Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Task Week 7 Fluid Imbalances
Uploaded by
Nathan MielOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Task Week 7 Fluid Imbalances
Uploaded by
Nathan MielCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|17608358
course task week 7 fluid imbalances
Nursing (Our Lady of Fatima University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
CABRERA, SOFIA NADINE
M
1. HYPERVOLEMIA
A patient was admitted in the medical ward with chief complaints of shortness of breath. Further
assessment reveals the following findings:
• BP –140/90 mm Hg
• HR –111 bpm
• RR –24 cpm
• +2 bipedal edema
• Bibasilar crackles upon auscultation
The doctor initially ordered furosemide 20 mg ampule TIV every 8 hours and the following laboratory
tests: Complete Blood Count (CBC), Serum Sodium, Serum Potassium, Blood Urea Nitrogen, Serum
Creatinine, Total Protein, and Chest X-ray.
1. Write down three (3) priority nursing diagnoses for the patient and create a hypothetical
FDAR.
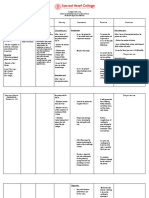
FOCUS DATA ACTION RESPONSE
• Patient was able to
exercise the deep
• Shortness breathing and
• Encourage deep
of breath coughing technique
breathing and
and was relieved
Ineffective Airway • RR of 24 coughing exercises.
from having
Clearance cpm • Maintain semi-
shortness of breath
• HR of 111 Fowler’s position
• Patient was able to
bpm • Monitor HR and RR
maintain a normal
RR of 18cpm and HR
of 90bpm
• Patient has clear
• Weigh client daily. lung sounds as
• Bibasilar
Observe for sudden manifested by the
crackles
weight gain. absence of
upon • Auscultate lung and pulmonary
Excess Fluid Volume auscultation heart sounds crackles.
• +2 bipedal • Elevate edematous • Patient has
edema extremities, and balanced intake and
handle with care output and stable
weight and an
absence of
edema
• BP of • Patient was able to
Hypertension 140/90 • Monitor BP maintain a normal
mmHg BP
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
CABRERA, SOFIA NADINE
M
2. What laboratory test may give the hint to the doctor about the oncotic pressure of the
patient?
➢ The serum creatinine provides a sufficient screen for advanced renal insufficiency, and
the serum albumin permits a useful approximation of the plasma oncotic pressure.
3. Create a drug study for FUROSEMIDE specifying the following:
1. Drug classification
2. Mechanism of action
3. Indication (*for the case of the patient mentioned above)
4. Contraindication
5. Side effects
6. Nursing Considerations
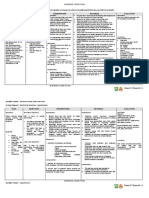
MECHANISM
DRUG INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
OF ACTION
Indicated in
Furosemide
adults for
works by
blocking the the
absorption of treatment
sodium, of edema
chloride, and associated
water from with • Increased
Furosemide congestive urination
the filtered
fluid in the heart • Dehydration • Assess
Generic • Muscle patient fluid
kidney failure, Lasix is
Name: Lasix cramps intake
tubules, cirrhosis of contraindicated in
causing a the liver, patients with • Itching or • Monitor daily
Drug
profound and renal anuria and in rash weight, I & O
Classification:
increase in the disease, patients with • Weakness • Monitor VS
Diuretics
output of including a • Dizziness before and
the history of • Diarrhea after
urine nephrotic hypersensitivity to • Constipatio administering
Dose: 20 mg
(diuresis). The syndrome. furosemide n the
onset of LASIX is • Spinning medication
Frequency: q
action after particularly Sensation
8 hours
oral useful
administration when an
is within one agent with
hour, and the greater
diuresis lasts diuretic
about 6-8
potential is
hours. desired.
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
CABRERA, SOFIA NADINE
M
2. HYPOVOLEMIA
A teenage patient was rushed to the emergency department due to wrist laceration from a suicide
attempt. The patient is lethargic and has the following findings upon assessment:
• BP –80/50 mm Hg
• HR –110 bpm
• RR –25 bpm
The doctor initially ordered fluid resuscitation with PNSS 1L, to fast-drip 200 cc then the remaining fluid
to run for 6 hours. Stat blood typing was ordered, and 3 units of whole blood was ordered to be
transfused immediately after proper cross-matching. The patient was hooked to oxygen 8 liters per
minute via face mask.
1. What parameters will the nurse check while the patient is undergoing rapid fluid
resuscitation?
➢ The adequacy of fluid resuscitation is measured by clinical parameters, not simply by
following a predetermined formula calculation. The recording of vital signs is generally made
hourly but changes in a patient's condition may necessitate more frequent recordings. If a
reaction occurs, the fluids must be stopped immediately, and the reaction noted. Patients
receiving fluid infusions need to have regular checks of their blood pressure, temperature,
pulse, respiration, and mental state.
