Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 9 Pharma
Uploaded by
Rachelle CambaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 9 Pharma
Uploaded by
Rachelle CambaCopyright:
Available Formats
ARAO, JUAN KARLO
PHARMACOLOGY BSN 2-A-9
OCTOBER 24, 2022
Make a drug study on the individual drugs discussed in this course unit. Type them in word and submit them here.
Search for 2 new drugs for each classification of Respiratory drugs not discussed in this course unit and include them in the drug study.
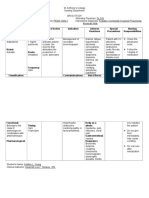
DRUG STUDY
DRUG
DOSAGE
THERAPEUTIC ACTION
ADVERSE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATION
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
Antihistamines
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Diphenhydramine Capsules, tablets: 25 Competes for H1- CNS: Drowsiness, dizziness, headache, Contraindicated in Adjust dose according to
mg, 50 mg. receptor sites on effector fatigue, disturbed coordination, tingling patients hypersensitive to coagulation test results Monitor
cells, thus blocking CV: Palpitation, tachycardia, mild drug as well as in those cardiovascular status especially with
Syrup: 6.25 mg/5 mL, histamine release hypotension with acute asthma, pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
12.5 mg/5 mL Special Senses: Tinnitus, vertigo, dry narrow-angle glaucoma,
nose, throat prostatic hypertrophy, Monitor for adverse effects
Injection: 50 mg/mL GI: Dry mouth, nausea, epigastric bladder neck obstruction especially in children and the older
distress, anorexia, vomiting, constipation and GI obstruction adult.
Urogenital: Urinary frequency or
retention, dysuria. Supervise ambulation and use side-
Body as a Whole: Hypersensitivity, rails as necessary. Drowsiness is
urticaria, photosensitivity, anaphylactic most prominent during the first few
shock). days of therapy and often
Respiratory: Thickened bronchial disappears with continued therapy.
secretions, wheezing, sensation of chest Older adults are especially likely to
tightness manifest dizziness, sedation, and
hypotension
Chlorpheniramine Tablets: 2 mg, 4 mg. Effective antihistamine Body as a Whole: Sensation of chest Contraindicated in Monitor for CNS depression and
reaction resulting in tightness. patients hypersensitive to sedation, especially when
Sustained-release decreasing allergic CV: Palpitation, tachycardia, mild drug as well as in those chlorpheniramine is given in
tablets: 8 mg, 12 mg. symptomatology hypotension or hypertension. with acute asthma, combination with other CNS
Syrup: 2 mg/5 mL GI: Epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, narrow-angle glaucoma, depressants.
vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea. prostatic hypertrophy,
CNS: Drowsiness, sedation, headache, bladder neck obstruction Monitor BP in hypertensive patients
dizziness, vertigo and GI obstruction since chlorpheniramine may elevate
Special Senses: Dryness of mouth, nose, BP.
and throat, tinnitus, vertigo, acute
labyrinthitis, thickened bronchial
secretions, blurred vision, diplopia.
Urogenital: Urinary frequency or
retention, dysuria
Upper Respiratory System
2 new Drugs of Antihistamines
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Hydroxyzine Tablets: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 Tranquilizes CNS: Drowsiness (usuall Contraindicated in patients Evaluate alertness. Drowsiness may occur
mg depression of y transitory), sedation, hypersensitive to drug as well as and usually disappears with continued
hypothalamus and dizziness, headache. in those with psychoses or therapy or following reduction of dosage.
Syrups: 10 mg/5 mL brain-stem reticular CV: Hypotension. depression.
formation, rather GI: Dry mouth. Monitor condition of oral membranes daily
Injection: 25 mg/mL, 50 mg/mL than cortical areas. Body as a when patient is on high dosage of
In addition, it is an Whole: Urticaria, hydroxyzine.
effective agent for dyspnea, chest tightness,
pruritus wheezing, involuntary Reevaluate usefulness of drug periodically.
motor activity (rare).
Reduce dosage of the depressant up to
Hematologic: Phlebitis, 50% when CNS depressants are
hemolysis, thrombosis. prescribed concomitantly
Skin: Erythematous
macular eruptions,
erythema multiforme,
digital gangrene from
inadvertent IV or
intraarterial injection,
injection site reactions.
Promethazine Tablets: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 25 mg Competes with CNS: Akathisia, CNS Contraindicated in patients Monitor patient’s hematologic status as
histamine for H1 - stimulation, confusion, hypersensitive to drug as well as ordered because promethazine may cause
Oral solution: 6.25 mg/5 mL, 10 receptor sites, dizziness in those with prostatic bone marrow depression
mg/5 thereby antagonizing CV: Bradycardia, hypertrophy and bladder neck
many histamine hypertension, obstruction. Tell patient to use a calibrated device to
Solution for injection: 25 mg/mL, 50 effects and reducing hypotension, tachycardia ensure accurate doses of promethazine
mg/mL. allergy signs and EENT: Blurred vision; syrup.
symptoms. diplopia; dry mouth, nose,
Suppositories: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 Urge patient to avoid alcohol and other
and throat; nasal
mg CNS depressants during therapy.
congestion; tinnitus;
vision changes
ENDO: Hyperglycemia
GI: Anorexia, cholestatic
jaundice
HEME: Agranulocytosis,
leukopenia
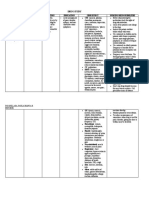
Nasal and Systemic Decongestants
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Pseudoephedrin Tablets: 30 mg, 60 mg. Effective as a nasal Body as a Whole: Transient Contraindicated in patients Take baseline BP and other vital signs
e decongestant. stimulation, tremulousness, hypersensitive to drug as well
Sustained release tablets: 120 difficulty in voiding. as in those with coronary artery Monitor HR and BP, especially in those
mg, 240 mg. CV: Arrhythmias, disease, glaucoma, and with a history of cardiac disease. Report
palpitation, tachycardia. hyperthyroidism. tachycardia or hypertension.
