Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Refresher HYD Part2
Uploaded by
Lionel LapuzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Refresher HYD Part2
Uploaded by
Lionel LapuzCopyright:
Available Formats
NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHER
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for 5. A cubic tank is filled with 1.5 m of
each of the following questions. Mark only oil, sp gr 0.752. Find the force acting
one answer for each item by shading the box on the side of the tank, in kN, when the
corresponding to the letter of your choice acceleration is 4.9 m/s2 vertically
on the answer sheet provided. STRICTLY NO upward.
ERASURES ALLOWED. GOOD LUCK. A. 12.4 C. 18.7
B. 9.30 D. 6.22
NOTE: A times B is represented by A×B or
A*B. A raised to the power n is 6. A turbine is rated at 450 kW when the
expressed as A^n. All problems are 1 flow of water through it is 0.609 m3/s.
point each. Assuming an efficiency of 87%, what head
is acting on the turbine, in meters?
A. 75.3 C. 65.5
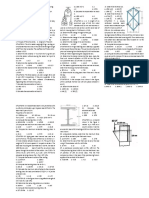
1. A water- filled bulb within a chamber is B. 90.8 D. 86.6
connected to the outside by two U- tube
manometers as shown in the figure. Situation 1. The cubic tank shown is half
Determine the gauge pressure (kPa) in full of water.
the bulb.
A. 102.8 C. 78.1
B. 85.7 D. 93.2
7. Find the pressure on the bottom of the
tank in kPa.
A. 37.4 C. 17.8
B. 14.7 D. 22.7
8. Calculate the force exerted by the
2. A symmetrical trapezoidal channel fluids on the tank wall in KN.
having sides sloping 1V:1.5H is laid on A. 69 C. 83
a slope of 0.00065 m. Calculate the B. 105 D. 124
hydraulic mean depth for a base width of 9. Determine the location of the center of
4.1 m, depth of flow is 1.6 m and n = pressure on the wall from the water
0.014? surface in meters.
A. 0.93 C. 1.17 A. 0.315 C. 1.815
B. 1.05 D. 1.29 B. 1.185 D. 0.500
3. In a bakery, water enters a mixing Situation 2. Water flows in an earth canal,
chamber at the rate of 150 liters per trapezoidal, bottom width 3 m, sides
sec through Pipe A, while cooking oil sloped 3 horizontal on 1 vertical, at a
with specific gravity of 0.80 is forced depth of 62 cm. The canal is on a slope
at 30 liters per sec through pipe B. of 0.0008 and Manning’s n = 0.022.
Assuming the liquids are
incompressible and from a 10. Calculate the amount of flow in m3/s.
homogeneous mixture of oil globules in A. 1.67 C. 2.22
water, evaluate the density of the
B. 3.04 D. 3.82
mixture in kg/m3 leaving through a pipe
of diameter 300 mm 11. Calculate the shearing stress in Pa.
A. 712 C. 967 A. 2.27 C. 2.94
B. 876 D. 1000 B. 3.42 D. 3.08
4. A block of wood floats in water with 50
12.If the seepage rate is estimated at 46
mm projecting above the water surface.
cm /day, what is the discharge after a
When placed in glycerin of sp gr 1.35,
length of flow of 1 kilometer?
the block projects 76 mm above the
A. 1.08 C. 2.26
surface of that liquid. Determine the
B. 3.29 D. 2.18
specific gravity of the wood.
A. 0.67 C. 0.57
B. 0.84 D. 0.91
NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHER
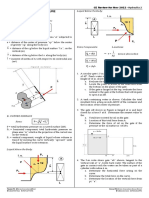
Situation 3. A jet of water issues out from
a fire hydrant nozzle fitted at a height
of 3 m from the ground at an angle of
45° with the horizontal. If the jet
under a particular flow condition
strikes the ground at a horizontal
distance of 15 m from the nozzle.
13. Find the jet velocity, in m/s.
A. 9.85 C. 10.29
B. 11.07 D. 13.33
14.Determine the maximum height the jet can
reach above the nozzle, in meters.
A. 2.47 C. 2.85
B. 4.05 D. 3.12
15.How far horizontally is the location of
the maximum height from the nozzle, in
meters?
A. 7.21 C. 6.25
B. 8.15 D. 15
16.A type of shock where the flow undergoes
a sudden transition from swift flow to
tranquil flow.
A. water hammer
B. hydraulic jump
C. non-uniform flow
D. celerity
17.A fluid property that measures the
fluid’s resistance to shear stress.
