Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 3
Uploaded by
Qurat AinniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 3
Uploaded by
Qurat AinniCopyright:
Available Formats
Section & group no.: ________________ Roll No.
:________________
EE216:Electronic Devices & Circuits
Experiment 3
Objectives
To build a full-wave rectifier and measure its various characteristics.
Components required
4 x 1N4007 diodes, 2.2 Ω and 10 KΩ resistors, 220/24 VAC transformer.
Abbreviations
DSO: Digital Storage Oscilloscope
DMM: Digital Multimeter
NOTES
Keep all connections as short as possible.
Before applying DC power supplies to the circuit make sure that they are all set to
zero volts.
Switch off the power supplies before making any change in the circuit.
Always measure a resistor “out of circuit”
Use a pencil to draw all the graphs.
Don’t touch the transformer while it is powered ON.
Show the transformer connections to the lab instructor before powering ON.
Wrong connections may short circuit the secondary of the transformer
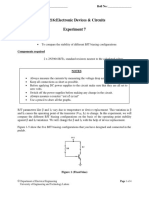
1- Connect a full-wave bridge rectifier with RL = 10 KΩ as shown in Figure 1. Supply the
input from the 220/24 VAC transformer. Don’t use the center-tap of the transformer. Find
C1so that the ripple amplitude is not more than 10% of the input peak voltage.
C1 = _______
© Department of Electrical Engineering Page 1 of 5
University of Engineering and Technology Lahore
Section & group no.: ________________ Roll No.:________________
Figure 1
2- Observe Vout on DSO and plot it below. Label all voltage levels.
Horizontal: __________/div. Vertical: ___________/div.
3- Measure the ripple peak-to-peak amplitude:
VR(pk-pk)(calc.) :______________ VR(pk-pk)(meas.) :______________
4- Now observe the voltage across the diode on the DSO and plot it below. Label all voltage
levels.
Horizontal: __________/div. Vertical: ___________/div.
© Department of Electrical Engineering Page 2 of 5
University of Engineering and Technology Lahore
Section & group no.: ________________ Roll No.:________________
5- Measure the peak negative voltage across the diode using DSO.
VD(-ve pk.)(calc.) :______________ VD(-ve pk.)(meas.) :______________
6- Now insert a 2.2 Ω resistor in series with the any one of the 4 diodes. Observe the voltage
across the 2.2 Ω resistor and plot it below. Label all voltage levels.
Horizontal: __________/div. Vertical: ___________/div.
7- Using the observation in the previous step, measure the peak current through the diode
ID(pk.)(calc.) :________________ ID(pk.)(meas.) :______________
© Department of Electrical Engineering Page 3 of 5
University of Engineering and Technology Lahore
Section & group no.: ________________ Roll No.:________________
8- Assuming that the waveform across the 2.2 Ω resistor is a perfect triangle, calculate the
average current through the diode. Show your calculation below:
ID(av.)(calc.) :________________
9- Using a DMM measure the average voltage across the 2.2 Ω resistor. Use this
measurement to find the average diode current.
ID(av.)(meas.) :________________
10- Remove 2.2 Ω resistor. Remove the Capacitor. Observe Vout on DSO and plot it below.
Label all voltage levels.
Horizontal: __________/div. Vertical: ___________/div.
11- Using a DMM measure the average Vout.
Vout(av.)(calc.) :________________ Vout(av.)(meas.) :______________
© Department of Electrical Engineering Page 4 of 5
University of Engineering and Technology Lahore
Section & group no.: ________________ Roll No.:________________
12- Find all the above values by simulating the circuit of Figure 1. Use the following model
for the diode.
.MODEL D1n4007 d
+IS=7.02767e-09 RS=0.0341512 N=1.80803 EG=1.05743
+XTI=5 BV=1000 IBV=5e-08 CJO=1e-11
+VJ=0.7 M=0.5 FC=0.5 TT=1e-07
+KF=0 AF=1
13- Save all the simulation results in a laptop, one per group. Bring it with you in the next lab
session for viva.
