Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 15 Notes
Uploaded by
Angel Lea Regalado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pages1) A corporation is a separate legal entity formed through operation of law, not agreement, to conduct business.
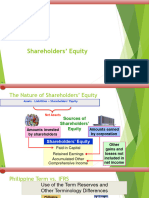
2) A corporation's equity section consists of share capital, which includes authorized, issued, subscribed, and unissued shares.
3) There are two main classes of shares - ordinary shares, which receive residual profits/assets, and preference shares, which have priority over dividends and assets upon liquidation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) A corporation is a separate legal entity formed through operation of law, not agreement, to conduct business.
2) A corporation's equity section consists of share capital, which includes authorized, issued, subscribed, and unissued shares.
3) There are two main classes of shares - ordinary shares, which receive residual profits/assets, and preference shares, which have priority over dividends and assets upon liquidation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesChapter 15 Notes
Uploaded by
Angel Lea Regalado1) A corporation is a separate legal entity formed through operation of law, not agreement, to conduct business.
2) A corporation's equity section consists of share capital, which includes authorized, issued, subscribed, and unissued shares.
3) There are two main classes of shares - ordinary shares, which receive residual profits/assets, and preference shares, which have priority over dividends and assets upon liquidation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
CHAPTER 15: ACCOUNTING FOR o share capital
CORPORATIONS ▪ preference share capital
(preferred stock)
Corporation ▪ ordinary share capital
• The Philippine Corporation Code defines a (common stock)
corporation as ▪ subscribed share capital
o “an artificial being created by (subscribed capital stock)
operation of law, having the right of ▪ subscription receivable (as a
succession and the powers, attributes deduction)
and properties expressly authorized ▪ share dividends distributable
by law or incident to its existence.” (stock dividends payable)
o is a separate legal entity ▪ capital liquidated (as a
distinguished from its owners deduction)
o formed through operation of law, not ▪ share premium (additional
mere agreement paid-in capital)
o continues to exist notwithstanding o other components of equity
the withdrawal, death, insolvency or o treasury shares (treasury stock)
incapacity of the owners • the following transactions affect the
o only dissolved through operation of accounting for a corporation’s equity
law o authorization, subscription, and
o operations are subject to a higher issuance of shares
degree of government regulation o acquisition and reissuance of
treasury shares
Organization of a corporation o retirement of shares
• formed by at least 5 but not more than 15 o donated capital
natural persons of legal age and majority are o distributions to owners (dividends)
residents of the PH
• the entity’s articles of incorporation state the Accounting for share capital
entity's "authorized capital stock" • uses one of the following:
• authorize capital stock is the maximum o memorandum method
number of shares an entity may issue ▪ only a memorandum is made
• excess shares issued is illegal for the authorized
• must amend articles to issue more capitalization
• to amend articles, there must be a majority ▪ subsequent issuances of
vote of the board plus a vote by shareholders shares are credited to the
representing at least two-thirds of share capital account
outstanding share capital is needed o journal entry method
• amended articles shall become effective only ▪ the authorized capitalization
upon SEC’s approval is recorded by crediting
‘authorized share capital’ and
• at least 25% of the corporation’s authorized
debiting “unissued share
capitalization must be subscribed and at
capital’
least 25% of the total subscription must be
▪ difference between the two
paid upon subscription
accounts represent the issued
• the paid-up capital cannot be less than five
share capital
thousand pesos
• the more commonly used method is the
memorandum method
Shareholders’ equity
• authorized share capital
• is the residual interest in the assets of a
o represents the maximum number of
corporation after deducting all its liabilities
shares fixed in the entity’s authorized
• equivalent of ‘owner’s equity”
articles of incorporation that can be
• components:
subscribed and issued to Classes of Share capital
shareholders • classified into two
• unissued share capital o ordinary share capital (ordinary share
o represents the portion of the capital)
authorized share capital not yet o preference share capital (preferred
issues and is still available for stock)
subscription and issuance
• subscription Ordinary shares
o a contract between the purchaser or • represent the residual corporate interest that
shares (investor) and the issuer beats the ultimate risk of loss and receives
(corporation) in which the purchaser the benefits of success
promises to buy shares of the • ordinary shareholders are guaranteed neither