Liquid: 15 mg/5 mL, 30 mg/5 mL. CNS: Nervousness, dizziness
, headache, sleeplessness,
Drops: 7.5 mg/0.8 mL.
numbness of extremities.
GI: Anorexia, dry mouth,
nausea, vomiting.
Ephedrine Capsules: 25 mg. It contracts dilated
CNS: Headache, insomnia, Contraindicated in patients Check BP repeatedly during first 5 min,
arterioles of nasal nervousness hypersensitive to drug as well then q3–5min until stabilized.
Injection: 50 mg/mL. mucosa, thus CV: Palpitation, tachycardia, as in those with pregnancy
reducing precordial pain Monitor I&O ratio and pattern, especially
Nasal spray: 0.25%. engorgement and GU: Difficult or painful in older male patients. Encourage patient
edema and urination, acute urinary to void before taking medication.
Nasal gel: 1%. facilitating retention
ventilation and GI: Nausea, vomiting, Monitor for systemic effects of nose
drainage anorexia. drops that can occur because of
excessive dosage from rapid absorption
Body as a Whole: Sweating,
of drug.
thirst
2 new Drugs of Nasal and Systemic Decongestants
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Oxymethazoline Solution: 0.025%, 0.05% Constricts smaller Special Senses: Burning, stinging, Contraindicated in patients Monitor for S&S of excess use. If
arterioles in nasal dryness of nasal mucosa, sneezing. hypersensitive to drug as well noted, discuss possibility of rebound
passages and has Body as a Whole: Headache, light- as in those with children <2 y. congestion.
prolonged headedness, drowsiness, insomnia,
decongestant palpitations, rebound congestion. Take baseline BP and other vital
effect signs.
Tetrahydrozoline Ophthalmic solution: 0.05% Effective for Special Senses: Transient Contraindicated in patients Monitor patient’s hematologic status
allergic reactions of stinging, irritation, sneezing, dryness hypersensitive to drug as well as ordered Monitor for S&S of excess
Nasal solution: 0.1% the eye and nose. , headache, tremors, drowsiness, as in those with glaucoma or use. If noted, discuss possibility of
light-headedness, insomnia, other serious eye diseases. rebound congestion.
palpitation.
Body as a Whole: With overdose: Take baseline BP and other vital
marked drowsiness, sweating, coma, signs.
hypotension, shock, bradycardia
Expectorants
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Guaifenesin Syrup: 100 mg/5 mL Reduces viscosity CNS: drowsiness, headache, Contraindicated in patients Advise patient to notify health care
of tenacious weakness, depression, hypersensitive to drug as well professional of all Rx or OTC
Oral solution: 100 mg/5 mL secretions by dizziness, fatigue, insomnia, as in those with medications, vitamins, or herbal products
increasing irritability. phenylketonuria. being taken and to consult with health
Capsules: 200 mg respiratory tract EENT: tinnitus. Resp: care professional before taking other
fluid. Mobilization dyspnea. medications, especially cough, cold, or
Tablets: 100 mg, 200 mg and subsequent CV: bradycardia, chest pain, allergy remedies
expectoration of hypotension, palpitations
Extended-release tablets: 600 mg, mucus. Advise patient to notify health care
GI: constipation, dry mouth,
120 professional if dry mouth or constipation
abdominal pain
persists. Frequent mouth rinses, good
oral hygiene, and sugarless gum or candy
may minimize dry mouth
Instruct patient and family on proper
technique for
BP monitoring. Advise them to check BP
at least weekly and to report significant
changes
2 new Drugs of Expectorants
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Potassium Iodide Oral solution: Adults and children. Inhibits release of CNS: Confusion, fatigue, Acute bronchitis, Addison’s Be aware that potassium iodide
50 to 250 mg three times a day for thyroid hormone headache, heaviness or disease, dehydration, heat shouldn’t be given to patients with
10 to 14 days before surgery. into circulation, thus weakness in legs, paresthesia cramps, hyperkalemia, tuberculosis because drug may cause
alleviating CV: Irregular heartbeat hypersensitivity to iodides or pulmonary irritation and increased
Oral: Adults. 50 to 250 mg three symptoms caused EENT: Burning in mouth or their components, secretions.
times a day or 500 mg every 4 hr. by excessive throat, increased salivation, hyperthyroidism, iodism, renal
thyroid hormone metallic taste, sore teeth or impairment, tuberculosis Monitor serum potassium level regularly
Tablets: Adults and adolescents. gums in patients with renal impairment
100 to 150 mg stimulation.
GI: Diarrhea, epigastric pain, because of the risk of hyperkalemia
Potassium iodide
also blocks thyroid indigestion, nausea, vomiting
Tablets: Children age 1 and over. Monitor thyroid function test results
uptake of HEME: Eosinophilia
130 mg periodically to assess drug’s
radioactive iodine MS: Arthralgia
effectiveness.
Tablets: Children under age 1. 65 isotopes released SKIN: Acneiform lesions,
mg as a result of urticaria Advise patient taking potassium iodide
radiation exposure Other: Angioedema, oral solution or syrup to use a calibrated
lymphadenopathy. measuring device to ensure accurate
doses.
Guaifenesin- Tablets: 60mg, 375mg Increases fluid and CNS: Insomnia, headache, Contraindicated in patients with Monitor patient’s reaction to drugs.
pseudoephedrin mucus removal dizziness, and irritability. hypersensitivity to guaifenesin
e from the CV: Tachycardia Monitor vital signs.
upper respiratory EENT: Swelling (tongue. Patients should take care to avoid
tract by increasing Throat) irritants that stimulate their cough.
the GI: Nausea
volume of Urogenital: problems in Do not take more or less of it or take it
secretions and urinating more often than prescribed by your
doctor
reducing their
adhesiveness and
surface tension.
