Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Ex 6
Uploaded by
Joshua DoctorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Ex 6
Uploaded by
Joshua DoctorCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ________________________________________________ Date: _________________
Group No.: _________________
5-Simple-Rules: Print answers CLEARLY and LEGIBLY. Erasures are discouraged. Observe proper grammar and sentence construction. Cheating is
inacceptable. Turn in the Lab Report on or before your schedule ends. (A markdown will be imposed should you fail to comply!)
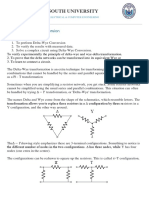
DELTA–TO-WYE (PI–TO–TEE) EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
Objectives:
To become familiar with delta to wye transformation and its usefulness in circuit analysis.
Materials:
Multimeter
Breadboard
10 Resistors (7 of R=10kΩ and 3 of R1=R2=R3=3.3kΩ)
Miscellaneous: wire and hand tools
Procedure:
Part 1. PreLab Calculation
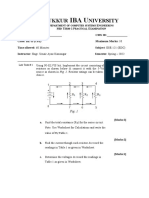
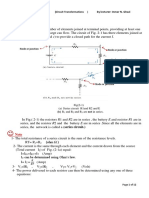
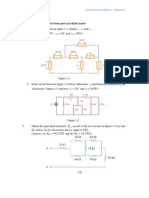
1. Three resistors are connected in a Δ-configuration as shown below in Figure 1. Determine the resistor values for the
equivalent Y-connected circuit. (Show your solution)
Figure 1
2. Solve for the currents i1 and i2 shown in Figures 2 and 3. (Show your solution)
EE 131.1 Laboratory Exercise # 6 AY 2017-2018
Part 2. Delta and Wye Connected Resistors
1. Construct the circuits shown in Figure 1 on your breadboard using resistors of the closest standard value (you can also use
two resistors in series for each of the calculated resistors to get a closer value). Using your multimeter, measure the
resistance between a-b, b-c, and c-a terminals of each configuration and compare the results with the expected/computed
values. Record your results in Table 1.
Delta Configuration Wye Configuration
Measured Calculated Measured Calculated
Ra-b
Ra-c
Rb-c
Table 1
2. Construct the circuits shown in Figures 2 and 3 on your breadboard.
3. Measure the indicated i1 and i2 current values for all the components in the circuit. Record your results in Table 2.
Measured Calculated
(mA) (mA)
i1
i2
Table 2
Questions:
1. Are the circuits between (a) and (d) nodes in Figures 2 and 3 equivalent or not? What is equivalent circuit? (10 pts)
2. What is the benefit of Δ-Y transformation that is used in this experiment? (15 pts)
3. How could you alternatively verify Figure 2 and 3 resistive circuits equivalency between (a) and (d) nodes? (10 pts)
4. What could cause any difference between i1 and i2 currents? Give at least two reasons. (10 pts)
Conclusion: (25 pts)
EE 131.1 Laboratory Exercise # 6 AY 2017-2018
You might also like
- Lab Manual 6Document9 pagesLab Manual 6mughalayeza87No ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersFrom EverandDesign and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersNo ratings yet
- Circut LabDocument46 pagesCircut Labmohammad alaliNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 01: Verification of Star/delta Load Transformation Using Resistive LoadDocument3 pagesExperiment # 01: Verification of Star/delta Load Transformation Using Resistive LoadAbdul MoeezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Edc TheoryDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Edc TheoryUmair AyazNo ratings yet
- Lab #1Document25 pagesLab #1Ryan Shea0% (2)
- Eee141 Lab ManualDocument29 pagesEee141 Lab ManualSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Format ECA4-5Document15 pagesLab Report Format ECA4-5ihassam balochNo ratings yet
- C2 Exp2.1Document8 pagesC2 Exp2.1NicoNo ratings yet
- Lab 02-Equivalent ResistanceDocument5 pagesLab 02-Equivalent ResistanceAbraizNo ratings yet
- North South University: Lab 4: Delta-Wye ConversionDocument6 pagesNorth South University: Lab 4: Delta-Wye ConversionJobayer RahamanNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 4Document4 pagesLab Experiment 4Saad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 3 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document3 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 3 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesLab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsIslam Fathy FaragNo ratings yet
- MIT Electrical Electronics Open Ware 6.002-3 Handout S07015 Homework Hw2Document3 pagesMIT Electrical Electronics Open Ware 6.002-3 Handout S07015 Homework Hw2John Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 4 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document4 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 4 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- Lab 5-Ca-IDocument6 pagesLab 5-Ca-IIram NaseemNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument7 pagesStar DeltagopikrishnaraoNo ratings yet
- DC-Lab Report 04Document8 pagesDC-Lab Report 04Shahriar Ahsan JohaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 10 Verifying Characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ObjectiveDocument10 pagesExperiment No 10 Verifying Characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ObjectiveMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- University Malaysia Perlis: Electric Circuit TheoryDocument7 pagesUniversity Malaysia Perlis: Electric Circuit TheoryRomulo TuiqalauNo ratings yet
- Lab1-Week 3aDocument4 pagesLab1-Week 3apropigismeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws ExperimentallyDocument3 pagesExperiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws ExperimentallyWaseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Exp02v H1Document6 pagesExp02v H1jaswinder singhNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document11 pagesLab 03afnanmirza106No ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument10 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Engineering and Architecturezed cozNo ratings yet
- LAB AssignmentDocument4 pagesLAB AssignmentAlwani IzzatiNo ratings yet
- EEE 4604 Experiment 03Document4 pagesEEE 4604 Experiment 03Tanzina kabir HiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document10 pagesLab 3Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Part A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesPart A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesHAZNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Department Dee 30071 - Electronic Computer Aided DesignDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering Department Dee 30071 - Electronic Computer Aided DesignTharanidaran 23No ratings yet
- Ece 331 Lab Manual Spring 2021Document86 pagesEce 331 Lab Manual Spring 2021haiderNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2MitpdfNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 (3420)Document12 pagesLab 3 (3420)Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Exp#9 Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument9 pagesExp#9 Common Emitter ConfigurationHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- Engr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEngr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveJonathan MischNo ratings yet
- Lab#2 OpAmps 110420 V7Document4 pagesLab#2 OpAmps 110420 V7FrenkiNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgChpvWiQ0xybgPO6 2RIms h5Am0M9y7hi49lkT4mDBNGchtp9 DSJZ Liv4F8H44CbPBa0gJGmvf8aMAD3vd-LY pjvFv5BMFyZutvYKER6ntwax-6faQZw5aSQJEaLp-sICAyxU91C66xDocument8 pagesACFrOgChpvWiQ0xybgPO6 2RIms h5Am0M9y7hi49lkT4mDBNGchtp9 DSJZ Liv4F8H44CbPBa0gJGmvf8aMAD3vd-LY pjvFv5BMFyZutvYKER6ntwax-6faQZw5aSQJEaLp-sICAyxU91C66xJared TeneberNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No 2 CA IDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT No 2 CA Ishafaq.ftNo ratings yet
- Twin T NetworkDocument2 pagesTwin T NetworkVijayalakshmi Prakash100% (1)
- Lab 5: Digital To Analog and Analog To Digital Converter: Telecommunication Electronics Laboratory Exercise 5Document7 pagesLab 5: Digital To Analog and Analog To Digital Converter: Telecommunication Electronics Laboratory Exercise 5Nilesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- American University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesAmerican University of Sharjah Department of Electrical EngineeringNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Lab 11Document14 pagesLab 11Zain AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics DPP PDFJaspreet kaur100% (1)
- Phy 3 MergedDocument22 pagesPhy 3 MergedKiyotaka AyanokōjiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis LabDocument34 pagesCircuit Analysis LabveeraNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1576267955 PDFDocument6 pagesAttachment 1576267955 PDFAhmad RaheelNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet 6Document7 pagesLab Sheet 6Inimatic .SyndromeNo ratings yet
- ECE1250F16 NC Lab3 NodeVDocument5 pagesECE1250F16 NC Lab3 NodeVCarl0217No ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 2 Paper 2 2013Document14 pagesCAPE Unit 2 Paper 2 2013CAPE Past PapersNo ratings yet
- Engr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEngr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveJonathan MischNo ratings yet
- Electrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeDocument7 pagesElectrical Principles (Elp) Time Allowed: 1 Hours: Cems CodeLimNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics and Microcontroller Applications Winter 2019 Answer PaperDocument15 pagesDigital Electronics and Microcontroller Applications Winter 2019 Answer PaperShreyas KingeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Document92 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Qasim LodhiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Kirchhoff's Laws, Mesh and Nodal Analysis - 230103 - 154435Document6 pagesLab 5 - Kirchhoff's Laws, Mesh and Nodal Analysis - 230103 - 154435Mohammed A. ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Lab#2 OpAmps 110921 V1Document5 pagesLab#2 OpAmps 110921 V1FrenkiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2HAMM3TNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 2Document12 pagesالمحاضرة 2Nim Nim GhaziNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Diode CharacteristicsAnas AzamNo ratings yet
- Elex 3Document4 pagesElex 3Joshua DoctorNo ratings yet
- Elex 1Document4 pagesElex 1Joshua DoctorNo ratings yet
- Elex 4Document4 pagesElex 4Joshua DoctorNo ratings yet
- Elex 2Document4 pagesElex 2Joshua DoctorNo ratings yet
- Electronic DevicesDocument21 pagesElectronic DevicesJoshua DoctorNo ratings yet
- SCXI Chassis: Heading NI SCXI-1000, NI SCXI-1000DC, NI SCXI-1001Document3 pagesSCXI Chassis: Heading NI SCXI-1000, NI SCXI-1000DC, NI SCXI-1001hariya03240681No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BCO 2opDocument10 pagesChapter 2 BCO 2opBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Fiber WDM DWDMDocument39 pagesFiber WDM DWDMCat SmithNo ratings yet
- Gprs ModemDocument2 pagesGprs ModemAdityaNo ratings yet
- Survival Craft VHF 2Document7 pagesSurvival Craft VHF 2Kunal SinghNo ratings yet
- 5W Monaural Power Amplifier: Audio Output For TV ApplicationDocument3 pages5W Monaural Power Amplifier: Audio Output For TV ApplicationJose DelmarNo ratings yet
- CommScope - OWN - Solution Overview - Jan2024 - Silknet - GeorgiaDocument44 pagesCommScope - OWN - Solution Overview - Jan2024 - Silknet - GeorgiaratiimiqashavidzeNo ratings yet
- ZA B250 D8P EngDocument6 pagesZA B250 D8P EngSerbanComanNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave RL Circuit With A Free-Wheeling DiodeDocument7 pagesHalf-Wave RL Circuit With A Free-Wheeling Diodehamza abdo mohamoud100% (2)
- On IoT With PythonDocument15 pagesOn IoT With PythonKaustubh KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Mini Project: Electrical Engineering Technology (BELET)Document20 pagesMini Project: Electrical Engineering Technology (BELET)Ahmad hamzaNo ratings yet
- Defining The Loop: - 20 Ma DC Is Coming From DCS or JB Want To Check. ThatDocument3 pagesDefining The Loop: - 20 Ma DC Is Coming From DCS or JB Want To Check. ThatNazeer Ahamad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ec2207 - Digital Electronics Lab ManualDocument83 pagesEc2207 - Digital Electronics Lab ManualasrafalisNo ratings yet
- 555 OscillatorsDocument6 pages555 OscillatorsNelson Naval CabingasNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document8 pagesLab 1Mulugeta AbebawNo ratings yet
- Design Guide For The Packaging of High Speed Electronic CircuitsDocument5 pagesDesign Guide For The Packaging of High Speed Electronic CircuitsNgo van ChungNo ratings yet
- DP Misc 14060 DriversDocument745 pagesDP Misc 14060 Driversberto_716No ratings yet
- Technics SL p999Document58 pagesTechnics SL p999garberer1100% (1)
- V V V V: Tutorial 1 ( Questions 4, 5 and 6 Are From Past Year Final Exams)Document3 pagesV V V V: Tutorial 1 ( Questions 4, 5 and 6 Are From Past Year Final Exams)Mohd RashdanNo ratings yet
- IES CONV Electrical Engineering 2006Document12 pagesIES CONV Electrical Engineering 2006jitenNo ratings yet
- Computer Generations: First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum TubesDocument2 pagesComputer Generations: First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum TubesAbNo ratings yet
- Augmented Spark Gap Igniter For Propellants: Descr Mouser Part NumberDocument3 pagesAugmented Spark Gap Igniter For Propellants: Descr Mouser Part NumberFrançois LeroyNo ratings yet
- Embedded Based Customized Wireless Message Circular System For College, Industries.Document77 pagesEmbedded Based Customized Wireless Message Circular System For College, Industries.Shorya Kaushik33% (3)
- Philips AA5 AADocument6 pagesPhilips AA5 AAКрасимир_КостадиновNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Inrush Current Detection & Harmonic Sharing in Differential Relay ProtectionDocument6 pagesPower Transformer Inrush Current Detection & Harmonic Sharing in Differential Relay ProtectionasrinivasareddyNo ratings yet
- 10bt70405-Embedded and Realtime SystemsDocument1 page10bt70405-Embedded and Realtime SystemstejaNo ratings yet
- Alpha Displa PDFDocument114 pagesAlpha Displa PDFAnonymous 4TfVSnIrnBNo ratings yet
- GD300 Manual PDFDocument328 pagesGD300 Manual PDFMario ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Gate Driver Circuit For Three Phase InverterDocument13 pagesGate Driver Circuit For Three Phase InverterMarc TcheukabaNo ratings yet