Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 3
Uploaded by
Ahmed Razi UllahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 3
Uploaded by
Ahmed Razi UllahCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electrical Engineering
Faculty Member: _______________ Dated: ________________
Semester: _____________ Section: ________________
EE215: ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
Lab 03: IV Characteristics of pn-junctions
PLO4/CLO4 PLO5/CLO5 PLO8/CLO6 PLO9/CLO7
Name Reg. No Viva /Quiz / Analysis Modern Ethics and Individual
Lab of data in Tool Usage Safety and
Performanc Lab Teamwork
e Report 5 marks 5 marks
5 marks
5 marks 5 marks
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 1
Lab 03: IV Characteristics of pn-junctions
Objective: To Study the Characteristics & Applications of Diodes
1. The primary purpose of this lab is to develop a working knowledge of diode. Diodes can
be used in variety of circuits for various applications such as rectifiers, clippers/clampers
and voltage regulators.
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
2. The following components and test equipment is required.
PN Diode (D1N4002 or any other diode of the same family)
Oscilloscope
Function Generator
Resistors (1k)
Capacitors
Power Supply
The Experiment:
3. The experiment is broken down into two exercises. Each exercise has further been
divided into parts. Part I involves the simulation of the circuit on PSpice using Orcad-
Capture module. The second part involves the practical setup of this circuit and making
required measurements, tabulation and its analysis.
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 2
Exercise – I (Part A) [Simulation]
4. The first part of the experiment is to draw a graph of the I-V relationship of a diode using
PSpice; this may be .accomplish by using the DC sweep analysis mode of the
simulation.
Figure-1A_1
Draw the circuit shown in figure 1A_1 on OrCad capture. Please make sure you have
saved the file.
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 3
Since we are analyzing a diode, we would need to draw its I-V characteristic curve. To
do that, we need to simulate our circuit using DC Sweep profile settings.
Change the profile setting as shown in figure 1A_3. Please make sure that you know
what do we mean by DC Sweep and how various value changes would affect the graph
obtained.
You should make sure that the name of the voltage source is V1. If there is a different
name then you should change it accordingly.
Place the current marker/probe at the anode(upper pin) of the diode and run the
simulation.
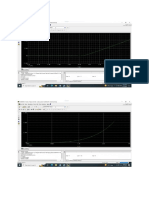
Observe the plot.
Now Change the Values of DC Sweep and enter 0.1 for Start Value.
Repeat the experiment by selecting logrithmic scale. This can be done by simply
selecting the options shown in the given figure 1A_2.
Note: Only change the scale on the X-Axis to log this can be done by pressing the
button with Vertical lines as shown in figure 1A_2.
Use these
to convert
into log
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 4
(Figure 1A_2)
(Figure 1A_3)
Save both graphs and sketch them with explanation. Also, answer the following
questions:
o How can you explain the behavior of the diode by looking at the logarithmic
curve?
o What differences do you observe in the logarithmic curve and linear curve?
Which scale would help you understand the diode behavior better?
Diode resistance is an important parameter of the diode. To observe the change in RD
with reference to increasing voltage, you need to follow the following steps:
o Simulate the circuit given in figure 1A_1 using linear scale DC sweep simulation
profile.
Start Value:0
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 5
End Value:5
Increment:0.2
o After simulation, add trace as shown in the given figure 1A_4:
o Change the X-Axis to VD or V(D1:1)
o Observe the graph obtained
Figure 1A_4
The graph that you had seen so far was between Vin and ID. Now change the x-axis variable
by following the steps as shown in figure 1A_5, figure 1A_6 and figure 1A_7. This would be
ID vs VD curve of the diode. How can you explain the behavior of the diode from this curve?
(Figure 1A_5) – Go to axis settings
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 6
(Figure 1A_6) – Here select the option “Axis Variable”
(Figure 1A_7) – Add V(D1:1) as your x-axis variable
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 7
Answer the following questions
o Spot the threshhold/cut-in voltage of the diode from the I-V characteristic
graph? Do you think it is a silicon based diode or germanium based diode?
Explain your answer.
o Explain the behaviour of RD with respect to VD as observed in the graph drawn.
Exercise – I (Part B) [Implementation]
(Figure 1B_1)
5. This part of the experiment helps the students to set a simple diode circuit and take
measurements for drawing the I-V curves.
Procedure
On a breadboard, setup the circuit given as shown in figure 1B_1.
Apply the input voltage gradually increasing it from 0V and onwards, in steps of 0.2 volts.
Measure and tabulate the values of ID and VD until VD becomes almost constant
Observations/Measurements:
Plot ID vs VD forward characteristics using both linear scale and logarithmic scale. Please
make sure that you use MS Word/excel features for both linear scale and logarithmic
scale plot and include the plot in your lab report. Please follow the lab report format
provided by the instructor.
Determine the threshold voltage of the diode and explain if it is Silicon or Germanium
based diode.
Calculate the values of RD at different input voltages. Plot the graph and explain.
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 8
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 9
EE215: Electronic Devices and Circuits Page 10
You might also like
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Lab 03Document11 pagesLab 03afnanmirza106No ratings yet
- Lab 3 (3420)Document12 pagesLab 3 (3420)Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE215 Lab 7: Zener & Limiter Circuits ApplicationsDocument5 pagesEE215 Lab 7: Zener & Limiter Circuits ApplicationsSher EjazNo ratings yet
- Zener LimiterDocument5 pagesZener LimitersameeNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesLab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsIslam Fathy FaragNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2tarekabdelhalimsedik555No ratings yet
- EE 100 A Microelectronic CircuitsDocument8 pagesEE 100 A Microelectronic CircuitsJohn evergreenNo ratings yet
- ECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingDocument8 pagesECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingAreeba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument29 pagesElectrical Engineering Laboratorybrhanu degeneNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- FSU Electronics PrelabDocument7 pagesFSU Electronics Prelabcamaguey5No ratings yet
- Simulate DC Circuits & Analyze Voltmeter LoadingDocument6 pagesSimulate DC Circuits & Analyze Voltmeter Loadingjaswinder singhNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedDocument15 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedOk BabyNo ratings yet
- KAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Document18 pagesKAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Max TanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Exp 08 Analog DiscoveryOrM2kDocument24 pagesExp 08 Analog DiscoveryOrM2kMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Lab2 DiodesDocument5 pagesLab2 DiodeschilloutbrahNo ratings yet
- Basic Lab Equipment and Circuit MeasurementsDocument14 pagesBasic Lab Equipment and Circuit MeasurementsAsma GulzarNo ratings yet
- ECE20L 2 ACTIVITY 2 Semiconductor DiodesDocument10 pagesECE20L 2 ACTIVITY 2 Semiconductor DiodesDuque Raza - BlexelereyNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 Pre-Lab - Intro To SIMetrixDocument4 pagesExpt 1 Pre-Lab - Intro To SIMetrixCarlo JimenezNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesDocument8 pagesActivity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesskskskskNo ratings yet
- Mymensingh Engineering College: Date of Experiment: 01/09/2020 Submisssion Date: 08/01/2020 SignatureDocument5 pagesMymensingh Engineering College: Date of Experiment: 01/09/2020 Submisssion Date: 08/01/2020 Signature1101 MilonNo ratings yet
- Ece 331 Lab Manual Spring 2021Document86 pagesEce 331 Lab Manual Spring 2021haiderNo ratings yet
- Activity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFDocument7 pagesActivity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFRaymund TanapNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab No.8 (BJT Common Emitter I-V Characteristics)Document5 pagesEDC Lab No.8 (BJT Common Emitter I-V Characteristics)Umair WaqasNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab No.7 (Clamper and Multiplier)Document5 pagesEDC Lab No.7 (Clamper and Multiplier)Umair WaqasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Department Dee 30071 - Electronic Computer Aided DesignDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering Department Dee 30071 - Electronic Computer Aided DesignTharanidaran 23No ratings yet
- l1 f2f PN Junction Characteristics Student Kit Dec2021Document15 pagesl1 f2f PN Junction Characteristics Student Kit Dec2021Jeff HaikalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document5 pagesExperiment 3Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Linear ElectronicsDocument102 pagesLaboratory Manual For Linear ElectronicssamactrangNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document8 pagesReport 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE236 Prelab1Document1 pageEE236 Prelab1bhavikNo ratings yet
- EEE206 Device Lab ManualDocument117 pagesEEE206 Device Lab ManualGiaa RahmanNo ratings yet
- DIAC Characteristic TrainerDocument14 pagesDIAC Characteristic TrainersanNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab1Document13 pagesLCA Lab1Rizwan HanifNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 1Document7 pagesEDC Lab 1Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 4 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document4 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 4 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- C-20 P e Practicle ComletetDocument80 pagesC-20 P e Practicle Comletetamrutha cNo ratings yet
- ECE 202 - Exp 1Document4 pagesECE 202 - Exp 1Nusrat FatemaNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Diodes, LED-s and Diode applicationsDocument4 pagesLab 01 Diodes, LED-s and Diode applicationsKassadiNo ratings yet
- PN Zenernv6501Document47 pagesPN Zenernv6501Madhur Patidar0% (1)
- Experiment 1 Uncontrolled RectifierDocument11 pagesExperiment 1 Uncontrolled RectifierNoel TeporaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Document92 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Qasim LodhiNo ratings yet
- LabInstr EE320L Lab7Document9 pagesLabInstr EE320L Lab7baig79No ratings yet
- EE331 Lab 1 v2Document13 pagesEE331 Lab 1 v2Áo ĐenNo ratings yet
- Digital TrainerDocument9 pagesDigital TrainerChristopher M. MuanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document6 pagesLab 2dueshawn09No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Report RubricDocument10 pagesPower Electronics Lab Report RubricMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- ECD Lab 1Document8 pagesECD Lab 1Rehan BasharatNo ratings yet
- North South University: Lab 4: Delta-Wye ConversionDocument6 pagesNorth South University: Lab 4: Delta-Wye ConversionJobayer RahamanNo ratings yet
- Exp 45Document11 pagesExp 45tanmay sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diode Application Sample Photo Source or Website of PhotoDocument11 pagesSemiconductor Diode Application Sample Photo Source or Website of PhotoRaymund TanapNo ratings yet
- Diode Wave Shaping Circuits: Course - Section: - Name: Signature: - DateDocument15 pagesDiode Wave Shaping Circuits: Course - Section: - Name: Signature: - DateVince AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- BJT Security Alarm CircuitDocument4 pagesBJT Security Alarm CircuitsameeNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab No.9 (BJT ApplicationsTransistor Switches-Security Alarm)Document4 pagesEDC Lab No.9 (BJT ApplicationsTransistor Switches-Security Alarm)Umair WaqasNo ratings yet
- EEE111 - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesEEE111 - Lab ManualAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- Elvis II y MultisimDocument17 pagesElvis II y MultisimHermes PolancoNo ratings yet
- LCS LAB 05 AsfarDocument25 pagesLCS LAB 05 AsfarAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Counters and Shift RegistersDocument8 pagesLab 5 Counters and Shift RegistersAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 DSPBEE13Document17 pagesLab 7 DSPBEE13Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Project DLDDocument14 pagesProject DLDAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document8 pagesReport 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 12-28-2022 16.04Document8 pagesCamScanner 12-28-2022 16.04Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE215 Lab 1: Operation of Electronic InstrumentsDocument15 pagesEE215 Lab 1: Operation of Electronic InstrumentsAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 DSPDocument15 pagesLab 6 DSPAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Ez BikeDocument14 pagesEz BikeAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab-12 EdcDocument5 pagesLab-12 EdcAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE222 Lab 2: Memory, Arithmetic and Logical OperationsDocument7 pagesEE222 Lab 2: Memory, Arithmetic and Logical OperationsAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Report 3Document6 pagesReport 3Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE 222 Assignment No 1Document17 pagesEE 222 Assignment No 1Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Scans PDF DocsDocument9 pagesCamScanner Scans PDF DocsAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab - 3 Pics RaziDocument5 pagesLab - 3 Pics RaziAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Wood Work Pattern Making Basic Workshop PracticeDocument6 pagesWood Work Pattern Making Basic Workshop PracticeAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document9 pagesLab 2Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab8 2-Bit Binary Adder-SubtractorDocument11 pagesLab8 2-Bit Binary Adder-SubtractorAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Machining an Adapter on a LatheDocument2 pagesMachining an Adapter on a LatheAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- EE215 Lab 1: Operation of Electronic InstrumentsDocument15 pagesEE215 Lab 1: Operation of Electronic InstrumentsAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Measuring Technqiue Basic Workshop PracticeDocument5 pagesMeasuring Technqiue Basic Workshop PracticeAhmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Bose - Lifestyle CD-20 - Service ManualDocument96 pagesBose - Lifestyle CD-20 - Service ManualStevenNo ratings yet
- Track Feed ChargerDocument9 pagesTrack Feed ChargertharunNo ratings yet
- Aes3 2003Document29 pagesAes3 2003dj_alekNo ratings yet
- DFT AcronymsDocument4 pagesDFT Acronymspravallika vysyarajuNo ratings yet
- Android 3.1 USB HostDocument20 pagesAndroid 3.1 USB HostBa DanNo ratings yet
- Sony hcd-fc8, fc9 PDFDocument140 pagesSony hcd-fc8, fc9 PDFRaymundo Moran LopezNo ratings yet
- Current Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection DisplaysDocument4 pagesCurrent Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection Displaysgangwar_neeteshNo ratings yet
- 4V Drive PCH MOSFET: RRH090P03Document6 pages4V Drive PCH MOSFET: RRH090P03MoisesNo ratings yet
- 1.USB-CAN Bus Interface Adapter & CANalyst-II Analyzer ManualDocument32 pages1.USB-CAN Bus Interface Adapter & CANalyst-II Analyzer ManualTariqMaqsood75% (4)
- Conectores Amphenol PTDocument54 pagesConectores Amphenol PTMario FabrisNo ratings yet
- Control appliances via SMS with Arduino and GSM moduleDocument4 pagesControl appliances via SMS with Arduino and GSM moduleGopinathManoharanNo ratings yet
- p80c51bh IntelDocument21 pagesp80c51bh Intelyash_pachauryNo ratings yet
- 1979 IC MasterDocument2,398 pages1979 IC MasterIliuta JohnNo ratings yet
- User Manual WINOXLR 3-6-14 ProductsDocument59 pagesUser Manual WINOXLR 3-6-14 ProductslotNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Communications: Abhijit Bhowmick Sense VIT, Vellore, TN, IndiaDocument38 pagesWireless and Mobile Communications: Abhijit Bhowmick Sense VIT, Vellore, TN, IndiaBharghav RoyNo ratings yet
- Yamaha rx-v677 htr-6067 Rx-A740 SMDocument171 pagesYamaha rx-v677 htr-6067 Rx-A740 SMsteel biteNo ratings yet
- Niton XL2 - 800Document2 pagesNiton XL2 - 800Kandula RajuNo ratings yet
- CCM PFC Controller IC for High Power Efficiency AppsDocument2 pagesCCM PFC Controller IC for High Power Efficiency AppsAntonio Dalio67% (3)
- ScriptDocument5 pagesScriptGhiffar Hidathe JirhochosenseiNo ratings yet
- Aten General Catalogue 09Document94 pagesAten General Catalogue 09microsyscom2No ratings yet
- Brochure SVC Light The Next GenerationDocument12 pagesBrochure SVC Light The Next Generationnabg1991No ratings yet
- SX-4000+XSP-1000 Brochure (Eng) - PreviewDocument6 pagesSX-4000+XSP-1000 Brochure (Eng) - PreviewLiang ChengNo ratings yet
- Krbkna22s0000129 UpsDocument31 pagesKrbkna22s0000129 UpsSompon ModekamNo ratings yet
- Multipath & Fading EffectsDocument6 pagesMultipath & Fading EffectsmbcgoudarNo ratings yet
- Electronics DC Plugs & JacksDocument2 pagesElectronics DC Plugs & JacksWaseem ArshadNo ratings yet
- Automatic Door Opener With PIC12C508Document3 pagesAutomatic Door Opener With PIC12C508Victoryback BackNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Determine Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of Potential Apparatus RequiredDocument6 pagesAIM: To Determine Resistance Per CM of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph of Potential Apparatus RequiredMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Acer Aspire 1710Document118 pagesService Manual Acer Aspire 1710Quique FerNo ratings yet
- YD2025H 2.4W Stereo Audio AmplifierDocument4 pagesYD2025H 2.4W Stereo Audio AmplifierMarceloNo ratings yet