company’s stocks at an agreed price dividends nor assets upon dissolution, but
• subscription receivable they generally control the management and
o represents the unpaid portion of the tend to profit the most if the entity is
subscription price successful
o more commonly presented as a • the Corporation Code prohibits the issuance
deduction from the related of only preference shares without ordinary
subscribed share capital (contra shares
equity account) • ordinary shareholders enjoy the same rights
• subscribed share capital with no preference over other shareholders
o represents the portion of the • four basic rights of ordinary shareholders
authorized share capital that is o right to attend and vote in
subscribed but not yet issued shareholders’ meetings
• share capital o right to purchase additional shares
o represents the potion of the (preemptive right or stock right)
authorized share capital that is ▪ protects shareholders for
already issued involuntary dilution of their
• share certificate ownership interests
o is a document that evidences o right to share in the corporate profits
ownership of a share (also known as right to dividends)
• share capital is credited (under o right to share in the net assets of the
memorandum method) and unissued share corporation upon liquidation
capital is credited (under journal entry • a shareholder who holds more shares
method) only upon the issuance of shares normally will have more voting rights
• under the Corporation Code, shares and • some corporations have more than one type
shares certificates are issued to subscribers of ordinary shares (Class A and Class B)
only upon full payment of the subscription • one class of ordinary shares will have more
price voting rights than the other class, called
• the Corporation Code prohibits the issuance ‘super voting’ shares
of shares in exchange for promissory notes • issuing super voting shares if to five key
or future services company insiders greater control of voting
• the corporation must receive first the full rights to control corporate policies and
consideration before shares are issued management decisions
• share capital (unissued share capital) is
directed credited for cash subscriptions Preference shares
• subscription receivable is more commonly • are shares that give the holders thereof
presented as contra equity account (a certain preferences over other shareholders
deduction in equity) rather than as an asset • such preferences may include priority claims
as applied under traditional US GAAP over dividends and/or net assets of the
• most companies use the memo method corporation upon liquidation
• in exchange for preferences, preference Legal capital
shareholders sacrifice certain rights of • is the portion of contributed capital that
ordinary shareholders (voting rights) cannot be distributed to the owners during
• purpose of preference share is to broaden the lifetime of the corporation unless the
investor appeal by increasing the corporation is dissolved and all of its
opportunity to generate equity financing liabilities are settled first
• based on the concept of trust fund doctrine
Share premium which states that the share capital of a
• share premium (additional paid-in capital) corporation is a trust fund held for the
arises from various sources which include protection of its creditors
the following • computed as follows:
o excess of subscription price over par o for par value shares, legal capital is
value or stated value the aggregate par value of shares
o excess of reissuance price of cost of issued and subscribed
treasury shares issued o for no-par value shares, legal capital
o distribution of small stock dividends is the total consideration received or
• share capital and subscribed share capital are receivable from shares issued or
credited at par value regardless of the subscribed
subscription price ▪ total consideration refers to
• share premium is credited at the subscription the subscription price
date even for subscriptions that are not yet inclusive of any amount in
paid, provided that the total subscription excess of stated value
price will be collected • in case of no-par value shares, legal capital
includes the share premium of ordinary
Par value and No-par value shares shares
• a par value share is one with a peso fixed • preference shares can only be issued as par
value in the articles of incorporation, value shares, thus the share premium of the
purpose is to fix the amount of issuance preference shares is not included (?)
price
o a par value share cannot be issued Share issuance costs
below its par value • include regulatory fees, legal, accounting,
• a no-par value share is one without a peso and other professional fees, commissions
value fixed in the articles of incorporation and underwriter’s fees, printing costs of
o a no-par value share has a stated certificates, and documentary stamp tax and
value (issued value) which is also other transaction taxes
indicated in the articles but not in the • are deducted from any resulting share
share certificate premium from the issuance
• par value and no-par value shares are • if share premium is insufficient, the excess
