Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Topic 4
Uploaded by
Fatin Nur DiniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes Topic 4
Uploaded by
Fatin Nur DiniCopyright:
Available Formats
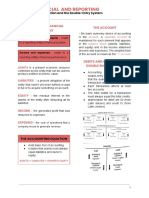
Topic 4
Accounting Cycle
Accounting cycle = accounting process that begins with analyzing and journalizing
transactions and ends with the post-closing trial balance
Fiscal year = the annual accounting period adopted by a business
Fiscal years begin with the first day of the month selected and end on the last day of the
following twelfth month
Natural business year = period of 12 consecutive months ending at a low point of an
organization's activities.
Nature of the Adjusting Process
adjusting process = the analysis and updating of accounts at the end of the period before the
financial statements are prepared.
adjusting entries = The journal entries that bring the accounts up to date at the end of the
accounting period are called
accrual basis of accounting = revenues are reported on the statement of profit or loss and
other comprehensive income in the period in which they are earned.
cash basis of accounting = revenues and expenses are reported on the statement of profit or
loss and other comprehensive income in the period in which cash is received or paid.
Current assets Property, Plant, Current Liabilities Permanent
Equipment Accounts
/ Fixed Assets / Real Account
/ Plant Assets
o Cash o Equipment o Accounts payable Balance account
o Accounts o Machinery o Notes payable carried forward
receivable o Building o Wages payable
o Notes receivable o Interest payable
o Supplies o Unearned fees
o Other prepaid
expenses
Types of Accounts Requiring Adjustment
Prepaid expenses Unearned revenues Accrued revenues Accrued expenses Depreciation Expense
advance payment advance receipt of unrecorded revenues unrecorded expenses Fixed assets
of future expenses future revenues and that have been earned that have been depreciate as they are
and are recorded as are recorded as and for which cash incurred and for used or consumed in
assets when cash liabilities when cash has yet to be which cash has yet to the business
is paid. is received. received. be paid operations.
-service performed -wages/salaries -depreciation
equipment/buildings
Transaction Transaction Transactions Transaction
-cash is paid in -cash is received for -revenue has been -an expense has been
advance for an unearned revenue. earned but has not incurred but has not
expense been recorded. been recorded.
Expense=Debit Cash=Debit No impact since the No impact since the
Cash=Credit Unearned revenue has not been expense has not been
revenue=Credit recorded. recorded.
Adjustment Adjustment Adjustment Adjustment Expense Dr.
-an end of period -an end of period -an end of period -an end of period Contra Assets Cr.
adjustment is adjustment is needed adjustment is needed adjustment is needed
needed to update to update the to recognize accrued to recognize the
the prepaid unearned revenue revenue. accrued expense.
expense account account.
Assets (turun) Cr. Liabilities (turun) Dr. Assets AR (naik) Dr. Liabilities (naik) Cr.
Owner equity Owner equity (naik) Owner equity (naik) Owner equity (naik)
(naik) Dr. Cr. Cr. Dr.
Expense = Revenue=understated Revenue=understated Expense=understated Expense=understated
understated
Net Net Net Net
Revenue Net income=understated income=understated income=overstated income=overstated
income =
overstated Liabilities=overstated Assets=understated Liabilities=understated Assets=overstated
Assets = overstated Owner Owner Owner Owner
Equity=understated Equity=understated equity=overstated equity=overstated
Liabilities = no
change
Owner equity =
overstated
Methods
1.Straigh Line
Cost-Value
Estimated useful life
2.Reducing Balance
You might also like
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Adjusting AccountsDocument43 pagesAdjusting AccountsChowdhury Mobarrat Haider Adnan100% (1)
- Acacia School Development Plan Proposal v4Document40 pagesAcacia School Development Plan Proposal v4Tim EburneNo ratings yet
- Midterm Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMidterm Cheat SheetvikasNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyDocument9 pagesPointers To Review: FABM 2: Recording Phase: Answer KeyMaria Janelle BlanzaNo ratings yet
- FARreviewerDocument5 pagesFARreviewerKimNo ratings yet
- Accounting at A GlanceDocument14 pagesAccounting at A GlanceNiyaz AhamedNo ratings yet
- 2 - FSA1 Handout (Topic 2) - MechanicsDocument59 pages2 - FSA1 Handout (Topic 2) - MechanicsGuyu PanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument12 pagesFinancial Accounting and ReportingDiane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Income 2Document26 pagesMeasurement of Income 2Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Business MathDocument4 pagesBusiness MathPamela MarieNo ratings yet