© Department of Electrical Engineering Page 5 of 5
University of Engineering and Technology Lahore
You might also like
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- KAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Document18 pagesKAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Max TanNo ratings yet
- Zener LimiterDocument5 pagesZener LimitersameeNo ratings yet
- EE331 Lab 1 v2Document13 pagesEE331 Lab 1 v2Áo ĐenNo ratings yet
- Diode As RectifiersDocument13 pagesDiode As RectifiersShahZaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- EDC Manual 2016Document138 pagesEDC Manual 2016AmbikaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesLab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsFasil EndalamawNo ratings yet
- Voltage Divider Bias Stability for BJTsDocument13 pagesVoltage Divider Bias Stability for BJTsroden fabregasNo ratings yet
- Circuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesDocument8 pagesCircuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesCesar Santiago Bolaño SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lab#11 EEDocument16 pagesLab#11 EEJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- ECD Lab 2 PDFDocument12 pagesECD Lab 2 PDFMaryam MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesLab Report 1: Diode I-V CharacteristicsIslam Fathy FaragNo ratings yet
- ECE3710 Lab 1: Resistors and Basic Resistive CircuitsDocument6 pagesECE3710 Lab 1: Resistors and Basic Resistive CircuitsParker Santo DomingoNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesDocument8 pagesActivity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesskskskskNo ratings yet
- Workshop 02Document5 pagesWorkshop 02Damith ErangaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document10 pagesLab 3Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document11 pagesLab 03afnanmirza106No ratings yet
- ENT 162 Analog Electronics Lab ReportDocument12 pagesENT 162 Analog Electronics Lab ReportJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Lab #2 - DiodesDocument16 pagesLab #2 - DiodescrackintheshatNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Design RecordDocument5 pagesAmplifier Design RecordEdgarNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument7 pagesDC CircuitsAmeer Bakry ZulkiffliNo ratings yet
- EDC Exp1-4Document16 pagesEDC Exp1-4manojNo ratings yet
- EE-212 Lab Report: Introduction to Basic Electronics EquipmentDocument24 pagesEE-212 Lab Report: Introduction to Basic Electronics EquipmentFazaila ImranNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocument11 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Laboratory ManualrabiasamadNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocument10 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Laboratory ManualrabiasamadNo ratings yet
- A Manual To A LabDocument6 pagesA Manual To A Lab1d22No ratings yet
- Lab 3 (3420)Document12 pagesLab 3 (3420)Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Elvis II y MultisimDocument17 pagesElvis II y MultisimHermes PolancoNo ratings yet
- Lab1 DiodesDocument4 pagesLab1 DiodesDavid TandjayaNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab I ManualsDocument101 pagesEDC Lab I ManualskattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument34 pagesBasic ElectronicsAdnan Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Series AC CircuitsDocument4 pagesLab 6 Series AC CircuitsRaquel Jimena Rey PradaNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 4Document15 pagesEDC Lab 4i222200 Muhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- ECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingDocument8 pagesECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingAreeba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Activity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFDocument7 pagesActivity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFRaymund TanapNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab ManualDocument81 pagesECE Lab Manualumaranitg2188No ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document6 pagesLab Report 1morelight302No ratings yet