A. viscosity
B. density
C. bulk modulus of elasticity
D. surface tension
18. The vena contracta of a circular orifice
is approximately diameter
downstream from the inner face of the
orifice plate:
A. 1/2
B. 1/3
C. 1/4
D. 2/3
19.When the ship’s metacenter and center
of gravity coincide at same point then
the vessel is said to be in:
A. equilibrium
B. stable equilibrium
C. unstable equilibrium
D. neutral equilibrium
20.A force within the surface layer of a
liquid that causes the layer to behave
as an elastic sheet.
A. celerity
B. buoyant force
C. surface tension
D. capillarity
~o0o~
Nothing Follows
You might also like
- Irrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsDocument6 pagesIrrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Cebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designDocument3 pagesCebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designNikki Marie G OclaritNo ratings yet
- (XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Document9 pages(XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Fely Joy RelatoresNo ratings yet
- Eview Nnovations November 2021 Ce Board Exam RENDON 2 (Hydraulics)Document3 pagesEview Nnovations November 2021 Ce Board Exam RENDON 2 (Hydraulics)Fleight VandollinNo ratings yet
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pages2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNo ratings yet
- Hydrau 1Document3 pagesHydrau 1Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Hydrau 4Document3 pagesHydrau 4Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDocument3 pagesApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS: MAY 2022 CE BOARD EXAM - RENDON 5 (HydraulicsDocument3 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS: MAY 2022 CE BOARD EXAM - RENDON 5 (HydraulicsMayya BonaNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2FDocument2 pagesCE Refresher Nov 2022 - Tuzon - Set 7 F2Femielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- 601Document8 pages601Allan Añavisa Ostique Jr.No ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET HydraulicsDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET HydraulicsErika Rose LaronNo ratings yet
- Rendon 4 - Refresher HYDDocument2 pagesRendon 4 - Refresher HYDMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 7Document2 pagesHyd Ref 7emielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- Refresher GEO Part1Document2 pagesRefresher GEO Part1Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Document9 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Civil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011Document83 pagesCivil-Engineering-Reviewer-NOV 2011aomine100% (1)
- Review Innovations Manila - Cebu - Davao First Evaluation ExamDocument2 pagesReview Innovations Manila - Cebu - Davao First Evaluation Examaja øNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDocument1 pageRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- ACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnDocument2 pagesACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnMark Christian HerreraNo ratings yet
- CE Board Exam Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesCE Board Exam Review QuestionsMayya BonaNo ratings yet
- RC 3Document4 pagesRC 3Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsDocument1 pageHydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Eval 2 November 2022 Batch 1 WDDocument6 pagesEval 2 November 2022 Batch 1 WDMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Design Preboard 3 ADocument8 pagesDesign Preboard 3 ALester Sarmiento100% (1)
- Alejandro 1 - Refresher MATH PDFDocument2 pagesAlejandro 1 - Refresher MATH PDFAlliah Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 4 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 4 MsteMyra ComiaNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWDocument6 pagesPREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWWinter DeeneNo ratings yet
- GEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMDocument2 pagesGEOTECHNICAL AND HYDRAULICS ENGINEERING EVALUATION EXAMArianna Denyse Gasgonia100% (1)
- Refresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusDocument1 pageRefresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusJessa Mae CabusNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam No. 1 - ManilaDocument8 pagesEvaluation Exam No. 1 - ManilaTaehyung KimNo ratings yet
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- STEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONDocument3 pagesSTEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeDocument15 pagesMapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeNicole RodilNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- Review Innovations First Evaluation ExamDocument4 pagesReview Innovations First Evaluation ExamKiesha SantosNo ratings yet
- Steel tripod, wrench, frame and arch beam load calculationsDocument19 pagesSteel tripod, wrench, frame and arch beam load calculationsRenne Jude Rollorata100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Exam in Fluids1Document4 pagesExam in Fluids1Prince Winderic Gaza AclanNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set ADocument2 pagesPREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set AEngr. HLDCNo ratings yet
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Document7 pagesLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenNo ratings yet
- November 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review InnovationsDocument7 pagesNovember 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review Innovationsaja øNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 3 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 3 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- Hge Pre-Board QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesHge Pre-Board QuestionnairegregNo ratings yet
