100% found this document useful (1 vote)
678 views25 pagesBasement Construction
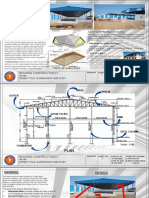
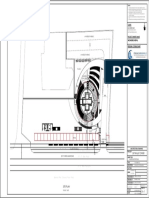
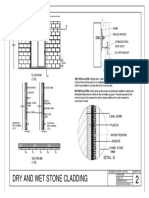
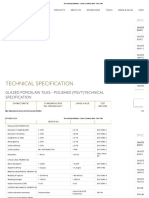
Retaining walls and basement construction are discussed. Basements require retaining walls to support surrounding soil and resist water pressure. There are various types of basements depending on materials, design, construction, and space usage. Proper waterproofing and drainage are essential to prevent moisture issues. Common waterproofing methods include monolithic concrete structures, drained cavity walls with a water drainage system, and membrane barriers applied internally or externally. Joints must be sealed to prevent water infiltration. Mastic asphalt is a common waterproofing material used for external tanking of basement structures.
Uploaded by
Aayu ShCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
678 views25 pagesBasement Construction
Retaining walls and basement construction are discussed. Basements require retaining walls to support surrounding soil and resist water pressure. There are various types of basements depending on materials, design, construction, and space usage. Proper waterproofing and drainage are essential to prevent moisture issues. Common waterproofing methods include monolithic concrete structures, drained cavity walls with a water drainage system, and membrane barriers applied internally or externally. Joints must be sealed to prevent water infiltration. Mastic asphalt is a common waterproofing material used for external tanking of basement structures.
Uploaded by
Aayu ShCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd