Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DIAC Characteristic Trainer
Uploaded by
sanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DIAC Characteristic Trainer
Uploaded by
sanCopyright:
Available Formats
DIAC Characteristic Trainer
NV6531
Learning Material
Ver 1.1
141-B, Electronic Complex,
Pardeshipura, Indore- 452 010 India
Tel.: 91-731- 4211500
Toll-free:1800-103-5050
Email: info@nvistech.com
Website: www.nvistech.com
NV6531
DIAC Characteristic Trainer
NV6531
Table of Contents
1. Introduction 3
2. Features 4
3. Technical Specifications 5
4. Theory 6
5. Experiment 9
To study the VI Characteristic of DIAC with positive biasing and plot the
curve between V & I.
6. Warranty 13
7. List of Accessories 14
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 2
NV6531
Introduction
“NV6531 DIAC Characteristic Trainer” is remarkable and frequently used laboratory
equipment which is designed to explain basic fundamentals of DIAC and their
working. Using this Trainer student can understand the basic concept of DIAC which
is a basic part of Power Electronics. A VI Characteristic can be drawn by the student
which helps students to understand the behaviour of DIAC.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 3
NV6531
Features
A low cost trainer demonstrating VI Characteristic of DIAC.
Exclusive presentation and easy illustration.
Provided with inbuilt Power supply of +35V & -35V.
DPM Based Highly preceised Voltmeter & Ammeter.
Learning Material CD
2 year warranty
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 4
NV6531
Technical Specification
Mains Supply : 230 V AC ±10%, 50 Hz
Power Supply Output : +35V DC (250 mA)
-35V DC (250 mA)
Voltmeter : 0-35V (max.)
Ammeter : 0-50mA (max.)
Dimensions (mm) : 345×240×110
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 5
NV6531
Theory
Power Electronics:
Introduction:
Power electronic converters can be found wherever there is a need to modify the
electrical energy form (i.e modify its voltage, current or frequency). Therefore, their
power range from some milliwatts (as in a mobile phone) to hundreds of megawatts
(e.g in a HVDC transmission system). With "classical" electronics, electrical currents
and voltage are used to carry information, whereas with power electronics, they carry
power.
The first very high power electronic devices were mercury arc valves. In modern
systems the conversion is performed with semiconductor switching devices such as
diodes, thyristors and transistors. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with
transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial
amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC converter (rectifier) is the
most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices,
e.g., television sets, personal computers, battery chargers, etc. The power range is
typically from tens of watts to several hundred watts. In industry the most common
application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction
motor. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of
megawatts.
The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and
output power
AC to DC (rectification)
DC to AC (inversion)
DC to DC (chopping)
AC to AC
Principle:
As efficiency is at a premium in a power electronic converter, the losses that a power
electronic device generates should be as low as possible. The instantaneous dissipated
power of a device is equal to the product of the voltage across the device and the
current through it (P = VI). From this, one can see that the losses of a power device
are at a minimum when the voltage across it is zero (the device is in the On-State) or
when no current flows through it (Off-State). Therefore, a power electronic converter
is built around one (or more) device operating in switching mode (either On or Off).
With such a structure, the energy is transferred from the input of the converter to its
output by bursts.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 6
NV6531
Applications:
Power electronic systems are virtually in every electronic device. For example,
around us:
DC/DC converters are used in most mobile devices (mobile phone, pda.) to
maintain the voltage at a fixed value whatever the charge level of the battery
is. These converters are also used for electronic isolation and power factor
correction.
AC/DC converters (rectifiers) are used every time an electronic device is
connected to the mains (computer, television,...)
AC/AC converters are used to change either the voltage level or the frequency
(international power adapters, light dimmer). In power distribution networks
AC/AC converters may be used to exchange power between utility frequency
50 Hz and 60 Hz power grids.
DC/AC converters (inverters) are used primarily in UPS or emergency light.
During normal electricity condition, the electricity will charge the DC battery.
During blackout time, the DC battery will be used to produce AC electricity at
its output to power up the appliances.