Mucolytic
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Acetylcystein Effervescent tablets: 500 mg, 2.5 g. Liquefies abnormal, CNS: Chills, dizziness, Contraindicated in patients Be aware that it may be necessary to dilute
e thickened, or viscid drowsiness, fever, headache hypersensitive to drug as well 20% inhalation or instillation solution with
Solution for inhalation: 10%, 20% mucus secretions in CV: Edema, hypertension, as in those with respiratory normal saline solution or sterile water
chronic pulmonary hypotension, tachycardia insufficiency, asthma, or when acetylcysteine is used to liquefy
Solution for injection: 20% disorders. EENT: Rhinorrhea, stomatitis, history of bronchospasm secretions.
stridor, tooth damage
GI: Anorexia, constipation, Watch for signs of hepatotoxicity
hepatotoxicity, nausea,
vomiting Assess type, frequency, and
characteristics of patient’s cough.
RESP: Bronchospasm, chest
Particularly note sputum.
tightness, cough.
Monitor patient for tachycardia
Instruct patient to notify prescriber
immediately about nausea, rash, or
vomiting, as well as feeling dizzy or
lightheaded, shortness of breath, or
wheezing
Carbocisteine Syrup: 250mg/5ml Carbocisteine is a Endo: Hypothyroidism Contraindicated in patients Advise the patient to take small, frequent
mucolytic agent for GI: Nausea, vomiting, hypersensitive to the active meals to alleviate some of the GI
the adjunctive diarrhea, gastrointestinal substance; patients with active discomfort associated with these drugs.
therapy of bledding peptic ulceration.
respiratory tract CNS: Headache, dizziness, Advise the patient to avoid driving or
disorders urinary incontinence, performing dangerous tasks if dizziness
characterized by palpitations. and drowsiness occur to prevent
excessive, viscous Resp: Shortness of breath, patient injury.
mucus, including bronchorrhea
chronic obstructive Alert the patient that these drugs may be
Derm: Stevens-Johnsons
airways disease. found in OTC preparations and that care
syndrome, erythema
should be taken to avoid excessive doses.
multiforme
Offer support and encouragement to help
the patient cope with the disease and with
the drug regimen.
2 new Dugs of Mucolytic
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Ambroxol Tablet: 30mg Improvement of GI: Nausea, vomiting, Contraindicated in patients Monitor for S&S of aspiration of excess
mucociliary diarrhoea, dyspepsia, dry hypersensitive to drug as well secretions, and for bronchospasm;
clearance and mouth or throat, abdominal as in those with gastric withhold drug and notify physician
enhancement of pain, heartburn, oral or ulceration immediately if either occur.
fluid secretion pharyngeal hypoaesthesia,
which facilitates Lab test: monitor ABGs, pulmonary
dysgeusia.
expectoration and functions and pulse oximetry as indicated.
eases cough. Derm: Stevens-Johnson
syndrome, toxic epidermal
necrolysis (TEN), erythema Have suction apparatus immediately
multiforme. available. Increased volume of respiratory
Other: anaphylactic reactions tract fluid maybe liberated; suction or
endotracheal aspiration may be
necessary to establish and maintain an
open airway
Report difficulty with clearing the airway
or any other respiratory distress
Dornase Alfa Inhalation; 1 mg/mL solution Hydrolyzes the Respiratory: Hoarseness, sore Contraindicated in patients Monitor for improvement in dyspnea and
DNA in sputum of throat, voice alterations, hypersensitive to drug sputum clearance.
CF patients and pharyngitis, laryngitis, cough,
reduces sputum rhinitis. Monitor for S&S of hypersensitivity.
viscosity. Use of Other: Conjunctivitis, chest Patients with a history of hypersensitivity
dornase pain, rash to bovine pancreatic dornase are at high
significantly risk.
reduces number of
upper respiratory Monitor for adverse effects; rarely,
infections acquired dosage adjustments may be required.
by patients with CF.
Antitussives
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Dextromethorpha Capsules: 30 mg. Controls cough CNS: Dizziness, drowsiness, Contraindicated in patients Take baseline BP and other vital signs
n spasms by CNS depression with very hypersensitive to drug as well
Lozenges: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, depressing cough large doses; excitability, as in those with children <2 y, Monitor for dizziness and drowsiness,
15 mg. center in medulla. especially in children. asthma, productive cough, especially when concurrent therapy with
Temporarily GI: GI upset, constipation, persistent or chronic cough. CNS depressant is used.
Liquid: 10 mg/15 mL, 3.5 mg/5 relieves coughing abdominal discomfort.
mL spasm
Syrup: 15 mg/15 mL, 10 mg/5 mL
2 new Dugs of Antitussives
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Benzonatate Capsules: 100 mg Decreases Body as a Whole: Low incidence. Contraindicated in patients Auscultate lungs anteriorly and
frequency and CNS: Drowsiness, sedation hypersensitive to drug as well posteriorly at scheduled intervals.
intensity of headache, mild dizziness. as in those with pregnancy
nonproductive GI: Constipation, nausea. Observe character and frequency of
cough Skin: Rash, pruritus. coughing and volume and quality of
sputum. Keep physician informed
Codeine Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg Potentiates about CV: Palpitation, hypotension, Contraindicated in patients Record relief of pain and duration of
one-sixth that of orthostatic hypotension, hypersensitive to drug as well analgesia.
Injection: 15 mg/5 mL morphine; bradycardia, tachycardia, as in those with acute asthma.
antitussive activity circulatory collapse. Evaluate effectiveness as cough
is also a little less GI: Nausea, vomiting, constipation. suppressant. Treatment of cough is
than that of CNS: Dizziness, light-headedness, directed toward decreasing frequency
morphine. drowsiness, sedation, lethargy, and intensity of cough without abolishing
euphoria, agitation; restlessness, cough reflex, need to remove bronchial
exhilaration, convulsions, narcosis, secretions.
respiratory depression.
Urogenital: Urinary retention. Supervision of ambulation and use other
safety precautions as warranted since
drug may cause dizziness and light-
headedness.
