrogNo ratings yet
- Tetravac Suspension For Injection ENG SMPCDocument15 pagesTetravac Suspension For Injection ENG SMPCFelix Daniel ParvuNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Acute Communicable Disease Control Manual (B-73) Revision - February 2012Document2 pagesTetanus: Acute Communicable Disease Control Manual (B-73) Revision - February 2012Hisashi Ren MinamotoNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Hepatitis A Maurice HillemanDocument19 pagesIntroduction: Hepatitis A Maurice Hillemanahmed solimanNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine Study Side EffectsDocument1 pageTetanus Toxoid Vaccine Study Side EffectsIrveen Joy Ramirez75% (4)
- Tetanus: Introduced in 1930s (DT) and 1952/3 (DTP) NotifiableDocument8 pagesTetanus: Introduced in 1930s (DT) and 1952/3 (DTP) NotifiableDaphne Ongbit JaritoNo ratings yet
- Contraindications VaccinesDocument19 pagesContraindications VaccinesAbbyFerNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and PreventionDocument4 pagesTetanus Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and PreventionSneha SnehaNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument47 pagesTetanusSyamsul Arifin100% (3)
- Adult ScheduleDocument3 pagesAdult ScheduleerilarchiNo ratings yet
- Boostrix Pi UkDocument1 pageBoostrix Pi Ukdr.haskowskiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAlea Silvera50% (2)
- ImunostimulanDocument47 pagesImunostimulanSyarifa tris hidayantiNo ratings yet
- Immunization TetanusDocument6 pagesImmunization TetanusMaheenKhanNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument5 pagesTetanusales_sandriNo ratings yet
- Ats, TT, Tig: Anti Tetanus Serum, Tetanus Toxoid, Tetanus Immuno-GlobulinDocument15 pagesAts, TT, Tig: Anti Tetanus Serum, Tetanus Toxoid, Tetanus Immuno-Globulinjisoo100% (2)
- DSTetanus ToxoidDocument2 pagesDSTetanus ToxoidAlyssa Jade SandovalNo ratings yet
- Pen TaximDocument5 pagesPen TaximtimvrghsNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument5 pagesBrand NameJunrey AbarcaNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument18 pagesDiphtheriaShishir ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Expanded Immunization Report 1Document54 pagesExpanded Immunization Report 1RIK HAROLD GATPANDAN100% (1)
- Expanded Program On Immunization CHNDocument4 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization CHNgeralynroseNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Verorab Contents: Indication / ActionDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Verorab Contents: Indication / ActionAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Adult Immunization Recommendations SummaryDocument5 pagesAdult Immunization Recommendations SummaryHannah Caburian RemoNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument37 pagesTetanusMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- Nit 21Document3 pagesNit 21Maylanie VergaraNo ratings yet
- Tetanus Case PresentationDocument18 pagesTetanus Case PresentationDesiree Guerra100% (1)
- What Are Rheumatic Heart Disease and Rheumatic Fever?Document4 pagesWhat Are Rheumatic Heart Disease and Rheumatic Fever?Neiqui Aubrey Antaran CañeteNo ratings yet
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument33 pagesAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsVimala BohoNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Inflammation NCLEX ReviewDocument4 pagesImmunology and Inflammation NCLEX ReviewBSN CMUNo ratings yet
- Longer Authorised: Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument39 pagesLonger Authorised: Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsEllaNo ratings yet
- Comvac3 Pres InfoDocument1 pageComvac3 Pres InfoSai SapNo ratings yet
- ATLS-9e Elearn Tetanus.v1 PDFDocument2 pagesATLS-9e Elearn Tetanus.v1 PDFAdolfo Rfael Gomez EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Oet Reading 2.0 Test 2 Solved 1Document23 pagesOet Reading 2.0 Test 2 Solved 1Sanjana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument4 pagesExpanded Program On ImmunizationMac Lester DumagNo ratings yet
- Hexyon LeafletDocument49 pagesHexyon LeafletEllaNo ratings yet
- Tetagam 2146469.PA0800 - 009 - 002..000001product Leaflet Approved.141017Document2 pagesTetagam 2146469.PA0800 - 009 - 002..000001product Leaflet Approved.141017abba,drNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument39 pagesVaccinationhaddi awanNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument40 pagesImmunizationHilyaJae-heeNo ratings yet
- "Expanded Program On Immunization": Angeles University FoundationDocument12 pages"Expanded Program On Immunization": Angeles University FoundationJaillah Reigne CuraNo ratings yet
- Primary Prevention: CDC: Immunization SchedulesDocument4 pagesPrimary Prevention: CDC: Immunization Schedulesjourey08No ratings yet