- Summary of Adjusting Entries: Prepaid ExpenseDocument2 pagesSummary of Adjusting Entries: Prepaid ExpenseJane SalendrezNo ratings yet
- 1 To 10Document111 pages1 To 10JorniNo ratings yet
- Review Session - NUS ACC1002 2020 SpringDocument50 pagesReview Session - NUS ACC1002 2020 SpringZenyuiNo ratings yet
- Accounting Lecture 1Document3 pagesAccounting Lecture 1Karl haddadNo ratings yet
- Fabm 4THDocument3 pagesFabm 4THDrahneel MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Professional Accounting PackageDocument72 pagesProfessional Accounting PackageAnmol poudelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemalonNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries and Merchandising BusinessDocument5 pagesAdjusting Entries and Merchandising BusinessLing lingNo ratings yet
- Accounting PointsDocument4 pagesAccounting PointsLovely IñigoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and PrinciplesDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and Principlesd_hambrettNo ratings yet
- Far 1 ReviewerDocument12 pagesFar 1 ReviewerMargarette RobiegoNo ratings yet
- Accounting ProcessDocument13 pagesAccounting ProcessXiavNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING CYCLE STEP 1 TO 4 With IllustrationsDocument6 pagesACCOUNTING CYCLE STEP 1 TO 4 With IllustrationsmallarilecarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation and Double Entry BookkeepingDocument29 pagesAccounting Equation and Double Entry BookkeepingArvin ToraldeNo ratings yet
- Acct 018 Chapter 4 5Document4 pagesAcct 018 Chapter 4 5rivera.roshelleNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting: Basic Accounting Made Easy Author: Win Ballada Prepared By: Michael AlonzoDocument18 pagesBasic Accounting: Basic Accounting Made Easy Author: Win Ballada Prepared By: Michael Alonzoroland uson91% (35)
- Accounts, Accountants and AccrualsDocument20 pagesAccounts, Accountants and Accrualsjcmail999446No ratings yet
- Accounting RatiosDocument17 pagesAccounting RatiosVijayKapoorNo ratings yet
- Double Entry System & Accounting Equation: by - Mrs. Dilshad D. JalnawallaDocument34 pagesDouble Entry System & Accounting Equation: by - Mrs. Dilshad D. JalnawallaTufail GanaieNo ratings yet
- ABO ReviewerDocument3 pagesABO ReviewerJulianne Hazel EpeNo ratings yet
- Fam - 1Document20 pagesFam - 1shahidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Analyzing TransactionsDocument3 pagesLesson 4: Analyzing TransactionsDante SausaNo ratings yet
- !!!!guide To Cash FlowsDocument3 pages!!!!guide To Cash Flowsws. cloverNo ratings yet
- THE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Document10 pagesTHE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Che AllejeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Financial StatementsDocument10 pagesLesson 3 - Financial StatementsUnknownymousNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Accounting ProcessDocument4 pages2 - The Accounting ProcessWea AmorNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows-Indirect MethodDocument2 pagesStatement of Cash Flows-Indirect MethodHossein ParvardehNo ratings yet
- Accounting C2 Lesson 2 PDFDocument6 pagesAccounting C2 Lesson 2 PDFJake ShimNo ratings yet
- Ch03 WRD25e InstructorDocument70 pagesCh03 WRD25e InstructorFiskal Reguler 15No ratings yet
- Accountancy: Shaheen Falcons Pu CollegeDocument13 pagesAccountancy: Shaheen Falcons Pu CollegeMohammed RayyanNo ratings yet
- Entrep - Debit Credit JournalDocument47 pagesEntrep - Debit Credit JournalCampos, Kristine Joyce A.No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management: Cash in BankDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management: Cash in BankMaria Angelicka Gallardo BernabeNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows (CA5106)Document17 pagesStatement of Cash Flows (CA5106)rhbqztqbzyNo ratings yet
- Accrual vs. Cash AccountingDocument33 pagesAccrual vs. Cash AccountingAbhishek ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Principle of Accounting 1Document25 pagesPrinciple of Accounting 1Quỳnh Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- FABM2-Chapter 1Document31 pagesFABM2-Chapter 1Marjon GarabelNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DiscussionDocument10 pages1st Quarter DiscussionCHARVIE KYLE RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows Ca5106Document57 pagesStatement of Cash Flows Ca5106Bon juric Jr.No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fundamentals and Accounting CycleDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Fundamentals and Accounting CyclecoyNo ratings yet