Monitor for nausea, a common side
effect. Report nausea accompanied by
vomiting. Change to another analgesic
may be warranted
2 new Dugs of Antitussives
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Benzonatate Capsules: 100 mg Decreases Body as a Whole: Low incidence. Contraindicated in patients Auscultate lungs anteriorly and
frequency and CNS: Drowsiness, sedation hypersensitive to drug as well posteriorly at scheduled intervals.
intensity of headache, mild dizziness. as in those with pregnancy
nonproductive GI: Constipation, nausea. Observe character and frequency of
cough Skin: Rash, pruritus. coughing and volume and quality of
sputum. Keep physician informed
Codeine Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg Potentiates about CV: Palpitation, hypotension, Contraindicated in patients Record relief of pain and duration of
one-sixth that of orthostatic hypotension, hypersensitive to drug as well analgesia.
Injection: 15 mg/5 mL morphine; bradycardia, tachycardia, as in those with acute asthma.
antitussive activity circulatory collapse. Evaluate effectiveness as cough
is also a little less GI: Nausea, vomiting, constipation. suppressant. Treatment of cough is
than that of CNS: Dizziness, light-headedness, directed toward decreasing frequency
morphine. drowsiness, sedation, lethargy, and intensity of cough without abolishing
euphoria, agitation; restlessness, cough reflex, need to remove bronchial
exhilaration, convulsions, narcosis, secretions.
respiratory depression.
Urogenital: Urinary retention. Supervision of ambulation and use other
safety precautions as warranted since
drug may cause dizziness and light-
headedness.
Monitor for nausea, a common side
effect. Report nausea accompanied by
vomiting. Change to another analgesic
may be warranted
Lower Respiratory System
Sympathomimetics
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Albuterol Tablets: 2 mg, 4 mg Decreases airway Body as a Whole: Hypersensitivity Contraindicated in patients Monitor therapeutic effectiveness
resistance, reaction. hypersensitive to drug as well which is indicated by significant
Extended-release tablets: 4 facilitates mucus CNS: Tremor, anxiety, nervousness, as in those with pregnancy. subjective improvement in pulmonary
mg, 8 mg. drainage, and restlessness, convulsions, weakness, function within 60–90 min after drug
increases vital headache, hallucinations. administration.
Syrup: 2 mg/5 mL. capacity. CV: Palpitation, hypertension,
hypotension, bradycardia, reflex Monitor for: S&S of fine tremor in
Capsules for inhalation: 200 fingers, which may interfere with
tachycardia.
mcg. precision handwork; CNS stimulation,
Special Senses: Blurred vision, dilated
pupils. particularly in children 2–6 y,
Solution for inhalation (hyperactivity, excitement,
0.083%, 0.5%. GI: Nausea, vomiting.
nervousness, insomnia), tachycardia,
Other: Muscle cramps, hoarseness
GI symptoms.
Consult physician about giving last
albuterol dose several hours before
bedtime, if drug-induced insomnia is
a problem.
Metaproterenol Tablet: 10 mg, 20 mg. Bronchodilator; CNS: Nervousness, weakness, Contraindicated in patients Monitor respiratory status. Auscultate
controls drowsiness, tremor (particularly after hypersensitive to drug as well lungs before and after inhalation to
Syrup: 10 mg/5 mL. bronchospasm in PO administration), headache, fatigue. as in those with cardiac determine efficacy of drug in
asthmatics. CV: Tachycardia, hypertension, cardia arrhythmias associated with decreasing airway resistance.
Metered dose inhaler: 75 mg, c arrest, palpitation. tachycardia, hyperthyroidism
150 GI: Nausea, vomiting, bad taste. and pregnancy. Monitor cardiac status. Report
mg. Urogenital: Occasional difficulty in tachycardia and hypotension.
micturition and muscle cramps.
Solution for inhalation: 0.4%, Monitor Vital signs.
0.6%, 5%. Respiratory: Throat irritation, cough,
exacerbation of asthma.
2 new drugs of Sympathomimetics
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Epinephrine Inhalation: 1:100, 1:1000, Constricts bronchial GI: Nausea, vomiting. Contraindicated in patients Monitor BP, pulse, respirations, and
2.25% arterioles and inhibits CV: Precordial hypersensitive to drug as urinary output and observe patient closely
histamine release, thus pain, palpitations, hypertension, MI well as in those with following IV administration. Epinephrine
Spray: 0.35 mg, 0.2 mg reducing congestion and , tachyarrhythmias narrow-angle glaucoma; may widen pulse pressure. If disturbances
edema and increasing including ventricular fibrillation. hemorrhagic, traumatic, or in cardiac rhythm occur, withhold
Nasal Solution 0.1%, tidal volume and vital RESP: Bronchial and pulmonary cardiogenic shock epinephrine and notify physician
0.5%, 1%, 2% capacity. Relaxes edema. immediately.
uterine smooth Urogenital: Urinary retention.
musculature and inhibits Skin: Tissue necrosis with Keep physician informed of any changes in
uterine contractions. repeated injections. intake-output ratio.
Imitates all actions of Metabolic: Metabolic acidoses,
sympathetic nervous Use cardiac monitor with patients receiving
elevated serum lactic acid,
system except those on epinephrine IV. Have full crash cart
transient elevations of blood
arteries of the face and immediately available.
glucose.
sweat glands.
Nervous System: Altered state of Check BP repeatedly when epinephrine is
perception and thought, psychosis. administered IV during first 5 min, then q3–
5min until stabilized.
Monitor blood glucose & HbA1c for loss of
glycemic control if diabetic
Terbutaline Tablets: 2.5 mg, 5 mg Relieves bronchospasm CNS: Nervousness, Contraindicated in patients Assess vital signs: Baseline pulse and BP
tablets in chronic obstructive tremor, headache, light- hypersensitive to drug as and before each dose. If significantly
pulmonary disease headedness, drowsiness, fatigue, well as in those with altered from baseline level, consult
Aerosol 0.2 mg aerosol (COPD) and significantly seizures. severe hypertension and physician.
increases vital capacity. CV: Tachycardia, hypotension or coronary artery disease.