DIAC
The DIAC, or diode for alternating current, is a trigger diode that conducts current
only after its breakdown voltage has been exceeded momentarily. When this occurs,
the resistance of the diode abruptly decreases, leading to a sharp decrease in the
voltage drop across the diode and, usually, a sharp increase in current flow through
the diode. The diode remains "in conduction" until the current flow through it drops
below a value characteristic for the device, called the holding current. Below this
value, the diode switches back to its high-resistance (non-conducting) state. This
behavior is bidirectional, meaning typically the same for both directions of current
flow.
Most DIACs have a breakdown voltage around 30 V. In this way, their behavior is
somewhat similar to (but much more precisely controlled and taking place at lower
voltages than) a neon lamp.
DIACs have no gate electrode, unlike some other thyristors they are commonly used
to trigger, such as TRIACs. Some TRIACs contain a built-in DIAC in series with the
TRIAC's "gate" terminal for this purpose.
DIACs are also called symmetrical trigger diodes due to the symmetry of their
characteristic curve. Because DIACs are bidirectional devices, their terminals are not
labeled as anode and cathode but as A1 and A2 or MT1 ("Main Terminal") and MT2.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 7
NV6531
Symbol of DIAC:
The basic arrangement of the semiconductor layers of the DIAC is shown in figure
Figure 1
where:
T1 : Main Terminal 1
T2 : Main Terminal 2
DIAC is basically a two terminal parallel inverse combination of semiconductor layer
that permits triggering in either direction. The characteristic of the device clearly
demonstrated that there is breakdown voltage in either direction.
DIAC Characteristics:
Figure 2
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 8
NV6531
Experiment
Objective :
To study the VI Characteristic of DIAC with positive biasing and plot the curve
between V & I.
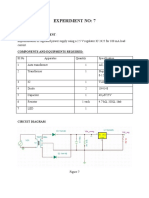
Apparatus Required :
1. NV6531 DIAC Characteristic Trainer
2. 2mm Patch Cord
Circuit Diagram:
Figure 3
Procedure:
Positive Biasing:
1. Make the connections as shown in the above figure.
2. Connect the +35V DC supply to the circuit by connecting the point 1 with
point 4 with the help of patch cord.
3. Rotate the potentiometer P1 in fully anti-clock wise direction.
4. Now connect point 2 with point 8 to make the grounds common.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 9
NV6531
5. Connect the voltmeter across the DIAC. For that connect the +Ve terminal of
Voltmeter with the point 7 and connect the -Ve terminal of the voltmeter with
the point 8.
6. Now connect the Ammeter in the circuit for that connect the +Ve terminal of
the ammeter to the point 5 and connect the -Ve terminal of the Ammeter to the
point 6.
7. Connect the mains cord to the trainer & switch ‘On’ the supply.
8. Here you will observe that there is no current flow in the circuit and as well as
no voltage across the DIAC.
9. Increase the voltage across the DIAC in steps of 1V by rotating the potentiometer
P1 in clockwise direction and note down the readings for Voltage and Current in
the following table.
10. Now plot the VI curve for taken readings.
Observation Table 1:
Serial Number DIACE DIACE DIACE DIACE
Voltage Va Current Ia Voltage -Va Current Ia
10
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 10
NV6531
Negative Biasing:
10. Now connect the -35V DC supply to the circuit by connecting the point 3
with point 4 with the help of patch cord.
11. Repeat the process from step 3 to step 9.
12. Now plot the VI curve for taken readings.
Result Analysis:
VI Characteristic with Positive Biasing
Sr.No. DAIC Voltage DIAC Current 28 27 0
Va (in Volt) Ia (in mA) 29 28 0
1 0 0 30 29 0
2 1 0 31 30 0
3 2 0 32 30.9 0
4 3 0 33 20.6 6.78
5 4 0 34 20.1 10.42
6 5 0 35 19.9 13.64
7 6 0 36 19.7 15.41
8 7 0
9 8 0
10 9 0
11 10 0
12 11 0
13 12 0
14 13 0
15 14 0
16 15 0
17 16 0
18 17 0
19 18 0
20 19 0
21 20 0
22 21 0
23 22 0
24 23 0
25 24 0
26 25 0
27 26 0
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 11
NV6531
VI Characteristic with Negative Biasing
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 12
NV6531
Warranty
1. We guarantee the instrument against all manufacturing defects during 24
months from the date of sale by us or through our dealers.