- Basic AccountingDocument17 pagesBasic AccountinglizNo ratings yet
- Accounting Classification & Accounting EquationDocument25 pagesAccounting Classification & Accounting EquationMadadib 08No ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle of A Service Business: Chapter 10-11Document2 pagesAccounting Cycle of A Service Business: Chapter 10-11des marzanNo ratings yet
- Classification of AccountsDocument6 pagesClassification of AccountsdddNo ratings yet
- PPT1-Financial Statements & AnalysisDocument42 pagesPPT1-Financial Statements & AnalysisKumudNo ratings yet
- Final Accounts Guide for Business OwnersDocument7 pagesFinal Accounts Guide for Business OwnersSushank Kumar 7278No ratings yet
- Business ModelDocument29 pagesBusiness ModelTirsolito SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting RefresherDocument132 pagesBasic Accounting RefresherJustine BalonaNo ratings yet
- Simplify accounting with Tally ERP 9Document90 pagesSimplify accounting with Tally ERP 9SHAHULNo ratings yet
- Acctg201 - Prelim Part 1Document9 pagesAcctg201 - Prelim Part 1Rowena GayasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Literature ReviewAzhar Mahmood MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Anthony Ludovici - A Defence of Aristocracy (1915 White Pages Ver)Document480 pagesAnthony Ludovici - A Defence of Aristocracy (1915 White Pages Ver)ulfheidner9103No ratings yet
- (E6) Exercise For Unit 6Document2 pages(E6) Exercise For Unit 6Lê Cẩm YênNo ratings yet
- Archean Mafic Rocks and Their GeochemistryDocument12 pagesArchean Mafic Rocks and Their GeochemistrygajendraNo ratings yet
- BUS 365 Principles of Marketing: Prof. A. Della BittaDocument33 pagesBUS 365 Principles of Marketing: Prof. A. Della Bittasaeed786786No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance I - Lecture 7bDocument20 pagesCorporate Finance I - Lecture 7bSandra BempongNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster in Indonesia: Risty Khoirunisa Presentation SkillDocument11 pagesNatural Disaster in Indonesia: Risty Khoirunisa Presentation SkillRisty KhoirunisaNo ratings yet
- Renaissance Political CultureDocument28 pagesRenaissance Political CultureRuben K. JusteNo ratings yet
- RecipesDocument102 pagesRecipesmajaklipa100% (3)
- Middle School English Planning GuideDocument8 pagesMiddle School English Planning GuideVictoria GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Picasso's Blue Period - WikipediaDocument24 pagesPicasso's Blue Period - WikipediaDinesh RajputNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 Reading MaterialsDocument5 pagesWEEK 11 Reading MaterialsVineetha Victor GonsalvezNo ratings yet
- Rel-08 Description 20130121Document254 pagesRel-08 Description 20130121Alexandre BeckerNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1Document18 pagesEdexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1farhadmustafa128No ratings yet
- Air Asia Final ProjectDocument59 pagesAir Asia Final Projectmanaswini sharma B.G.No ratings yet
- Familymart in China The Divorce of A 20year International PartnershipDocument11 pagesFamilymart in China The Divorce of A 20year International Partnershipsonali mahajan 833No ratings yet
- Electric BellsDocument36 pagesElectric Bellsmedassan7No ratings yet
- Sex Work in Cyberspace Who Pays The PriceDocument14 pagesSex Work in Cyberspace Who Pays The PriceйцукеячсмNo ratings yet
- Saqeeb PPT LiqueurDocument21 pagesSaqeeb PPT LiqueurSæqéëb Æl HæssåñNo ratings yet
- U2000 & PRS Operation Introduce V1.0Document25 pagesU2000 & PRS Operation Introduce V1.0Nam PhamNo ratings yet
- Investigation of An Animal Mutilation Injuries in Cache County, UtahDocument33 pagesInvestigation of An Animal Mutilation Injuries in Cache County, UtahLionel Elyansun100% (1)
- New Holland E55Bx Tier 4 Compact Hydraulic Excavator Service Repair ManualDocument21 pagesNew Holland E55Bx Tier 4 Compact Hydraulic Excavator Service Repair ManualggjjjjotonesNo ratings yet
- Defamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawDocument9 pagesDefamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawSugar Fructose GalactoseNo ratings yet
- The Mona LisaDocument7 pagesThe Mona LisacicasmileNo ratings yet
- English For Business: Level 1Document24 pagesEnglish For Business: Level 1anonymous9196806No ratings yet
- Feed Management of Sheep and Goats Formulation, Ingredients, Organic, DIY Feed Mix, and Feeding PracticesDocument6 pagesFeed Management of Sheep and Goats Formulation, Ingredients, Organic, DIY Feed Mix, and Feeding PracticesAdusumelli AkshayNo ratings yet
- Black Pepper Cultivation GuideDocument26 pagesBlack Pepper Cultivation GuideReny FranceNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (Download)Document4 pagesCurriculum Vitae (Download)Hilary RivasNo ratings yet