Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Draft NCP
Uploaded by
Romelyn OrdillasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Draft NCP
Uploaded by
Romelyn OrdillasCopyright:
Available Formats
Ordillas, Romelyn, A.
NCM109a
BSN 2B Group 5
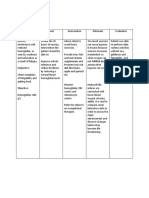
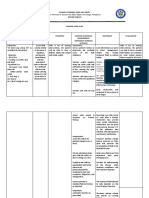
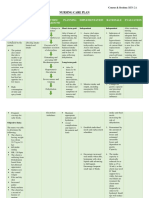
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Excess fluid STG: INDEPENDENT STG:
Data: volume After 8 hours of nursing Establish rapport. To gain client’s trust and GOAL MET
None related to intervention, the client’s cooperation. After 8 hours of nursing
decrease in blood pressure will be intervention, the client’s
regulatory within the normal range blood pressure is within the
mechanisms and have a normal fluid normal range and a normal
Objective Data: with balance. Monitor and record vital To monitor the progress fluid balance AEB excretion
Hematuria potential of signs. of the client’s condition. of excessive fluid through
Proteinuria water as urine and blood pressure of
Edema evidenced LTG: 110/80mmHg
Severe by edema, After 3 days of nursing
edema on elevated intervention the client Assess changes in intake and To reveal any signs and LTG:
both eyelids blood will have a normal fluid output, headache, urinary symptoms of possible GOAL MET
and legs pressure balance. output, and electrolyte renal failure. After 2 weeks of nursing
160/92 balance. intervention, the patient will
mmHg demonstrate behaviors,
(blood Observe behavior changes Changes in behavior may lifestyle changes to reduce
pressure) related to hypertension. indicate need for safety risk factors of injury AEB
precautions associated avoidance of foods rich in
with seizure activity as a protein, potassium and
result of cerebral sodium and increasing intake
changes. of carbohydrates rich foods.
Inform parents to report any Provides for a prompt
weight gain, hematuria with intervention to prevent
decreased urine output, severe renal damage.
complaints of headache and
anorexia.
Teach parents regarding Provides nourishment
dietary inclusion and while the disease is being
restriction; provide a list of resolved.
foods to include and avoid
foods that comply with
sodium, potassium, protein
allowances.
Reinforce to parents the need To ensure ongoing
for follow-up care and monitoring of child for
supervision. chronic renal disease or
infection.
DEPENDENT
Encourage foods low in To provide nutrition
sodium, potassium, and during the acute period
protein and instruct client to with the limitation of
increase intake of food high in potassium during
carbohydrates as ordered. oliguria, sodium with the
presence of edema,
protein limitation if
\ oliguria is prolonged.
Limit fluids as ordered; allow
intake of the amount lost via To avoids additional
urine and insensible losses. fluid retention and edema
in the presence of renal
damage.
Administer diuretics as
ordered by the physician. Diuretics are medications
used to increase the
amount of water and salt
expelled from the body
to urine or to excrete
excess fluid.
You might also like
- Assessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesAssessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Uterine MyomaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Uterine Myomashiramu86% (50)
- The Complete Diabetes Diet Cookbook :The Ultimate Nutrition Guide For Beginners With Food List, Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Complete Diabetes Diet Cookbook :The Ultimate Nutrition Guide For Beginners With Food List, Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Triads in MedicineDocument6 pagesTriads in MedicinedeaceNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisDocument3 pagesAguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisSophia Kaye Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationcamile buhangin100% (1)
- Whole-Body FDG PET Imaging in OncologyDocument305 pagesWhole-Body FDG PET Imaging in OncologyTurki100% (5)
- CASE STUDY TablesDocument9 pagesCASE STUDY TablesMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDocument7 pagesCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPDocument4 pagesUncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- VALDEZ - Nursing Process of Diabetes Mellitus PDFDocument4 pagesVALDEZ - Nursing Process of Diabetes Mellitus PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Immunology Practice Questions With AnswersDocument21 pagesImmunology Practice Questions With AnswersBigBoosting100% (2)
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Renal DiseaseNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- Designing and Planning of 100 Bedded HospitalDocument30 pagesDesigning and Planning of 100 Bedded HospitalJessica SravanthiNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Keto Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight Rapidly And Reinstating Overall Health With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Keto Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight Rapidly And Reinstating Overall Health With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LactuloseDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LactuloseCath Bril100% (1)
- Risk For Imbalanced NutritionDocument3 pagesRisk For Imbalanced Nutritionaudreyann.acobNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalYnezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis & INTERVENTIONDocument10 pagesNursing Diagnosis & INTERVENTIONK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Clinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1Document11 pagesClinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1JezraleFame AntoyNo ratings yet
- NCP JabitisDocument4 pagesNCP JabitisFrancis Adrian Lañojan PernitesNo ratings yet
- Tin NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesTin NCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ckd-Janry FinalDocument6 pagesNcp-Ckd-Janry Finalcjpalapuz07No ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document6 pagesCase Study 5Anthony jesusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Renal FailureRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- PIIS0085253815550461Document10 pagesPIIS0085253815550461KatNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Adime 2 UchcDocument9 pagesAdime 2 Uchcapi-307029735No ratings yet