Injection: 1 mg/mL Promotes relaxation of hypertension, palpitation, maternal Most adverse effects are transient;
injection vascular smooth muscle, and fetal tachycardia. however, rapid heart rate may persist for a
contraction of GI and GI: Nausea, vomiting. relatively long time.
urinary sphincters, Body as a Whole: Sweating,
increase in renin, muscle cramps. Be aware that muscle tremor is a fairly
pancreatic beta-cell common adverse effect that appears to
secretion, and serum subside with continued use.
HDL-cholesterol
concentration. Increases Monitor for symptoms of hypoglycemia in
uterine relaxation neonates born of a mother who used
(thereby preventing or terbutaline during pregnancy.
abolishing high
intrauterine pressure). Monitor patient being treated for premature
labor for CV S&S for 12 h after drug is
discontinued. Report tachycardia promptly.
Monitor I&O ratio. Fluid restriction may be
necessary. Consult physician.
Anticholinergics
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Ipratropium Solution for inhalation: Inhibits acetylcholine Special Senses: Blurred vision Contraindicated in patients Monitor respiratory status;
0.02%. at its receptor sites, (especially if sprayed into eye), hypersensitive to drug auscultate lungs before and after
thereby blocking difficulty in accommodation, acute eye inhalation.
Inhaler: 18 mcg. cholinergic broncho pain, worsening of narrow-angle
motor tone glaucoma. Report treatment failure
Nasal spray: 0.03%, 0.06%. (bronchoconstriction); GI: Bitter taste, dry oropharyngeal (exacerbation of respiratory
also abolishes membranes. With higher doses: symptoms) to physician.
vagally mediated nausea, constipation.
reflex bronchospasm Respiratory: Cough, hoarseness,
triggered by such exacerbation of symptoms, drying of
nonspecific agents as bronchial secretions, mucosal ulcers,
cigarette smoke, inert epistaxis, nasal dryness.
dusts, cold air, and a Skin: Rash, hives.
range of Urogenital: Urinary retention.
inflammatory CNS: Headache
mediators (e.g.,
histamine).
2 new drugs of Anticholinergics
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Tiotropium Dry powder capsules for Prevents CNS: CVA, depression, difficulty Contraindicated in patients Monitor patient’s renal function, as
inhalation: 18 mcg. acetylcholine from speaking, dizziness, insomnia, hypersensitive to drug or in ordered, especially in patients with
attaching to paresthesia those with prostatic moderate to severe renal
Inhalation solution: 1.25 mcg muscarinic CV: Angina, atrial fibrillation, chest hyperplasia and bladder neck impairment, because tiotropium is
receptors on pain, hypercholesterolemia, obstruction excreted mainly by the kidneys.
membranes of hypertension, palpitations
smooth-muscle EENT: Application site irritation, Monitor patient with renal dysfunction
cells. By blocking blurred vision, cataract, dry mouth, closely for anticholinergic effects.
acetylcholine’s dysphonia, epistaxis, eye pain, Monitor patient’s pulmonary function,
effects in the glaucoma as ordered, to evaluate the
bronchi and RESP: Cough, paradoxical effectiveness of tiotropium
bronchioles, bronchospasm, upper respiratory tract
tiotropium relaxes infection Instruct patient on the proper use of
smooth muscles the HandiHaler inhalation device, if
and causes prescribed.
bronchodilation
Tell patient to place the capsule into
the center chamber of the inhalation
device and then to press and release
the button on the side of the
inhalation device to pierce the
capsule
Aclidinium Dry powder metered-dose Acts as an CNS: headache. Contraindicated in patients Instruct patient in proper use of
inhaler: 400 mcg anticholinergic by EENT: worsening of narrow-angle hypersensitive to drug or it inhaler and to take medication as
inhibiting the M3 glaucoma. components. directed. Omit missed doses and
receptor in Resp: paradoxical bronchospasm. take next dose at the usual time; do
bronchial smooth GU: urinary retention not double doses.
muscle, which
causes Advise patient to have a rapid-acting
bronchodilatation. bronchodilator available for use at all
times to treat sudden symptoms.
Notify health care professional
immediately if sudden shortness of
breath occurs immediately after
using aclidinium inhaler
Explain need for pulmonary function
tests prior to and periodically during
therapy to determine effectiveness of
medication
Methylxanthine Derivatives
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Aminophylline Tablets: 100 mg, 200 mg. Respiratory CNS: Nervousness, restlessness, Contraindicated in patients Monitor for S&S of toxicity (generally
smooth muscle depression hypersensitive to drug as well related to theophylline serum levels
Sustained release tablets: relaxant that CV: Cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardia as in those with cardiac over 20 mg/mL).
225 mg. results in (with rapid IV), hyperventilation, chest arrhythmias
bronchodilation. pain, severe hypotension, cardiac Observe patients receiving parenteral
Oral liquid: 105 mg/5 mL. arrest. drug closely for signs of hypotension,
GI: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, arrhythmias, and convulsions until
Injection: 250 mg/10 mL. hematemesis, diarrhea, epigastric serum theophylline stabilizes within
pain. the therapeutic range.
Suppositories: 250 mg, 500
mg. Monitor & record vital signs and I&O.
A sudden, sharp, unexplained rise in
heart rate may indicate toxicity.
Caffeine Tablets: 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 Effective in CV: Tingling of face, flushing, Contraindicated in patients Monitor vital signs closely as large
mg managing neonatal palpitation, tachycardia or bradycardia, hypersensitive to drug as well doses may cause intensification
apnea, and as an ventricular ectopic beats. as in those with acute MI, rather than reversal of severe drug-
Solution: 250 mg/mL adjuvant for pain GI: Nausea, vomiting; epigastric symptomatic cardiac induced depressions.
control in discomfort, gastric irritation arrhythmias, palpitations and
Caffeine citrate injection: 20 headaches and CNS: Nervousness, peptic ulcer Observe children closely following
mg/mL following dural insomnia, restlessness administration as they are more
puncture. Relief of Respiratory: Tachypnea. susceptible than adults to the CNS
headache is Special Senses: Scintillating scotomas, effects of caffeine.
perhaps due to tinnitus.
mild cerebral Urogenital: Increased urination,
vasoconstriction diuresis.
action and
increased vascular
tone. It acts as a
bronchodilator in
asthma and may
improve
psychomotor
performance
through CNS
stimulation
2 new Drugs of Methylxanthine Derivatives
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ACTION ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIO NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
NS
Dyphylline Tablet: 200 mg, 400 mg Drug has bronchodilator effects. CNS: Headache, irritability, Contraindicated in Monitor therapeutic effectiveness;
restlessness, dizziness, insomnia, patients usually occurs at a blood level of at
Elixir: 100 mg/15 mL, light-headedness, muscle hypersensitive to least 12 mcg/mL.