distinguished by the presence or absence of is charge to retained earnings
value per share on the share certificate
issued Treasury shares
• under the Corporation Code, no-par values • are an entity’s own shares that were
should not be issued less than five pesos previously issued but are subsequently
(P5) per share reacquired but not retired
• excess of subscription price over the stated • under the Corporation Code, an entity may
value is credited to share premium reacquire its previously issued shares only if
• under the Corporation Code, ordinary shares it has sufficient unrestricted earnings
may be issued as either par or no-par value
shares Accounting for treasury shares
• but preference shares should only be issued • treasury shares are accounted for using the
as par value shares cost method
• reacquisition and subsequent reissuance of shares are removed from the books of
treasury shares are recorded at cost accounts
• treasury shares are presented as a deduction • any difference between the total amount
in the shareholders’ equity (contra equity removed and the retirement cost is
account) accounted for as follows:
• retained earnings represent cumulative o if the par value and related share
profits (net of losses, distribution to owners, premium of the retired shares exceed
and other adjustments) that are retained in the retirement cost, the difference is
the business and not yet distributed to the credited to share premium –
shareholders retirement
• total retained earnings may consist of o if the par value and related share
o unrestricted premium of the retired shares are less
▪ the portion of retained than the retirement cost, the
earnings that is available for difference is debited to the following
future distribution to the in the order of priority
shareholders ▪ share premium – treasury
o appropriated (restricted) shares
▪ the portion of retained ▪ retained earnings
earnings that is not available • when shares are reacquired and immediately
for distribution unless the retired, there is no need to set up a treasury
restriction is subsequently share account
reversed • the par value and related share premium of
• when treasury shares are reissued the related the retired shares are immediately debited,
appropriated retained earnings are reverted with a corresponding credit to cash
back to unrestricted earnings • in the accounting for treasury shares and
• when treasury shares are reissued at more retirement of shares, retained earnings may
than the reacquisition cost, the excess of the be decreased but never increased
reissuance price over the cost is credited to
share premium – treasury shares, this forms Donated capital
part of the total share premium • arises from gifts received by the corporation
• when treasury shares are subsequently from nonreciprocal transactions
reissued at below the reacquisition cost, the • donated capital may arise from the following
excess of the cost over the reissuance price o donations from shareholders
is debited to the following in the order of ▪ credited to share premium
priority: o donations from the government
o any balance in share premium – ▪ recognized as government
treasury shares arising from the same grants
class of share capital o donations from other sources
o if the balance share premium – ▪ these are recognized as
treasury shares is insufficient or if it income when
has no outstanding balance, any • the conditions
excess is debited to retained earnings attached to the
donation are fulfilled
Retirement of shares or are reasonably
• shares are considered retired if they have expected to be
been reacquired and cancelled in accordance fulfilled
with SEC regulations • the donation becomes
• retired shares cannot be reissued anymore receivable
• when shares are retired, total par value and • the criteria for asset
the related share premium of the retired recognition are met
• donations from shareholders may be in the
form of
o cash
▪ recognized at the amount of
cash received or receivable
o noncash assets
▪ recognized at the fair value of
the noncash assets
o entity’s own shares
▪ initially recorded through
memo entry
▪ donated capital is only
recognized when the donated
shares are reissued
▪ no asset is generated until
reissued
▪ if donated shares are not to be
resold, the entity should
effect a formal reduction of
its authorized capital by
retiring the shares received
You might also like
- Summary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownFrom EverandSummary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Capital Companies in PolandDocument6 pages5.1 Capital Companies in PolandBianca SăvulescuNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Topic 7 Share Capital Types, Shares and Shareholders' RightsDocument34 pagesWeek 5 Topic 7 Share Capital Types, Shares and Shareholders' RightsmendiexiaNo ratings yet
- Corporation - Contributed Capital - Initial Share TransactionsDocument38 pagesCorporation - Contributed Capital - Initial Share TransactionsIvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Introduction To Company Accounting SDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Introduction To Company Accounting Skhoagoku147No ratings yet