- Tetanus Immune Globulin (Human) : Hypertet® S/DDocument2 pagesTetanus Immune Globulin (Human) : Hypertet® S/DPuji Arifianti RamadhanyNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsNizz Totanes BercesNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPDocument9 pagesVILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Villahermosa - GDM NCPDocument9 pagesVillahermosa - GDM NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NIFEDIPINEDocument5 pagesNIFEDIPINEJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Tetralogy of FallotDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Tetralogy of FallotJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Villahermosa ReflectionDocument1 pageVillahermosa ReflectionJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP Villahermosa CTSDocument6 pagesNCP Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Reading Villahermosa CTSDocument9 pagesReading Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Epidemiology, StellaDocument32 pagesBreast Cancer Epidemiology, StellaLamchabbek NajouaNo ratings yet
- NHS COVID Pass Vaccination RecordsDocument1 pageNHS COVID Pass Vaccination RecordsSHWE LINo ratings yet
- UDISE 23-24 VV Student Data Fields RequiredDocument33 pagesUDISE 23-24 VV Student Data Fields Requiredjdipti677No ratings yet
- AES Surveillance WHO GuidelinesDocument15 pagesAES Surveillance WHO GuidelinesPrabir Kumar ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea BrochureDocument2 pagesDiarrhea BrochureJessoliver GalvezNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 VirusDocument15 pagesCOVID-19 VirusDr.Hussam HusseinNo ratings yet
- BIOC3364 - 2021 Lecture Notes AsthmaDocument26 pagesBIOC3364 - 2021 Lecture Notes AsthmachrystalNo ratings yet
- Prevalence and Associated Factors of Diabetic Foot at Risk Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Attending Primary Health Clinics in KuantanDocument9 pagesPrevalence and Associated Factors of Diabetic Foot at Risk Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Attending Primary Health Clinics in Kuantanlailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines For The Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk: Supplementary DataDocument18 pages2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines For The Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk: Supplementary DataElena CosminaNo ratings yet
- Implementasi Model Kesehatan Reproduksi Berbasis Masalah Pada Remaja Putri Di Indonesia Tahun 2018Document8 pagesImplementasi Model Kesehatan Reproduksi Berbasis Masalah Pada Remaja Putri Di Indonesia Tahun 2018Jeni Christi LimaheluNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument5 pagesHepatitis BAmple CasaclangNo ratings yet
- IMSLP664696-PMLP1066603-The Dilemma All Clarinet Version-Score and PartsDocument12 pagesIMSLP664696-PMLP1066603-The Dilemma All Clarinet Version-Score and PartsJoseph RouquetteNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pasien Ruangan Rsup Ham Muhammad Qadri RamadhanDocument7 pagesDaftar Pasien Ruangan Rsup Ham Muhammad Qadri RamadhanRama TanjungNo ratings yet
- XXXXX Yyyyy, MPH, MS: Ducation The Ohio State UniversityDocument6 pagesXXXXX Yyyyy, MPH, MS: Ducation The Ohio State UniversityKate TNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Bullous PemphigoidDocument2 pagesA Case Study On Bullous PemphigoidMedtext PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Jihan Rahma Fadillah 46-50Document14 pagesJihan Rahma Fadillah 46-50Hendry RahmanantoNo ratings yet
- USMLE 2020 Recall MR MurphyDocument42 pagesUSMLE 2020 Recall MR MurphyChurschmann Spiral100% (9)
- Frozen Raw Tuna - , Osamu CorporationDocument6 pagesFrozen Raw Tuna - , Osamu CorporationRibka Kristania HadhiwaluyoNo ratings yet
- Data Collection SheetDocument3 pagesData Collection SheetZoila CamiasNo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Inflamatoria IntestinalDocument14 pagesEnfermedad Inflamatoria IntestinalMi5kaNo ratings yet
- IM RheumatologyDocument56 pagesIM RheumatologySujoud AbuserdanehNo ratings yet
- Sunitinib Sarcoma (ImmunoSarc2) - Cancer Research UDocument8 pagesSunitinib Sarcoma (ImmunoSarc2) - Cancer Research UKen HoNo ratings yet
- ChleraDocument26 pagesChleraadelekeyusufNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology: Glossary of Commonly Used Physical Therapy Prefixes and SuffixesDocument26 pagesMedical Terminology: Glossary of Commonly Used Physical Therapy Prefixes and SuffixesAhmed Khaled100% (1)
- 900 World Fact SheetsDocument2 pages900 World Fact SheetsNik rabekNo ratings yet
- An Unforgettable NightmareDocument4 pagesAn Unforgettable NightmareBrian TongNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument7 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyDaren GocoNo ratings yet
- IDSA 2005 and 2016 HAP/VAP Guideline DifferencesDocument13 pagesIDSA 2005 and 2016 HAP/VAP Guideline DifferencesAdeh MahardikaNo ratings yet
- African TrypanosofmesDocument18 pagesAfrican Trypanosofmessafsaf99No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Pregnant Woman at Risk of InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Pregnant Woman at Risk of InfectionJoanne Therese ArbasNo ratings yet