160 mg/15 mL twitching, convulsions. xanthine compounds;
CV: Palpitation, tachycardia, extrasyst apnea in newborns. Take medication consistently with or
Injection: 250 mg/mL oles, flushing, hypotension. Safe use during without food at the same time each
GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pregnancy (category day.
anorexia, epigastric distress. C) or lactation is not
Respiratory: Tachypnea. established. Avoid alcohol and also large amounts
Other: Albuminuria, fever, dehydration of coffee and other xanthine-
containing beverages (e.g., tea,
cocoa, cola) during therapy.
Consult physician before taking OTC
preparations. Many OTC drugs for
coughs, colds, and allergies contain
ephedrine or other sympathomimetics
and xanthines (e.g., caffeine,
theophylline, aminophylline).
Doxofylline Capsule (oral): 300mg There is evidence that doxofylline CNS: Irritability, insomnia, and Contraindicated in Monitor vital signs.
may exert anti-inflammatory headache. patient who have
Solution (oral): 2g actions by reducing the pleurisy CV: Tachycardia heart problems, Doxofylline should not be
induced by the inflammatory GI: Nausea, vomiting, and stomach pregnant, and low administered together with other
Powder for solution mediator platelet activating factor pain blood pressure. xanthine derivatives, including
(Oral): 200mg (PAF) according to a rat study. It beverages and foods containing
is suggested that doxofylline may caffeine.
Injection, solution play an important role in
(IV): 300mg/100ml attenuating leukocyte diapedesis, Daxofylline should be given to a
supported by mouse preclinical pregnant woman only if clearly
studies where doxofylline needed.
administration was associated
with inhibited leukocyte migration Use with caution in patients with
across vascular endothelial cells hypertension, heart disease,
in vivo and in vitro. Unlike hypoxemia, hyperthyroidism, chrome
theophylline, doxofylline does not right ventricular failure, congestive
inhibit tumor necrosis factor- heart failure, liver disease, renal
induced interleukin (IL)- secretion disease, in those with history of
in ASM cells peptic ulcer and in elderly.
Intranasal Glucocorticoids
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Budesonide Inhalation: 32 Inhibit against CNS: Dizziness, emotional lability, facial Contraindicated in patients Monitor closely for S&S of
mcg/inhalation multiple cell types edema, nervousness, headache, agitation, hypersensitive to drug as hypercorticism if concomitant
(e.g., neutrophils, confusion, insomnia, drowsiness. well as in those with ongoing doses of ketoconazole or other
Capsule: 3 mg macrophages) and CV: Chest pain, hypertension, palpitations, lactation. CYP3A4 inhibitors
mediators (e.g., sinus tachycardia.
histamine, GI: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, gastroenteritis Monitor patients with moderate
cytokines) involved Hematologic: Epistaxis. to severe liver disease for
in allergic and Metabolic: Hypokalemia, weight gain. increased S&S of
nonallergic/irritant- Respiratory: Bronchospasms, infections, cough hypercorticism.
mediated , rhinitis, sinusitis, dyspnea, hoarseness,
inflammation.
wheezing.
Urogenital: Intermenstrual bleeding, dysuria
Dexamethasone Tablets: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, Inhibits anti- CNS: Euphoria, insomnia, convulsions, Contraindicated in patients Monitor and report S&S of
0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 inflammatory and increased ICP, vertigo, headache, psychic hypersensitive to drug as Cushing's syndrome or other
mg, 4 mg, 6 mg immunosuppressio disturbances. well as in those with acute systemic adverse effects.
n properties. CV: CHF, hypertension, edema. infections, active or resting
Oral solution: 0.5 mg/5 Endocrine: Menstrual tuberculosis, vaccinia, or Monitor neonates born to a
mL, 0.5 mg/0.5 mg. irregularities, hyperglycemia; cushingoid state; varicella mother who has been receiving
growth suppression in children; hirsutism. a corticosteroid during
Topical aerosol: 0.01%, GI: Peptic ulcer with possible perforation, pregnancy for symptoms of
0.04%. abdominal distension, nausea, increased hypoadrenocorticism.
appetite, heartburn, dyspepsia,
pancreatitis, bowel perforation, oral Monitor for S&S of a
candidiasis. hypersensitivity reaction. The
acetate and sodium phosphate
formulations may contain
bisulfites, parabens, or both;
these inactive ingredients are
allergenic to some individuals
2 new Drugs of Intranasal Glucocorticoids
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Budesonide Inhalation: 32 Inhibit against CNS: Dizziness, emotional lability, facial Contraindicated in patients Monitor closely for S&S of
mcg/inhalation multiple cell types edema, nervousness, headache, agitation, hypersensitive to drug as hypercorticism if concomitant
(e.g., neutrophils, confusion, insomnia, drowsiness. well as in those with ongoing doses of ketoconazole or other
Capsule: 3 mg macrophages) and CV: Chest pain, hypertension, palpitations, lactation. CYP3A4 inhibitors
mediators (e.g., sinus tachycardia.
histamine, GI: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, gastroenteritis Monitor patients with moderate
cytokines) involved Hematologic: Epistaxis. to severe liver disease for
in allergic and Metabolic: Hypokalemia, weight gain. increased S&S of
nonallergic/irritant- hypercorticism.
mediated Respiratory: Bronchospasms, infections, cough
inflammation. , rhinitis, sinusitis, dyspnea, hoarseness,
wheezing.