- CorporationDocument5 pagesCorporationaj7939408No ratings yet
- Acc 109-CFE RevDocument5 pagesAcc 109-CFE RevGhie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 Financing The CompanyDocument34 pagesLecture14 Financing The CompanyHarishvardhanNo ratings yet
- Stockholders' Equity Part 1Document43 pagesStockholders' Equity Part 1rhaypensoyNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3Document20 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3Gali jizNo ratings yet
- Parcoac - CorporationDocument2 pagesParcoac - CorporationSSG100% (1)
- Presented by Ankur Srivastava IBMR-IBS, BangaloreDocument25 pagesPresented by Ankur Srivastava IBMR-IBS, BangaloreAnkur SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- L35 - 36share Capital and Its AlterationDocument27 pagesL35 - 36share Capital and Its AlterationSudhanshu Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Kind of SharesDocument22 pagesUnit 3 Kind of SharesKrishnaveni KNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Corporation (Review)Document54 pagesAccounting For Corporation (Review)lgmisajonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 16 NotesAngel Lea RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms SheDocument8 pagesDefinition of Terms ShesampdnimNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ankur Srivastava IBMR-IBS, BangaloreDocument25 pagesPresented by Ankur Srivastava IBMR-IBS, BangaloreInfofree987No ratings yet
- Pro ElecDocument8 pagesPro Elecshaina.planco4No ratings yet
- Shares & Share Capital FinalDocument37 pagesShares & Share Capital FinalRupal Bharat Bhansali100% (1)
- Accounting For Limited Companies: An OverviewDocument32 pagesAccounting For Limited Companies: An OverviewAninditaBasuNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A Corporation (BL2AST)Document23 pagesAdvantages of A Corporation (BL2AST)Francis Emmanuel TolentinoNo ratings yet
- You Do Note Iz The Liar Iz The PeykDocument23 pagesYou Do Note Iz The Liar Iz The Peyksalamat lang akinNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Revised Corporation CodeDocument34 pagesNotes On The Revised Corporation CodeZuleira Parra100% (9)
- Companies Act Lecture PresentationDocument34 pagesCompanies Act Lecture PresentationNatrium SodiumNo ratings yet
- Share CapitalDocument17 pagesShare Capitalzydeco.14No ratings yet
- ACT1122 - CFAS - Corporation OverviewDocument28 pagesACT1122 - CFAS - Corporation OverviewAndrea Mae Anne AgasangNo ratings yet
- Handouts CorporationDocument9 pagesHandouts CorporationMayNo ratings yet
- Ast - Midterm Assignment 2Document12 pagesAst - Midterm Assignment 2Vinus Aleysa ObregonNo ratings yet
- E. Power To Acquire Own Shares: Inc., G.R. No. 216130, August 3, 2016Document26 pagesE. Power To Acquire Own Shares: Inc., G.R. No. 216130, August 3, 2016Al PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument8 pagesBusiness Lawankita mishraNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 CORPORATIONDocument4 pagesNotes 2 CORPORATIONVictor Angelo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and DividendsDocument43 pagesCorporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividendsanon_355962815No ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2Document18 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2Aimae Inot MalinaoNo ratings yet
- F4 Share Capital NotesDocument5 pagesF4 Share Capital NoteskalinovskayaNo ratings yet
- Session 7 - Equity - For Students and MoodleDocument74 pagesSession 7 - Equity - For Students and Moodless9723No ratings yet
- What Is A No Par ValueDocument9 pagesWhat Is A No Par Valuelala reyesNo ratings yet
- Outline: SYNCH AUGUST 20, 2021Document19 pagesOutline: SYNCH AUGUST 20, 2021Ramielle LabayNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Paprcor Chap 567Document3 pagesQuizlet Paprcor Chap 567mxndcysecond02No ratings yet
- Company Law: Kinds of CompaniesDocument14 pagesCompany Law: Kinds of CompaniesRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Institutional Structure FirmsDocument17 pagesInstitutional Structure FirmsGeorge KolbaiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter XI - Financing The Corporation Capital StructureDocument14 pagesChapter XI - Financing The Corporation Capital StructurediwalikhaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document7 pagesTopic 4Regine TorrelizaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Companies: BCM 1204: Accounting in Business IiDocument49 pagesAccounting For Companies: BCM 1204: Accounting in Business IiMaryjoy KilonzoNo ratings yet
- Bus Ass - Joo - S04B - Attack OutlineDocument11 pagesBus Ass - Joo - S04B - Attack OutlineWilliamMunny1100% (4)
- Share in CompanyDocument18 pagesShare in CompanyHeer ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document51 pagesChap 11Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For CorporationDocument5 pagesAccounting For CorporationZariyah RiegoNo ratings yet
- Share Capital-ADocument142 pagesShare Capital-Ahippop kNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 On Lesson 14. Corporate Formation and Shareholders EquityDocument6 pagesNotes 1 On Lesson 14. Corporate Formation and Shareholders EquityJan Tricia G. PabularconNo ratings yet