- Total Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyDocument2 pagesTotal Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyJocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Second Preboard Exam - MsteDocument8 pagesSecond Preboard Exam - MsteCzatrina QuintasNo ratings yet
- Steel PDFDocument3 pagesSteel PDFCj Delos Reyes Macanas100% (1)
- Structural Soln Nov 2018 PDFDocument19 pagesStructural Soln Nov 2018 PDFrey martiNo ratings yet
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 pagesSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2 SolutionDocument5 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 2 SolutionLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- HGE Refresher QuestionsDocument8 pagesHGE Refresher QuestionsCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Structural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)Document4 pagesStructural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- Math Refresher Module 1Document4 pagesMath Refresher Module 1Nicole RodilNo ratings yet
- RI PREBOARD_APRIL_2023_HGE.PDFDocument6 pagesRI PREBOARD_APRIL_2023_HGE.PDFRichelle Faye VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 7Document2 pagesHyd - 7SamNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 6Document2 pagesHyd Ref 6Dominick TaguinodNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part3Document2 pagesRefresher MATH Part3Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part2Document1 pageRefresher MATH Part2Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part4Document2 pagesRefresher MATH Part4Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher MATH Part5Document2 pagesRefresher MATH Part5Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- NOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHER TIPSDocument2 pagesNOVEMBER 2022 CE BOARD EXAM REFRESHER TIPSLionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher GEO Part2Document2 pagesRefresher GEO Part2Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Refresher GEO Part1Document2 pagesRefresher GEO Part1Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- 5 Otto CycleDocument22 pages5 Otto CycleLionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 DesignofconnectionsDocument32 pagesChapter7 DesignofconnectionsLionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- Time Sheet - JulyDocument3 pagesTime Sheet - JulyraghuNo ratings yet
- Pup News LetterDocument24 pagesPup News LetterArielle RamirezNo ratings yet
- Geographical Diagram of Bangalore CityDocument1 pageGeographical Diagram of Bangalore CityRavi Shankar VNo ratings yet
- OSI 17th DistrictDocument703 pagesOSI 17th DistrictClifford Stone100% (1)
- ASNT Level III Study Guide Topical OutlineDocument4 pagesASNT Level III Study Guide Topical OutlineAwaisNo ratings yet
- ISO 11452 4 2001 BCI SampleDocument8 pagesISO 11452 4 2001 BCI SampleSanthosh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- AP-1000b - Ap-900 Vs Dynapac f30w (Qelq9792)Document12 pagesAP-1000b - Ap-900 Vs Dynapac f30w (Qelq9792)firman manaluNo ratings yet
- AI Applications and Psychology PDFDocument12 pagesAI Applications and Psychology PDFfuturistzgNo ratings yet
- Spherical TankDocument6 pagesSpherical Tankhgag selimNo ratings yet
- Pentium Processor Architecture Features and Performance OptimizationDocument18 pagesPentium Processor Architecture Features and Performance OptimizationJain Marshel BNo ratings yet
- 1 Review 28.08.2019Document28 pages1 Review 28.08.2019Vijay VjNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Well CompletionsDocument17 pagesIntelligent Well CompletionsHamdan Hamzah0% (1)
- National Roundabout Conference 2005 Preliminary FindingsDocument9 pagesNational Roundabout Conference 2005 Preliminary FindingsMEHDI FARROKHINo ratings yet
- Training Course BrochureDocument4 pagesTraining Course BrochureGodofredo PabloNo ratings yet
- Creation of Websphere Process Server Custom Server ProfileDocument39 pagesCreation of Websphere Process Server Custom Server Profilesatya.sid8421100% (3)
- Venkata NarayananDocument5 pagesVenkata NarayananVenkat Narayanan SNo ratings yet
- Dry BlockDocument2 pagesDry BlockSheik SulthanNo ratings yet
- Little Man Computer NotesDocument6 pagesLittle Man Computer Noteskahlilavm0% (1)
- Reparatii DrujbaDocument279 pagesReparatii Drujbaest_nuNo ratings yet
- Portworx Disaster RecoveryDocument5 pagesPortworx Disaster RecoveryAbdul Razak KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Creating A Safe Home Routine - 19477Document2 pagesCreating A Safe Home Routine - 19477徐海东No ratings yet
- JBL 2242H 800W 460mm Subwoofer with Super Vented Gap CoolingDocument2 pagesJBL 2242H 800W 460mm Subwoofer with Super Vented Gap Coolingadalberto teranNo ratings yet
- DR6000MK3Document2 pagesDR6000MK3Stanley Ochieng' OumaNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Air Separation Unit, Oxy-CombustionDocument15 pagesCryogenic Air Separation Unit, Oxy-CombustionHWANG INBUMNo ratings yet
- Precog's IEM Ranking List-7Document6 pagesPrecog's IEM Ranking List-7RubenNo ratings yet
- Survey Research: Maria Lucia BarronDocument46 pagesSurvey Research: Maria Lucia BarronWendy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Oracle ArchitectureDocument5 pagesThe Basics of Oracle Architecturebhuvan_boseNo ratings yet
- Overview of MEMDocument5 pagesOverview of MEMTudor Costin100% (1)
- AZWA Perfume Strategy AnalysisDocument13 pagesAZWA Perfume Strategy AnalysisHery pratama putraNo ratings yet
- Create Oracle database and tables for employee recordsDocument18 pagesCreate Oracle database and tables for employee recordszubaNo ratings yet