2. For a patient who will undergo a blood transfusion, enumerate the steps that the nurse should
prudently undertake while performing the procedure.
• Assess the client’s vital signs, physical examination including fluid balance and heart and
lung sounds and any unusual symptoms
• Verify doctor’s order for the number and type of units and the desired speed of
infusion. Note and schedule to administer pre-medication ordered by a physician
(usually 30 minutes prior to transfusion).
• Prepare the patient by introducing self, verifying the client’s identity, explaining the
procedure and its purpose, instructions on what to report by the client during the
procedure, providing privacy, and assisting to a comfortable position.
• If the client has an IV solution infusing, check whether the IV catheter and solution are
appropriate to administer blood.
• Perform hand hygiene and observe appropriate infection prevention procedures.
• Prepare the infusion equipment. Apply gloves and close all the clamps on the Y-set.
Spike into the saline solution and hang the container on the IV pole about 1 meter
above the venipuncture site.
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
CABRERA, SOFIA NADINE
M
• Open the upper clamp on the saline solution tubing and squeeze the drip chamber until
it covers the filter and 1/3 of the drip chamber above the filter. Then prime the tubing
and close both clamps.
• Start the saline solution. If an IV solution incompatible with blood is infusing, stop the
infusion and discard the solution and tubing according to agency policy. Attach the
blood tubing primed with normal saline to the IV catheter. Open the saline and main
flow rate clamps and adjust the flow rate. Use only the main flow rate clamp to adjust
the rate. Allow a small amount of solution to infuse to make sure there are no problems
with the flow or with the venipuncture site.
• Obtain the correct blood component for the client. Check for
• the following:
a. Doctor’s order with the requisition
b. Requisition form and the blood bag label with a laboratory technician
(Client’s name, ID number, blood type and Rh group, blood donor number, and
expiration date) at the blood bank. Observe blood for abnormal color, RBC clumping,
gas bubbles, and extraneous material.
c. With another nurse, verify the doctor’s order, transfusion consent form, client
identification, blood unit identification, blood type, expiration date, compatibility, and
appearance.
d. If any of the information does not match exactly, notify the charge nurse and
the blood bank. Do not administer blood until discrepancies are corrected or clarified.
e. Sign the appropriate form with the other nurse according to agency policy.
f. Make sure that the blood is left at room temperature for no more than 30
minutes before starting the transfusion. Blood must be returned to the blood bank if it
has not been started.
• Prepare the blood bag. Invert the blood bag gently several times to mix the cells with
the plasma. Expose the port on the blood bag and spike the remaining Y-set into the
bag. Hang the bag on the IV pole.
• Establish the blood transfusion. Close the upper clamp below the saline solution and
open the upper clamp below the blood bag. Readjust the flow rate with the main clamp
3. List down three (3) priority nursing diagnoses for the patient and create a hypothetical FDAR.
FOCUS DATA ACTION RESPONSE
• Assess emotional and
psychological factors • The patient was able
Blood loss due to
Fatigue • Provide a quiet place to perform physical
wrist laceration
so the patient can rest activities
well.
• Patient was able to
Hypotension BP of 80/50 mmHg • Monitor BP
maintain a normal
BP
Tachypnea / • RR of 25 • Monitor HR and RR • Patient was able to
Tachycardia cpm maintain a normal RR
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
CABRERA, SOFIA NADINE
M
• HR of 110 of 18cpm and HR of
bpm 90bpm
Downloaded by NATz Miel (natzmiel92@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document12 pagesWeek 7MARIKA BALONDONo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Cu 7Document6 pagesCu 7VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Hyper Vole MiaDocument7 pagesHyper Vole MiaMICHELLE BIANCA PATRICE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Modern Mayr-Medicine & VIVAMAYR-Principle: Good digestion, better lifeFrom EverandModern Mayr-Medicine & VIVAMAYR-Principle: Good digestion, better lifeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan for FeverDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for FeverRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pulmonary Tuberculosisjenypot90% (96)
- Nursing Care Plan for Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Pulmonary TuberculosisLionel Richie Pedraza50% (2)
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3James Francisco GarcesaNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperthermia IBPDocument4 pagesNCP Hyperthermia IBPJohn Patrick CuencoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Cu7Document5 pagesNCMB 312 Cu7Demierish DimaanoNo ratings yet
- طوارئDocument9 pagesطوارئbestmsaasNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument1 pageConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Caro NCPDocument17 pagesCaro NCPAbegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Adenosine 8-28-22Document1 pageAdenosine 8-28-22ladawskiNo ratings yet
- DMMMSU Nursing Drug Study on NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDMMMSU Nursing Drug Study on NorepinephrineNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing and Pharmacology Course Task #4Document3 pagesCommunity Health Nursing and Pharmacology Course Task #4Michelle Angela AlombroNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- NCP & DSDocument4 pagesNCP & DSKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERNDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERNAlgen UbasaNo ratings yet