Urogenital: Intermenstrual bleeding, dysuria
Dexamethasone Tablets: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, Inhibits anti- CNS: Euphoria, insomnia, convulsions, Contraindicated in patients Monitor and report S&S of
0.75 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 inflammatory and increased ICP, vertigo, headache, psychic hypersensitive to drug as Cushing's syndrome or other
mg, 4 mg, 6 mg immunosuppressio disturbances. well as in those with acute systemic adverse effects.
n properties. CV: CHF, hypertension, edema. infections, active or resting
Oral solution: 0.5 mg/5 Endocrine: Menstrual tuberculosis, vaccinia, or Monitor neonates born to a
mL, 0.5 mg/0.5 mg. irregularities, hyperglycemia; cushingoid state; varicella mother who has been receiving
growth suppression in children; hirsutism. a corticosteroid during
Topical aerosol: 0.01%, GI: Peptic ulcer with possible perforation, pregnancy for symptoms of
0.04%. abdominal distension, nausea, increased hypoadrenocorticism.
appetite, heartburn, dyspepsia,
pancreatitis, bowel perforation, oral Monitor for S&S of a
candidiasis. hypersensitivity reaction. The
acetate and sodium phosphate
formulations may contain
bisulfites, parabens, or both;
these inactive ingredients are
allergenic to some individuals
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Zafirlukast Tablets: 10 mg, 20 mg. Inhibits airway edema, Body as a Whole: Generalized pain, asthenia, myalgia, Contraindicated in patients Assess respiratory status and airway
smooth muscle fever, back pain. hypersensitive to drug as well as function regularly.
constriction, and cellular CNS: Headache, dizziness. in those with acute asthma
activity. GI: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, attacks. Monitor closely PT and INR with
dyspepsia; liver dysfunction, increased liver function concurrent warfarin therapy.
tests, hepatic failure.
Other: Churg-Strauss syndrome (fever, muscle aches Monitor closely phenytoin level with
and pains, weight loss). concurrent phenytoin therapy.
Zileuton Tablets: 600 mg. Decreased frequency Body as a Whole: Pain, asthenia, myalgia Contraindicated in patients Assess respiratory status and airway
and severity of acute CNS: Headache, dizziness, insomnia, nervousness, hypersensitive to drug as well as function regularly.
asthma attacks somnolence. in these with active liver disease
CV: Chest pain. Reduce theophylline dose and closely
GI: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, constipation monitor theophylline levels; closely
Skin: Pruritus. monitor PT and INR with warfarin
therapy; closely monitor phenytoin level
Other: Conjunctivitis, hypertonia, lymphadenopathy,
with phenytoin therapy
vaginitis, UTI, leukopenia.
Closely monitor HR and BP for
excessive beta blockade with
propranolol therapy.
Lung Sulfucant
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Beractant Suspension: 25 mg/mL Lowers minimum CV: Transient bradycardia. Contraindicated in patients Monitor heart rate, color, chest
surface tension and Respiratory: Oxygen desaturation. hypersensitive to drug as well as expansion, facial expressions, oximeter,
restores pulmonary Other: Increased probability of posttreatment nosocomial in those with nosocomial and endotracheal tube patency and
compliance and sepsis in surfactant-treated infants was observed in the infections. position, during administration. Most
oxygenation in controlled clinical trials but was not associated with adverse effects occur during dosing.
premature infants increased mortality.
Monitor frequently with arterial or
transcutaneous measurement of
systemic oxygen and CO2.
2 new Drugs of Lung Sulfucant
DRUGS DOSAGE THERAPEUTIC ADVERSE EFFECTS CONTRAINDICATIONS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ACTION
Poractant Vial: 120 mg/1.5 mL, 240 mg/3 mL Alleviates respiratory CV: Bradycardia, hypotension. Contraindicated in patients Stop administration of poractant alfa and
distress syndrome Respiratory: Intratracheal tube blockage, hypersensitive to porcine or take appropriate measures if any of the
(RDS) in premature oxygen desaturation poractant alpha. following occur: Transient episodes of
infants caused by bradycardia, decreased oxygen saturation,
deficiency of surfactant reflux of poractant alfa into endotracheal
tube, or airway obstruction. Dosing may
resume after stabilization.
Do not suction airway for 1 h after poractant
alfa instillation unless there is significant
airway obstruction
Calfactant Suspension: 35mg/mL Effectively relieves and CV: Bradycardia. Contraindicated in patients with Monitor closely during and after
prevents RDS in Respiratory: Cyanosis, airway obstruction, nosocomial infections. administration adjustments in oxygen
neonates reflux of surfactant into endotracheal tube. therapy and ventilator pressures are usually
needed.
This drug will help baby to breathe properly
and support normal respiratory function.