2. The guarantee covers manufacturing defects in respect of indigenous
components and material limited to the warranty extended to us by the original
manufacturer and defect will be rectified as far as lies within our control.
3. The guarantee will become INVALID.
a. If the instrument is not operated as per instruction given in the learning
material.
b. If the agreed payment terms and other conditions of sale are not followed.
c. If the customer resells the instrument to another party.
d. Provided no attempt have been made to service and modify the instrument.
4. The non-working of the instrument is to be communicated to us immediately
giving full details of the complaints and defects noticed specifically
mentioning the type and sr. no. of the
5. instrument, date of purchase etc.
6. The repair work will be carried out, provided the instrument is dispatched
securely packed and insured with the railways. To and fro charges will be to
the account of the customer.
DISPATCH PROCEDURE FOR SERVICE
Should it become necessary to send back the instrument to factory please observe the
following procedure.
1. Before dispatching the instrument please write to us giving full details of the
fault noticed.
2. After receipt of your letter our repairs dept. will advise you whether it is
necessary to send the instrument back to us for repairs or the adjustment is
possible in your premises.
Dispatch the instrument (only on the receipt of our advice) securely packed in original
packing duly insured and freight paid along with accessories and a copy of the details
noticed to us at our factory address.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 13
NV6531
List of Accessories
1. Mains Cord……………………………………………………………...1 No.
2. 2mm Patch Cords 12”………………………………………………….10 Nos.
3. Learning Material CD………………………………………………….1 No.
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 14
You might also like
- Ece2201 SJB Lab1Document8 pagesEce2201 SJB Lab1Areeba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Beginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsFrom EverandBeginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PN Zenernv6501Document47 pagesPN Zenernv6501Madhur Patidar0% (1)
- EDC Lab 1Document7 pagesEDC Lab 1Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- V5371ae NotDocument185 pagesV5371ae NotSherif100% (1)
- Experiment No: 7: Aim of The ExperimentDocument4 pagesExperiment No: 7: Aim of The ExperimentAtul SahNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab EXPERIMENTS - MergedDocument73 pagesADE Lab EXPERIMENTS - Mergedjainhassan4848No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Iit Delhi Summer Internship Report 2016Document31 pagesDokumen - Tips Iit Delhi Summer Internship Report 2016Shammas MohamedNo ratings yet
- Electronics Projects - DC Motor Speed Control Using H-Bridge - EngineersGarageDocument1 pageElectronics Projects - DC Motor Speed Control Using H-Bridge - EngineersGarageMmeli NtwanaYebhoza DubeNo ratings yet
- GR15 PDFDocument41 pagesGR15 PDFomkar maitreeNo ratings yet
- ZeshanDocument5 pagesZeshanMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lab #2 - DiodesDocument16 pagesLab #2 - DiodescrackintheshatNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 and 9Document8 pagesLab 8 and 9SARANG ABBASINo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument6 pagesDatasheetمحمد مهدی حسنیNo ratings yet
- Udit Singh - Lab Manual - Electrical Engineering - Exp 1 and 2-PreetiDocument10 pagesUdit Singh - Lab Manual - Electrical Engineering - Exp 1 and 2-PreetiUdit Singh.No ratings yet
- Temperature Monitoring System FinalDocument49 pagesTemperature Monitoring System Finals_srireddy78% (9)
- 12v DC To220v Ac Inverter ReportDocument35 pages12v DC To220v Ac Inverter Reportabhishek kalshetti100% (3)
- Edc Manual RoseDocument48 pagesEdc Manual RoseRagabindu GuruNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument16 pagesAcknowledgementSourav MahariNo ratings yet
- Medidor Tri - MS3UI7E3-User Manual V3.0Document19 pagesMedidor Tri - MS3UI7E3-User Manual V3.0Jossemar Bartolo OnayramNo ratings yet
- Vivekanand Education Society'S: Institute of TechnologyDocument9 pagesVivekanand Education Society'S: Institute of TechnologyFazle RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ingenieria Mecatrónica: 1. Objetives General ObjectiveDocument8 pagesIngenieria Mecatrónica: 1. Objetives General ObjectivePaulo ChiribogaNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 2Document16 pagesEDC Lab 2Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 2Document16 pagesEDC Lab 2Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Zener LimiterDocument5 pagesZener LimitersameeNo ratings yet
- Earth Leakage TesterDocument3 pagesEarth Leakage TesterPravin MevadaNo ratings yet
- ELEC30x0 Lab8Document6 pagesELEC30x0 Lab8Lûtwàmä JôëNo ratings yet
- Digital Object Counter Using MicrocontrollerDocument60 pagesDigital Object Counter Using MicrocontrollerKishan Amara82% (22)
- Lab 03Document11 pagesLab 03afnanmirza106No ratings yet
- Exp 08 Analog DiscoveryOrM2kDocument24 pagesExp 08 Analog DiscoveryOrM2kMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab ManualDocument124 pages3 Lab ManualSejal SitaniNo ratings yet
- NV6503Document45 pagesNV6503sandeep_226250% (2)
- Regulated Power SupplyDocument19 pagesRegulated Power SupplyRonn Albert GabucayNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report SampleDocument6 pagesMini Project Report SampleApoorvMaheshwari100% (1)
- Silicon Transistor: PNP Silicon Epitaxial Transistor For Driving Fluorescent Indicator PannelDocument5 pagesSilicon Transistor: PNP Silicon Epitaxial Transistor For Driving Fluorescent Indicator PannelpiroNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document10 pagesLab 3Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument29 pagesElectrical Engineering Laboratorybrhanu degeneNo ratings yet
- Portable Advertising BoardDocument10 pagesPortable Advertising BoardRicha BajajNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 (3420)Document12 pagesLab 3 (3420)Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Diode ExperimentsDocument8 pagesDiode ExperimentsSanthosh VaradanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering and Technology, SRM IST, ChennaiDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering and Technology, SRM IST, ChennaiRajinNo ratings yet
- 5V DC Power Supply: Mrinal KeshriDocument11 pages5V DC Power Supply: Mrinal KeshriOm Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- EC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswersDocument83 pagesEC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswerssunandaalurNo ratings yet
- INVT P2 ManualDocument20 pagesINVT P2 ManualmarlonrafaelNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis (EE - 116) DE-44 Mechatronics: SyndicateDocument7 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis (EE - 116) DE-44 Mechatronics: SyndicateXi PetaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Breadboard ImplementationDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 Breadboard ImplementationJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument23 pagesPPTyashNo ratings yet
- Mymensingh Engineering College: Date of Experiment: 01/09/2020 Submisssion Date: 08/01/2020 SignatureDocument5 pagesMymensingh Engineering College: Date of Experiment: 01/09/2020 Submisssion Date: 08/01/2020 Signature1101 MilonNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Project Report PDF FreeDocument34 pagesAutomatic Street Light Project Report PDF FreeAnkit kumar 08No ratings yet
- EE-252-Electronic Devices & Digital Electronics Laboratory Manual/ RecordDocument85 pagesEE-252-Electronic Devices & Digital Electronics Laboratory Manual/ RecordkishorebabNo ratings yet
- ECA-Labmanual BookDocument56 pagesECA-Labmanual BookL Hari Venkatesh100% (2)
- QB106455Document10 pagesQB106455sanjay sNo ratings yet
- HVDC PowerDocument70 pagesHVDC PowerHibba HareemNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University School of Engineering and Architecture Department of Electronics EngineeringDocument10 pagesSaint Louis University School of Engineering and Architecture Department of Electronics EngineeringBeta TesterNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document9 pagesLab 0549 - 103 - Umair HossainNo ratings yet
