Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetically Coupled Coils
Uploaded by
JOHN LLOYD PEREZOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnetically Coupled Coils
Uploaded by
JOHN LLOYD PEREZCopyright:
Available Formats
LABORATORY REPORT NO.
: 4
Analysis of circuits with magnetically couple-coils
OBJECTIVES:
1. Design a circuit an ideal transformer circuit diagram
2. Determine the electrical quantities in each electrical components in the circuit by means of
application of circuit analysis techniques
3. Compare the values obtained using a circuit simulation and values obtained by means of
manual computation
4. To understand the working principle of circuits with magnetically coupled coils
MATERIALS:
AC Voltage Source (12 cis 0 Vrms, 60hz)
1- 30 ohms resistor
1- 12 ohms resistor
Coupled Inductors in which the primary and secondary coils have an inductance 4 henries
and the coupling constant is 0.5)
Multimeter
DISCUSSION & PROCEDURE:
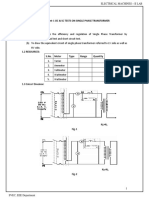
Figure 1. Ideal Transformer Circuit Diagram
The figure above is an example of example of an ideal transformer circuit diagram. An ideal
transformer comprises of two coils embracing a common magnetic circuit of infinite permeability
and zero loss. So, this means a transformer is said to be ideal when the output power will be the
same as with the input power. The power loss in an ideal transformer becomes zero making it as 100
percent efficient. Referring to the figure above, the electrical components use in the circuit diagram
is a coupled inductor, resistor, and an AC voltage source where the quantities were already stated
above.
ELEN112L – ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT NO. 4
1 | PAGE
Procedure:
1. Design a circuit diagram of an ideal transformer using the materials
stated above.
2. Place the AC voltage source in the input power side of the diagram
and connect the 30-ohm resistor in series with the voltage source and
the primary coil.
3. On the output side of the circuit diagram, connect the 12-ohm resistor
in series with the secondary coil.
4. Using a multimeter, measure the mesh current (1) flowing on the input
side, it is done by measuring the current flowing in the resistor. Mesh
Current (2) on the output side can be also measured by measuring the
current flowing in the 12-ohm resistor. The voltage drop across the
resistor can be computed by multiplying the mesh current (2) to the
12-ohm resistor.
MEASUREMENTS & RESULTS:
Figure 2. Simulation of the Ideal transformer
circuit diagram
Figure 3. Multimeter Readings
The multimeter (XMM2) shows the voltage and current reading in the output side while the
multimeter (XMM1) shows the current reading in the input side of the transformer diagram. With
ELEN112L – ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT NO. 4
2 | PAGE
these values, we can say that the primary current is 10.576 mA, while on the secondary current is
5.288 mA. The primary voltage is already given which is 12 Vrms but the voltage drops across the 30-
ohm resistor is unknown but it can easily find by multiplying the primary current to the 30-ohm
resistance. The process on getting the voltage drop across the 12-ohm resistor is just the same on
computing the voltage drop across the 30-ohm resistor.
Figure 4. manual Computation
The values obtained using manual computation is not the same with the values obtained in the
simulation. But the values are close exhibiting a very small margin of error. In computing the
electrical quantities, the mesh analysis method was used to solve for the currents in primary and
secondary. As you can see in the process in the figure above, we cannot proceed to mesh analysis
if we did not get the mutual inductance and the reactance of the inductors including the
reactance of the mutual inductance. The mutual inductance can be easily computed by
multiplying the coupling constant to the square root of the product of the couple coils.
Table 1. Summary of the Obtained Electrical Quantities
PRIMARY SECONDARY VOLTAGE DROP ACROSS
CURRENT CURRENT R2
(mA) (mA) (mV)
SIMULATION 10. 576 5.288 63.453
MANUAL 10.605 5.303 63.637
COMPUTATION
ELEN112L – ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT NO. 4
3 | PAGE
OBSERVATION & CONCLUSION:
I observe that the values obtained using the simulation and through manual computation is
not the same although they are very close. This means that as long as you know the process on
analyzing a circuit with magnetically couple coils even without a simulator you can get the correct
answer. I also observe that the mutual inductance is very important because you cannot make then
mesh analysis correctly if you forget to get the mutual inductance and the reactance of the
inductance. I also observe that it is true that an ideal transformer is 100 percent efficient because it
has no power loss. The power can be obtained by multiplying the primary current to the primary
voltage or multiplying he secondary voltage to the secondary current and the result must be equal.
I therefore conclude that is very important to understand ideal transformer and how power in
the transformer transfer from the primary to secondary. It is a stepping stone to further understand
other types of transformers which are considered as non-ideal transformers.
*FORMAT
Margins: Top – 1.25”, Bottom – 1”, Left – 1”, Right – 0.5”
Paper layout size: A4
Do not remove header and footer.
Edit the laboratory report number and title.
Font size: Century Gothic 10
Font color: Black
Spacing: 1
No space before and after the paragraph
*Convert your files into pdf before submitting
*For laboratory report grading, read the rubrics included in your syllabus.
*Delete all words in RED before submitting the report.