- INtususs Nursing DiagDocument5 pagesINtususs Nursing DiagVictoria EdwardsNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPSebastianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- 8NCP S For ColostomyDocument23 pages8NCP S For ColostomylovelykissNo ratings yet
- Case No. 5 Rle - PernitoDocument4 pagesCase No. 5 Rle - PernitoAlecxia Nicole PernitoNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementDocument6 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementakoitsmeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Renal DialysisDocument14 pagesRenal Dialysisjhodane100% (1)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisdesaatibagosNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient With Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient With Diabetes MellitusNajla Khairunnisa100% (1)
- NCP DeficientDocument3 pagesNCP DeficientFRANCISCO, QUENNIE MARIE D.No ratings yet
- المستند (7) Document3 pagesالمستند (7) Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument3 pagesNCP Acute GlomerulonephritisrahimsyusophNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Hydrationin Cats With CKDDocument2 pagesMaintaining Hydrationin Cats With CKDSavira AzhariNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCP FormatGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Mikaella GacostaNo ratings yet
- NCP SPH 5Document3 pagesNCP SPH 5jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Review: Berkeley N Limketkai, Wendi Lebrett, Lisa Lin, Neha D ShahDocument10 pagesReview: Berkeley N Limketkai, Wendi Lebrett, Lisa Lin, Neha D ShahAdiel OjedaNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- Potassium Homeostasis, Chronic Kidney Disease, And.14Document7 pagesPotassium Homeostasis, Chronic Kidney Disease, And.148ctvnvpbnpNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Alcoholic LiverDocument22 pagesNutrition in Alcoholic LiverMariana Soto MontañoNo ratings yet
- The Updated Diabetes Diet Book ;The Complete Nutrition Guide For Newly Diagnosed With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Updated Diabetes Diet Book ;The Complete Nutrition Guide For Newly Diagnosed With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- BSN4B-GEC205-PerformaceTask-ORDILLAS, Romelyn A.Document16 pagesBSN4B-GEC205-PerformaceTask-ORDILLAS, Romelyn A.Romelyn OrdillasNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal External - DocsDocument2 pagesLongitudinal External - DocsRomelyn OrdillasNo ratings yet
- FINAL1Document3 pagesFINAL1Romelyn OrdillasNo ratings yet
- GC Geria ToolDocument16 pagesGC Geria ToolRomelyn OrdillasNo ratings yet
- Short Blessed TestDocument3 pagesShort Blessed TestRomelyn OrdillasNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergency ProcedureDocument2 pagesMedical Emergency ProcedureAmeena HarisNo ratings yet
- DR DR D C Lalenoh MKes SpAnKNA KAO-Kul Pakar Bencana Perut 1-5-14Document65 pagesDR DR D C Lalenoh MKes SpAnKNA KAO-Kul Pakar Bencana Perut 1-5-14Siva OrohNo ratings yet
- Post Herpetic Neuralgia andDocument63 pagesPost Herpetic Neuralgia andEndahD'LamdaNo ratings yet
- Dental HospitalDocument7 pagesDental HospitalNISHANTKUMAR PATELNo ratings yet
- 0527C BRIGHT IDEAS NUMBER 5 - Risk Assessment Tool - SB - V1Document1 page0527C BRIGHT IDEAS NUMBER 5 - Risk Assessment Tool - SB - V1sunrise755No ratings yet
- Salbutamol Therapy For Food Impaction In.34Document1 pageSalbutamol Therapy For Food Impaction In.34Ana Clara ReisNo ratings yet
- Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: One Year in Review 2023Document11 pagesSeronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: One Year in Review 2023drcristianogalhardiNo ratings yet
- Read More About MBT Sepsityper IVD Workflow 1682516329Document8 pagesRead More About MBT Sepsityper IVD Workflow 1682516329Jose ZelayaNo ratings yet
- Tasneef 2019 UpdateDocument2 pagesTasneef 2019 UpdateYL LYNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Assay Assay Version Assay TypeDocument7 pagesTest Report: Assay Assay Version Assay TyperosmayaniimutzNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Law and Ethics For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition Jahangir MoiniDocument23 pagesTest Bank For Law and Ethics For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition Jahangir Moinifrankmooreepmgoaqjkb100% (23)
- Dosemetric Evaluation of HDR BrachytherapyDocument1 pageDosemetric Evaluation of HDR BrachytherapySaad SaeedNo ratings yet
- State-Specific Requirements For Initial Medical Licensure (Aug 2012)Document6 pagesState-Specific Requirements For Initial Medical Licensure (Aug 2012)maximusveritasNo ratings yet
- Profile PDFDocument60 pagesProfile PDFAkash Prem KolliNo ratings yet
- CC Product CatalogDocument53 pagesCC Product CatalogDON TVNo ratings yet
- Changing Epidemiology of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in The Last DecadeDocument8 pagesChanging Epidemiology of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in The Last DecadeAlline CastroNo ratings yet
- Pathologytextbooks 2007Document2 pagesPathologytextbooks 2007Mckarey RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Vulvar Cancer: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and PathologyDocument2 pagesVulvar Cancer: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and PathologyAde YonataNo ratings yet
- 2009 06 11-Publicconsultation DraftDocument37 pages2009 06 11-Publicconsultation Draftchris2272No ratings yet
- Cohort StudyDocument44 pagesCohort StudyShaimaa AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- hsns273 Corrected 2Document21 pageshsns273 Corrected 2api-526511003100% (1)
- 3698-Article Text-38129-1-10-20210910Document8 pages3698-Article Text-38129-1-10-20210910Nova RizkenNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPlbegontezNo ratings yet
- Treatment For HemorroidDocument10 pagesTreatment For HemorroidGreg Fuentes LptNo ratings yet
- Dry CoughDocument3 pagesDry Coughnevismn3498No ratings yet