- Exp#9 Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument9 pagesExp#9 Common Emitter ConfigurationHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics LabDocument59 pagesApplied Physics LabEngr Waqas MalikNo ratings yet
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuit Applications Lab GuideDocument11 pagesDiode Circuit Applications Lab GuideSonDinhQuangNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedDocument11 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedShabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportMy SunNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics PracticalDocument9 pagesBasic Electronics Practicalasfadare100% (2)
- Lab 4 (To Plot V-I Curve of Zener Diode and Use It As Zener Limiter)Document5 pagesLab 4 (To Plot V-I Curve of Zener Diode and Use It As Zener Limiter)afaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- ECEM312 Electronics 1 Lab Diode and LED CharacterizationDocument46 pagesECEM312 Electronics 1 Lab Diode and LED CharacterizationDanilyn Padillo LucioNo ratings yet
- Activity On DC Power Supply Circuits PDFDocument8 pagesActivity On DC Power Supply Circuits PDFRaymund TanapNo ratings yet
- PElabmanual (Fall 2022)Document32 pagesPElabmanual (Fall 2022)Qurat Ul AinNo ratings yet
- EE1071 - Lab ManualDocument26 pagesEE1071 - Lab ManualRogsNo ratings yet
- Course: Electronic Circuit Devices Lab No: 05 Title: Single Stage Common Emitter Amplifier Design CID: - DateDocument6 pagesCourse: Electronic Circuit Devices Lab No: 05 Title: Single Stage Common Emitter Amplifier Design CID: - DateAamir ChohanNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab No.8 (BJT Common Emitter I-V Characteristics)Document5 pagesEDC Lab No.8 (BJT Common Emitter I-V Characteristics)Umair WaqasNo ratings yet
- V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode and its Application as Zener LimiterDocument4 pagesV-I Characteristics of Zener Diode and its Application as Zener LimiterShahZaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- Lab - 07 14ME - Sec ADocument4 pagesLab - 07 14ME - Sec AKhanSaadNo ratings yet
- ELEC30x0 Lab8Document6 pagesELEC30x0 Lab8Lûtwàmä JôëNo ratings yet
- ECE110S E F - S: Laboratory InstructionsDocument34 pagesECE110S E F - S: Laboratory InstructionsJonathan LeungNo ratings yet
- ELEC ENG 2EI5 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits I Final Exam SolutionsDocument7 pagesELEC ENG 2EI5 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits I Final Exam SolutionsSonDinhQuangNo ratings yet
- Lab MACE 10492-1 - N3Document10 pagesLab MACE 10492-1 - N3Ng Hui MingNo ratings yet
- Digital TrainerDocument9 pagesDigital TrainerChristopher M. MuanNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Experiment7 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment7 PDFQurat AinniNo ratings yet
- EDC Lectures 1,2Document14 pagesEDC Lectures 1,2Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document4 pagesExperiment 6Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document5 pagesExperiment 9Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document4 pagesExperiment 8Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- EE216:Electronic Devices & Circuits Experiment 4: Section & Group No.: - Roll No.Document2 pagesEE216:Electronic Devices & Circuits Experiment 4: Section & Group No.: - Roll No.Rehan bhattiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document3 pagesExperiment 5Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document3 pagesExperiment 1Qurat AinniNo ratings yet
