Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control Application
Uploaded by
rudresh singhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Control Application
Uploaded by
rudresh singhCopyright:
Available Formats
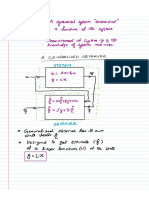
CONTROL APPLICATION
1. Step response: The step response is obtained when we multiply the Laplace transform
of (Heaviside step functions, 1/s) with the transfer function of the system. Step response
tells us about the behaviour of output of system when its input is changed instantly from
0 to1 in very short duration of time.
2. Transient: when the input changes the transient period starts, during which the system
is not really in control of the input, and system seems to be influenced by something
other than input.
3. Steady state: it is the period after the transients have died out, now the output is in the
influence of the input and system is settled down.
4. Proportional control: It helps the system to reduce the steady state error, which makes
the system more stable.
5. Integral control: Integral control (also known as reset control): With the help of
integral control we can eliminate steady state error.
6. Frequency response: it can be represented as a graphical sketch between
gain(magnitude) against frequency. It describes the SSR (steady state response) of
system to sinusoidal input (with different frequency).
7. Proportional integral derivative control: by using PID controller we can reduce the time
constant of the system which make them to respond faster to the disturbances, it also
increases stability of the system.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Non Linear ExamsDocument2 pagesNon Linear Examsrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet With HintsDocument3 pagesProblem Sheet With Hintsrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- L18 ObserversDocument6 pagesL18 Observersrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Ell700 Major Solution KeyDocument2 pagesEll700 Major Solution Keyrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Problem Linear SystemDocument3 pagesProblem Linear Systemrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Ell 701Document7 pagesEll 701rudresh singhNo ratings yet
- AptdDocument28 pagesAptdrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument21 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndromerudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Ackermann's FormulaDocument1 pageAckermann's Formularudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystoniaDocument20 pagesMuscular Dystoniarudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Beskin Fascinating Fractions LMLDocument89 pagesBeskin Fascinating Fractions LMLrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ordinary Differential Equations: Third Edition Athanassios G. KartsatosDocument232 pagesAdvanced Ordinary Differential Equations: Third Edition Athanassios G. Kartsatosrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Torque Rotational Dynamics Problem-SolvingDocument6 pagesTorque Rotational Dynamics Problem-Solvingrudresh singhNo ratings yet