You might also like
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 pagesLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- Benzodiazepines Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines Drug Studyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Book - MOSBY'S DENTAL DRUG REFERENCE PDFDocument1,496 pagesBook - MOSBY'S DENTAL DRUG REFERENCE PDFMohamed Faizal78% (9)
- Test Bank For Pharmacology A Patient Centered Nursing Process Approach 9th EditionDocument16 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology A Patient Centered Nursing Process Approach 9th EditionMichael Pupo73% (15)
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Personality Disorders PDFDocument35 pagesPersonality Disorders PDFABHINAVNo ratings yet
- Pharma Week 1-5Document25 pagesPharma Week 1-5Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- DRUG STUDY LamotrigineDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY LamotrigineP B0% (2)
- Pharmaceuticals Manufacturing - What Do We Know About The Occupational Health and Safety Hazards For Women Working in The Industry PDFDocument61 pagesPharmaceuticals Manufacturing - What Do We Know About The Occupational Health and Safety Hazards For Women Working in The Industry PDFCostas JacovidesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Human and Health Rights in Relation To Sustainable2Document17 pagesHuman and Health Rights in Relation To Sustainable2ptkabworldNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol (ASMALIN)Document2 pagesSalbutamol (ASMALIN)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument2 pagesPhenobarbitalhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- ChlorpromazineDocument3 pagesChlorpromazineMarinel Agulto100% (1)
- IMCI Chart BookletDocument66 pagesIMCI Chart Bookletnorwin_033875No ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- DRUG STUDY OnlyDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY OnlyShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Camba-Course Task 9Document19 pagesCamba-Course Task 9Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine Drug TabulationDocument2 pagesDiphenhydramine Drug TabulationMeriyah EdzyleNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Chemical Effect: CNS: DizzinessDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chemical Effect: CNS: DizzinessGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Ipatropium and SalbutamolDocument5 pagesIpatropium and SalbutamolAndrea Karl PenarandaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- W9 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesW9 PharmacologyEh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-AkinetonDocument2 pagesDrug Study-AkinetonKrizia KrizhNo ratings yet
- Anti PsychotisDocument21 pagesAnti Psychotissuresh sataguniNo ratings yet
- V. Implementation Management A. MedicationsDocument3 pagesV. Implementation Management A. MedicationsSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAlex Silvano0% (1)
- Parales, Danish Stephanie C. BSN 3Y1-2: Her Home Medications Include MonthlyDocument8 pagesParales, Danish Stephanie C. BSN 3Y1-2: Her Home Medications Include MonthlyJanaica Juan0% (1)
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Er Drug Study 1Document3 pagesEr Drug Study 1Rey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationDocument3 pagesClassification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- (Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveDocument4 pages(Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Maam ChitaDocument4 pagesDrug Study Maam ChitaKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Therepeutic RecordDocument23 pagesDrug Therepeutic RecordARFE SILVANONo ratings yet
- Injections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolDocument3 pagesInjections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolthesarayoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument19 pagesEmergency DrugsMean Elepaño50% (2)
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DRDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DRNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand Namemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsDocument7 pagesPharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug-StudyDocument3 pagesTramadol Drug-StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- MeclizineDocument2 pagesMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Hyoscine-N-butylbromide (HNBB)Document1 pageHyoscine-N-butylbromide (HNBB)Kyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MedicationsDocument10 pagesDrug Study Medicationsamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- ClozapineleponexDocument1 pageClozapineleponexAaron Paul RomualdezNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ClonazepamDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY ClonazepamP BNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therepeutic RecorDocument23 pagesDrug Therepeutic RecorARFE SILVANONo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument7 pagesDrug Study FormatHAIDER JULAILINo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Ncma 217 - Week 2Document15 pagesNcma 217 - Week 2Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Camba-Course Task 8Document86 pagesCamba-Course Task 8Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Course TaskDocument13 pagesWeek 7 Course TaskRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- NCMA 217 LEC PRELIM - JHBDocument49 pagesNCMA 217 LEC PRELIM - JHBRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Notes Week 1-5Document8 pagesEthics Notes Week 1-5Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Camba-Course Task 4Document5 pagesCamba-Course Task 4Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Ethics PrelimDocument12 pagesEthics PrelimRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Case StudyDocument39 pagesAsthma Case StudyDimitris TasiouNo ratings yet
- Vaccination BOON or BANEDocument5 pagesVaccination BOON or BANERushil BhandariNo ratings yet
- Kassean & Juwaheer 26Document15 pagesKassean & Juwaheer 26Noush BakerallyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)Document23 pagesLecture 1 Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)A to z type videosNo ratings yet
- J Villanueva Group 2Document22 pagesJ Villanueva Group 2Caryl Jole PaligsaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Relationship Is Between Therapist and Patient and Has Always Been Viewed As SacredDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Relationship Is Between Therapist and Patient and Has Always Been Viewed As Sacredcbargrad100% (1)
- Example of A NHS Risk Rating MatrixDocument2 pagesExample of A NHS Risk Rating MatrixRochady SetiantoNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument4 pagesResumeAaRomalyn F. ValeraNo ratings yet
- Prospectus: 1 ReservationsDocument8 pagesProspectus: 1 ReservationsvarunNo ratings yet
- Resumes For Physical Therapists: Resume Assessment, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesResumes For Physical Therapists: Resume Assessment, Diagnosis and TreatmentSuganya BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Interpretation: LPL - PSC Chandigarh Sector 19-D Booth No:-3, Sector:-19-D ChandigarhDocument5 pagesInterpretation: LPL - PSC Chandigarh Sector 19-D Booth No:-3, Sector:-19-D ChandigarhSanNo ratings yet
- 2018 MUSE Inspire Conference - Show and Tell SessionsDocument13 pages2018 MUSE Inspire Conference - Show and Tell SessionsMichele LambertNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryDocument2 pagesLaparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryNycoNo ratings yet
- Halamang GamotDocument32 pagesHalamang GamotJasmin PastoresNo ratings yet
- Pecial Eature: Transitions in Pharmacy Practice, Part 3: Effecting Change-The Three-Ring CircusDocument7 pagesPecial Eature: Transitions in Pharmacy Practice, Part 3: Effecting Change-The Three-Ring CircusSean BlackmerNo ratings yet
- Hauber 2019Document10 pagesHauber 2019Laura HdaNo ratings yet
- g8 Health q3 LM Disease 130908005904 PDFDocument64 pagesg8 Health q3 LM Disease 130908005904 PDFkenneth cannillNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter 1 V Final Autosaved 2 1Document57 pagesResearch Chapter 1 V Final Autosaved 2 1Mirate JessNo ratings yet
- CWU Psy 3Document8 pagesCWU Psy 3Codillia CheongNo ratings yet
- The Extent of Influence of Factors On Cigarette Smoking Among TeenagersDocument4 pagesThe Extent of Influence of Factors On Cigarette Smoking Among TeenagersLESTHER DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Improving Lives of South Sudanese Communities Through Water and Sanitation: The Story of Salva DutDocument1 pageImproving Lives of South Sudanese Communities Through Water and Sanitation: The Story of Salva DutUNICEF South SudanNo ratings yet
- Aiia Walk in Interview 31072015Document5 pagesAiia Walk in Interview 31072015Kirankumar MutnaliNo ratings yet
- Uti StudiesDocument10 pagesUti Studiesapi-302840362No ratings yet