- PI044H - Technical Data Sheet Winding 05Document7 pagesPI044H - Technical Data Sheet Winding 05juan echeverryNo ratings yet
- Curvas de Diparo de FusiblesDocument1 pageCurvas de Diparo de FusiblesFlaKo Man La AmeNazaNo ratings yet
- LGB-19DZT User ManualDocument66 pagesLGB-19DZT User Manualshaft22No ratings yet
- iF25/S iF15/S: Instruction ManualDocument48 pagesiF25/S iF15/S: Instruction ManualuserNo ratings yet
- CTRD-CS6621 User V 2.4Document69 pagesCTRD-CS6621 User V 2.4Didik Istio HartonoNo ratings yet
- Canon CXDI-31 X-Ray - Service Manual PDFDocument209 pagesCanon CXDI-31 X-Ray - Service Manual PDFTony Nava0% (1)
- Unit 10 - Week 7: Assignment 7Document9 pagesUnit 10 - Week 7: Assignment 7venkatNo ratings yet
- CAN ULC-S301-M88 Standard For Central and Monitoring Station Burglar Alarm SystemsDocument31 pagesCAN ULC-S301-M88 Standard For Central and Monitoring Station Burglar Alarm SystemsdenizNo ratings yet
- L70-BRA7 P5 (ICT Pulse)Document2 pagesL70-BRA7 P5 (ICT Pulse)Victor Rodriguez RIverosNo ratings yet
- Tahseen Team Apple Glossary Part 1Document13 pagesTahseen Team Apple Glossary Part 1Abdulrahman AlabdanNo ratings yet
- Micno KE300 User Manual V2.0Document171 pagesMicno KE300 User Manual V2.0Danny Espinoza Castro89% (9)
- Coaxial Cable (Noise Immunity) HuhuDocument10 pagesCoaxial Cable (Noise Immunity) HuhuMohd Izzat Abd GhaniNo ratings yet
- File K3G450PB2405 248272 Datasheet ENGDocument7 pagesFile K3G450PB2405 248272 Datasheet ENGHùng Hồ XuânNo ratings yet
- hcf4060 PDFDocument10 pageshcf4060 PDFdzaki55No ratings yet
- Electric: For Dummies Everything Need KnowDocument2 pagesElectric: For Dummies Everything Need KnowDhanraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Psi 2017 Catalog TXT 1 1Document408 pagesPsi 2017 Catalog TXT 1 1Hector SotoNo ratings yet
- Voss 232 38104 - SuspensionPart - Katalog - Gesamt KomprimiertDocument320 pagesVoss 232 38104 - SuspensionPart - Katalog - Gesamt KomprimiertMatt NagyNo ratings yet
- SKF Blohm+Voss Shaft SIMPLAN SealsDocument4 pagesSKF Blohm+Voss Shaft SIMPLAN SealsMarlon Alejandro Arboleda TapiaNo ratings yet
- FusionServer++X6000+V6+High Density+Server+DatasheetDocument5 pagesFusionServer++X6000+V6+High Density+Server+Datasheetsetyo210391No ratings yet
- Staubli Jacquard Parts and Bonas Systems ComponentsDocument6 pagesStaubli Jacquard Parts and Bonas Systems ComponentsReparacell CelularesNo ratings yet
- (AD - DIESEL) - (24-01-2020) : Parts ListDocument16 pages(AD - DIESEL) - (24-01-2020) : Parts ListVyacheslav ShatalovNo ratings yet
- Compressor Nebulizer NE-C29: Instruction ManualDocument23 pagesCompressor Nebulizer NE-C29: Instruction ManualAsiez VanBahdimNo ratings yet
- 56 143 5TC Coupler Brake Installation Service InstructionsDocument4 pages56 143 5TC Coupler Brake Installation Service InstructionsIvan PachecoNo ratings yet
- 0288194 - B02 (19010185《NICE3000new电梯一...Document320 pages0288194 - B02 (19010185《NICE3000new电梯一...Le Huynh LongNo ratings yet
- The Superbolt Tool: Work Smarter. Not HarderDocument4 pagesThe Superbolt Tool: Work Smarter. Not HarderNestor VeraNo ratings yet
- LC1D4011 Telemecanique LC1-D40-11 Contactor ReplacementDocument1 pageLC1D4011 Telemecanique LC1-D40-11 Contactor ReplacementBobNo ratings yet
- Electrical Schemati Iw55/110btd Punch&shear Hyd DurmaDocument12 pagesElectrical Schemati Iw55/110btd Punch&shear Hyd DurmaÁLVARO IVÁN SANDOVAL TARAZONANo ratings yet
- D180 CRAWLER DOZER WORKSHOP MANUALDocument261 pagesD180 CRAWLER DOZER WORKSHOP MANUALelshind100% (1)
- Powercommand 2.3 Control System: Specification SheetDocument7 pagesPowercommand 2.3 Control System: Specification SheetJoseLunaNo ratings yet
- Quikspray Carrousel Electric PartsDocument5 pagesQuikspray Carrousel Electric Partsnathan.jennerNo ratings yet