ELEN112L – ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT NO. 4
4 | PAGE
You might also like
- Power in Ac CircuitsDocument5 pagesPower in Ac CircuitsJOHN LLOYD PEREZNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Transformer: Circuit ModelDocument10 pagesExperiment 4: Transformer: Circuit ModelManuel AquinoNo ratings yet
- EES612 Lab2Document19 pagesEES612 Lab2kombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- High Current MeasurementsDocument39 pagesHigh Current MeasurementskingNo ratings yet
- EE313 Class6Document21 pagesEE313 Class6Zahid MarwatNo ratings yet
- Experimental Method 3 PDFDocument14 pagesExperimental Method 3 PDFtungpham2014No ratings yet
- LAB No: 10: To Build and Analyze DC/DC Buck ConverterDocument10 pagesLAB No: 10: To Build and Analyze DC/DC Buck ConverterManahil AshrafNo ratings yet
- Exp1 The Single Phase TransformerDocument8 pagesExp1 The Single Phase Transformernaveen rajNo ratings yet
- Efca 2 Lab 1vDocument8 pagesEfca 2 Lab 1vM Fa RizNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1 2 Lab ManualDocument47 pagesElectrical Machines 1 2 Lab ManualJom Ancheta BautistaNo ratings yet
- Itmf 2013-07-1 Freiburg EnuDocument6 pagesItmf 2013-07-1 Freiburg EnubcqbaoNo ratings yet
- Nouveau Document Microsoft WordDocument7 pagesNouveau Document Microsoft WordAbdelkarim MessaoudiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing Using MatlabDocument6 pagesTransformer Testing Using MatlabPramodTeliNo ratings yet
- ELEC313 Lab#2Document6 pagesELEC313 Lab#2Ali MoharramNo ratings yet
- Core and Copper Losses of A Single Phase TransformerDocument7 pagesCore and Copper Losses of A Single Phase TransformerAsim NoonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Document20 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Alzen Galpao Enage100% (1)
- Analog Electronic WattmetrDocument2 pagesAnalog Electronic WattmetrKaran AnejaNo ratings yet
- ENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasDocument3 pagesENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasJuan Glicerio C. ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics LabDocument6 pagesPower Electronics LabRafeyNo ratings yet
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- ELEC3105 Lab4Document10 pagesELEC3105 Lab4James AllenNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Final-1Document6 pagesExp 1 Final-1Noman AsgharNo ratings yet
- Tel20104 Lab 6 & 7 PDFDocument19 pagesTel20104 Lab 6 & 7 PDFNur HidayahNo ratings yet
- 00225647Document5 pages00225647thavaselvanNo ratings yet
- ECD Exp 4Document2 pagesECD Exp 4Saad MerajNo ratings yet
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument11 pagesCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- Report Lab 1Document7 pagesReport Lab 1Naufal FitriNo ratings yet
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Document55 pagesEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowNo ratings yet
- Drosila Jebarani Computation of Electrical Stresses and Fault Diagnosis in Transformer WindingDocument12 pagesDrosila Jebarani Computation of Electrical Stresses and Fault Diagnosis in Transformer WindingSamuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument60 pagesBee Lab Manualravi828No ratings yet
- Voltage DividerDocument11 pagesVoltage DividerLorshiel Anne TusingNo ratings yet
- AC Chopper-Auto Trans PDFDocument6 pagesAC Chopper-Auto Trans PDFBui DaiNo ratings yet
- Offset-Free Bidirectional Current Source For Impedance MeasurementDocument4 pagesOffset-Free Bidirectional Current Source For Impedance MeasurementHerman ToothrotNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Power TransformersDocument52 pagesThe Basics of Power TransformersLOGA NATHAN KNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimDocument14 pagesExperiment No. 06 B: Title: DC-Power Supply: Block Diagram, Operation and Working AimStar LordNo ratings yet
- LAB BeeDocument16 pagesLAB Bee22-03844No ratings yet
- Tests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Document11 pagesTests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Walmy FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3ph Transformer - Short Circuit TestDocument7 pages3ph Transformer - Short Circuit TestlpestanaNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument62 pagesBee Lab ManualSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Linear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFDocument71 pagesLinear Circult Analysis Lab-Manual - 16jun 2016 PDFHaris -No ratings yet
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocument44 pagesElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Ii EEEN 221 Single-Phase Transformers Pako Oteng 19000839 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering Ii EEEN 221 Single-Phase Transformers Pako Oteng 19000839 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringPako OtengNo ratings yet
- High Voltage High Frequency Pulse Transformer, A Design AnalysisDocument3 pagesHigh Voltage High Frequency Pulse Transformer, A Design Analysiskar mugilanNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamDocument52 pagesElectrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamMy EverythingNo ratings yet
- Practical Report TransformerDocument3 pagesPractical Report TransformerJesus MachaconNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Document21 pagesAssignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- VOM Measurement AnalogDocument23 pagesVOM Measurement AnalogMark Philip MarananNo ratings yet
- Simulation of 3 Phase Power Transformer Using COMSOL MultiphysicsDocument3 pagesSimulation of 3 Phase Power Transformer Using COMSOL MultiphysicsMeine XNo ratings yet
- RLC LabreportDocument7 pagesRLC LabreportMark Christian Cuenca Magbuhat100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project 12Document19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 12BatmanNo ratings yet
- Transformer Equivalent Circuit: 2D Case Study (Static Problems-Translational Geometry)Document5 pagesTransformer Equivalent Circuit: 2D Case Study (Static Problems-Translational Geometry)javed shaikh chaandNo ratings yet
- Man Dache 2006Document5 pagesMan Dache 2006Radouan RadwanNo ratings yet
- Oliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 4Document5 pagesOliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 4TheNinjaDragon gamingNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Linear RegulatorDocument11 pagesPower Supply Linear RegulatorSurbhi100% (1)
- Lab 02-Potential Transformers Fall 2019Document8 pagesLab 02-Potential Transformers Fall 2019Aliza SharifNo ratings yet
- Yog Patil - Expt. No. 3Document8 pagesYog Patil - Expt. No. 3Yog PatilNo ratings yet
- PLC Based Load Sharing On Slide ShareDocument28 pagesPLC Based Load Sharing On Slide ShareHemu Bhai PatelNo ratings yet