Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
camile buhanginOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
camile buhanginCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
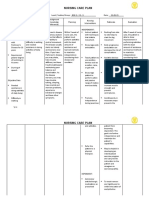
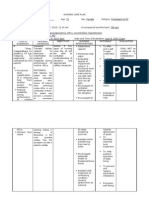
Subjective: Impaired physical After 1-3 days of Instruct patient with techniques Rocking from side to side helps to After 1-3 days of
“He was mobility related nursing intervention, that initiate movement. start the leg movement. nursing intervention,
diagnosed with to Parkinson’s the patient will Instruct patient to get out of the Parkinson disease causes rigidity the patient’s
Parkinson’s disease as improve and chair by moving to edge of the tremors, bradykinesia and may functional mobility
Disease 2 evidenced by maintain functional seat, placing hands on arm result in difficulty getting out of a was improved
months ago” tremor and mobility as long as supports, bending forward, and chair.
shuffling gate possible within then rocking to a standing
Objective: limitations of disease position.
Tremblin process Teach the patient to concentrate A special walking technique must
g of arms on walking erect and use a wide- be learned to offset the shuffling
and hands based gait. gait and the tendency to lean
Can walk If client is mostly immobile, forward.
but slowly encourage him or her to attend a Chair exercises have been shown
Shuffling low-intensity aerobic chair to increase flexibility and balance
gait exercise class that includes
stretching and strengthening chair
exercises.
Instruct patient to raise the head
of the bed and make position These measures reduce
changes slowly. Teach patient to orthostatic hypotension.
dangle legs a few minutes before
standing. Avoid dehydration and
maintain adequate dietary salt.
Provide warm baths and Helps relax muscles and relieve
massages. painful muscle spasms that
Administer anti parkinsonian accompany rigidity.
drugs as prescribed by the
physician (Levadopa and
carbidopa)
JAY CAMILLE S. BUHANGIN BSN-3
You might also like
- Parkinson's Disease NCPDocument1 pageParkinson's Disease NCPAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado67% (3)
- Improve Memory and Reduce Frustration with Targeted Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageImprove Memory and Reduce Frustration with Targeted Nursing InterventionsHarmony Grace0% (1)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument17 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- NCP Formulation (Older Adult)Document3 pagesNCP Formulation (Older Adult)maria khalifa0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Document2 pagesAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Myasthenia Gravis DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Myasthenia Gravis DateSheryl Ann Barit Pedines100% (1)
- Improve Sleep with 36 Nursing Diagnosis TipsDocument3 pagesImprove Sleep with 36 Nursing Diagnosis TipsYah Genn QuibenNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesAssessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's Diseaseria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Nursing Care PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- Tachycardia NCPDocument2 pagesTachycardia NCPRemita Hutagalung50% (4)
- Nutrition NCPDocument3 pagesNutrition NCPMarielle Adrienne Bitancor100% (1)
- Assignment in NCM 114Document1 pageAssignment in NCM 114camile buhanginNo ratings yet
- 5 Day Workout RoutineDocument14 pages5 Day Workout RoutineRadu Baciu100% (3)
- Good - Penis Enlargement Guide Including PicturesDocument19 pagesGood - Penis Enlargement Guide Including Pictureserkinguler0% (1)
- ENGL120 Grammar 1-1 - Three Kinds of VerbsDocument16 pagesENGL120 Grammar 1-1 - Three Kinds of VerbsKarla CepedaNo ratings yet
- 8-Week Training Plan To Run 3 Times A Week-SheetsDocument4 pages8-Week Training Plan To Run 3 Times A Week-SheetsBrooksRunningNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- NCP For Cervical SpondylosisDocument3 pagesNCP For Cervical Spondylosishannah0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisJe ZalNo ratings yet
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoNo ratings yet
- NCP For Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageNCP For Activity IntoleranceKristine LonyenNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pain - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument5 pagesNCP For Pain - Rheumatoid Arthritisveorjan100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocument5 pagesDisturbed Sleeping PatternEllenare RacionNo ratings yet
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityradarsoulNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- Promoting Optimal Sleep Patterns Through Non-Pharmacological InterventionsDocument2 pagesPromoting Optimal Sleep Patterns Through Non-Pharmacological InterventionsNoriel LacsinaNo ratings yet
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocument1 pageNCP Sleep DisturbanceKrystel Cate DelaCruz DamianNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancePatrick Arvin Ballesteros BarcarseNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPkristina_zamoraNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ears Nose ThroatDocument1 pageNCP For Ears Nose ThroatMcmac YangoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale ResponseDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale Responsekhate fonteNo ratings yet
- Managing Impaired Physical Mobility Due to PoliomyelitisDocument4 pagesManaging Impaired Physical Mobility Due to PoliomyelitisRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 pagesNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesDocument2 pagesNursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesKimberly Subade Mandilag100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDocument4 pagesNursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP For OxygenationDocument6 pagesNCP For OxygenationChriz LechNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaKen100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- Multiodular non toxic goiter nursing care planDocument1 pageMultiodular non toxic goiter nursing care plankzbreakerrNo ratings yet
- NCP Ischemic StrokeDocument3 pagesNCP Ischemic StrokeEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- Parkinsons Nurse Care PlanDocument8 pagesParkinsons Nurse Care PlanshaleahNo ratings yet
- NCP For MGDocument1 pageNCP For MGSandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- 312 MR NathanielDocument2 pages312 MR NathanielCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsChristine Lebico100% (1)