- NCP For Septicemia - PernitesDocument3 pagesNCP For Septicemia - PernitesFrancis Adrian Lañojan PernitesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term GoalDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term Goalfaker than fakeNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- NCP - Delivery RoomDocument8 pagesNCP - Delivery RoomAUBREY MARIE . GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Abc Case 5Document19 pagesAbc Case 5Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentIrish May SignioNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Fourniers GangreneDocument13 pagesDrugstudy Fourniers GangrenemarinordNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac OutputYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- NCP - NCM 109 High-Risk Mother - CORITANA & ROBLESDocument4 pagesNCP - NCM 109 High-Risk Mother - CORITANA & ROBLESKimberly Almacen RoblesNo ratings yet
- NCP For Tuberculosis.Document7 pagesNCP For Tuberculosis.Kirstie ClaireNo ratings yet
- Society For Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia: OS-MRS Calculator Tools - Farmacologiaclinica.infoDocument1 pageSociety For Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia: OS-MRS Calculator Tools - Farmacologiaclinica.infoHizami Norddin100% (2)
- Tams NCP and DrugDocument5 pagesTams NCP and DrugNicholas Xavier VenturaNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Heart FailuerDocument19 pagesSeminar - Heart Failuermustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- ECART MEDS Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesECART MEDS Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoy AvwenaghaghaNo ratings yet
- Or - Postoperative PhaseDocument10 pagesOr - Postoperative Phase11 - JEMELYN LOTERTENo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Shortness of Breath Possible Evidence by CuesDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Shortness of Breath Possible Evidence by CuesLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument8 pagesCardiologyMa. Kristina Cazandra IbañezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for MedicationsDocument5 pagesNursing Responsibilities for Medicationsしゃいな ふかみNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Fluid Volume DeficitDocument5 pagesAssessing and Treating Fluid Volume DeficitJennifer B. PascualNo ratings yet
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocument1 pageTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (2)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAmple CasaclangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Client with Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Client with Ineffective Breathing PatternPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Criteria Interventio N Rational e Evaluatio N Discharg e Planning Subjective: Short Term: Independe NT Indepen Dent Short Term: MDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Criteria Interventio N Rational e Evaluatio N Discharg e Planning Subjective: Short Term: Independe NT Indepen Dent Short Term: MLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument2 pagesPulmonary EmbolismAnjana BasilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNursing Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Fluid Volume DeficitBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac Failure Nursing CareDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failure Nursing CareSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- ncp tableDocument6 pagesncp tableShivani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Cardiomegaly Patient Mr. BDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan for Cardiomegaly Patient Mr. BWindasariNo ratings yet
- CT Week7Document8 pagesCT Week7Princess Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan:: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/18/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. IsananDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan:: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/18/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. IsananSofia LopezNo ratings yet
- Impaired Electrolytes NCPDocument2 pagesImpaired Electrolytes NCPNora BacolNo ratings yet
- PE Assessment, Care PlanDocument49 pagesPE Assessment, Care PlanBryan BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patients with Respiratory and Fever ConditionsDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patients with Respiratory and Fever ConditionsJhon D.No ratings yet
- FNCPDocument2 pagesFNCPNathan MielNo ratings yet
- HLTH9226 Technology Application Journal - INSTRUCTIONS - S2020Document1 pageHLTH9226 Technology Application Journal - INSTRUCTIONS - S2020Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Assessing the Development of eHealth in the Philippines from 1997 to 2020Document12 pagesAssessing the Development of eHealth in the Philippines from 1997 to 2020Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- E HealthDocument17 pagesE HealthNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Theories of Perception and Recent Empirical WorkDocument223 pagesTheories of Perception and Recent Empirical WorkNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Law & Healthcare Administration HLTH9224 Part2 # 3Document1 pageLaw & Healthcare Administration HLTH9224 Part2 # 3Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- 10.4324 9781315385907 