- Short and Long Term Finance Incl Islamic Finance Lecture 3Document60 pagesShort and Long Term Finance Incl Islamic Finance Lecture 3Ambreen RabbaniNo ratings yet
- LW1A06 Lecture 4 Shares and ShareholdersDocument75 pagesLW1A06 Lecture 4 Shares and ShareholdersfaiszaNo ratings yet
- Share Capital and Basic Legal Documents of A CompanyDocument62 pagesShare Capital and Basic Legal Documents of A CompanyMuneebNo ratings yet
- ACA Accounting Lecture Chap 11-16-14jul2022Document50 pagesACA Accounting Lecture Chap 11-16-14jul2022Nguyễn Thanh Thanh HươngNo ratings yet
- SHAREs & Share CapitalDocument48 pagesSHAREs & Share CapitalRajvi DedhiaNo ratings yet
- Capital of The CompanyDocument28 pagesCapital of The CompanyLusajo MwakibingaNo ratings yet
- Equity Markets: Bulatao, Clemente, Dalope, Mercado, Nelmida, Ramilo, SantosDocument206 pagesEquity Markets: Bulatao, Clemente, Dalope, Mercado, Nelmida, Ramilo, SantosJayveerose BorjaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Corporate Finance - Shares-1Document45 pagesTopic 8 Corporate Finance - Shares-1Bernard ChrillynNo ratings yet
- Finance & Accounts (Basics)Document7 pagesFinance & Accounts (Basics)Prashu DwivediNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document38 pagesCH 06James Patrick Antonio100% (2)
- Customer AnalysisDocument33 pagesCustomer AnalysisMuhammad Ali Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Project Management and Construction EngineeringDocument2 pagesProject Management and Construction EngineeringKentDemeterio67% (3)
- Sample Investment Manager AgreementDocument19 pagesSample Investment Manager Agreementamy alvaroNo ratings yet
- MNCs Role in Underdeveloped CountriesDocument31 pagesMNCs Role in Underdeveloped CountriesNainaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Krishna Maruti LTDDocument7 pagesFinancial Analysis of Krishna Maruti LTDAnsh SardanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Physical Infrastructure: Policy Issues: StructureDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Physical Infrastructure: Policy Issues: Structurevikram inamdarNo ratings yet
- 4417 - Hiep Nam Le - SITXFIN004Document12 pages4417 - Hiep Nam Le - SITXFIN004jsoin0% (1)
- MBA/D-21 Financial Reporting, Statements and AnalysisDocument2 pagesMBA/D-21 Financial Reporting, Statements and AnalysisSuman Naveen JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 & 7 Homework PacketDocument6 pagesChapter 6 & 7 Homework PacketJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- External and Industry Environment Analysis: Dr. K. RangarajanDocument17 pagesExternal and Industry Environment Analysis: Dr. K. Rangarajansanghamitra20012No ratings yet
- PPP PresentationDocument16 pagesPPP Presentationm.musamali5322100% (1)
- IEPM 2020 Part 1 V4 PDFDocument49 pagesIEPM 2020 Part 1 V4 PDFRestu Dinda PagamundiNo ratings yet
- Uber Pricing Strategies and Marketing Communications: Brian RavennaDocument7 pagesUber Pricing Strategies and Marketing Communications: Brian RavennarakshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-5-240 - Fraud - Compatibility ModeDocument35 pagesLecture 4-5-240 - Fraud - Compatibility ModeSourav MahadiNo ratings yet
- ORCO Financial HighlightsDocument1 pageORCO Financial HighlightsbscjjwNo ratings yet
- Optimum Medical Solutions - Export BrochureDocument2 pagesOptimum Medical Solutions - Export BrochureOptimum Medical Solutions100% (1)
- Intermat Solutions: Significant Savings in Maintenance, Repair and Operations (MRO)Document2 pagesIntermat Solutions: Significant Savings in Maintenance, Repair and Operations (MRO)Naveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Software FileDocument12 pagesSoftware FileSANDEEP CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Ittner, C. D. (2020)Document25 pagesIttner, C. D. (2020)J. RanNo ratings yet
- Capital One BankDocument4 pagesCapital One BankAllen SIMEON88% (8)
- How To Write A Driving School Business Plan: Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesHow To Write A Driving School Business Plan: Executive SummaryLucas Reigner KallyNo ratings yet
- RIL Acquisition of Network18Document2 pagesRIL Acquisition of Network18Kritika MahalwalNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Accounting SN MaheshwariDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Management Accounting SN Maheshwaridisha guptaNo ratings yet
- Organisational StructureDocument62 pagesOrganisational StructureTom P Muchel'leNo ratings yet
- IPR Practice SheetDocument6 pagesIPR Practice SheetAarya PariharNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Related Multiple Choice Theory Questions:: D. None of TheseDocument81 pagesAnswer Key To Related Multiple Choice Theory Questions:: D. None of TheseThird YearNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Finance CycleDocument15 pagesChapter 7 - Finance Cyclecarmel andreNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 3 Managerial AccountingDocument4 pagesWritten Assignment Unit 3 Managerial AccountingKelvin kikanaeNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesDay 1 Financial ManagementEricka DeguzmanNo ratings yet