- AB 01 Charakterystyki Diody Si Zener LEDDocument30 pagesAB 01 Charakterystyki Diody Si Zener LEDilesh22100% (1)
- Fall 2019 PEE I LAB 5Document25 pagesFall 2019 PEE I LAB 5Andrew Park0% (1)
- Rbs Engineering Technical Campus Bichpuri, AgraDocument20 pagesRbs Engineering Technical Campus Bichpuri, AgraVipin KushwaNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Machine Vision Lighting - Part IIIDocument4 pagesA Practical Guide To Machine Vision Lighting - Part IIIChai Jien WeiNo ratings yet
- External Command in 10 Steps For Revit 2015Document2 pagesExternal Command in 10 Steps For Revit 2015JigneshNo ratings yet
- Overboard Dump ValveDocument3 pagesOverboard Dump ValveekabudiartiNo ratings yet
- 6.hydraulic Pressure SpesificationDocument3 pages6.hydraulic Pressure SpesificationTLK ChannelNo ratings yet
- sITE aVAIL 29-07-2021Document58 pagessITE aVAIL 29-07-2021ogbodoemaNo ratings yet
- Advant Controller 4050series eDocument124 pagesAdvant Controller 4050series eABVSAINo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Information SystemDocument47 pagesHospital Management Information SystemNisarg100% (1)
- Lordk Edid 6507-Case Study Assignment 1 2 3Document34 pagesLordk Edid 6507-Case Study Assignment 1 2 3api-310042469No ratings yet
- Structural Equation Model : Determinant of Customer Satisfaction and It S Implications On Customer EngagementDocument15 pagesStructural Equation Model : Determinant of Customer Satisfaction and It S Implications On Customer EngagementGSA publishNo ratings yet
- SMDocument36 pagesSMharan2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To PSoCDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To PSoCtptuyen2246No ratings yet
- Ch2 Snapshot 20 LightingDocument4 pagesCh2 Snapshot 20 Lightinggarych72No ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety of Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)Document20 pagesOccupational Health and Safety of Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)hitm357100% (1)
- BK Report and ProjectDocument55 pagesBK Report and ProjecttesfuNo ratings yet
- Agile Project ManagementDocument109 pagesAgile Project ManagementSundar Varadarajan100% (1)
- Vogt Valves: Catalog & Application ManualDocument161 pagesVogt Valves: Catalog & Application ManualAngelique DeanNo ratings yet
- 1 Pre-Lab: Lab 07: Sampling, Convolution, and FIR FilteringDocument12 pages1 Pre-Lab: Lab 07: Sampling, Convolution, and FIR Filteringdemetrickn0% (1)
- Xid-2025857 1Document6 pagesXid-2025857 1Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmicTradingNew PDFDocument15 pagesAlgorithmicTradingNew PDFSriheri DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- The Scientist PDFDocument68 pagesThe Scientist PDFPetcu Adrian100% (1)
- Washpipe Assembly Washpipe Assembly: Service ManualDocument60 pagesWashpipe Assembly Washpipe Assembly: Service ManualIvan Kawempy100% (4)
- Guidelines in Test ConstructionDocument8 pagesGuidelines in Test ConstructionSharlene Fae Fabicon86% (7)
- AULA 13 - RespondidoDocument4 pagesAULA 13 - RespondidoRanyelle WanessaNo ratings yet
- 200+ Network Management Tools - Open Source, Free and Commercial SoftwareDocument29 pages200+ Network Management Tools - Open Source, Free and Commercial SoftwarenscintaNo ratings yet
- MN5200 Issue1.1 APR2009Document2 pagesMN5200 Issue1.1 APR2009Roger ReisNo ratings yet
- Weatherford Artificial Lifts Reciprocating Rod Lift OverviewDocument7 pagesWeatherford Artificial Lifts Reciprocating Rod Lift OverviewKentodalNo ratings yet
- MSETCL - Approved Vendor ListDocument11 pagesMSETCL - Approved Vendor ListNavaneetha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixDocument53 pagesChapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixAntwon KellyNo ratings yet
- Trial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformDocument5 pagesTrial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformAzim MohammedNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: Avoiding Common Mistakes in Gas DetectionDocument1 pageConfined Spaces: Avoiding Common Mistakes in Gas Detectiontrravi1983No ratings yet