- Peplau-Nursing ProcessDocument4 pagesPeplau-Nursing ProcessSunija SelvamNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- NCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Document4 pagesNCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Akio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- MENTAL STATUS EXAM (Buhangin, Jay Camille)Document1 pageMENTAL STATUS EXAM (Buhangin, Jay Camille)camile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Psych NotesDocument9 pagesPsych Notescamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We NeedDocument5 pagesCardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We Needcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs GuideDocument12 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs Guidecamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- How To Perform A Psychiatric Nursing AssessmentDocument11 pagesHow To Perform A Psychiatric Nursing Assessmentcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Effects of Anxiety on Student Performance in the New NormalDocument11 pagesEffects of Anxiety on Student Performance in the New Normalcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Abg Interpretation and InterventionDocument2 pagesAbg Interpretation and Interventioncamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Introduction (Performance of The Nursing Students This New Normal)Document4 pagesIntroduction (Performance of The Nursing Students This New Normal)camile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Final TopicDocument13 pagesFinal Topiccamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten SY. 2020-2021Document2 pagesKindergarten SY. 2020-2021camile buhanginNo ratings yet
- GERIATRICE HEALTH CARE TEAM-FinalDocument6 pagesGERIATRICE HEALTH CARE TEAM-Finalcamile buhangin100% (2)
- It Has Also Interrupted Universities and Facilities Including The Studies of The Future Front Liners Which Are The Nursing StudentsDocument4 pagesIt Has Also Interrupted Universities and Facilities Including The Studies of The Future Front Liners Which Are The Nursing Studentscamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: The ConceptDocument8 pagesExecutive Summary: The Conceptcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOSOCIAL Care in elderly-MODULE 5Document8 pagesPSYCHOSOCIAL Care in elderly-MODULE 5camile buhangin100% (1)
- 5 Trends in Nursing InformaticsDocument2 pages5 Trends in Nursing Informaticscamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- 5 Trends in Nursing InformaticsDocument2 pages5 Trends in Nursing Informaticscamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Performances of Student-Nurses This New Normal Learning SchemeDocument3 pagesPerformances of Student-Nurses This New Normal Learning Schemecamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Information and Computer LiteracyDocument1 pageInformation and Computer Literacycamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- What Is The Immerging Ethical Dilemma All About?: Subscribe To UnlockDocument1 pageWhat Is The Immerging Ethical Dilemma All About?: Subscribe To Unlockcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- What Is The Immerging Ethical Dilemma All About?: Subscribe To UnlockDocument1 pageWhat Is The Immerging Ethical Dilemma All About?: Subscribe To Unlockcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Combating Internet AddictionDocument9 pagesPreventing and Combating Internet Addictioncamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- 5 Trends in Nursing InformaticsDocument2 pages5 Trends in Nursing Informaticscamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Studies ApoorvDocument47 pagesClinical Case Studies ApoorvApoorvNo ratings yet
- Crossfit Workout ProgramDocument1 pageCrossfit Workout ProgramJessielle0% (1)
- Rikli and Jones TestDocument5 pagesRikli and Jones TestNimisha Dhakad100% (2)
- T80/F T85/F Owner's Manual SEO Optimized TitleDocument120 pagesT80/F T85/F Owner's Manual SEO Optimized TitlePaulo DiasNo ratings yet
- Big 24 V4 - Week 1Document2 pagesBig 24 V4 - Week 1John RohrerNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Core Stability Exercise Program On TDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Core Stability Exercise Program On TyenrilisnaNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Sales Advertisements: Reebok'S AdvertismentDocument3 pagesEthical Issues in Sales Advertisements: Reebok'S AdvertismentmegaNo ratings yet
- PE 1 Grade 12Document8 pagesPE 1 Grade 12Jandel CabildoNo ratings yet
- My HobbyDocument1 pageMy HobbyVika PervakNo ratings yet
- India's only complete school magazine promotes self-reliance in youthDocument32 pagesIndia's only complete school magazine promotes self-reliance in youthsupriyaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual To Accompany System Dynamics 3rd Edition 9780471333012Document34 pagesSolutions Manual To Accompany System Dynamics 3rd Edition 9780471333012aheadwullmtyhf100% (44)
- 3 Ways To Be A Ninja - Wikihow FunDocument8 pages3 Ways To Be A Ninja - Wikihow FunJimmy GillNo ratings yet
- TRX MMA Workout PDFDocument1 pageTRX MMA Workout PDFpelelemanNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test in Physical EducationDocument2 pagesFirst Summative Test in Physical EducationDainielle Marie PascualNo ratings yet
- FitSimplifyResistanceTubeBandEbook PDFDocument35 pagesFitSimplifyResistanceTubeBandEbook PDFAnthony DinicolantonioNo ratings yet
- Plyometric TrainingDocument91 pagesPlyometric TrainingNatasha Veljanovska Stojkoski100% (1)
- Sangat StudioDocument5 pagesSangat Studiosanja9balerNo ratings yet
- P.E Q3 To Be PrintedDocument10 pagesP.E Q3 To Be PrintedJanine Amion AndoNo ratings yet
- Derived PositionDocument14 pagesDerived Positionbhavesh jain83% (18)
- OLAÑO - Activity 1 and Reflection 1Document2 pagesOLAÑO - Activity 1 and Reflection 1OLAÑO JOHN ROBERTNo ratings yet
- Answer Key in PeDocument4 pagesAnswer Key in PeJun Greg MaboloNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Ingles Ivan Martinez 2558005Document7 pagesTrabajo de Ingles Ivan Martinez 2558005Santiago martinezNo ratings yet
- Hope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDocument16 pagesHope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDonajei Rica100% (2)
- Relationships Between Reaction TimeDocument52 pagesRelationships Between Reaction Timeyt opalNo ratings yet
- HOPE 3-Module 8-Week 5-6Document9 pagesHOPE 3-Module 8-Week 5-6Freya SalorNo ratings yet
- 1B GRAMMAR Present Simple: Is EatsDocument1 page1B GRAMMAR Present Simple: Is EatsB Mc100% (1)