PreviewpdfDocument82 pages10.4324 9781315385907 PreviewpdfNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Guide School Based Mental Health enDocument27 pagesGuide School Based Mental Health enNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Electronic Health Record Journal 4Document1 pageElectronic Health Record Journal 4Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Draft#1Document4 pagesReaction Paper Draft#1Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Management and Resposibilities Ethics Group - NathanDocument2 pagesManagement and Resposibilities Ethics Group - NathanNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Modified Endorsement SheetDocument1 pageModified Endorsement SheetNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Toxic Work Environment and Low Morale HR MGT NathanDocument6 pagesToxic Work Environment and Low Morale HR MGT NathanNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Ethics Journal #2Document2 pagesEthics Journal #2Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Resume RonDocument2 pagesResume RonNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Modified Endorsement SheetDocument1 pageModified Endorsement SheetNathan MielNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosterNathan MielNo ratings yet
- Labor Watch 4Document2 pagesLabor Watch 4Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Logo-Therapy Notes.Document7 pagesLogo-Therapy Notes.Nathan Miel50% (2)
- Biological Theories of AgingDocument33 pagesBiological Theories of AgingRabia100% (2)
- Labor Watch 3Document1 pageLabor Watch 3Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Labor Watch 3Document1 pageLabor Watch 3Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Labor Watch 5Document2 pagesLabor Watch 5Nathan MielNo ratings yet
- Ecg Basic ConceptsDocument18 pagesEcg Basic ConceptsDaniel SolonyaNo ratings yet
- Universal PrecautionDocument10 pagesUniversal PrecautionParth VasaveNo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2021 January 11 1 Inline Supplementary Material 3Document6 pagesBmjopen 2021 January 11 1 Inline Supplementary Material 3Diana AvramNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Tachycardia Storm Management in ADocument6 pagesVentricular Tachycardia Storm Management in Aselandia nisrinaNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR. Dr. Benny E. Wiryadi, SP - KK (K)Document30 pagesProf. DR. Dr. Benny E. Wiryadi, SP - KK (K)Margaretta WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument12 pagesLung CancerАнастасия ОстапенкоNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Injuries: Patrick Nieboer Traumachirurg UMC GroningenDocument40 pagesBone and Joint Injuries: Patrick Nieboer Traumachirurg UMC Groningen童善林No ratings yet
- Journal (10 24 22)Document3 pagesJournal (10 24 22)Louigen DagaydayNo ratings yet
- Informe DEMO Del Holter de Arritmia Contec TLC9803Document14 pagesInforme DEMO Del Holter de Arritmia Contec TLC9803Edward MoralesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS)Document21 pagesClinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS)dannetteNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 NotesDocument8 pagesPhysical Education Class 12 Chapter 3 NotesAanchal Pandey100% (1)
- History TakingDocument4 pagesHistory TakingaliNo ratings yet
- Here Are The Pediatric Nursing BulletsDocument4 pagesHere Are The Pediatric Nursing BulletsMary Janine Joy RimanoNo ratings yet
- 14.4 Cancer ScreeningDocument2 pages14.4 Cancer Screeningvenkat krishnanNo ratings yet
- Bells Palsy Nelsons TextBook of Pediatrics 20th EditionDocument3 pagesBells Palsy Nelsons TextBook of Pediatrics 20th EditionKRIZIA CORRINE CAINGCOY SAN PEDRONo ratings yet
- Niple PainDocument13 pagesNiple PainPUPUT NUGRAHANo ratings yet
- WSAVA 2018 - Proceedings E-BookDocument365 pagesWSAVA 2018 - Proceedings E-BookCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectShivam Shankar AnandNo ratings yet
- Performing Pain AssessmentDocument58 pagesPerforming Pain Assessmentjannaelemento11No ratings yet
- Profil Hasil Pemeriksaan CT-Scan Pada Pasien Tumor Paru Di Bagian Radiologi RSUD Dr. Zainoel Abidin Periode Juli 2018-Oktober 2018Document6 pagesProfil Hasil Pemeriksaan CT-Scan Pada Pasien Tumor Paru Di Bagian Radiologi RSUD Dr. Zainoel Abidin Periode Juli 2018-Oktober 2018Dheana IsmaniarNo ratings yet
- 2442 11241 1 PBDocument6 pages2442 11241 1 PBRemon P SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- 4 Mezil & Abed, 2021 Review - Complication of Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pages4 Mezil & Abed, 2021 Review - Complication of Diabetes Mellitusbangd1f4nNo ratings yet
- Ritas Story Healing Breast Cancer HolisticallyDocument3 pagesRitas Story Healing Breast Cancer HolisticallyMNo ratings yet
- Lectire-Hypoxia 2020Document21 pagesLectire-Hypoxia 2020Bol Dhalbeny Malual100% (1)
- Physical Education Handouts TitleDocument3 pagesPhysical Education Handouts TitletisinikNo ratings yet
- 11 Domestic Violence Detection Amid The COVID-19Document5 pages11 Domestic Violence Detection Amid The COVID-19pequitas1522No ratings yet
- Biliary Tract Cancers: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Document96 pagesBiliary Tract Cancers: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Sabbir RaihanNo ratings yet
- Notes On UtiDocument15 pagesNotes On UtiSaleh Mohammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Experiences Checklist First Findings Nijenhuis Et Al 2002Document30 pagesTraumatic Experiences Checklist First Findings Nijenhuis Et Al 2002EduardusNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAspirin Drug StudyIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)